Analyzing Chinas Big Problem: Xi Jinpings Unsolvable Challenges
Analysis chinas big problem that xi jinping cant solve – Analyzing China’s Big Problem: Xi Jinping’s Unsolvable Challenges, this article delves into the multifaceted issues that China faces under Xi Jinping’s leadership. From economic stagnation to demographic shifts, environmental concerns, and political tensions, China’s future hangs in the balance. This analysis explores the complexities of these challenges and examines whether Xi Jinping’s policies can effectively address them.
While China has experienced remarkable economic growth in recent decades, it now faces a slowdown fueled by global trade wars, an aging population, and environmental degradation. These interconnected issues pose significant obstacles to China’s continued development and raise questions about the long-term sustainability of its economic model.
Economic Challenges
China’s economic growth has been a defining feature of its rise to global prominence. However, recent years have witnessed a slowdown in this growth, posing significant challenges to Xi Jinping’s leadership. This slowdown has raised concerns about the sustainability of China’s economic model and the potential impact on its domestic and international standing.
Economic Slowdown and Its Impact on Xi Jinping’s Leadership
The slowing economic growth has undoubtedly impacted Xi Jinping’s leadership. While China’s economic performance remains impressive compared to other major economies, the slowdown has raised questions about the effectiveness of Xi Jinping’s economic policies. The Chinese Communist Party (CCP) has long emphasized economic growth as a key indicator of its legitimacy and success.
A sustained period of sluggish growth could erode public confidence in the CCP and Xi Jinping’s leadership.
Analyzing China’s economic woes, it’s clear that Xi Jinping faces a tough challenge in managing the country’s rapid growth while navigating the complexities of global trade. The recent surge in inflation, exacerbated by supply chain disruptions, is a prime example.
This issue isn’t isolated to China; as seen in the news, Biden is set to visit the Port of Los Angeles, highlighting the global nature of this problem, as described in this article: biden to visit port of los angeles casting inflation as a global problem.
Ultimately, the ability to address inflation and ensure economic stability will be crucial in determining the long-term success of Xi Jinping’s leadership.
Comparison with Previous Periods of Economic Slowdown
The current economic slowdown is not unprecedented. China has experienced periods of economic slowdown in the past, notably during the global financial crisis of 2008-2009. However, the current slowdown is characterized by several unique features that distinguish it from previous periods.
Analyzing China’s big problem that Xi Jinping can’t solve reminds me of the ongoing trial against Alex Jones, where he’s facing damages for his false claims about the Sandy Hook shooting being a hoax. The trial highlights the danger of spreading misinformation, just as China’s economic and social issues stem from a lack of transparency and accountability.
Both situations demonstrate the power of truth and the consequences of its suppression.
- Firstly, the current slowdown is more prolonged and persistent than previous downturns. While the 2008-2009 crisis led to a sharp decline in economic growth, the recovery was swift and robust. The current slowdown, however, has been more gradual and persistent, raising concerns about a potential “new normal” of slower growth.
- Secondly, the current slowdown is occurring against a backdrop of rising trade tensions with the United States. The trade war has imposed significant costs on Chinese businesses and disrupted global supply chains, exacerbating the economic slowdown.
- Thirdly, the current slowdown is accompanied by a growing debt burden, particularly in the corporate and local government sectors. This raises concerns about financial stability and the potential for a debt crisis.
Trade War with the United States and Its Impact on Chinese Businesses, Analysis chinas big problem that xi jinping cant solve
The trade war with the United States has been a major factor contributing to China’s economic slowdown. The US has imposed tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods, while China has retaliated with tariffs on US products. This has disrupted global supply chains, increased costs for businesses, and reduced consumer confidence.
The trade war has particularly impacted industries that are heavily reliant on exports to the US, such as manufacturing and agriculture.
- For example, the US tariffs on Chinese steel and aluminum have hurt Chinese steelmakers, while the tariffs on soybeans have impacted Chinese farmers.
- The trade war has also created uncertainty and instability for businesses, making it difficult for them to plan for the future.
Effectiveness of Xi Jinping’s Economic Policies
Xi Jinping has implemented a number of economic policies to address the challenges of slowing growth and the trade war. These policies include:
- Stimulus measures, such as infrastructure spending and tax cuts, to boost domestic demand.
