Why the Democratic Republic of Congo Struggles to Contain Mpox
Why the democratic republic of the congo is struggling to contain mpox – Why the Democratic Republic of Congo is struggling to contain Mpox sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), a nation grappling with poverty, conflict, and a fragile healthcare system, is facing a formidable challenge in its fight against Mpox.
The outbreak, fueled by a confluence of socioeconomic, healthcare, and cultural factors, has exposed vulnerabilities in the DRC’s public health infrastructure, highlighting the urgent need for a multifaceted response.
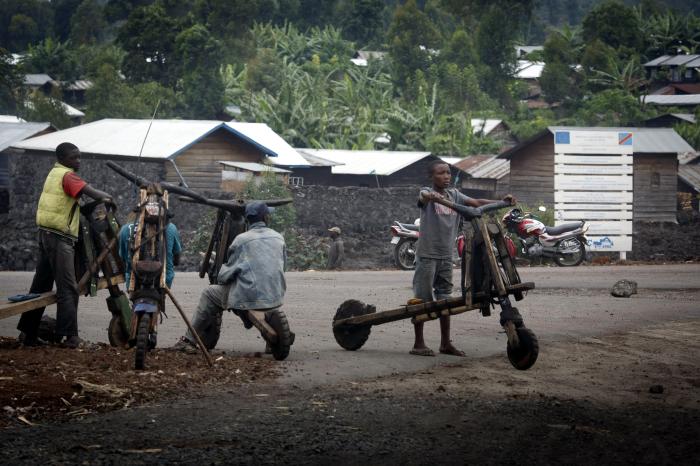
The DRC’s struggle to contain Mpox is a complex issue, intertwined with the country’s ongoing socioeconomic challenges. Poverty, limited access to healthcare, and a lack of resources have created fertile ground for the virus to spread. The DRC’s healthcare system, already strained by decades of conflict and underfunding, is ill-equipped to handle a major outbreak.
Limited access to vaccines and antiviral treatments, coupled with inadequate surveillance and reporting systems, further hinder the country’s ability to effectively control the spread of Mpox. Cultural beliefs and practices also play a significant role in the transmission of the virus, posing unique challenges for public health campaigns.
Socioeconomic Factors
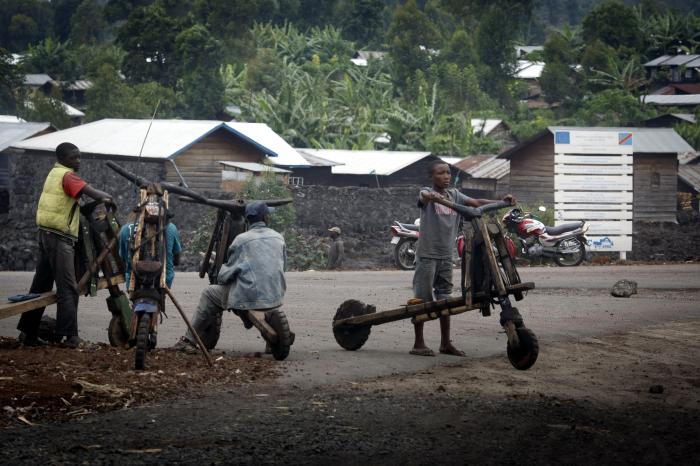

The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) faces significant socioeconomic challenges that hinder its ability to effectively contain the Mpox outbreak. These challenges create a complex and challenging environment for public health interventions.
Poverty and Lack of Access to Healthcare
Poverty and limited access to healthcare are major contributing factors to the spread of Mpox in the DRC. A substantial portion of the population lives below the poverty line, lacking access to essential healthcare services, including preventive measures, diagnosis, and treatment.
This lack of access makes it difficult for individuals to receive timely medical attention and contributes to the spread of the virus.
Limited Resources and Infrastructure
The DRC faces a shortage of resources and infrastructure, making it difficult to implement effective disease control measures. The healthcare system is strained, with limited healthcare workers, inadequate facilities, and insufficient medical supplies. This lack of resources hampers the ability to conduct widespread testing, contact tracing, and vaccination campaigns, hindering the efforts to contain the outbreak.
Displacement and Conflict
The DRC has been plagued by decades of conflict and instability, leading to widespread displacement and humanitarian crises. This displacement creates overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions, which can facilitate the transmission of Mpox. The conflict also disrupts healthcare services, making it difficult for individuals to access treatment and preventive measures.
Specific Socioeconomic Challenges
- High Population Density:The DRC has a large and rapidly growing population, with high population density in urban areas, increasing the risk of Mpox transmission.
- Limited Access to Safe Water and Sanitation:Inadequate access to safe water and sanitation facilities contributes to the spread of infectious diseases, including Mpox.
- Lack of Education and Awareness:Limited access to education and awareness campaigns about Mpox hinder prevention efforts. Many individuals lack knowledge about the virus, its transmission, and how to protect themselves.
