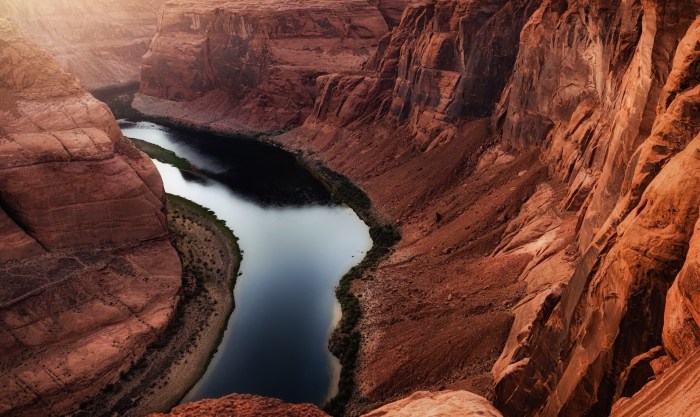
Ongoing Megadrought Puts the West in Uncharted Waters
Ongoing megadrought puts the west in uncharted waters, a stark reality that’s forcing us to confront the consequences of climate change and unsustainable water practices. This prolonged drought, stretching back decades, is unlike anything seen before in the region, impacting everything from water supplies to ecosystems and economies.
The severity of the megadrought is unprecedented, pushing the West towards a future where water scarcity becomes the defining challenge.
From the shrinking snowpack in the Sierra Nevada to the drying up of reservoirs and rivers, the megadrought is transforming the landscape of the West. Cities are facing water rationing, farmers are struggling to irrigate crops, and ecosystems are teetering on the brink of collapse.
The economic and societal impacts are far-reaching, threatening livelihoods, sparking conflicts over water resources, and even forcing people to relocate. This is a crisis that demands urgent action, requiring a paradigm shift in how we manage water resources and adapt to a drier future.
Impacts on Ecosystems: Ongoing Megadrought Puts The West In Uncharted Waters
The ongoing megadrought in the Western United States is having profound and widespread impacts on ecosystems, pushing them beyond their natural resilience and threatening their long-term viability. These impacts are not only evident in the decline of plant and animal populations but also in the increased risk of wildfires and the potential for ecological tipping points.
The ongoing megadrought in the West is forcing us to rethink everything, from water conservation to food security. It’s a reminder that even basic necessities like food can be vulnerable to unforeseen challenges, like the recent consumer protection issues food safety warning for ez noble sushi ez noble sushi is voluntarily recalling the products which contained unlabeled allergens.
These kinds of events highlight the need for vigilance and adaptability as we navigate the uncharted waters of a changing climate.
Biodiversity Loss
The megadrought is causing significant biodiversity loss across the Western landscape. Many plant and animal species are struggling to adapt to the changing conditions, leading to declines in population size and range. For example, the decline of the Pinyon pine, a key species in the Southwest, has led to a decrease in the populations of animals that rely on it for food and habitat, such as the pinyon jay and the Abert’s squirrel.
The loss of these keystone species can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem, disrupting food webs and altering ecological processes.
Forest Health and Wildfire Risk
The megadrought is exacerbating forest health issues, making trees more susceptible to pests, diseases, and wildfires. Drought stress weakens trees, making them more vulnerable to attacks by bark beetles and other insects. These insects can kill trees, creating large swaths of dead trees that provide fuel for wildfires.
The ongoing megadrought gripping the West is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet’s systems. While we grapple with the challenges of water scarcity, it’s important to remember that societal inequities, like the staggering 192 billion dollar gender gap in art , can also have a significant impact on our ability to adapt to such crises.
Finding solutions to the megadrought will require a multifaceted approach that addresses both environmental and social issues.
The combination of drought, dead trees, and increased human activity has led to an increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires in the West. These fires can devastate forests, release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and contribute to the ongoing drought cycle.
Changes in Ecosystem Dynamics
The megadrought is causing significant changes in ecosystem dynamics, leading to shifts in plant and animal communities and altering the overall structure and function of ecosystems. For instance, the decline of native grasses in grasslands is allowing invasive species to take over, further degrading the ecosystem and reducing its ability to support biodiversity.
These changes can also lead to the emergence of new ecological relationships, as species adapt to the changing conditions and compete for limited resources.
The ongoing megadrought in the West is a stark reminder of the fragility of our environment. It’s a story of resilience, adaptation, and the need for collective action. And while we’re on the topic of resilience, the story of John Travolta and Kirstie Alley’s enduring friendship, as detailed in the article john travolta and kirstie alley a love story cnn , is a testament to the power of human connection.
Just like the West, we need to find ways to weather the storms and come out stronger on the other side.
