
Boeing Ousts Space Unit Head After Astronauts Stranded, Billions Lost
Boeing ousts head of troubled space unit after astronauts left stranded billions in losses. The aerospace giant has faced a series of setbacks in its space program, culminating in the recent incident where astronauts were left stranded in orbit due to technical failures.
This event, coupled with billions of dollars in losses, has led to the removal of the head of Boeing’s space unit, a decision that reflects the company’s desperate need to regain public trust and restore its reputation in the space industry.
The incident involving the stranded astronauts has brought to light the significant challenges Boeing has faced in its space program. The company’s reliance on outdated technology and its failure to address critical safety concerns have contributed to these issues. This incident has also highlighted the financial strain Boeing has been under, with the space unit’s troubles costing the company billions of dollars.
These losses have impacted the company’s overall business, raising concerns about its future prospects in the competitive space industry.
Boeing’s Decision to Oust Space Unit Head

Boeing’s decision to remove Jim Chilton, the head of its troubled space unit, came after a series of setbacks and delays in the company’s ambitious space program. These challenges have resulted in significant financial losses and strained relationships with customers, particularly NASA.
Timeline of Events Leading to Chilton’s Removal
The decision to remove Chilton was the culmination of a series of events that highlighted the difficulties faced by Boeing’s space unit.
- December 2019:Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft, designed to transport astronauts to the International Space Station, failed to reach its intended orbit during its first uncrewed test flight. This was a major setback for the company, as it was vying for NASA’s commercial crew program contract alongside SpaceX.
- August 2020:Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft was finally launched on its second uncrewed test flight, but this mission also experienced technical issues, forcing the company to delay its first crewed flight.
- April 2021:Boeing successfully completed its first crewed flight of the Starliner spacecraft, marking a significant milestone for the company. However, the delay in launching this mission had already cost Boeing millions of dollars and further strained its relationship with NASA.
- November 2022:Boeing announced a delay in the launch of its next crewed Starliner mission, citing technical issues and further pushing back the schedule for its space program.
- January 2023:Boeing announced that it was removing Jim Chilton as the head of its space unit, citing the need for “fresh leadership” and a “renewed focus” on its space program.
Challenges Faced by Boeing’s Space Unit
The space unit’s struggles were not solely due to technical issues. The company also faced challenges in areas such as:
- Cost overruns:The Starliner program has been plagued by cost overruns, leading to significant financial losses for Boeing.
- Schedule delays:The delays in launching the Starliner spacecraft have pushed back the company’s space program timeline and caused further financial losses.
- Competition from SpaceX:Boeing’s space unit has faced intense competition from SpaceX, which has successfully launched numerous missions and secured a large share of NASA’s commercial crew program contract.
- Pressure from NASA:NASA has been critical of Boeing’s performance on the Starliner program, expressing concerns about the company’s ability to deliver a reliable and safe spacecraft.
Impact of Chilton’s Removal
Chilton’s removal is a significant event for Boeing and the company’s space program. It remains to be seen whether this change in leadership will be enough to address the challenges faced by the space unit and restore confidence in the company’s ability to compete in the rapidly evolving space industry.
The Stranded Astronauts Incident
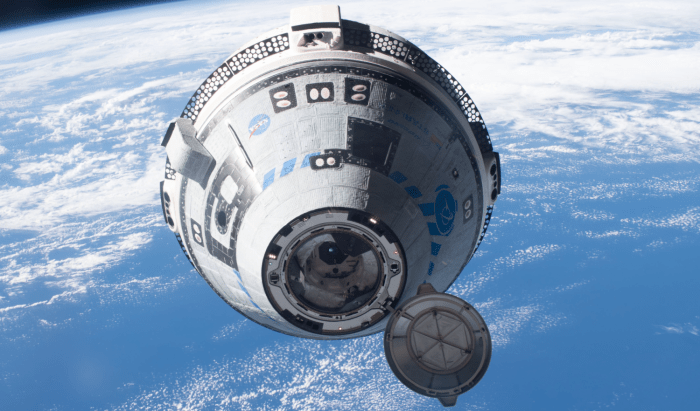
The incident involving stranded astronauts, which occurred during a commercial spaceflight mission, significantly impacted Boeing’s reputation and raised concerns about the reliability of its space systems. The incident highlighted crucial issues regarding the company’s spaceflight capabilities and its commitment to safety.
Boeing’s decision to oust the head of their troubled space unit after astronauts were left stranded and billions were lost is a stark reminder that even the most established companies can face major setbacks. It’s interesting to draw parallels with the ongoing issues with the Horizon system in the UK postal service, where most sub postmasters are still reporting issues with Horizon as more than half have unexplained discrepancies.
Both situations highlight the critical importance of robust systems and reliable technology, especially when dealing with complex operations and public trust. Boeing’s woes serve as a cautionary tale, demonstrating the high stakes involved in pushing technological boundaries without adequate safeguards in place.
