Ultimate Blockchain Business Strategy Guide: A Comprehensive Roadmap
The Ultimate Blockchain Business Strategy Guide sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a world where decentralized technology is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. This guide is your roadmap to navigating the complex landscape of blockchain, empowering you to leverage its transformative potential for your organization.
From understanding the core principles of blockchain to exploring its diverse applications across industries, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of this cutting-edge technology. We delve into the strategic considerations involved in developing a successful blockchain strategy, covering everything from identifying use cases to implementing secure and compliant solutions.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting to explore the world of blockchain, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights you need to unlock the true value of this transformative technology.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
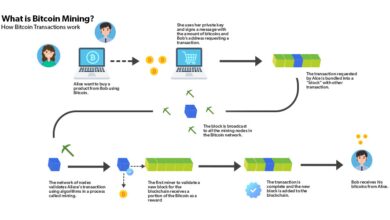
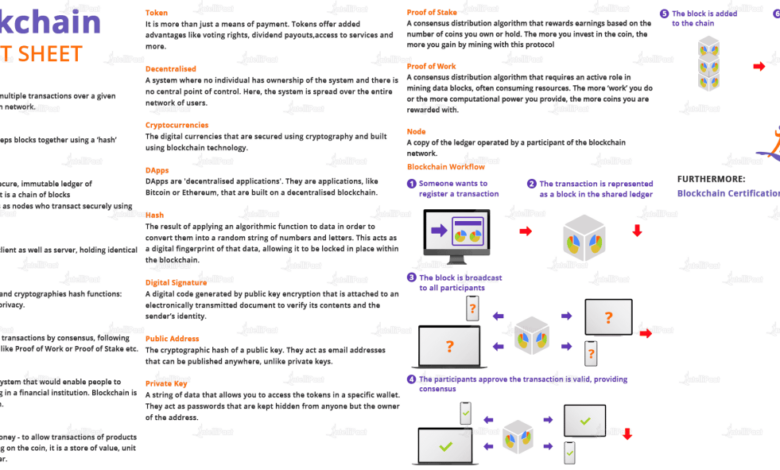
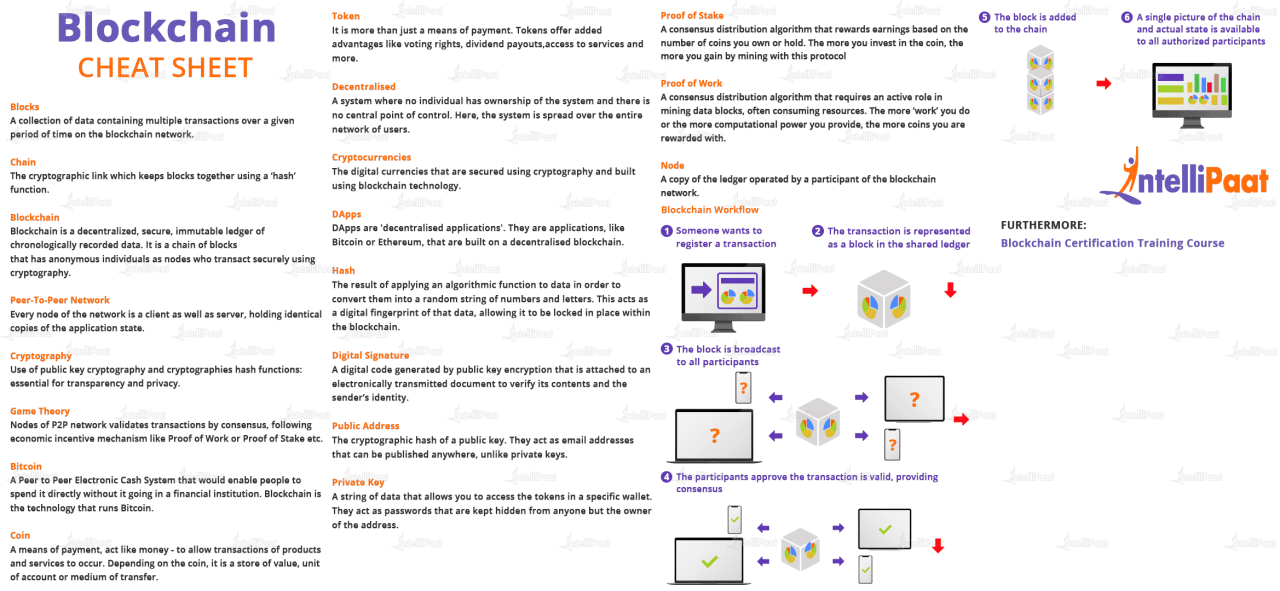
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing various industries and disrupting traditional business models. It is a decentralized, immutable, and transparent ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This guide delves into the core principles of blockchain technology, exploring its key features and highlighting examples of different blockchain platforms.