- Weak Health System:The DRC’s healthcare system is fragile, with limited capacity to respond effectively to outbreaks. This includes insufficient healthcare workers, inadequate infrastructure, and limited access to essential medical supplies.
Healthcare System Challenges
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) faces significant challenges in its healthcare system, which are exacerbated by the ongoing Mpox outbreak. The country’s already fragile healthcare infrastructure is further strained by a lack of resources, limited access to essential services, and a shortage of skilled healthcare professionals.
The Democratic Republic of Congo’s struggle to contain mpox is compounded by a multitude of challenges, including limited access to healthcare and a fragile infrastructure. It’s a stark contrast to the news coming out of other parts of the world, like the UK, where childcare thousands register for subsidy scheme , providing much-needed support to families.
While this is a positive development, it highlights the vast disparities in resources and healthcare systems, which unfortunately leave countries like the DRC particularly vulnerable to outbreaks like mpox.
These factors collectively hinder the DRC’s ability to effectively respond to and contain the Mpox outbreak.
Shortage of Healthcare Professionals
The DRC faces a severe shortage of healthcare professionals, particularly in rural areas. This shortage is attributed to several factors, including limited training opportunities, poor working conditions, and inadequate compensation. The lack of qualified personnel directly impacts the quality and availability of healthcare services, making it difficult to effectively diagnose, treat, and manage Mpox cases.
For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the DRC has only one doctor for every 10,000 people, highlighting the severe shortage of healthcare professionals in the country.
Challenges in Accessing and Distributing Vaccines and Antiviral Treatments
The DRC’s healthcare system faces challenges in accessing and distributing vaccines and antiviral treatments for Mpox. Limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and logistical difficulties contribute to these challenges. The country’s vast size and poor road networks make it difficult to transport medical supplies to remote areas.
Additionally, the lack of cold chain infrastructure, essential for storing temperature-sensitive vaccines, further hampers their distribution. These factors limit the DRC’s capacity to effectively vaccinate and treat individuals affected by Mpox.
Inadequate Surveillance and Reporting Systems
The DRC’s surveillance and reporting systems for infectious diseases, including Mpox, are inadequate. The lack of a robust surveillance system hinders the timely identification and tracking of cases, making it difficult to assess the true extent of the outbreak. The weak reporting system, often characterized by delays and incomplete data, further hampers the effectiveness of the response.
These shortcomings make it challenging to implement effective control measures and monitor the progress of the outbreak.
Cultural and Behavioral Factors
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) faces unique challenges in containing the Mpox outbreak due to cultural beliefs, practices, and social norms that can inadvertently contribute to the spread of the virus. These factors play a significant role in the transmission dynamics of the disease, impacting the effectiveness of public health interventions.
Traditional Healing Practices
Traditional healing practices, deeply rooted in Congolese culture, can contribute to Mpox transmission. Traditional healers often use practices involving physical contact, such as massage, scarification, or the application of herbal remedies, which can facilitate the spread of the virus if the healer or the materials used are infected.
The Democratic Republic of Congo is facing a multitude of challenges in its fight against mpox, including a lack of resources, limited access to healthcare, and widespread misinformation. It’s a stark reminder that even as we celebrate victories like the Utah Grizzlies’ 6-3 win over the Colorado Avalanche, guenther keller guide utah to 6 3 win over avalanche the hockey writers utah hockey club latest news analysis more , we must also acknowledge the global health crises that continue to demand our attention.
The DRC’s struggle highlights the need for international cooperation and support to address the mpox outbreak and ensure that everyone has access to the care they need.
For instance, the practice of “nkisi,” a form of traditional medicine involving the use of animal parts, poses a potential risk for Mpox transmission if infected animals are used in the process.
Stigma and Misinformation, Why the democratic republic of the congo is struggling to contain mpox
The stigma associated with Mpox can hinder disease control efforts. In some communities, the disease is perceived as a shameful condition, leading individuals to conceal their symptoms or avoid seeking medical attention. Misinformation surrounding the virus, often spread through rumors and social media, can further exacerbate the situation.
For example, false claims that Mpox is a punishment from God or a curse can discourage individuals from seeking treatment and adopting preventive measures.
Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns are crucial for raising awareness about Mpox prevention and control measures. However, their effectiveness can be limited by factors such as low literacy rates, limited access to information technology, and cultural barriers. The messages conveyed in these campaigns must be tailored to the specific cultural contexts and beliefs of different communities.
For example, using traditional language and imagery in public health materials can enhance their relevance and appeal to the target audience.
The Democratic Republic of Congo’s fight against mpox is a stark reminder of the deep-seated inequities in global health. Limited resources, crumbling infrastructure, and widespread poverty make it difficult to contain the outbreak. It’s a situation that resonates with the chilling reality described in our voices are lost in the tide of intolerance sweeping america , where marginalized communities are often left behind in the face of crisis.
The struggle to contain mpox in Congo underscores the urgent need for global solidarity and equitable access to healthcare, especially for those most vulnerable.
