How Fed Rate Cuts Impact the Global Economy
How Fed rate cuts affect the global economy is a question that sparks debate among economists and investors alike. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, plays a pivotal role in setting interest rates, which in turn influences the flow of money, investment, and economic activity worldwide.
Understanding the intricate web of connections between Fed rate cuts and global economic performance is crucial for navigating the complexities of international finance.
When the Fed cuts interest rates, it becomes cheaper for businesses and individuals to borrow money. This can stimulate economic growth by encouraging investment and spending. However, the ripple effects extend far beyond US borders, impacting currency exchange rates, global investment flows, and the overall health of economies around the world.
Understanding the Fed Rate: How Fed Rate Cuts Affect The Global Economy
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. Its primary responsibility is to maintain the stability of the U.S. financial system and promote economic growth. One of the key tools the Fed uses to achieve these goals is setting interest rates.The Fed rate, also known as the federal funds rate, is the target interest rate that commercial banks charge each other for the overnight lending of reserves.
While the Fed does not directly set the interest rates that consumers and businesses pay, its actions significantly influence these rates.
Fed rate cuts can have a ripple effect across the globe, influencing everything from currency exchange rates to investment flows. These economic shifts can also have an impact on homeland security, as they can lead to increased instability and the potential for unrest.
The advancements in technology used by homeland security, like facial recognition and data analysis, homeland securitys tech effects , can be vital in navigating these complex situations. Ultimately, the economic policies of major nations like the United States have far-reaching consequences, impacting not just financial markets but also global security landscapes.
The Mechanism of Fed Rate Cuts
When the Fed cuts interest rates, it makes borrowing money cheaper for banks. This encourages banks to lend more money to businesses and individuals, stimulating economic activity. Lower interest rates also make it less expensive for businesses to invest in new projects and for consumers to make major purchases like homes or cars.
The Fed’s rate cuts can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, influencing factors such as:* Consumer spending:Lower interest rates make it cheaper to borrow money for things like cars and homes, leading to increased consumer spending.
Business investment
Businesses are more likely to invest in new projects and expansions when borrowing costs are lower.
Economic growth
The combined effects of increased consumer spending and business investment can lead to higher economic growth.
The Fed’s rate cuts can have a ripple effect across the globe, impacting everything from currency exchange rates to investment decisions. While economists debate the long-term consequences, it’s clear that these moves influence global economic sentiment. And speaking of sentiment, the news that a key injured Yankees reliever could return with a deep playoff run is sure to boost spirits among fans, proving that even in the face of uncertainty, hope can spring eternal.
Of course, the Fed’s decisions will ultimately have a greater impact on the global economy than a single baseball player’s return, but it’s a reminder that even in a world of complex financial issues, there’s always room for a little bit of optimism.
Examples of Historical Fed Rate Cuts
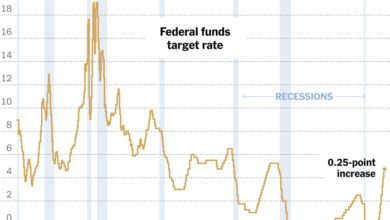
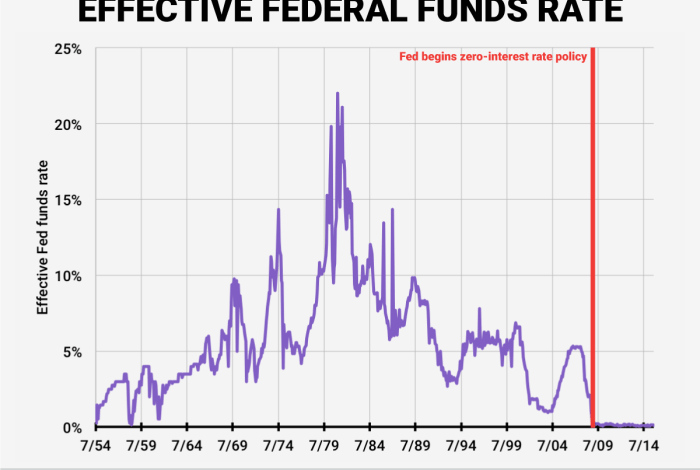
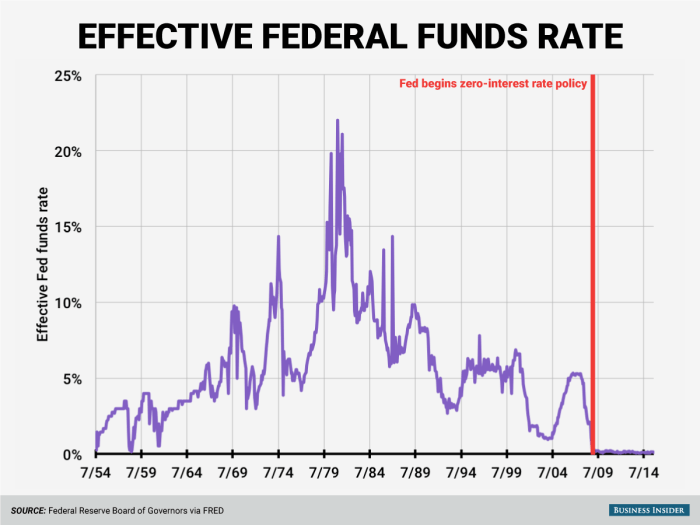
The Fed has a history of using rate cuts to stimulate the economy during periods of recession or economic slowdown.* The 2008 Financial Crisis:In response to the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed aggressively cut interest rates to near zero, aiming to boost borrowing and lending and prevent a deeper recession.