Decentralization
Decentralization is a fundamental principle of blockchain technology. Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized authorities, blockchain networks operate on a distributed ledger, eliminating the need for a single point of control. This distributed nature ensures that data is stored across multiple nodes, making it highly resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Immutability
Immutability refers to the unchangeable nature of blockchain records. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes permanently etched into the ledger, making it virtually impossible to alter or delete. This property ensures the integrity and trustworthiness of data, as it eliminates the risk of fraud or data tampering.
Transparency
Transparency is another defining characteristic of blockchain technology. All transactions on a blockchain are publicly accessible and verifiable, allowing anyone to view the history of transactions and track the movement of assets. This transparency fosters accountability and trust within the ecosystem.
Different Blockchain Platforms
There are numerous blockchain platforms, each with its unique characteristics and functionalities. Here are some notable examples:
- Bitcoin: The first and most widely known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin utilizes a blockchain to record and verify transactions. Its key features include decentralized governance, a proof-of-work consensus mechanism, and limited supply.
- Ethereum: A versatile platform that supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), Ethereum enables developers to create and deploy applications on its blockchain. Its key features include a Turing-complete virtual machine, a proof-of-work consensus mechanism, and a rich ecosystem of developers and applications.
- Hyperledger Fabric: A permissioned blockchain platform designed for enterprise use cases, Hyperledger Fabric offers features like modularity, scalability, and privacy-preserving capabilities. It is commonly used for supply chain management, trade finance, and identity management.
Blockchain Business Applications

Blockchain technology, with its decentralized, secure, and transparent nature, has emerged as a transformative force across various industries. Its applications extend far beyond cryptocurrencies, revolutionizing business processes, enhancing efficiency, and creating new opportunities.
Applications Across Industries
Blockchain’s potential to revolutionize various industries is immense. Here are some key areas where it is making a significant impact:
- Supply Chain Management:Blockchain enables secure and transparent tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, from origin to delivery. This eliminates counterfeiting, improves traceability, and reduces inefficiencies. For instance, Walmart uses blockchain to track the origin of its leafy greens, ensuring food safety and consumer trust.
- Financial Services:Blockchain streamlines financial transactions, reduces costs, and enhances security. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms leverage blockchain for peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading. For example, Ripple’s network facilitates cross-border payments, reducing transaction time and costs.
- Healthcare:Blockchain ensures secure storage and sharing of patient medical records, improving data privacy and interoperability. It also enables efficient drug tracking and supply chain management. For example, the MediLedger network tracks pharmaceutical products from manufacturing to distribution, preventing counterfeiting and ensuring product safety.
- Real Estate:Blockchain simplifies property transactions, reduces fraud, and enhances transparency. Smart contracts automate processes like escrow and title transfers, streamlining the buying and selling process. For example, Propy uses blockchain to digitize property records, enabling faster and more secure transactions.