- Reforms to improve the business environment and attract foreign investment.
- Efforts to promote innovation and technological upgrading.
The effectiveness of these policies is still being debated. Some argue that they have helped to stabilize the economy and prevent a sharper downturn. Others argue that they have been insufficient to address the underlying structural problems in the Chinese economy.
“The trade war has imposed significant costs on Chinese businesses and disrupted global supply chains, exacerbating the economic slowdown.”
Demographic Shifts

China’s rapidly aging population and shrinking workforce pose significant challenges to the country’s economic growth and social stability. These demographic shifts are a result of the country’s one-child policy, which was in effect for decades, and the increasing life expectancy.
The Challenges of China’s Aging Population
China’s aging population is a major concern for the government, as it puts pressure on the country’s social security system and healthcare resources. The number of people aged 65 and over is projected to reach 300 million by 2030, and the proportion of the population aged 65 and over is expected to reach 25% by 2050.
This will create a significant strain on the social security system, as the number of working-age people will decline, while the number of retirees will increase.
“China’s aging population is a major concern for the government, as it puts pressure on the country’s social security system and healthcare resources.”
The Impact of a Shrinking Workforce
A shrinking workforce is another major challenge facing China. The working-age population is expected to decline in the coming years, which will put pressure on economic growth. The decline in the workforce will also lead to a shortage of skilled labor, which could make it difficult for Chinese companies to compete in the global economy.
“A shrinking workforce is another major challenge facing China. The working-age population is expected to decline in the coming years, which will put pressure on economic growth.”
Analyzing China’s big problem that Xi Jinping can’t solve, it becomes clear that a lack of adaptability and openness to new ideas are key factors. Leaders who can navigate the complexities of the 21st century need a diverse set of skills, including strategic thinking, communication, and emotional intelligence.
To learn more about these essential leadership qualities, check out this insightful article on 10 most important leadership skills for the 21st century workplace and how to develop them. Perhaps, by embracing these skills, China can find a way to address the challenges that Xi Jinping faces.
Xi Jinping’s Policies to Address Demographic Challenges
Xi Jinping has implemented a number of policies to address the challenges posed by China’s aging population and shrinking workforce. These policies include:
- Relaxing the One-Child Policy: In 2016, the government relaxed the one-child policy, allowing couples to have two children. This was an attempt to boost the birth rate and increase the size of the workforce. However, the policy has not had a significant impact on the birth rate, as many couples are still choosing to have only one child.
- Promoting a More Inclusive and Equitable Society: The government has also implemented policies to promote a more inclusive and equitable society, such as increasing access to education and healthcare for all citizens. These policies are aimed at improving the quality of life for all Chinese citizens, regardless of their age or socioeconomic status.
- Investing in Automation and Artificial Intelligence: The government is also investing heavily in automation and artificial intelligence, which are seen as potential solutions to the labor shortage. This investment is aimed at improving productivity and reducing reliance on human labor.
Potential Solutions to Address the Aging Population and Shrinking Workforce
In addition to Xi Jinping’s policies, there are a number of other potential solutions to address the challenges posed by China’s aging population and shrinking workforce. These solutions include:
- Encouraging Immigration: China could encourage immigration from other countries to boost its workforce. This would require a significant shift in government policy, as China has traditionally been a country that has discouraged immigration.
- Promoting Entrepreneurship: The government could promote entrepreneurship, which would help to create new jobs and stimulate economic growth. This could be achieved through providing financial support to startups, reducing regulations, and promoting innovation.
- Investing in Education and Training: Investing in education and training programs could help to equip the workforce with the skills they need to compete in the global economy. This would also help to increase the productivity of the workforce and make it more attractive to employers.
- Encouraging Older Workers to Remain in the Workforce: The government could encourage older workers to remain in the workforce by offering incentives, such as tax breaks or subsidies. This would help to alleviate the labor shortage and provide older workers with the opportunity to continue contributing to the economy.
