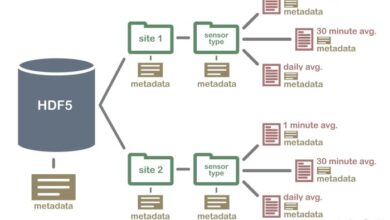
World Leading Research: Beyond Elite Universities
World leading research not confined to elite universities says ref, this is a bold statement that challenges the traditional model of scientific discovery. For centuries, prestigious universities have been considered the sole arbiters of groundbreaking research. However, a seismic shift is underway, with institutions and organizations outside the ivory towers emerging as powerful forces in scientific advancement.
This rise of non-traditional research hubs is fueled by a confluence of factors, including increased funding for independent research, the democratization of technology, and a growing recognition of the importance of addressing real-world problems. As a result, we are witnessing a new era of research where diverse perspectives and innovative approaches are driving progress across a wide range of fields.
The Rise of Non-Traditional Research Hubs

For decades, the landscape of research was dominated by elite universities, seen as the exclusive bastions of knowledge and innovation. This traditional model, however, is undergoing a significant shift, with a growing number of non-traditional research hubs emerging as powerful forces in scientific advancement.
Factors Contributing to the Shift
The rise of non-traditional research hubs can be attributed to a confluence of factors. Increased funding for independent research, technological advancements, and changing societal priorities have created fertile ground for new research centers to flourish.
- Increased Funding for Independent Research:The traditional reliance on university-based research has been challenged by a growing trend of private and public funding for independent research initiatives. Organizations like the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute have significantly invested in research projects outside of universities, fostering innovation and independence.
- Technological Advancements:The democratization of technology has played a pivotal role in enabling research outside of traditional institutions. Open-source software, cloud computing, and readily available scientific equipment have empowered researchers to conduct groundbreaking work in diverse settings. This has fostered a more collaborative and accessible research environment, breaking down traditional barriers to entry.
- Changing Societal Priorities:The focus of research is shifting towards addressing real-world challenges, such as climate change, public health, and technological disruption. This shift has led to a greater demand for research that is directly relevant to societal needs, prompting organizations outside of universities to step up and fill the gap.
Benefits of Decentralized Research: World Leading Research Not Confined To Elite Universities Says Ref
The traditional model of research, confined to elite universities, has long been the dominant paradigm. However, a growing movement is challenging this exclusivity, advocating for the benefits of decentralized research. By fostering research hubs in diverse environments, we can unlock a wealth of untapped potential and accelerate progress in addressing global challenges.
Real-World Problem Solving
Decentralized research thrives on its connection to real-world problems. Researchers embedded within communities can identify and address issues that might be overlooked in ivory towers. This proximity to the field allows for a deeper understanding of local contexts, fostering innovation tailored to specific needs.
For example, researchers in rural communities may develop sustainable agricultural practices that address local challenges like soil erosion or water scarcity. Similarly, researchers in urban settings can focus on issues like air pollution, transportation, or affordable housing.
It’s fascinating to see how world-leading research isn’t always confined to elite universities. Take the recent study on global travel trends, which found that hotel prices are on the rise. This is reflected in the statements made by Marriott, Hilton, and Hyatt, who all point to a confluence of factors driving these increases.
Why Marriott Hilton and Hyatt say hotel prices are only going up These findings, whether from academic institutions or industry giants, offer valuable insights into the evolving travel landscape.
Diverse Perspectives and Interdisciplinary Collaboration, World leading research not confined to elite universities says ref
Decentralized research fosters a rich tapestry of perspectives, drawing from diverse backgrounds, experiences, and disciplines. This cross-pollination of ideas can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and innovative solutions.For instance, a collaboration between anthropologists, engineers, and community leaders in a developing country might lead to the design of a low-cost water filtration system tailored to local needs and resources.
It’s refreshing to see that world-leading research isn’t confined to elite universities, as a recent report highlights. The “Were Sounding the Alarm Bells: Head Start Report Underscores Workforce Crisis” EdSurge News article emphasizes the critical need to address the growing workforce crisis in education, and this research underscores the importance of supporting diverse research environments and fostering innovation across institutions.
