Blockchain for Climate Action: Solving Our Biggest Challenge
Solving the no 1 issue of our time using blockchain technology to scale climate action – Can blockchain technology be the key to tackling the climate crisis? It’s a bold claim, but one that’s gaining traction as we face the urgent need for scalable climate solutions. This innovative technology, known for its decentralized and transparent nature, holds immense potential for revolutionizing how we address climate change.
From tracking carbon emissions to fostering sustainable energy markets, blockchain offers a new paradigm for environmental action.
Imagine a world where every step taken to combat climate change is recorded and verifiable on an immutable ledger. This is the promise of blockchain, a technology that could bring unprecedented transparency and accountability to climate initiatives. But how exactly does it work, and what are the real-world applications?
Let’s delve deeper into the exciting possibilities of blockchain for climate action.
Defining the Climate Crisis
The climate crisis is a defining challenge of our time, marked by unprecedented changes in the Earth’s climate system driven primarily by human activities. It is a complex and multifaceted issue, characterized by rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
We need bold solutions to tackle the climate crisis, and blockchain technology could be the key to scaling climate action. Imagine a world where carbon credits are tracked transparently and efficiently, empowering individuals and businesses to invest in a greener future.
But as we strive for this vision, the dream of the open road collides with the reality of 5 a gallon gas, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable transportation solutions. This is where blockchain can play a crucial role, driving innovation in electric vehicles, renewable energy, and sustainable transportation infrastructure.
By fostering transparency and accountability, blockchain can help us build a cleaner, more equitable future.
The Urgency and Scale of the Climate Crisis
The urgency of addressing the climate crisis stems from the rapid pace of change and the potential for catastrophic consequences. The Earth’s average temperature has increased by approximately 1 degree Celsius since the pre-industrial era, and is projected to continue rising at an alarming rate.
This warming is driven by the accumulation of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere.
Evidence of the Climate Crisis
Numerous scientific studies and observations provide compelling evidence of the climate crisis.
Solving the number one issue of our time, climate change, requires a global effort, and blockchain technology can be a powerful tool for scaling climate action. It’s inspiring to see the impact of small acts of kindness, like the story of a kind stranger who brought a Starbucks barista to tears with a life-changing interaction you just saved a life kind stranger brings starbucks barista to tears in life changing interaction.
Just as that single act of generosity made a world of difference, blockchain’s transparency and accountability can empower individuals and organizations to take collective action on climate change.
- Global average temperatures have risen steadily over the past century, with the warmest years on record occurring in recent decades.
- Sea levels have risen by about 20 centimeters in the past century, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems.
- Extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and hurricanes, are becoming more frequent and intense.
- The Arctic sea ice is melting at an unprecedented rate, contributing to rising sea levels and disrupting marine ecosystems.
Consequences of Inaction
The consequences of inaction on climate change are severe and far-reaching.
- Rising sea levels will displace millions of people and inundate coastal cities.
- Extreme weather events will cause widespread damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and human health.
- Climate change will exacerbate existing social and economic inequalities, particularly in developing countries.
- The loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services will have profound consequences for human well-being.
Blockchain Technology
The climate crisis demands innovative solutions, and blockchain technology emerges as a promising tool to amplify our efforts. Blockchain, a decentralized and transparent ledger, offers a unique framework for addressing the challenges of climate action.