- Government and Public Sector:Blockchain enhances transparency and accountability in government operations. It can secure voting systems, manage identity documents, and streamline public services. For example, Estonia has successfully implemented blockchain for digital identity and e-governance, leading to improved efficiency and citizen trust.
- Energy:Blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, promoting renewable energy adoption and reducing reliance on centralized grids. It also facilitates the tracking of energy consumption and carbon emissions. For example, Power Ledger’s platform allows individuals and businesses to buy and sell renewable energy directly, creating a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
- Art and Entertainment:Blockchain creates a secure platform for authenticating and trading digital assets, such as NFTs (non-fungible tokens). It empowers artists to monetize their work directly, bypassing intermediaries and establishing ownership rights. For example, Nifty Gateway is a platform for buying and selling NFTs, connecting artists with collectors and creating new revenue streams.
Real-World Examples of Successful Blockchain Implementations
- IBM Food Trust:This platform uses blockchain to track food products from farm to table, providing transparency and traceability. Walmart, Nestlé, and Dole are among the companies participating in this initiative, enhancing food safety and consumer trust.
- Maersk’s TradeLens:This blockchain-based platform connects various stakeholders in the global shipping industry, enabling efficient and transparent trade documentation and shipment tracking. This reduces delays, improves communication, and minimizes fraud.
- Ethereum’s Smart Contracts:These programmable contracts automate agreements and transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Ethereum’s blockchain has enabled the development of decentralized applications (dApps) in various sectors, including finance, gaming, and supply chain management.
Benefits of Blockchain Adoption
- Enhanced Security:Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic security make it highly resistant to hacking and fraud. This is particularly important for sensitive data like financial transactions, medical records, and supply chain information.
- Increased Transparency:All transactions on a blockchain are recorded and publicly accessible, providing transparency and accountability. This can improve trust and reduce corruption in various industries.
- Improved Efficiency:Blockchain automates processes, reduces paperwork, and streamlines transactions. This leads to cost savings and faster execution times, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Reduced Costs:By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain can significantly reduce transaction costs. This is particularly beneficial for cross-border payments and supply chain management.
- Increased Trust:The immutable nature of blockchain records fosters trust and confidence among stakeholders. This is crucial for building relationships and facilitating collaboration in various industries.
Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
- Scalability:As blockchain adoption grows, ensuring scalability and handling high transaction volumes can be challenging. Some blockchains struggle to process transactions quickly and efficiently, especially during peak times.
- Regulation:The regulatory landscape for blockchain technology is still evolving. Lack of clear guidelines can hinder adoption and create uncertainty for businesses.
- Technical Complexity:Implementing and managing blockchain solutions requires specialized technical expertise. Finding qualified personnel and integrating blockchain into existing systems can be challenging.
- Interoperability:Different blockchains are not always compatible, making it difficult to integrate them into existing systems and create a seamless ecosystem.
- Data Privacy:While blockchain offers enhanced security, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like GDPR is crucial. Addressing concerns about data ownership and access is essential.
Developing a Blockchain Business Strategy
A well-defined blockchain strategy is essential for any organization looking to leverage the transformative potential of this technology. This strategy should Artikel the organization’s vision, goals, and roadmap for integrating blockchain into its operations.
Steps Involved in Creating a Blockchain Strategy
A comprehensive blockchain strategy should be developed through a systematic process that involves several key steps. These steps ensure that the strategy is aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives and addresses potential challenges.
Building a successful blockchain business requires more than just a technical understanding of the technology. You need a strong entrepreneurial mindset, and that’s where the 11 mindset traits of successful entrepreneurs come into play. These traits, such as resilience, adaptability, and a vision for the future, are crucial for navigating the constantly evolving blockchain landscape.
By adopting these traits, you can build a solid foundation for your ultimate blockchain business strategy guide, setting yourself up for success in this exciting and dynamic industry.
