Stocks Fall Despite Strong Jobs Report: Investors Fear Bigger Fed Rate Hikes
Stocks fall despite strong jobs report as investors fear bigger fed rate hikes – Stocks Fall Despite Strong Jobs Report: Investors Fear Bigger Fed Rate Hikes. This unexpected market reaction might seem puzzling, but it reveals a complex interplay between economic data, investor sentiment, and the looming threat of aggressive interest rate hikes. While the recent jobs report painted a picture of robust economic growth, the stock market reacted with a sell-off, driven by concerns that the Federal Reserve might be forced to implement larger interest rate increases to curb inflation.
This situation underscores the delicate balance between economic growth and inflation control. Investors are wary of the potential impact of rising interest rates on corporate profits and overall economic activity. The fear is that aggressive rate hikes could stifle economic growth and lead to a recession, a scenario that would likely weigh heavily on corporate earnings and stock valuations.
The Unexpected Stock Market Reaction
The recent decline in the stock market despite a strong jobs report has left many investors baffled. This seemingly contradictory situation highlights the complex interplay between economic data, investor sentiment, and market psychology. While a robust jobs report typically signals a healthy economy and should boost stock prices, the market’s reaction suggests a different narrative.
The Disconnect Between Economic Data and Market Sentiment
The strong jobs report, with its low unemployment rate and robust job growth, should have been a positive catalyst for the stock market. However, investors appear to be more concerned about the potential for the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates more aggressively in response to a strong economy.
This fear of higher interest rates outweighs the positive implications of the jobs report, leading to a sell-off in the market.
The stock market took a tumble today, even with a strong jobs report, as investors worry about the Federal Reserve raising interest rates more aggressively than expected. It’s a tough time for the economy, and it seems like even good news isn’t enough to soothe investors’ nerves.
Meanwhile, commuters are facing major delays at Kings Cross station for the second day in a row , adding to the general feeling of uncertainty and disruption. It’s a reminder that even when the economy seems to be doing well, there are still plenty of challenges to overcome.
Historical Examples of Similar Situations
The current situation is not unprecedented. Historically, there have been instances where positive economic indicators have been met with market downturns. For example, in 1987, the stock market experienced a sharp decline known as “Black Monday,” despite a relatively strong economy.
This decline was attributed to factors such as excessive speculation and investor panic. Similarly, in 2018, the stock market experienced a significant correction, despite strong economic growth, due to concerns about rising interest rates and trade tensions.
The Role of Investor Sentiment and Market Psychology
Investor sentiment and market psychology play a significant role in driving market reactions. In the current situation, investors are likely worried about the potential for higher interest rates to stifle economic growth. This fear, coupled with a general sense of uncertainty about the future, has led to a risk-off sentiment in the market.
Investors are selling off stocks and seeking safer investments, such as bonds, which are less volatile.
The Fear of Larger Fed Rate Hikes: Stocks Fall Despite Strong Jobs Report As Investors Fear Bigger Fed Rate Hikes
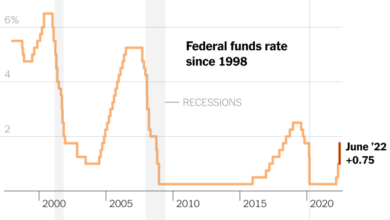
The recent stock market decline, despite a strong jobs report, highlights a growing concern among investors: the potential for more aggressive interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve. The Fed’s efforts to combat inflation have already led to several rate increases, and the market is now grappling with the implications of further tightening.
The Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Stock Valuations
Rising interest rates directly impact stock valuations by increasing the discount rate used to calculate the present value of future earnings. This discount rate reflects the opportunity cost of investing in stocks, as investors can now earn higher returns by investing in safer assets like bonds.
Consequently, higher interest rates lead to lower valuations for companies, as their future earnings are discounted more heavily.
The Potential Implications of Aggressive Rate Hikes on Economic Growth and Corporate Profits
Aggressive rate hikes can significantly impact economic growth and corporate profits. Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, potentially slowing down investment and hiring. This can lead to reduced economic activity, lower consumer spending, and ultimately, a decline in corporate profits.