This interdisciplinary approach allows for a holistic understanding of the problem, considering social, economic, and environmental factors.
It’s inspiring to see world-leading research emerging from beyond the walls of elite universities, showing that innovation can flourish anywhere. This reminds me of how emotionally intelligent people can achieve remarkable things by applying the “Tom Hanks Rule,” which emphasizes finding joy and meaning in everyday tasks, as outlined in this insightful article: how emotionally intelligent people use the tom hanks rule to get more out of work and life.
This perspective aligns perfectly with the idea that groundbreaking research doesn’t always require a prestigious institution, but rather a passionate and dedicated mind.
Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity
Decentralized research makes knowledge and opportunities accessible to a wider range of individuals, regardless of their geographic location or socioeconomic background. This inclusivity fosters a more equitable research landscape, empowering underrepresented communities and promoting global collaboration. For example, online platforms and open-source tools enable researchers in remote areas to access resources, share data, and collaborate with colleagues worldwide.
This democratization of research empowers researchers from diverse backgrounds to contribute to global knowledge.
Challenges Faced by Non-Traditional Research Hubs
While the rise of non-traditional research hubs offers exciting opportunities for innovation and knowledge creation, these hubs often face significant challenges that hinder their full potential. These challenges stem from factors such as access to resources, funding limitations, and the struggle for recognition within the established scientific community.
Access to Resources
Non-traditional research hubs often lack access to the same level of resources enjoyed by their counterparts in elite universities. This can include access to cutting-edge equipment, specialized laboratories, extensive libraries, and comprehensive research databases.
- Limited Infrastructure:Non-traditional research hubs may struggle to acquire and maintain sophisticated equipment, hindering their ability to conduct advanced research. For instance, a research center focusing on renewable energy might lack access to state-of-the-art solar panel testing facilities.
- Restricted Data Access:Non-traditional hubs may encounter difficulties accessing large-scale datasets or specialized research databases, which are often held by established institutions. This can limit their ability to analyze data, validate findings, and collaborate with other researchers.
- Lack of Expertise:Non-traditional hubs may lack access to a diverse pool of experienced researchers and technical staff, leading to challenges in conducting complex research projects and attracting top talent.
Funding Limitations
Securing adequate funding is a major hurdle for non-traditional research hubs. Traditional funding sources, such as government grants and private foundations, often prioritize established institutions with a proven track record of success.
- Competition for Grants:Non-traditional hubs face stiff competition for research grants from established institutions with greater resources and established reputations, making it challenging to secure funding for their projects.
- Limited Funding Sources:Non-traditional research hubs often rely on a smaller pool of funding sources, limiting their ability to secure substantial financial support for ambitious research endeavors.
- Lack of Venture Capital:Attracting venture capital for research projects can be difficult for non-traditional hubs, especially if their research focuses on areas that are not considered commercially viable in the short term.
Recognition and Visibility
Gaining recognition within the scientific community is crucial for non-traditional research hubs to attract talent, secure funding, and establish credibility. However, established research institutions often hold a dominant position in the scientific landscape, making it difficult for non-traditional hubs to gain visibility and recognition.
- Publication Bias:Traditional research journals may exhibit a bias towards publications from established institutions, making it harder for non-traditional hubs to get their research published and gain wider recognition.
- Limited Networking Opportunities:Non-traditional research hubs may have limited access to prestigious conferences and networking events where researchers can connect with peers and potential collaborators, impacting their ability to showcase their work and build connections within the scientific community.
- Lack of Institutional Support:Non-traditional research hubs may lack the institutional support and infrastructure that traditional universities provide, such as dedicated public relations teams and research dissemination strategies, hindering their ability to communicate their findings effectively to a wider audience.
Overcoming the Challenges
Despite these challenges, non-traditional research hubs can overcome these obstacles and thrive by adopting strategies that leverage their unique strengths and address their weaknesses.