Technical Failures and Operational Issues, Boeing ousts head of troubled space unit after astronauts left stranded billions in losses
The stranding of the astronauts was a direct consequence of a series of technical failures and operational issues. These failures stemmed from a combination of factors, including:
- Software glitches:The spacecraft’s software experienced critical glitches that disrupted its navigation and communication systems. These glitches caused the spacecraft to deviate from its planned trajectory, leading to the stranding.
- Hardware malfunctions:The incident also involved hardware malfunctions, such as a failure in the propulsion system. This malfunction prevented the spacecraft from performing necessary maneuvers to return to Earth safely.
- Communication breakdowns:Communication between the spacecraft and ground control was severely hampered due to the software glitches and hardware failures. This lack of communication hindered efforts to resolve the situation and bring the astronauts back safely.
- Inadequate safety protocols:The incident revealed shortcomings in Boeing’s safety protocols and procedures. The company’s contingency plans for such situations were inadequate, leading to a delayed response and a prolonged period of uncertainty for the stranded astronauts.
Impact on Boeing’s Reputation and Future Space Ventures
The incident had a profound impact on Boeing’s reputation, casting a shadow over its space exploration ambitions. The public perception of the company’s spaceflight capabilities was significantly tarnished, raising doubts about its ability to deliver reliable and safe space transportation.
This negative perception could deter future clients and investors, potentially hindering Boeing’s future space ventures. The incident also resulted in significant financial losses for Boeing, as the company had to invest substantial resources in resolving the situation and compensating for the stranded astronauts’ time and expenses.
The incident’s financial repercussions, coupled with the reputational damage, could negatively impact Boeing’s financial performance and its ability to secure funding for future space exploration projects.
Boeing’s recent shakeup, ousting the head of their troubled space unit after astronauts were left stranded and billions were lost, is a stark reminder of the high stakes in the industry. It’s a far cry from the callous disregard shown in this shocking moment thugs laugh as they mount pavement to run over cyclist , highlighting the stark contrast between calculated risk and reckless disregard for human life.
Boeing’s woes serve as a cautionary tale about the potential consequences of failing to deliver on promises, while the incident involving the cyclist underscores the need for accountability and a commitment to safety, even in the face of seemingly trivial acts.
Financial Losses and Implications

The ousting of the head of Boeing’s troubled space unit signals a significant financial blow to the company. The space unit’s struggles have resulted in substantial financial losses, stemming from various factors including development delays and launch failures.
Financial Losses
The financial losses incurred by Boeing’s space unit are significant and have a direct impact on the company’s overall financial performance. These losses can be attributed to several key areas:
- Development Costs:The development of the Starliner spacecraft, a key project for Boeing’s space ambitions, has been plagued with delays and technical issues. These delays have led to significant overruns in development costs, exceeding initial estimates. For instance, the Starliner program’s cost has ballooned to over $5 billion, significantly exceeding the initial budget.
Boeing’s recent troubles with their space unit, culminating in the ousting of their head and leaving astronauts stranded, are a stark reminder of the immense pressure and complexity involved in space exploration. It’s a far cry from the exciting world of Marvel Comics, where symbiotes like Venom and Carnage roam the galaxy, but the sheer power of these beings, as explored in all named symbiotes in marvel comics history ranked weakest to strongest , makes one wonder if even the most advanced technology can truly prepare us for the unknown dangers of the cosmos.
Perhaps Boeing’s space program needs a little more symbiote action to overcome its current setbacks.
- Launch Delays:Repeated delays in the Starliner’s launch schedule have further contributed to financial losses. Each delay incurs additional costs related to maintenance, testing, and personnel. The launch delays have also impacted Boeing’s ability to secure contracts and generate revenue from its space operations.
For example, NASA’s decision to delay the Commercial Crew Program, which relies on the Starliner, has cost Boeing valuable revenue streams.
- Launch Failures:The Starliner’s two failed test flights have resulted in substantial financial losses for Boeing. These failures involved costly hardware replacements, investigations, and redesigns. The cost of these failures is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, further exacerbating the financial burden on the space unit.
For instance, the first uncrewed test flight in 2019 ended prematurely due to software errors, costing Boeing an estimated $300 million.
Long-Term Financial Implications
The financial losses incurred by Boeing’s space unit have significant long-term implications for the company’s overall business. These implications include:
- Impact on Shareholder Value:The financial losses have eroded shareholder confidence in Boeing’s space ambitions. This erosion of confidence can lead to a decline in share price, impacting the company’s overall market value. For instance, Boeing’s stock price has experienced significant fluctuations in recent years, reflecting investor concerns about the space unit’s performance.
- Reduced Investment Capacity:The financial losses have reduced Boeing’s ability to invest in future space projects. This limited investment capacity could hinder the company’s ability to compete effectively in the increasingly competitive space industry. For example, Boeing may struggle to keep up with its rivals, such as SpaceX, which has secured significant funding and made rapid progress in its space ventures.
- Reputational Damage:The space unit’s troubles have tarnished Boeing’s reputation as a reliable and innovative aerospace company. This reputational damage could make it difficult for Boeing to secure future contracts and partnerships, particularly in the highly regulated space sector. For example, the Starliner’s failures have raised concerns about Boeing’s engineering capabilities and its commitment to safety, potentially impacting its ability to win future contracts with NASA and other space agencies.