- Define Business Objectives:The first step is to clearly define the business objectives that the organization aims to achieve through blockchain adoption. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a company might aim to improve supply chain transparency, reduce operational costs, or enhance customer trust through blockchain implementation.
While I’m deep in the trenches of crafting the ultimate blockchain business strategy guide, it’s hard to ignore the news. The trial against Alex Jones, for his false claims that the Sandy Hook shooting was a hoax, is a stark reminder of the responsibility we all have to spread accurate information.
It’s a stark reminder that while blockchain technology can revolutionize business, ethical and responsible use of information is paramount.
- Conduct a Feasibility Assessment:Once business objectives are established, it is crucial to conduct a thorough feasibility assessment of potential blockchain projects. This assessment should evaluate the technical, legal, regulatory, and financial aspects of implementing blockchain solutions. It is essential to consider the cost of development, integration, and ongoing maintenance, as well as the potential return on investment (ROI).
- Identify Potential Use Cases:Identifying potential blockchain use cases is a critical step in developing a robust strategy. This involves analyzing the organization’s existing processes and identifying areas where blockchain can deliver significant value. For instance, a financial institution might explore using blockchain for cross-border payments, while a healthcare provider might use it for secure patient data management.
- Prioritize Use Cases:After identifying potential use cases, it is essential to prioritize them based on their potential impact, feasibility, and alignment with the organization’s strategic goals. Prioritization helps ensure that the organization focuses on the most promising opportunities first.
- Develop a Pilot Project:Before embarking on full-scale blockchain implementation, it is recommended to develop a pilot project. This pilot project allows the organization to test the feasibility and effectiveness of the chosen blockchain solution in a controlled environment. The learnings from the pilot project can be used to refine the strategy and address any potential challenges.
- Build a Blockchain Ecosystem:A successful blockchain strategy requires building a robust ecosystem that includes key stakeholders such as technology partners, regulatory bodies, and other organizations in the blockchain space. This ecosystem provides support and collaboration opportunities for the organization’s blockchain initiatives.
- Develop a Governance Framework:Establishing a clear governance framework for blockchain projects is crucial. This framework should define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes for all stakeholders involved. It should also address issues such as data security, privacy, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Monitor and Evaluate:Continuous monitoring and evaluation of blockchain projects are essential for ensuring their success. This involves tracking key metrics such as cost savings, efficiency improvements, and user satisfaction. Regular evaluation helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that the strategy remains aligned with the organization’s evolving needs.
Building a solid blockchain business strategy isn’t just about technical know-how, it’s also about understanding the real-world implications of your work. The recent news of a Columbia graduate student brutally beaten in Manhattan, with his mother struggling for answers , serves as a stark reminder of the importance of security and safety in our increasingly digital world.
As we strive to create a more secure and transparent future with blockchain, we must also consider the human impact of our innovations, ensuring that our technology is used responsibly and ethically.
Blockchain Development and Implementation: Ultimate Blockchain Business Strategy Guide
Once you’ve formulated a robust blockchain business strategy, the next crucial step is to translate your vision into reality. This involves navigating the complex landscape of blockchain development and implementation.
Choosing a Blockchain Development Approach
The first decision you’ll face is whether to build your blockchain solution from scratch or leverage existing platforms. Each approach has its own advantages and drawbacks.
- Building a Custom Blockchain: This offers maximum flexibility and control, allowing you to tailor the blockchain to your specific needs. However, it also requires significant technical expertise and resources, making it a complex and time-consuming endeavor. It’s best suited for businesses with unique requirements that can’t be met by existing platforms.
- Utilizing Existing Platforms: This provides a faster and more cost-effective way to get started. Established platforms like Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and R3 Corda offer pre-built infrastructure and tools, simplifying development and reducing the learning curve. This approach is ideal for businesses seeking a quicker time to market or lacking the resources for custom development.
Selecting the Right Blockchain Platform
Choosing the right blockchain platform is a critical step. Factors to consider include:
- Scalability: The platform should be able to handle the anticipated transaction volume and growth of your business. Consider factors like transaction speed, throughput, and the platform’s capacity for future expansion.