Blockchain Principles and Decentralization
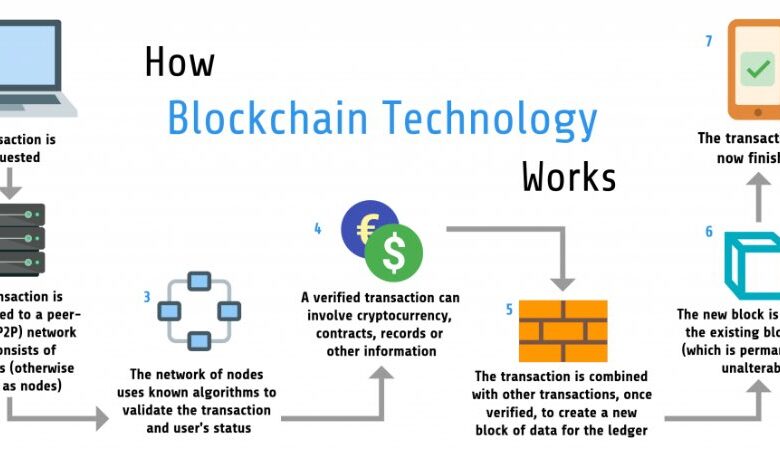
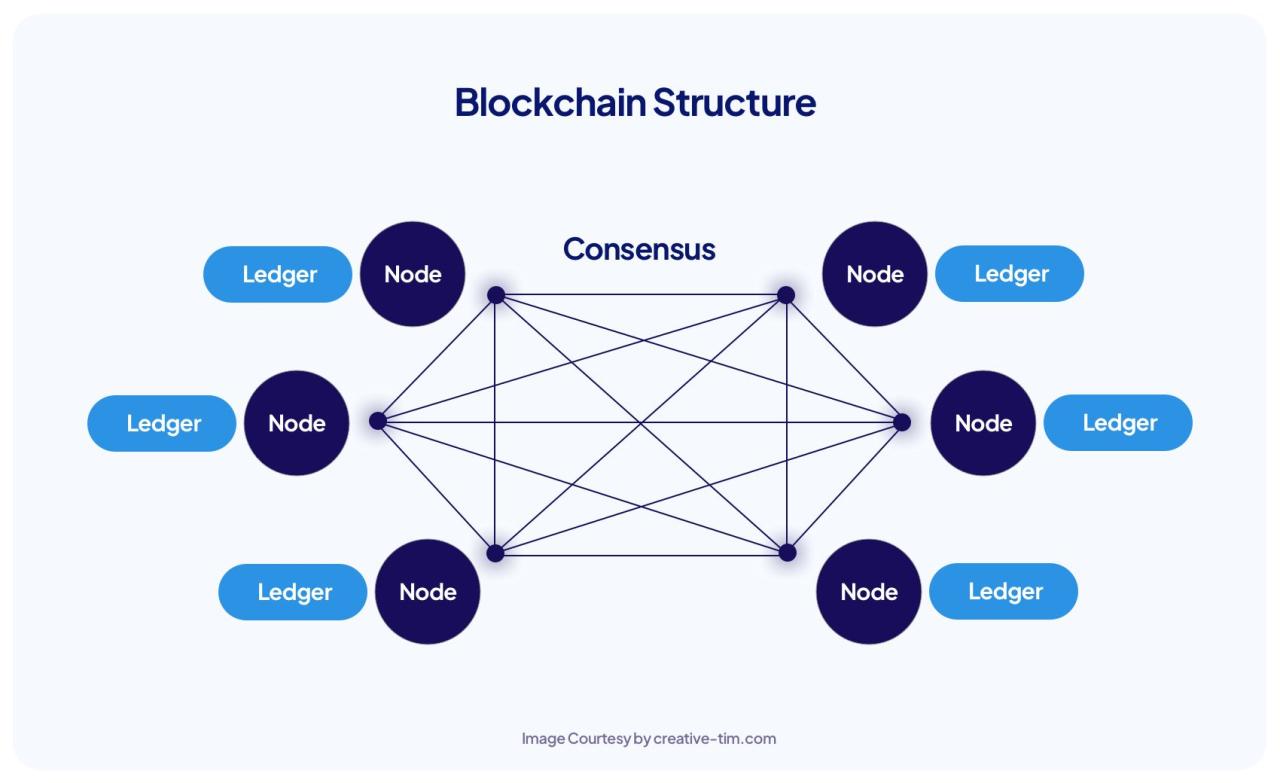
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers, known as nodes. This distributed nature ensures that the data is immutable and transparent, making it highly secure and tamper-proof. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the need for a central authority, promoting trust and accountability among participants.
Blockchain’s Role in Climate Action
Blockchain can significantly contribute to climate action by enhancing transparency, accountability, and efficiency in environmental initiatives. Its key applications include:
Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain enables the tracking of emissions and carbon offsets, ensuring their authenticity and integrity. For example, companies can use blockchain to record their carbon emissions, making this data readily accessible to stakeholders.