Government Response and International Support: Why The Democratic Republic Of The Congo Is Struggling To Contain Mpox
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has faced significant challenges in containing the Mpox outbreak, and the government’s response has been a crucial factor in determining the effectiveness of control measures. While there have been efforts to address the outbreak, there are areas where improvements are needed, and international support has played a vital role in bolstering the DRC’s response.
Government Response
The DRC government has taken steps to address the Mpox outbreak, including establishing a national task force, deploying surveillance teams, and implementing public health measures. However, challenges have hampered the effectiveness of the response.
- Limited resources and inadequate funding have constrained the government’s ability to effectively implement control measures. The DRC’s healthcare system is already overburdened, and the Mpox outbreak has placed additional strain on resources.
- The government’s response has been hampered by logistical difficulties, particularly in remote areas with limited access to healthcare infrastructure and communication networks.
- Coordination between different levels of government has been challenging, leading to inconsistencies in messaging and implementation of control measures.
- Misinformation and stigma surrounding Mpox have hindered public health efforts. There have been reports of discrimination and violence against individuals suspected of having the virus.
International Support
International organizations and donor agencies have provided significant support to the DRC’s Mpox response.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has provided technical assistance, training, and supplies to strengthen surveillance, case management, and public health messaging.
- The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) has focused on supporting community engagement and awareness-raising campaigns to address stigma and misinformation.
- The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has provided funding for the procurement of vaccines and antiviral medications.
Strengthening International Collaboration
There are areas where international collaboration can be strengthened to enhance Mpox control efforts in the DRC.
- Increased funding is crucial to support the government’s response, particularly for strengthening surveillance, case management, and public health messaging.
- Improved coordination between international organizations and the DRC government is essential to ensure a more effective and efficient response.
- Support for community engagement and awareness-raising campaigns is vital to address stigma and misinformation surrounding Mpox.
- Research and development of new vaccines and antiviral treatments specifically tailored to the Mpox virus circulating in the DRC are essential for long-term control of the outbreak.
Lessons Learned and Future Strategies
The Democratic Republic of Congo’s (DRC) struggle to contain the Mpox outbreak offers valuable lessons for strengthening public health systems and preventing future outbreaks. Understanding these lessons and implementing effective strategies is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations and ensuring a more robust response to future health emergencies.
Strengthening Disease Surveillance and Response Systems
Effective disease surveillance is paramount for early detection and rapid response to outbreaks. The DRC’s experience highlights the need for a comprehensive approach to surveillance, including:
- Improved data collection and reporting:The DRC’s surveillance system faces challenges in data collection, reporting, and analysis. Strengthening these aspects is crucial for timely identification of outbreaks and informed decision-making. This can be achieved by investing in training for healthcare workers, improving laboratory capacity, and implementing robust data management systems.
- Community engagement:Engaging communities in surveillance activities is vital. Empowering community health workers and building trust through community outreach programs can significantly improve the detection of cases and promote early reporting.
- Real-time data sharing and analysis:The DRC needs to enhance its capacity for real-time data sharing and analysis. This involves strengthening communication channels between different levels of the health system and utilizing data analytics tools to identify trends and patterns.
- Rapid response teams:Establishing well-equipped and trained rapid response teams is essential for quickly containing outbreaks. These teams should be able to conduct contact tracing, provide medical care, and implement infection control measures.
Improving Access to Healthcare and Essential Resources
The DRC’s healthcare system faces significant challenges, including limited access to healthcare services, particularly in remote areas. To effectively address Mpox and other health emergencies, the DRC needs to:
- Strengthening primary healthcare:Investing in primary healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare workers, and expanding access to essential medicines and supplies is crucial. This will help prevent the spread of Mpox and other diseases, and improve overall health outcomes.
- Improving access to healthcare in remote areas:The DRC needs to develop innovative strategies to reach vulnerable populations in remote areas. This could include mobile clinics, telemedicine services, and community-based health programs.
- Addressing social determinants of health:Poverty, malnutrition, and lack of education contribute to health vulnerabilities. Addressing these social determinants of health is essential for improving overall health outcomes and reducing the impact of outbreaks.
Public Health Interventions to Prevent and Control Mpox Outbreaks
Preventing future outbreaks requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Vaccination campaigns:Expanding access to safe and effective Mpox vaccines is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations. This requires procuring sufficient vaccine supplies, developing efficient distribution systems, and implementing effective vaccination programs.
- Antiviral treatments:Providing access to antiviral treatments for infected individuals can help reduce the severity of the disease and prevent further transmission.
- Public health education and awareness campaigns:Educating the public about Mpox, its symptoms, and prevention strategies is essential for reducing the spread of the virus. These campaigns should be culturally appropriate and tailored to specific populations.
- Infection control measures:Implementing strict infection control measures in healthcare settings and other public spaces is crucial for preventing transmission. This includes promoting hand hygiene, using personal protective equipment, and isolating infected individuals.