Environmental Sustainability: Analysis Chinas Big Problem That Xi Jinping Cant Solve
China’s rapid economic growth has come at a significant environmental cost, resulting in severe air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change. This presents a formidable challenge for Xi Jinping’s administration, as balancing economic progress with environmental protection is a complex and multifaceted task.
Xi Jinping’s Environmental Policies
Xi Jinping has made environmental protection a central pillar of his administration, introducing a series of ambitious policies aimed at promoting sustainable development. These policies include:
- The “Ecological Civilization” concept, which emphasizes the harmonious relationship between humans and nature.
- The “Green Development” strategy, which prioritizes environmental protection in economic decision-making.
- The “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan,” aimed at reducing air pollution in major cities.
- The “Water Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan,” focused on improving water quality in rivers and lakes.
Effectiveness of Xi Jinping’s Policies
While these policies have resulted in some progress, the effectiveness of Xi Jinping’s environmental initiatives remains a subject of debate. While air quality in major cities has improved, pollution levels remain a concern. The government’s ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions have been met with mixed results.
Furthermore, the implementation of environmental regulations has been inconsistent, with enforcement often lagging behind policy pronouncements.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
China’s environmental policies are often compared with those of other major economies, particularly the United States and the European Union. While China has made significant strides in recent years, it still lags behind these developed economies in terms of environmental regulations and enforcement.
However, China has also implemented some innovative environmental initiatives, such as the establishment of a national carbon trading market, that could serve as models for other countries.
Successful Environmental Initiatives
Despite the challenges, China has witnessed some notable successes in its environmental efforts. Examples include:
- The establishment of national parks, such as the Three Parallel Rivers region, which has helped to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable tourism.
- The promotion of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which has contributed to reducing carbon emissions.
- The development of green technologies, such as electric vehicles and energy-efficient appliances, which are becoming increasingly popular in China.
Political and Social Tensions
China’s rapid economic growth has come at a cost, fueling significant social and political tensions. While the country has achieved remarkable progress in lifting millions out of poverty, economic inequality has widened, creating a simmering discontent among segments of the population.
This, coupled with growing political dissent, poses a potential threat to the stability of the Chinese state.
The Potential for Social Unrest
The widening gap between the rich and poor in China has been a growing concern for several years. The concentration of wealth in the hands of a select few, while many struggle to make ends meet, has led to widespread resentment and frustration.
This resentment is further amplified by the perception of corruption and unfairness in the system.
- For example, the 2018 protests in the city of Shaoyang, Hunan Province, erupted after a local official was caught embezzling public funds. These protests, while quickly suppressed, highlight the potential for social unrest to erupt in response to perceived injustices.
- Additionally, the growing cost of living, particularly in major cities, has put a strain on middle-class families. The rising cost of housing, education, and healthcare has eroded the sense of economic security that many Chinese citizens once enjoyed.
This economic frustration, coupled with the lack of political freedoms and avenues for dissent, has created a volatile environment in China. While the government has implemented measures to address inequality, such as raising the minimum wage and expanding social welfare programs, these efforts have been insufficient to quell the growing discontent.
The Influence of Social Media and the Internet
The internet and social media have played a significant role in shaping public opinion and facilitating dissent in China. While the government has strict controls over online content, these platforms have nonetheless become a powerful tool for disseminating information and organizing protests.
- For instance, the use of WeChat, a popular messaging app in China, to coordinate protests in Hong Kong in 2019 demonstrated the potential for social media to circumvent government censorship and mobilize large numbers of people.
- The Chinese government has attempted to counter the influence of social media by implementing strict censorship measures, including the Great Firewall, which blocks access to many foreign websites and social media platforms. However, the proliferation of virtual private networks (VPNs) and other methods of circumventing censorship has made it difficult for the government to maintain complete control over online discourse.
The rise of online activism and the spread of dissenting views online present a significant challenge to the Chinese government’s control over information and public opinion.
Xi Jinping’s Consolidation of Power
Xi Jinping’s consolidation of power has had a profound impact on China’s political and social landscape. His efforts to centralize power, eliminate dissent, and tighten control over the media have led to a more authoritarian and less tolerant political environment.
- Xi Jinping’s crackdown on dissent has targeted not only political opponents but also individuals who express views critical of the government. This crackdown has extended to the internet, with social media platforms being closely monitored for any signs of dissent.