It’s a strange market we’re in right now. Stocks are falling despite a strong jobs report, because investors are worried about the Fed raising interest rates even more aggressively. Meanwhile, on the political front, the Senate just passed a major climate, health, and tax bill, a big win for Biden.
This bill is likely to have a big impact on the economy, but it’s hard to say how it will affect the stock market in the long run. I guess we’ll just have to wait and see how things play out.
Comparison to Previous Periods of Aggressive Monetary Tightening
The current situation is reminiscent of past periods of aggressive monetary tightening, such as the early 1980s under Paul Volcker. The Fed’s efforts to tame inflation at that time led to a sharp recession, but ultimately brought inflation under control.
However, the current economic landscape is different, with factors like supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions adding complexity to the situation.
“The Fed’s decision to raise rates aggressively is a double-edged sword. While it can help tame inflation, it also risks slowing economic growth and hurting corporate profits.”
[Expert name/Source]
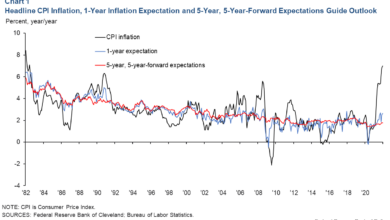
The Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates on the Economy
The relationship between inflation, interest rates, and economic growth is a complex one, with each factor influencing the others in a delicate balance. Understanding this interplay is crucial for navigating the economic landscape, especially during periods of high inflation and rising interest rates.
It’s a strange time in the markets, isn’t it? Stocks fell despite a strong jobs report, with investors seemingly more worried about the Fed’s potential rate hikes than the positive economic news. It’s almost like we’re all glued to the economic drama while the world of sports, like the Champions League, throws a wild card our way.
Experts are divided on who will take home the trophy this year, with Kylian Mbappé, Real Madrid, Barcelona, and even Arsenal all in the mix. You can read more about the Champions League predictions here. Meanwhile, back to the markets, it seems like the Fed’s shadow looms large, leaving investors to wonder what the future holds.
The Relationship Between Inflation, Interest Rates, and Economic Growth
Inflation, the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, can have a significant impact on economic growth. When inflation is high, consumers tend to spend less, as their purchasing power decreases. This reduced spending can lead to a slowdown in economic activity.
To counter inflation, central banks typically raise interest rates. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, discouraging businesses from investing and consumers from spending. This can also contribute to a slowdown in economic growth. However, higher interest rates can also attract foreign investment, strengthening the currency and potentially offsetting the negative impact on growth.
The Potential for a Recession
A recession is generally defined as two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth. Rising inflation and interest rates can increase the risk of a recession. High inflation erodes consumer purchasing power, leading to reduced demand. Higher interest rates can make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, hindering investment and potentially leading to job losses.
The combination of these factors can create a negative feedback loop, further slowing economic growth and potentially pushing the economy into a recession.
Key Economic Indicators and Their Current Trends
| Indicator | Current Trend | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation (CPI) | Rising | Reduces consumer purchasing power, potentially leading to a slowdown in economic growth. |
| Interest Rates (Federal Funds Rate) | Rising | Increases borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing economic growth and investment. |
| Unemployment Rate | Low | Indicates a strong labor market, but rising inflation and interest rates could lead to job losses. |
| GDP Growth | Slowing | Indicates a potential slowdown in economic activity, raising concerns about a recession. |
The Outlook for the Stock Market
The recent decline in the stock market, despite a strong jobs report, reflects investor concerns about the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) aggressive stance on interest rate hikes. This uncertainty has cast a shadow over the market’s future trajectory, leaving investors grappling with the potential implications of the Fed’s actions.
Potential Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts of Fed Rate Hikes
The Fed’s rate hikes aim to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thereby slowing economic growth. In the short term, this could lead to a slowdown in corporate earnings, as businesses face higher costs and reduced demand. This could further pressure stock prices, potentially leading to a correction or even a bear market.
However, the long-term impact depends on the Fed’s ability to successfully manage inflation without triggering a recession.