Societal and Economic Impacts
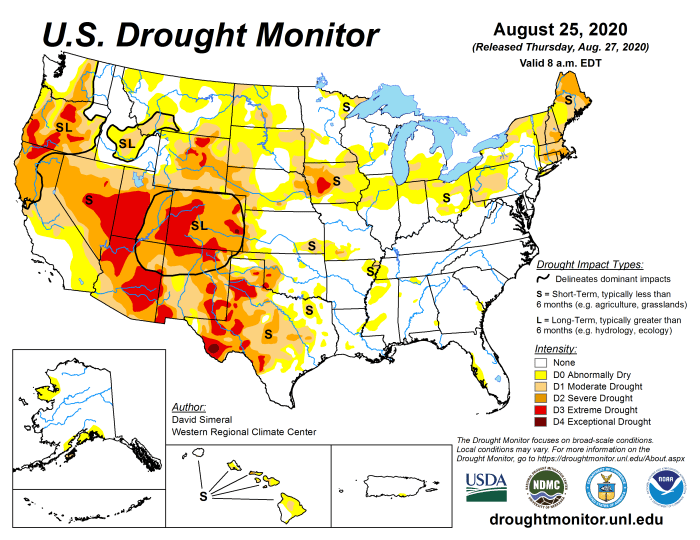
The ongoing megadrought in the Western United States is not just an environmental crisis; it is also a looming societal and economic catastrophe. Water scarcity, a direct consequence of the drought, is already straining communities and impacting critical industries, with the potential to trigger mass migration, economic decline, and social unrest.
The Potential for Mass Migration and Displacement
The scarcity of water, a fundamental resource for human life, will inevitably lead to mass migration and displacement. As water sources dwindle, communities reliant on agriculture and other water-intensive industries will face severe hardship, forcing residents to seek more hospitable environments.
The potential for mass migration is particularly alarming in rural areas where populations are already vulnerable and lack the resources to adapt to changing conditions.
Economic Consequences of Drought
The economic consequences of the megadrought are far-reaching and severe. Agriculture, a cornerstone of the Western economy, is particularly vulnerable. The lack of water will lead to reduced crop yields, livestock losses, and potentially, the abandonment of farmland. This will not only impact farmers and ranchers but also ripple through the food supply chain, leading to higher food prices and potential shortages.The tourism industry, another vital sector in the West, will also suffer significant economic losses.
The beauty and natural attractions of the region, such as national parks and forests, are heavily reliant on water. As water sources diminish, these attractions will become less appealing, leading to decreased tourism revenue and job losses.
The Potential for Social Unrest and Conflict over Water Resources
The dwindling water supply in the West is creating a powder keg of social unrest and conflict. As water scarcity intensifies, competition for this precious resource will escalate, leading to disputes between communities, states, and even nations. The potential for violence and instability cannot be ignored.For instance, the Colorado River, a lifeline for millions of people in the West, is facing unprecedented strain.
The river’s flow has been declining for decades, and the drought has exacerbated the situation. The seven states that rely on the Colorado River are now locked in a bitter struggle over water allocation, with each state vying for its share of a shrinking resource.
“The Colorado River is a symbol of the West’s prosperity and its future. But the megadrought is turning this symbol into a source of conflict.” Dr. Brad Udall, a water expert at Colorado State University.
The megadrought is not just an environmental crisis; it is also a societal and economic crisis with the potential to reshape the West for generations to come.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies
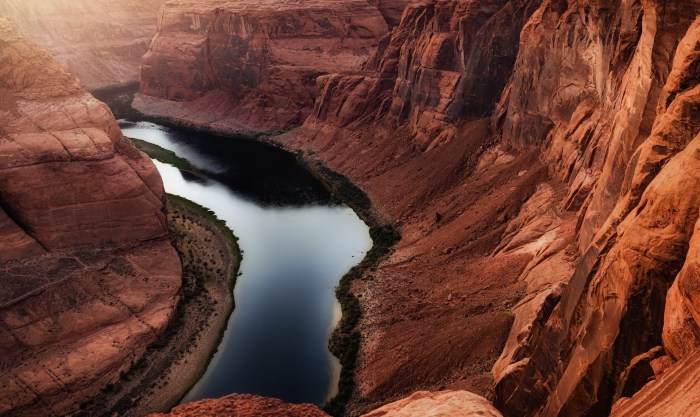

The ongoing megadrought in the Western United States presents a formidable challenge, demanding proactive adaptation and mitigation strategies to navigate this unprecedented water scarcity. These strategies aim to reduce the impacts of the drought and build resilience in the face of a changing climate.
Water Conservation
Water conservation is a cornerstone of adaptation to the megadrought. It involves reducing water consumption in various sectors, from residential and commercial use to agriculture and industry.