- The increasing concentration of power in the hands of Xi Jinping has raised concerns about the future of political reform in China. The erosion of institutional checks and balances and the suppression of dissent have made it difficult for any alternative voices to emerge.
While Xi Jinping’s consolidation of power has enhanced the government’s ability to maintain stability in the short term, it has also created a more volatile and unpredictable environment in the long run. The suppression of dissent and the lack of political freedom have created a simmering resentment that could erupt into open rebellion if left unchecked.
China’s Assertive Foreign Policy
China’s increasingly assertive foreign policy has generated significant friction with other countries, particularly in the Asia-Pacific region. This assertiveness has been fueled by China’s growing economic and military power, as well as its desire to project its influence on the global stage.
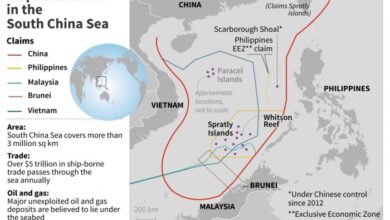
- China’s territorial claims in the South China Sea, its growing military presence in the region, and its economic coercion of smaller countries have raised concerns about its intentions. These actions have led to increased tensions with the United States, Japan, and other regional powers.
- China’s assertive foreign policy has also been met with resistance from within the country. Some Chinese citizens have expressed concerns about the government’s growing militarism and its willingness to engage in conflict. These concerns have been amplified by the government’s opaque decision-making process and its lack of transparency regarding its military activities.
China’s assertive foreign policy has created a complex and challenging environment for the country. While it has allowed China to project its power and influence on the global stage, it has also alienated potential allies and increased the risk of conflict.
Technological Innovation
China’s ambition to become a global leader in technology faces significant challenges, despite its impressive progress in recent years. The country’s quest to achieve technological self-reliance, particularly in critical sectors like semiconductors and artificial intelligence, is intertwined with geopolitical tensions and the need to address its own internal challenges.
The Impact of the US-China Trade War
The US-China trade war has significantly impacted China’s technological innovation landscape. The imposition of export controls on critical technologies, such as semiconductors and software, has hampered China’s ability to access advanced technologies and components. This has forced Chinese companies to invest heavily in domestic research and development, leading to advancements in areas like semiconductor design and manufacturing.
However, the trade war has also created uncertainty and slowed down the pace of technological collaboration between the two countries.
Leveraging Technological Strengths
China possesses significant technological strengths that it can leverage to address its economic and social challenges.
Examples:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):China is a global leader in AI research and development, with applications ranging from facial recognition and autonomous vehicles to healthcare and education. China can leverage its AI capabilities to improve efficiency in various sectors, enhance public safety, and address challenges related to aging population and healthcare.
- E-commerce and Digital Payment:China’s robust e-commerce infrastructure and widespread adoption of digital payment systems have created a thriving digital economy. These advancements can be used to promote financial inclusion, improve access to goods and services in rural areas, and foster entrepreneurship.
- Renewable Energy:China is a leading investor in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power. This commitment can help China reduce its reliance on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and create new economic opportunities in the green energy sector.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
China’s technological development trajectory can be compared with other major economies like the United States, Japan, and South Korea.
Comparison Points:
- Research and Development (R&D) Investment:China has significantly increased its R&D investment in recent years, surpassing the United States in absolute terms. However, the quality and impact of Chinese R&D still lag behind that of the US and other leading economies.
- Innovation Ecosystem:China is building a strong innovation ecosystem, with a focus on supporting startups and fostering entrepreneurship. However, the country still faces challenges in attracting and retaining top talent, as well as in protecting intellectual property.
- Technological Leadership:While China has made significant progress in areas like AI and mobile payments, it still lags behind the US in key areas like semiconductors and software. China’s ambition to become a global technological leader requires further investments in fundamental research and development, as well as in building a robust innovation ecosystem.
Final Thoughts
The challenges facing China under Xi Jinping’s leadership are formidable. While the government has implemented policies to address these issues, their effectiveness remains to be seen. The future of China hinges on its ability to navigate these complex challenges and find innovative solutions to ensure its long-term prosperity and stability.