The COVID-19 Pandemic
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed again lowered interest rates to zero and implemented other measures to support the economy, such as quantitative easing.These examples demonstrate how Fed rate cuts can be a powerful tool for influencing economic activity. However, the effectiveness of rate cuts can vary depending on various factors, including the overall state of the economy and the response of businesses and consumers.
Impact on Global Currency Markets
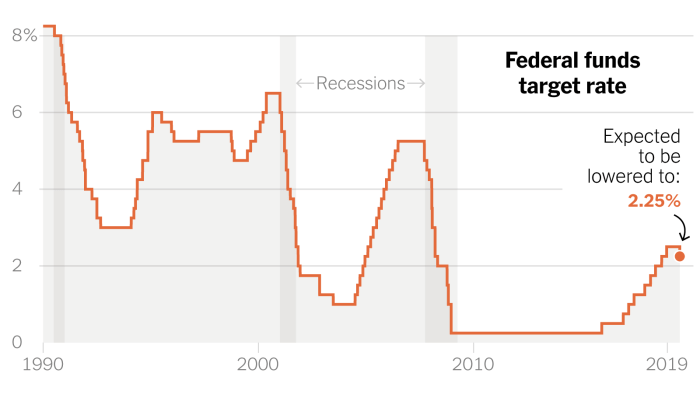
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions have a profound impact on global currency markets. By influencing the value of the US dollar, Fed rate cuts can ripple through international trade and investment flows, shaping economic landscapes across the globe.
Impact of Fed Rate Cuts on Currency Exchange Rates
The relationship between Fed rate cuts and currency exchange rates is largely driven by the principle of relative interest rates. When the Fed lowers interest rates, it makes borrowing cheaper in the US, potentially encouraging investors to seek higher returns in other countries with stronger currencies.
The ripple effects of Fed rate cuts reverberate across the globe, influencing everything from currency exchange rates to the affordability of housing. But beyond these tangible impacts, the decisions of the Fed also reflect a deeper, often unspoken, truth: the different valuations of life.
This perspective underscores how the Fed’s choices, while seemingly driven by economic data, are ultimately shaped by a complex interplay of cultural, social, and political factors. Understanding this nuanced context helps us navigate the complex landscape of global economics and appreciate the interconnectedness of seemingly disparate aspects of our world.
This outflow of capital can weaken the US dollar, making it cheaper to buy for those holding other currencies. Conversely, higher interest rates in the US tend to attract foreign investment, strengthening the dollar.
Impact of Fed Rate Cuts on the Value of the US Dollar
Fed rate cuts can lead to a depreciation of the US dollar against other currencies. This occurs because investors may seek higher returns in countries with stronger currencies, leading to a decrease in demand for the dollar and a subsequent decline in its value.For example, when the Fed lowered interest rates in 2019, the US dollar weakened against the euro and the Japanese yen.
This depreciation made US exports more competitive in global markets, but also increased the cost of imports for American consumers.
Implications of a Weaker US Dollar on Global Trade and Investment
A weaker US dollar can have significant implications for global trade and investment. For US exporters, a weaker dollar can boost competitiveness by making their products cheaper in foreign markets. This can lead to increased sales and economic growth in the US.
However, a weaker dollar also makes imports more expensive, potentially leading to higher inflation and reduced consumer spending.For foreign investors, a weaker dollar can make US assets, such as stocks and bonds, more attractive. This can lead to increased foreign investment in the US, boosting economic growth.
However, a weaker dollar can also make it more expensive for foreign companies to invest in the US, potentially hindering economic development.
A weaker US dollar can also impact global trade flows by making US exports more competitive while making imports more expensive. This can lead to shifts in the global supply chain and potentially create opportunities for other countries to become more competitive in international markets.
Effects on Global Investment and Capital Flows

Fed rate cuts can significantly influence global investment flows, particularly towards emerging markets. As interest rates in the US fall, investors may seek higher returns elsewhere, leading to increased capital inflows into emerging economies. However, this flow of capital can be volatile and subject to sudden reversals, potentially destabilizing emerging markets.
Impact on Emerging Markets
Lower US interest rates can make emerging market assets more attractive to international investors. This is because the relative return on investments in emerging markets becomes higher compared to US investments. For example, if US Treasury yields fall to 1%, while emerging market bonds offer yields of 5%, investors may be incentivized to shift their capital towards emerging markets.
- Increased Investment Flows:Lower US interest rates can attract foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment into emerging markets. This influx of capital can stimulate economic growth, support infrastructure development, and create job opportunities. For instance, during the 2010s, several emerging markets experienced substantial capital inflows following US rate cuts, leading to economic expansion and increased financial market activity.