- Security: The platform’s security features are paramount. Look for robust consensus mechanisms, cryptography, and security audits to ensure data integrity and protection against threats.
- Development Tools and Community: The availability of developer tools, libraries, and a vibrant community can significantly accelerate development and provide support. A strong community ensures access to resources, knowledge sharing, and collaboration.
- Cost: Consider the platform’s costs, including transaction fees, infrastructure requirements, and potential development expenses. Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of different platforms in relation to your budget and project scope.
- Regulation and Compliance: Ensure the platform complies with relevant regulations and industry standards. Compliance requirements can vary depending on your business and industry.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices
Implementing a blockchain solution involves several technical considerations and best practices:
- Smart Contract Development: Smart contracts are self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain. Their development requires meticulous planning and testing to ensure they function as intended. Prioritize security, reliability, and proper error handling in smart contract development.
- Data Management and Storage: Determine how data will be stored and managed on the blockchain. Consider factors like data privacy, security, and access control. Data management strategies should align with your business requirements and regulatory obligations.
- Testing and Deployment: Thorough testing is essential before deploying a blockchain solution. Conduct rigorous testing to identify and address potential issues. Start with small-scale deployments and gradually scale up as confidence grows.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating blockchain solutions with existing systems can be challenging. Plan for seamless integration, ensuring compatibility and data flow between systems.
- Security Audits and Monitoring: Regular security audits and monitoring are crucial to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities. Implement security measures and continuously monitor for potential threats.
Key Considerations for Successful Blockchain Implementation
Beyond technical aspects, several factors contribute to the success of blockchain implementation:
- Clear Business Objectives: Define clear and measurable business objectives for your blockchain project. Ensure the project aligns with your overall business strategy and delivers tangible value.
- Strong Leadership and Team: A dedicated team with expertise in blockchain technology, development, and business strategy is essential. Effective leadership and communication are crucial for project success.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaboration with other stakeholders, including technology providers, industry partners, and regulators, can accelerate development and enhance adoption.
- Change Management and Training: Prepare your organization for the adoption of blockchain technology. Provide training and support to ensure employees understand the new processes and systems.
- Continuous Improvement: Blockchain technology is constantly evolving. Embrace a culture of continuous improvement, staying updated on advancements and adapting your solutions as needed.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations

The rapidly evolving nature of blockchain technology presents unique challenges for legal and regulatory frameworks worldwide. As blockchain applications continue to expand, understanding the legal landscape and navigating regulatory complexities is crucial for any business venturing into this space. This section explores the legal and regulatory considerations for blockchain projects, highlighting potential risks and providing guidance for compliance.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology varies significantly across jurisdictions. While some countries have embraced blockchain and issued clear regulatory frameworks, others remain hesitant or are still developing their approach.
- United States:The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has taken a proactive approach to regulating blockchain-based securities, issuing guidance and enforcement actions related to initial coin offerings (ICOs). The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) has also weighed in on the regulation of cryptocurrencies.
However, the US regulatory landscape remains fragmented, with different agencies having jurisdiction over different aspects of blockchain technology.
- European Union:The EU has adopted a more comprehensive approach to regulating blockchain technology, with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applying to data processing involving blockchain. The EU is also exploring a regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies and stablecoins.
- China:China has taken a more restrictive approach to blockchain, banning ICOs and imposing strict regulations on cryptocurrency exchanges. However, the Chinese government has also expressed support for blockchain technology’s potential applications in other sectors.
Potential Legal and Compliance Risks
Blockchain projects face a range of legal and compliance risks, including:
- Securities Laws:Blockchain projects involving token offerings may be subject to securities laws, requiring registration or exemption. Failing to comply with securities regulations can result in significant penalties.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Regulations:Blockchain projects handling transactions involving digital assets must comply with AML and KYC regulations to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing. This often involves verifying the identities of users and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
- Data Privacy Laws:Blockchain projects may collect and process personal data, which must comply with data privacy laws like the GDPR. Ensuring data security and transparency is crucial to avoid legal repercussions.