A successful outcome would see inflation gradually declining, leading to a stabilization of interest rates and a return to economic growth. This scenario could support a rebound in the stock market, as investors regain confidence in the economy’s future. Conversely, a failure to control inflation could lead to prolonged high interest rates, hurting economic activity and potentially pushing the economy into a recession. In this case, the stock market could experience a prolonged downturn, with investors anticipating further economic headwinds.
Factors Influencing the Stock Market’s Trajectory
Several factors will shape the stock market’s direction in the coming months. These include:
- Inflation:The rate of inflation and the Fed’s response to it will be a key driver of market sentiment. If inflation continues to decline, it could boost investor confidence, leading to a market rebound. However, persistent high inflation could fuel further rate hikes, dampening economic growth and weighing on stock prices.
- Economic Growth:The pace of economic growth will also be a crucial factor. Strong economic growth could support corporate earnings and drive stock prices higher. Conversely, a slowdown in growth could lead to lower earnings and a decline in stock valuations.
- Interest Rates:The level of interest rates will directly impact the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates could slow economic growth and reduce corporate profits, potentially leading to a decline in stock prices. Conversely, a pause or reversal in rate hikes could boost investor confidence and support a market rebound.
- Geopolitical Events:Geopolitical events, such as the ongoing war in Ukraine, can create market volatility. These events can disrupt supply chains, impact energy prices, and create uncertainty about the global economic outlook, all of which can affect stock prices.
Investor Strategies for Navigating Market Uncertainty
In this uncertain market environment, investors should consider the following strategies:
- Diversification:Spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies can help mitigate risk and enhance portfolio resilience. This can help protect against losses in any single asset class or sector.
- Long-Term Perspective:Maintaining a long-term investment horizon can help weather market fluctuations. Focusing on fundamental value and long-term growth potential can help investors ride out short-term volatility and benefit from market cycles.
- Active Management:Active management strategies, such as adjusting portfolio holdings based on market conditions, can help investors navigate volatility and potentially outperform the market. This requires careful monitoring of economic indicators, company performance, and market trends.
- Risk Management:Implementing risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders or using derivatives to hedge against market declines, can help protect investments during periods of market volatility. This can help limit potential losses and preserve capital.
The Importance of Diversification and Risk Management

The recent market volatility underscores the importance of diversification and risk management in investment strategies. Diversification is a fundamental principle that aims to mitigate investment risk by spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies. By reducing the impact of any single investment’s performance on the overall portfolio, diversification helps to cushion potential losses and enhance the potential for long-term growth.
Investment Strategies for Managing Portfolios in Volatile Markets, Stocks fall despite strong jobs report as investors fear bigger fed rate hikes
Diversification can be achieved through various investment strategies. Here are some examples of how investors can manage their portfolios in a volatile market:
- Asset Allocation:This involves dividing investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. A balanced portfolio with a mix of assets can help to reduce overall risk and provide potential returns in different market conditions.
For instance, during periods of economic uncertainty, bonds may offer more stability than stocks.
- Sector Rotation:This strategy involves shifting investments between different industry sectors based on economic trends and market expectations. For example, an investor might move funds from the energy sector to the technology sector if they believe the technology sector is poised for stronger growth.
- Geographic Diversification:This strategy involves investing in assets located in different countries. By diversifying geographically, investors can reduce their exposure to specific economic or political risks in any single region. For instance, investing in a global stock fund allows for exposure to a broad range of international markets.
Understanding Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals
It is crucial for investors to understand their own risk tolerance and investment goals before implementing any diversification strategy. Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s ability and willingness to accept potential losses in pursuit of higher returns. Investment goals, on the other hand, are the specific financial objectives an investor aims to achieve.
For example, a young investor with a long investment horizon and a higher risk tolerance may be comfortable allocating a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks, while an older investor nearing retirement with a lower risk tolerance may prefer a more conservative approach with a greater allocation to bonds.
Understanding these factors helps investors to develop a portfolio that aligns with their individual circumstances and financial objectives.