- Currency Appreciation:The increased demand for emerging market assets can lead to currency appreciation. This makes imports cheaper and exports more expensive, potentially impacting trade balances. For example, the Brazilian Real and the Indian Rupee experienced significant appreciation in the aftermath of US rate cuts in 2019, driven by increased foreign investment.
- Potential for Volatility:While increased capital inflows can be beneficial, they can also create volatility in emerging markets. Sudden reversals in investment flows can lead to currency depreciation, asset price declines, and economic instability. For example, the “taper tantrum” of 2013, triggered by the anticipation of US rate hikes, resulted in significant capital outflows from emerging markets, leading to currency depreciations and market turmoil.
Implications for Global Economic Growth
Fed rate cuts can have a significant impact on global economic growth, influencing both short-term and long-term economic trends. The effects of these cuts can vary depending on the region and sector of the global economy, and it is crucial to understand these nuances to grasp the overall implications.
Short-Term Impact on Global Economic Growth
Rate cuts typically stimulate economic activity in the short term by making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This can lead to increased investment, spending, and overall economic growth. However, the magnitude of this effect can vary depending on several factors, including the level of existing interest rates, the state of the economy, and the confidence of businesses and consumers.
Long-Term Impact on Global Economic Growth
The long-term impact of Fed rate cuts on global economic growth is more complex and can depend on how the cuts are implemented and the broader economic context. While rate cuts can stimulate economic activity in the short term, they can also lead to higher inflation in the long term if not managed carefully.
Additionally, prolonged periods of low interest rates can lead to asset bubbles and increased financial instability.
Impact on Different Regions and Sectors, How fed rate cuts affect the global economy
The impact of Fed rate cuts can vary across different regions and sectors of the global economy. For instance, emerging markets may experience a surge in capital inflows as investors seek higher returns, potentially boosting economic growth. However, this can also lead to currency appreciation and make exports less competitive.
In developed economies, rate cuts can lead to increased consumer spending and business investment, but they may also weaken the currency and make imports more expensive.
Impact on Key Economic Indicators
The following table showcases the potential impact of Fed rate cuts on key economic indicators across major economies:
| Economic Indicator | United States | Eurozone | Japan | China |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | Increase | Increase | Increase | Increase |
| Inflation | Increase | Increase | Increase | Increase |
| Unemployment Rate | Decrease | Decrease | Decrease | Decrease |
| Currency Value | Depreciation | Depreciation | Depreciation | Appreciation |
It is important to note that these are just potential outcomes and the actual impact of Fed rate cuts on global economic growth can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors.
Considerations for Global Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) rate cuts have significant implications for global monetary policy, creating both opportunities and challenges for central banks worldwide. Coordinating monetary policy in a globalized world, where economies are interconnected, becomes crucial to manage the potential spillover effects of the Fed’s actions.
Challenges of Coordinating Monetary Policy
The Fed’s rate cuts can influence global currency markets, investment flows, and economic growth, prompting other central banks to adjust their own monetary policies. However, coordinating these adjustments presents significant challenges.
- Differing Economic Conditions:Each country faces unique economic circumstances, requiring tailored monetary policy responses. While the Fed may cut rates to stimulate the US economy, other countries may be facing different economic pressures, such as inflation or currency depreciation, requiring different policy approaches.
- Currency Volatility:Fed rate cuts can lead to currency depreciation in other countries, potentially causing inflation and economic instability. This necessitates careful coordination between central banks to manage exchange rate fluctuations and maintain price stability.
- Capital Flows:Fed rate cuts can attract capital flows to the US, potentially leading to capital outflows from other countries. This can put downward pressure on their currencies and impact their economic growth.
Potential Unintended Consequences of Fed Rate Cuts
While Fed rate cuts can stimulate the US economy, they can also have unintended consequences for other economies.
- Currency Wars:As countries try to devalue their currencies to gain a competitive advantage, they may engage in “currency wars,” leading to instability in global exchange rates and hindering international trade.
- Increased Risk Appetite:Fed rate cuts can encourage investors to take on more risk, potentially leading to asset bubbles and financial instability.
- Exacerbated Inequality:The benefits of Fed rate cuts may not be evenly distributed, potentially exacerbating income inequality within countries and globally.
Recommendations for Mitigating Risks
Global policymakers can take steps to mitigate the risks associated with Fed rate cuts.
- Enhanced Communication:Open and transparent communication between central banks is crucial to understand each other’s policy intentions and coordinate responses to Fed rate cuts. This can help prevent misinterpretations and market volatility.
- Flexible Monetary Policy:Central banks should maintain flexible monetary policies to adjust to changing economic conditions and manage the potential spillover effects of Fed rate cuts. This may involve using a range of policy tools, such as interest rates, reserve requirements, and quantitative easing.
- International Cooperation:Global institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), can play a vital role in facilitating coordination and cooperation between central banks. This can involve sharing information, providing technical assistance, and promoting policy consistency.