- Tax Laws:The taxation of blockchain transactions and digital assets varies across jurisdictions. Businesses need to understand the tax implications of their blockchain activities and ensure compliance with relevant tax laws.
- Intellectual Property Rights:Blockchain projects may involve the development and use of intellectual property, such as software, algorithms, or data. Protecting intellectual property rights is essential to avoid infringement claims.
Navigating Legal and Regulatory Challenges
To navigate legal and regulatory challenges in the blockchain space, businesses can take the following steps:
- Conduct Thorough Due Diligence:Before launching a blockchain project, businesses should conduct thorough due diligence to understand the relevant legal and regulatory requirements in their target jurisdictions. This includes consulting with legal and compliance experts specialized in blockchain technology.
- Develop a Strong Compliance Program:Implementing a robust compliance program is essential to mitigate legal and regulatory risks. This involves establishing clear policies and procedures, training employees, and conducting regular audits.
- Engage with Regulators:Proactive engagement with regulators can help businesses understand their expectations and ensure compliance. This may involve attending industry events, submitting comments on proposed regulations, and participating in regulatory sandboxes.
- Stay Informed of Regulatory Developments:The blockchain space is constantly evolving, and businesses need to stay informed of the latest regulatory developments. This includes subscribing to industry newsletters, attending conferences, and monitoring relevant government websites.
Security and Risk Management
While blockchain technology offers numerous advantages, it also presents unique security challenges and vulnerabilities that require careful consideration. This section delves into the security considerations and risk management strategies crucial for a successful blockchain business.
Security Challenges and Vulnerabilities
Blockchain security involves safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of the network, its transactions, and the underlying data. Several security challenges and vulnerabilities can compromise the security of blockchain systems:
- 51% Attacks:A malicious actor controlling more than 50% of the network’s computing power can potentially manipulate the blockchain, double-spend coins, and alter the transaction history. This is a significant threat to the consensus mechanism of Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities:Smart contracts, while automating processes, can contain vulnerabilities exploited by attackers. These vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access to funds, data manipulation, or even system failure.
- Key Management and Private Key Security:Losing or compromising private keys can result in the loss of access to digital assets. Secure key management and storage practices are essential to prevent unauthorized access and theft.
- Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns:Data stored on the blockchain is immutable, making it vulnerable to breaches if sensitive information is exposed. Privacy concerns arise as blockchain transactions are generally transparent and traceable.
- DDoS Attacks:Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks can overwhelm the network with excessive traffic, making it unavailable for legitimate users.
- Oracle Attacks:Oracles, used to feed external data into smart contracts, can be manipulated, potentially compromising the integrity of the contract’s execution.
Best Practices for Securing Blockchain Systems and Data
Securing blockchain systems and data is crucial for maintaining trust and protecting assets. Here are some best practices to implement:
- Use Robust Cryptography:Employ strong cryptographic algorithms for encryption, digital signatures, and hashing to secure data and transactions.
- Secure Key Management:Implement secure key management practices, such as multi-signature wallets, hardware wallets, and secure key storage solutions.
- Code Auditing and Security Reviews:Conduct thorough code audits and security reviews of smart contracts to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Regular Security Updates and Patches:Apply security updates and patches promptly to address known vulnerabilities and mitigate potential risks.
- Network Monitoring and Intrusion Detection:Implement network monitoring and intrusion detection systems to identify suspicious activities and potential threats.
- Secure Data Storage and Backup:Securely store and back up critical data to prevent loss in case of system failures or breaches.
- User Awareness and Training:Educate users about best practices for security, such as strong password management, avoiding phishing attacks, and recognizing fraudulent activities.