Impact on Boeing’s Space Program
The ousting of the head of Boeing’s space unit and the incident with the stranded astronauts have undoubtedly cast a shadow over the company’s space program. The incident highlights the critical need for improved safety protocols and reliable technology, while the financial losses incurred will undoubtedly impact future projects.
Potential Consequences for Future Space Missions and Projects
The incident has raised concerns about Boeing’s ability to deliver on its space commitments. The financial losses incurred, coupled with the reputational damage, could potentially impact future space missions and projects in several ways.
- Reduced Funding:The financial losses from the incident may lead to reduced funding for future space projects. Investors and government agencies may be hesitant to allocate funds to a company that has experienced such significant setbacks.
- Delayed Missions:The incident could lead to delays in future space missions as Boeing focuses on improving its safety protocols and technology. This could impact the company’s ability to meet deadlines and commitments to customers.
- Loss of Confidence:The incident could erode confidence in Boeing’s space capabilities. Customers, including NASA and other space agencies, may be less inclined to rely on Boeing for future missions.
- Increased Scrutiny:Boeing will likely face increased scrutiny from regulators and the public. This could lead to more stringent safety regulations and a more challenging environment for the company to operate in.
Comparison to Competitors
Boeing’s position in the space industry is currently under scrutiny, particularly when compared to its competitors. While the company has historically been a dominant player, recent events have raised questions about its ability to maintain its leadership.
- SpaceX:SpaceX, under the leadership of Elon Musk, has emerged as a strong competitor to Boeing in the space industry. SpaceX has a proven track record of successful missions, including the development of reusable rockets and the launch of commercial satellites.
The company’s innovative approach and focus on cost-effectiveness have positioned it as a serious contender in the space race.
- Blue Origin:Blue Origin, founded by Jeff Bezos, is another competitor that has made significant strides in the space industry. The company has developed its own launch vehicles and is actively pursuing space tourism and lunar exploration. Blue Origin’s focus on innovation and its deep pockets have made it a formidable competitor to Boeing.
Future Prospects for Boeing’s Space Unit: Boeing Ousts Head Of Troubled Space Unit After Astronauts Left Stranded Billions In Losses
Boeing’s space unit faces a challenging path to recovery, but with strategic planning and decisive action, it can regain its footing and reassert its position as a leader in the burgeoning space industry.
Rebuilding Trust and Confidence
Regaining trust is paramount for Boeing’s space unit. This requires a multi-pronged approach that addresses the root causes of the recent setbacks and demonstrates a commitment to transparency, accountability, and excellence.
- Thorough Investigation and Root Cause Analysis:A comprehensive and independent investigation into the Starliner issues and the broader organizational culture is essential to identify systemic problems and implement corrective measures. This investigation should be transparent and involve external experts to ensure objectivity and credibility.
- Clear and Transparent Communication:Boeing must communicate openly and honestly with stakeholders, including customers, investors, and the public, about the issues, the corrective actions being taken, and the timeline for achieving desired outcomes. This includes providing regular updates on progress and proactively addressing concerns.
- Stronger Leadership and Accountability:Appointing a new leader with a proven track record of success in complex engineering projects and a commitment to safety and quality is crucial. This leader should be empowered to make necessary changes and hold teams accountable for their performance.
Rebuilding the Space Unit
Boeing’s space unit needs to implement a robust plan to address the challenges and regain momentum. This plan should encompass key areas, including:
- Enhanced Engineering and Quality Processes:Implementing rigorous engineering and quality assurance processes is essential to prevent future failures. This includes adopting best practices from other industries, investing in advanced testing and simulation capabilities, and implementing robust quality control measures throughout the development cycle.
- Focus on Safety and Reliability:A culture of safety and reliability must be instilled throughout the organization. This involves prioritizing safety in all decisions, fostering a culture of open communication about safety concerns, and implementing robust safety protocols and procedures.
- Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations:Collaborating with other industry leaders, research institutions, and government agencies can provide access to cutting-edge technology, expertise, and resources. This includes partnerships on specific projects, joint research ventures, and shared development programs.
- Investing in Innovation and Emerging Technologies:Boeing must stay at the forefront of technological advancements in the space industry. This involves investing in research and development, exploring new technologies such as reusable launch vehicles, advanced propulsion systems, and space-based manufacturing, and fostering a culture of innovation.
Timeline for Implementation
- Phase 1: Immediate Action (6-12 Months):Conduct a thorough investigation, implement immediate corrective measures, and appoint a new leader for the space unit. Establish clear communication channels and initiate a comprehensive review of engineering and quality processes.
- Phase 2: Rebuilding and Strengthening (12-24 Months):Implement new engineering and quality processes, enhance safety protocols, and establish strategic partnerships. Begin development of new programs and technologies.
- Phase 3: Growth and Expansion (24-36 Months):Focus on winning new contracts, expanding capabilities, and establishing a strong market position. Launch new programs and demonstrate the successful implementation of new processes and technologies.