- Building Strategic Partnerships:Collaborating with established institutions, industry partners, and other non-traditional research hubs can provide access to resources, expertise, and funding opportunities. These partnerships can facilitate knowledge sharing, joint research projects, and the development of shared infrastructure.
- Developing Innovative Funding Models:Exploring alternative funding models, such as crowdfunding, social impact bonds, and philanthropic donations, can help diversify funding sources and reduce reliance on traditional grants.
- Highlighting Impact and Relevance:Emphasizing the practical relevance and societal impact of their research can attract funding and recognition. Focusing on research projects that address pressing societal challenges or have clear commercial applications can make their work more appealing to funders and stakeholders.
- Promoting Open Science Practices:Embracing open science principles, such as open access publishing, data sharing, and collaborative research, can increase visibility, attract talent, and foster innovation. Open science practices can also help build trust and credibility within the scientific community.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Traditional and Non-Traditional Research Environments
| Characteristic | Traditional Research Environment (Elite Universities) | Non-Traditional Research Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Resources | Access to state-of-the-art facilities, extensive libraries, and comprehensive research databases. | Limited access to resources, often reliant on partnerships and collaborations. |
| Funding | Strong track record of securing government grants, private foundations, and venture capital. | Limited access to traditional funding sources, often reliant on alternative funding models. |
| Recognition | High visibility within the scientific community, strong reputation for research excellence. | Challenges in gaining recognition, often overlooked by established institutions. |
| Flexibility | Bureaucratic structures can hinder innovation and flexibility. | More agile and adaptable, capable of responding quickly to emerging trends and opportunities. |
| Impact | Focus on fundamental research, often with long-term applications. | Emphasis on applied research with immediate societal or commercial relevance. |
| Diversity | Often dominated by established researchers and traditional disciplines. | More diverse range of researchers and disciplines, fostering interdisciplinary collaborations. |
The Future of Research
The decentralized research movement, fueled by the rise of non-traditional research hubs, holds the potential to revolutionize scientific discovery. By breaking down traditional barriers to research, we can unlock a wealth of untapped talent and perspectives, leading to a more diverse and innovative research landscape.
The Impact of Decentralized Research
Decentralized research has the potential to reshape the scientific landscape in several ways. By democratizing access to research resources and opportunities, it can:
- Foster a More Diverse Research Community:By removing the geographic and institutional limitations that have traditionally hindered participation in research, decentralized research can empower individuals from diverse backgrounds and locations to contribute to scientific progress. This increased diversity of perspectives and experiences can lead to more creative and innovative research approaches.
- Accelerate Scientific Discovery:With a wider pool of researchers and a more collaborative environment, decentralized research can accelerate the pace of scientific discovery. By breaking down silos and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, researchers can share knowledge and resources more effectively, leading to faster breakthroughs.
- Promote Open Science and Transparency:Decentralized research often encourages the sharing of data, methodologies, and results, fostering greater transparency and accountability in the scientific process. This can help to build trust in research findings and promote collaboration among researchers.
A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a community of citizen scientists in a remote village in India, equipped with low-cost, open-source technology, working together to study the impact of climate change on local biodiversity. They might discover a new species of plant with unique properties that could have significant implications for medicine or agriculture.
This discovery, made possible by a non-traditional research hub, could have a profound impact on global health and food security.
Benefits and Challenges of Decentralized Research
The future of research is likely to be more decentralized and accessible, bringing with it both benefits and challenges.
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Increased diversity of researchers and perspectives | Ensuring quality control and rigor in research |
| Accelerated scientific discovery | Maintaining ethical standards and responsible data management |
| Greater access to research resources and opportunities | Bridging the digital divide and providing equitable access to technology |
| Increased collaboration and knowledge sharing | Addressing potential biases and ensuring inclusivity in research |
Final Wrap-Up
The future of research is undeniably decentralized, with the potential for groundbreaking discoveries emanating from unexpected corners of the globe. This shift promises to unlock new avenues of innovation, leading to solutions that address pressing global challenges. By embracing the power of diverse research environments, we can unlock the full potential of human ingenuity and usher in a new era of scientific progress.