Risk Management Strategies for Blockchain Projects
Risk management is essential for mitigating potential threats and ensuring the success of blockchain projects. Here are some key strategies:
- Identify and Assess Risks:Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities specific to the blockchain project.
- Develop Risk Mitigation Strategies:Based on the risk assessment, create and implement strategies to mitigate identified risks.
- Implement Robust Security Controls:Establish and enforce strong security controls, such as access control, authentication, and data encryption.
- Regularly Monitor and Evaluate Risks:Continuously monitor and evaluate risks to identify emerging threats and adjust mitigation strategies accordingly.
- Establish Incident Response Plans:Develop and test incident response plans to handle security breaches or other unforeseen events effectively.
- Compliance with Regulations:Adhere to relevant regulations and industry best practices to ensure compliance and mitigate legal risks.
Blockchain Governance and Operations
Establishing clear governance structures and efficient operational processes is crucial for the success of any blockchain project. These aspects ensure transparency, accountability, and sustainable growth, fostering trust and confidence among stakeholders.
Governance Structures
A well-defined governance framework provides a roadmap for decision-making, conflict resolution, and the overall direction of the blockchain project. It Artikels roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Defining Roles and Responsibilities:Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, including developers, validators, community members, and governance bodies. This ensures a clear understanding of who is responsible for specific tasks and decisions.
- Establishing Decision-Making Processes:Implement a transparent and fair decision-making process, outlining the methods for proposing, discussing, and voting on changes or updates to the blockchain. This can involve consensus mechanisms, voting systems, or other governance models.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms:Establish clear procedures for resolving disputes that may arise among stakeholders. This could involve arbitration, mediation, or other mechanisms for fair and impartial resolution.
- Auditing and Monitoring:Implement regular audits and monitoring processes to ensure the integrity and security of the blockchain. This can include technical audits of the code, financial audits of the project’s finances, and monitoring of network activity.
Operational Efficiency
Effective blockchain operations are essential for ensuring smooth functioning, scalability, and resilience.
- Workflow Optimization:Implement efficient workflows for tasks such as transaction processing, data management, and network maintenance. This can involve automation, streamlining processes, and using appropriate tools and technologies.
- Scalability and Performance:Design the blockchain infrastructure to handle increasing transaction volumes and user activity. This may involve implementing scaling solutions, optimizing network performance, and ensuring efficient resource utilization.
- Security and Risk Management:Prioritize security and risk management by implementing robust security measures, conducting regular security audits, and having contingency plans in place to mitigate potential threats.
- Data Management and Privacy:Develop a comprehensive data management strategy that ensures the privacy and security of user data. This may involve data encryption, access control mechanisms, and adherence to relevant privacy regulations.
Stakeholder Engagement and Community Building, Ultimate blockchain business strategy guide
Active stakeholder engagement and community building are essential for the long-term success of any blockchain project.
- Communication and Transparency:Maintain open and transparent communication with stakeholders, providing regular updates on the project’s progress, challenges, and future plans. This builds trust and fosters a sense of community.
- Community Forums and Feedback Mechanisms:Establish forums and feedback mechanisms for stakeholders to engage with the project team, provide input, and contribute to decision-making processes. This can involve online forums, social media groups, or dedicated community platforms.
- Education and Outreach:Invest in education and outreach programs to educate stakeholders about blockchain technology, the project’s goals, and the benefits of participation. This helps foster understanding and build a strong and informed community.
- Incentivization and Rewards:Consider implementing incentive programs or rewards systems to encourage active participation and contribution from community members. This can involve token distribution, access to exclusive features, or other forms of recognition.
Future Trends and Innovations
The blockchain landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and applications emerging at a rapid pace. These advancements are reshaping the way businesses operate, opening up new opportunities and presenting challenges. This section explores some of the most prominent future trends and innovations in the blockchain space, examining their potential impact on business strategies and the future of blockchain technology.
