AIDS Around the World: A Global Health Crisis
AIDS Around the World sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. It’s a story that spans continents, impacting millions of lives, and demanding our collective attention.
This global health crisis has a long and complex history, with its roots in the early 1980s, but its effects continue to be felt today. We’ll delve into the numbers, the science, the stigma, and the ongoing fight for a brighter future.
The AIDS epidemic has had a profound impact on individuals, families, and communities around the world. From the devastating loss of life to the social and economic consequences, the effects are far-reaching and deeply felt. Understanding the complexities of this crisis is crucial to developing effective solutions and ensuring a more equitable and just world.
Global Response and Advocacy: Aids Around The World
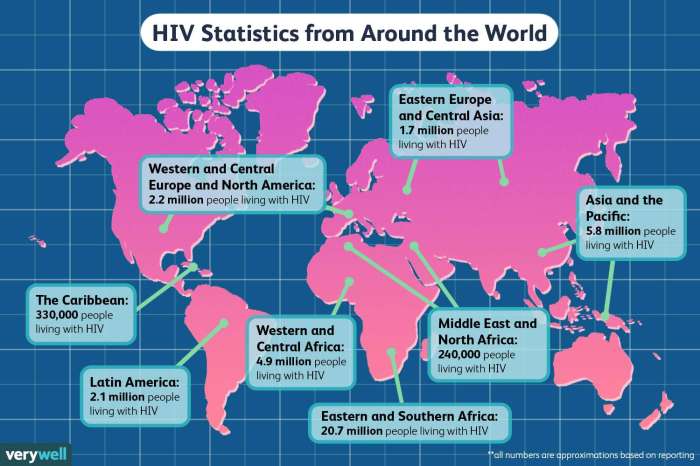
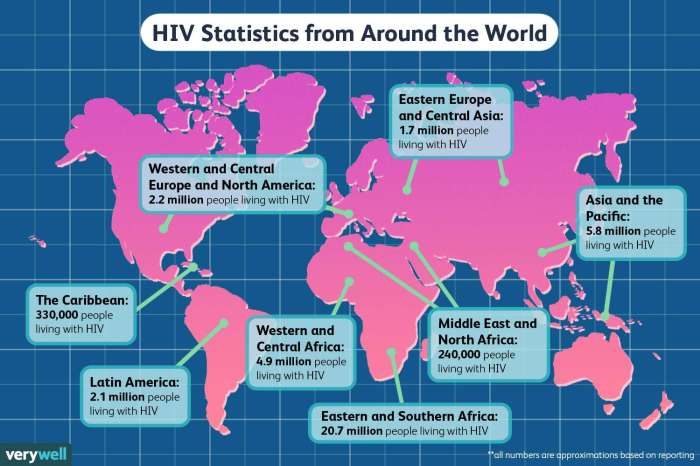
The global response to the HIV/AIDS epidemic has been a testament to international cooperation and advocacy. International organizations, governments, and communities have worked together to address this complex public health challenge, leading to significant progress in treatment, prevention, and care.
International Organizations’ Role
International organizations play a crucial role in coordinating the global response to HIV/AIDS. They provide financial support, technical expertise, and resources to countries most affected by the epidemic. These organizations also advocate for policies and programs that promote access to HIV prevention, treatment, and care services.
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS): UNAIDS is a leading organization in the global fight against HIV/AIDS. It works with governments, civil society, and other stakeholders to develop and implement comprehensive HIV responses. UNAIDS provides technical guidance, financial support, and advocacy for HIV prevention, treatment, and care programs.
- The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria: The Global Fund is a major source of financing for HIV programs in low- and middle-income countries. It provides grants to support a wide range of activities, including prevention, treatment, care, and support services.
- The World Health Organization (WHO): WHO provides technical guidance and support to countries on HIV prevention, treatment, and care. It also develops guidelines and standards for HIV services and conducts research on HIV/AIDS.
Key Initiatives and Programs
Several key initiatives and programs have been implemented to address the HIV/AIDS epidemic globally. These programs focus on various aspects of the epidemic, including prevention, treatment, care, and support.
- The President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR): PEPFAR is a US government initiative that provides funding for HIV prevention, treatment, care, and support programs in developing countries. It has been instrumental in expanding access to HIV services and reducing AIDS-related deaths.
- The Global Plan to End AIDS: The Global Plan is a framework for action to end the AIDS epidemic by 2030. It Artikels ambitious targets for reducing new HIV infections, increasing access to treatment, and eliminating AIDS-related deaths.
- The 90-90-90 targets: These targets aim to have 90% of people living with HIV diagnosed, 90% of diagnosed people receiving antiretroviral therapy, and 90% of people on treatment having suppressed viral loads by 2020. This ambitious goal has significantly impacted the global HIV response.
Advocacy and Community Engagement
Advocacy and community engagement are crucial in combating the HIV/AIDS epidemic. Advocacy efforts aim to influence policies, programs, and resource allocation to ensure that people living with HIV have access to the services they need. Community engagement empowers people living with HIV and their communities to participate in the design and implementation of HIV programs.
- Community-based organizations (CBOs): CBOs play a vital role in providing HIV services and advocating for the rights of people living with HIV. They often work in communities that are most affected by the epidemic and can reach people who may not have access to traditional healthcare services.
- People living with HIV (PLHIV): PLHIV are powerful advocates for their own rights and needs. They share their experiences and advocate for policies and programs that improve their lives and the lives of others living with HIV.
Examples of Successful Advocacy Campaigns, Aids around the world
Numerous successful advocacy campaigns have contributed to the global response to HIV/AIDS.
- The “Know Your Status” campaign: This campaign, launched by UNAIDS and other partners, encouraged people to get tested for HIV. The campaign helped to increase HIV testing rates and reduce the number of people who were unaware of their HIV status.
- The “Treatment is Prevention” campaign: This campaign, launched by WHO and other partners, emphasized the importance of antiretroviral therapy in preventing HIV transmission. The campaign highlighted the fact that people living with HIV who are on treatment and have suppressed viral loads are less likely to transmit the virus to others.
The fight against AIDS around the world is a complex one, requiring a multifaceted approach. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in this fight, often operating in areas where governments struggle to reach. These NGOs focus on a range of issues, from providing education and awareness campaigns to distributing essential medications and supporting vulnerable communities.
To learn more about the important work these NGOs do, check out this article on non governmental organizations on development issues. Ultimately, the success of the fight against AIDS depends on the collaborative efforts of governments, NGOs, and individuals alike.
The fight against AIDS is a global one, requiring international cooperation and resources. However, I believe that military intervention is not the answer. As I outlined in my recent blog post, why I opposed the resolution to authorize force , resorting to violence often exacerbates existing problems and undermines trust.
Instead, we need to focus on strengthening healthcare systems, promoting education, and addressing the root causes of the epidemic. Only through a compassionate and collaborative approach can we truly make a difference in the fight against AIDS around the world.
The global fight against AIDS has seen tremendous progress, but the fight is far from over. While we celebrate victories, it’s crucial to remember the ongoing struggle and the systemic issues that contribute to the spread of the virus. This reminds me of the recent article, ex feds blast 9 11 panel and bush , which highlights the need for accountability and transparency in addressing complex issues.
Just as we must hold those in power accountable for the AIDS crisis, we must also demand transparency and action from those responsible for preventing future tragedies. The fight against AIDS, like any fight for justice, requires unwavering commitment and a willingness to confront the uncomfortable truths.