Accountability and Verifiability
Blockchain provides a verifiable record of actions taken to mitigate climate change, fostering trust and accountability. This transparency helps monitor the progress of environmental projects and ensures that funds are used efficiently.
Imagine a world where climate action isn’t just a concept, but a reality, powered by the transparency and efficiency of blockchain technology. Just as a secret network of women bravely provided access to reproductive healthcare before Roe v. Wade, inside the secret network of women who performed abortions before roe , we can create a decentralized system that empowers communities to build a sustainable future.
With blockchain, we can track carbon emissions, incentivize renewable energy adoption, and empower individuals to make a real difference in the fight against climate change.
Efficient Resource Management
Blockchain facilitates the creation of decentralized marketplaces for renewable energy and carbon credits, allowing for more efficient resource allocation. This promotes the development of sustainable energy solutions and incentivizes environmentally responsible practices.
Examples of Blockchain Applications in Climate Action
Several initiatives are leveraging blockchain technology to address climate change:
- ClimateChain: This platform enables the tracking of carbon emissions and the trading of carbon credits, promoting transparency and accountability in carbon markets.
- Climate Collective: This platform uses blockchain to connect individuals and organizations committed to climate action, fostering collaboration and resource sharing.
- Energy Web Foundation: This organization develops blockchain-based solutions for the energy sector, enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and grid optimization.
Benefits of Blockchain for Climate Action
Blockchain offers numerous benefits for climate action:
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain provides an immutable record of emissions, carbon offsets, and environmental projects, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines processes like carbon credit trading and renewable energy transactions, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Improved Collaboration: Blockchain facilitates collaboration among stakeholders, promoting joint efforts to address climate change.
- Greater Trust: Blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature fosters trust and confidence in environmental initiatives.
Applications of Blockchain in Climate Action: Solving The No 1 Issue Of Our Time Using Blockchain Technology To Scale Climate Action
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency, immutability, and security features, presents a compelling solution for tackling the climate crisis. Its decentralized nature and ability to track and verify data make it an ideal tool for addressing various aspects of climate action.
Carbon Emission Tracking and Verification
Blockchain can play a pivotal role in accurately tracking and verifying carbon emissions, promoting transparency and accountability in carbon markets.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emission Tracking | Blockchain can record and track carbon emissions from various sources, including industries, transportation, and energy production. This data is stored immutably on a distributed ledger, making it tamper-proof and verifiable. |
|
|
| Carbon Emission Verification | Blockchain can facilitate the verification of carbon emission reduction projects, ensuring that claims of emission reductions are accurate and verifiable. |
|
|
Renewable Energy Trading and Markets
Blockchain technology can revolutionize renewable energy trading by enabling efficient, transparent, and secure transactions.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading | Blockchain can facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell renewable energy directly from each other, bypassing traditional intermediaries. |
|
|
| Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) | Blockchain can streamline the tracking and trading of RECs, which represent the environmental benefits of renewable energy generation. |
|
|
Sustainable Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can enhance transparency and accountability in supply chains, promoting sustainable practices and reducing environmental impact.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Origin Tracking | Blockchain can track the origin and journey of products throughout the supply chain, providing consumers with information about the sustainability of their purchases. |
|
|
| Environmental Impact Monitoring | Blockchain can monitor the environmental impact of production processes, providing data on resource consumption, emissions, and waste generation. |
|
|
Environmental Finance and Green Investments, Solving the no 1 issue of our time using blockchain technology to scale climate action
Blockchain can facilitate the development of new financial instruments and investment models that promote sustainable development.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Bonds | Blockchain can improve the transparency and accountability of green bonds, which are debt securities issued to finance environmentally friendly projects. |
|
|
| Impact Investing | Blockchain can facilitate impact investing, where investors seek to generate both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact. |
|
|
Climate Change Adaptation and Resilience Projects
Blockchain can support the development and implementation of climate change adaptation and resilience projects, enabling better coordination and resource allocation.
| Application | Description | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disaster Relief and Response | Blockchain can facilitate the efficient and transparent distribution of aid and resources during natural disasters, ensuring that assistance reaches those who need it most. |
|
|
| Climate Risk Assessment and Management | Blockchain can help communities and organizations assess and manage climate risks, such as sea-level rise, extreme weather events, and water scarcity. |
|
|
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain technology holds immense promise for addressing the climate crisis, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for its effective implementation.