- Residential and Commercial Water Conservation:Implementing water-efficient appliances, such as low-flow showerheads and toilets, can significantly reduce indoor water usage. Outdoor water conservation measures include using drought-tolerant landscaping, installing smart irrigation systems, and practicing water-wise gardening techniques.
- Agricultural Water Conservation:Farmers can adopt innovative irrigation technologies, such as drip irrigation and precision irrigation, which deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Implementing water-efficient crops and crop rotations can also reduce water demand.
- Industrial Water Conservation:Industries can optimize water usage through recycling and reuse programs, implementing water-efficient processes, and adopting closed-loop systems to minimize water waste.
Drought-Resistant Agriculture
Adapting agricultural practices to drought conditions is crucial for maintaining food production and economic stability.
- Developing Drought-Tolerant Crops:Investing in research and development to breed and cultivate drought-resistant crop varieties that can thrive with reduced water availability is essential. These crops can withstand dry conditions and produce yields despite limited water resources.
- Improving Soil Health:Healthy soil retains moisture better, enhancing drought resilience. Implementing practices like no-till farming, cover cropping, and organic matter addition improve soil structure and water retention capacity.
- Water Harvesting and Storage:Collecting rainwater and storing it for later use can provide a supplementary water source for irrigation, reducing reliance on dwindling water supplies.
Government Policies and Investments
Government policies and investments play a crucial role in mitigating the effects of the megadrought.
- Water Management Policies:Effective water management policies are essential for allocating water resources equitably and sustainably. This includes setting water use limits, promoting water conservation measures, and encouraging efficient water use in various sectors.
- Financial Incentives:Government incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, can encourage water conservation and the adoption of drought-resistant technologies. These incentives can make water-saving practices more financially attractive for individuals, businesses, and farmers.
- Infrastructure Investments:Investing in water infrastructure, such as dams, reservoirs, and water treatment plants, can enhance water storage and distribution capabilities, improving water security and resilience.
Technological Solutions
Technological solutions hold promise in addressing water scarcity, but they come with challenges and considerations.
- Desalination:Desalination plants remove salt from seawater to produce freshwater. While a potential solution, it is energy-intensive and can be costly, requiring careful assessment of its feasibility and environmental impact.
- Water Recycling and Reuse:Recycling wastewater for irrigation, industrial use, and even potable water production is a promising approach. Advanced treatment technologies can remove contaminants and ensure water quality meets safety standards.
The Future of the West
The ongoing megadrought, a stark reminder of the climate crisis’s impact, paints a challenging picture for the Western United States. The long-term consequences of this unprecedented water scarcity extend far beyond the immediate impacts on ecosystems, societal structures, and economic stability.
It necessitates a fundamental shift in our approach to water management and resource allocation, demanding innovative solutions and collaborative efforts to ensure the future of the West.
Long-Term Consequences
The megadrought’s long-term consequences are multifaceted and interconnected. Water scarcity will intensify, leading to increased competition for resources among different sectors, including agriculture, urban development, and environmental conservation. The decline in water availability will impact agricultural yields, leading to food insecurity, economic hardship, and potentially mass migration.
Additionally, the reduced water flow in rivers and streams will threaten aquatic ecosystems, impacting biodiversity and disrupting the delicate balance of natural habitats.
Paradigm Shift in Water Management
Addressing the megadrought requires a paradigm shift in water management. Traditional approaches, often focused on maximizing water use for specific sectors, are no longer sustainable. A more holistic approach, encompassing water conservation, efficiency improvements, and equitable allocation, is crucial. This shift necessitates prioritizing water conservation measures across all sectors, promoting water-efficient technologies, and implementing robust water-use regulations.
Innovative Solutions and Collaborations
Innovative solutions and collaborative efforts are vital to address the challenges posed by the megadrought. Water recycling and desalination technologies can significantly enhance water supply. Investing in drought-resistant crops and water-efficient irrigation systems can help maintain agricultural productivity.
Interstate and regional collaboration is essential for developing shared solutions, such as water transfer projects and drought-resistant infrastructure.
Examples of Innovative Solutions, Ongoing megadrought puts the west in uncharted waters
- Water Recycling:Cities like Los Angeles and San Diego have implemented advanced water recycling programs, treating wastewater to a high standard and using it for irrigation and industrial purposes, reducing their reliance on traditional water sources.
- Desalination:Coastal cities like San Diego and Tampa Bay are investing in desalination plants, which remove salt from seawater, providing a reliable source of fresh water. While expensive, desalination offers a potential solution for regions with limited freshwater resources.
- Drought-Resistant Crops:Agricultural researchers are developing drought-resistant crops, such as varieties of corn and wheat that require less water, improving resilience in arid regions.
- Water-Efficient Irrigation Systems:Modern irrigation technologies, such as drip irrigation, deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing water loss through evaporation. These systems have significantly reduced water consumption in agriculture.