Interoperability and Cross-Chain Communication
Interoperability, the ability for different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, is a critical aspect of blockchain adoption. As the number of blockchains grows, the need for interoperability becomes increasingly important. This allows for the creation of interconnected ecosystems, enabling businesses to leverage the strengths of different blockchains while mitigating the risks of relying on a single platform.
- Cross-Chain Bridges:These are protocols that facilitate the transfer of assets and data between different blockchains. They allow users to move tokens, NFTs, and other digital assets across different networks, enabling seamless interactions between different blockchain ecosystems.
- Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC):IBC is a protocol that enables communication and data transfer between different blockchains that implement the Cosmos SDK. This protocol is gaining popularity for its flexibility and scalability, facilitating the development of interconnected blockchain networks.
- Layer-2 Scaling Solutions:These solutions aim to improve the scalability and performance of existing blockchains by offloading transactions to secondary networks. They provide faster transaction speeds and lower fees, making blockchain technology more accessible to a wider range of users and applications.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a rapidly growing sector of the blockchain ecosystem, offering alternative financial services built on blockchain technology. DeFi protocols provide access to a wide range of financial products and services, including lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance, without the need for traditional intermediaries.
- Lending and Borrowing:DeFi platforms allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies, earning interest on their assets or accessing capital without needing to go through traditional financial institutions.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs):DEXs are platforms that allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other, eliminating the need for centralized exchanges. This offers greater privacy and security, as users retain control of their assets.
- Stablecoins:Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to the value of fiat currencies, such as the US dollar. They provide price stability and reduce volatility, making them suitable for use in DeFi applications and real-world transactions.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets that represent ownership of digital or physical items. They are gaining popularity in various industries, from art and collectibles to gaming and supply chain management.
- Digital Art and Collectibles:NFTs have revolutionized the art world, allowing artists to sell their digital creations directly to collectors without intermediaries. They provide proof of ownership and authenticity, making it possible to trade and track the history of digital assets.
- Gaming:NFTs are being used to create in-game items, characters, and virtual worlds, providing players with ownership and control over their digital assets. This can lead to new game economies and incentivize user engagement.
- Supply Chain Management:NFTs can be used to track the provenance of goods, ensuring authenticity and transparency throughout the supply chain. This can help businesses combat counterfeiting and improve consumer trust.
Blockchain-Based Identity Management
Traditional identity management systems are often centralized and vulnerable to security breaches. Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure alternative, providing individuals with greater control over their personal data.
- Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI):SSI systems allow individuals to control their own digital identities, storing their data securely on a blockchain. This empowers individuals to manage their data and share it selectively with trusted parties.
- Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs):DIDs are unique identifiers that are linked to a blockchain, providing a secure and verifiable way to identify individuals and organizations. This can be used for various applications, such as voting, healthcare records, and financial transactions.
- Data Privacy and Security:Blockchain-based identity management systems offer enhanced data privacy and security, as data is stored in a decentralized and encrypted manner, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to access it.
Enterprise Blockchain Solutions
Enterprise blockchain solutions are designed to meet the specific needs of businesses, providing a secure and transparent platform for managing operations, improving efficiency, and reducing costs.
- Supply Chain Management:Blockchain can be used to track goods throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and transparency. This can help businesses optimize logistics, reduce fraud, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Financial Services:Blockchain can be used to streamline financial processes, such as payments, settlements, and trade finance. This can reduce costs, improve efficiency, and enhance security.
- Healthcare:Blockchain can be used to manage patient records, track medical supplies, and facilitate secure data sharing between healthcare providers. This can improve patient care and enhance data privacy.
Last Word
As we conclude our journey through the Ultimate Blockchain Business Strategy Guide, it’s clear that blockchain is more than just a buzzword. It’s a powerful force shaping the future of business, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and trust. By embracing this technology and leveraging its potential, organizations can unlock a new era of growth and success.
So, let’s embrace the future of business, together.