Scalability and Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, has been a significant concern. PoW-based blockchains require substantial computational power to validate transactions, leading to high energy consumption. This has raised concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology, potentially undermining its sustainability goals.
Regulatory Frameworks and Legal Complexities
The rapidly evolving nature of blockchain technology has presented challenges in establishing clear regulatory frameworks. Lack of standardized regulations can create uncertainty for businesses and hinder innovation. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain can pose challenges in enforcing legal obligations and resolving disputes.
Interoperability Between Blockchain Platforms
The fragmented landscape of blockchain platforms, with various protocols and standards, poses a significant obstacle to interoperability. The lack of seamless communication between different blockchain networks can hinder the exchange of data and collaboration between different stakeholders.
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
Widespread adoption of blockchain technology for climate action requires overcoming a lack of awareness and understanding of its potential. Many stakeholders, including policymakers, businesses, and individuals, may not be familiar with the applications and benefits of blockchain technology. This knowledge gap can hinder the development and implementation of blockchain-based solutions.
Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges
- Transition to More Energy-Efficient Consensus Mechanisms:Exploring and adopting alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or Proof-of-Authority (PoA), which require significantly less energy, can significantly reduce the environmental impact of blockchain networks.
- Develop Clear and Harmonized Regulatory Frameworks:Collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and experts is crucial to develop clear and harmonized regulatory frameworks that promote innovation while addressing potential risks.
- Promote Interoperability Standards:Developing standardized protocols and interoperability solutions can enable seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchain platforms, facilitating collaboration and broader adoption.
- Increase Awareness and Education:Investing in education and outreach initiatives to raise awareness about the potential of blockchain technology for climate action can foster greater understanding and encourage wider adoption.
Future Directions and Opportunities
The integration of blockchain technology into climate action is still in its early stages, but its potential to revolutionize how we address the climate crisis is immense. As the technology matures and its applications become more sophisticated, we can expect to see even greater strides in climate action initiatives.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Blockchain technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations and applications emerging regularly. This dynamism is a key driver of the technology’s potential in climate action. Some key emerging trends include:
- Decentralized Renewable Energy Markets:Blockchain can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and communities to buy and sell renewable energy directly from each other, bypassing traditional energy grids and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. For example, the Power Ledger platform enables homeowners with solar panels to sell excess energy to their neighbors, creating a local energy market that is more efficient and sustainable.
- Carbon Credit Tracking and Verification:Blockchain’s immutability and transparency make it ideal for tracking and verifying carbon credits, ensuring their authenticity and preventing fraud. This can enhance the integrity of carbon markets and encourage greater participation in carbon offsetting programs. The Climate Chain Coalition, for instance, uses blockchain to track and manage carbon emissions data, ensuring accurate reporting and accountability.
- Green Finance and Investment:Blockchain can streamline and enhance green finance initiatives by facilitating the issuance and trading of green bonds, promoting investments in sustainable projects, and providing transparent data on environmental impact. The World Bank has issued blockchain-based green bonds, demonstrating the potential of this technology to mobilize capital for climate action.
- Sustainable Supply Chain Management:Blockchain can create transparent and traceable supply chains, allowing businesses to track the origin and environmental impact of their products and materials. This can help consumers make informed choices about sustainable products and encourage companies to adopt more environmentally responsible practices.
For example, the Provenance platform uses blockchain to track the journey of coffee beans from farm to cup, ensuring ethical sourcing and sustainable practices.
Wrap-Up
As we move forward, the potential of blockchain to drive climate action is undeniable. While challenges remain, the innovative spirit of this technology, coupled with a global commitment to sustainability, offers a glimmer of hope for a greener future.
By embracing blockchain’s transformative power, we can unlock a new era of environmental responsibility, one where transparency, accountability, and collaboration pave the way for a more sustainable world.






