
Why Alt Protein Wont Save the Planet
Why alt protein wont save the planet – Why alt protein won’t save the planet sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. While the idea of replacing traditional meat with plant-based, cultivated, or insect-based alternatives seems like a promising solution to environmental concerns, the reality is more complex.
The environmental impact of alt protein production, challenges in scaling up, and consumer acceptance all play a role in determining its true potential.
This article delves into the intricacies of alt protein production, exploring its environmental footprint, economic viability, and consumer appeal. We’ll examine the challenges of scaling up production to meet global demand, analyze the role of government policies, and discuss the potential of emerging technologies in shaping the future of this industry.
Environmental Impact of Alt Protein Production
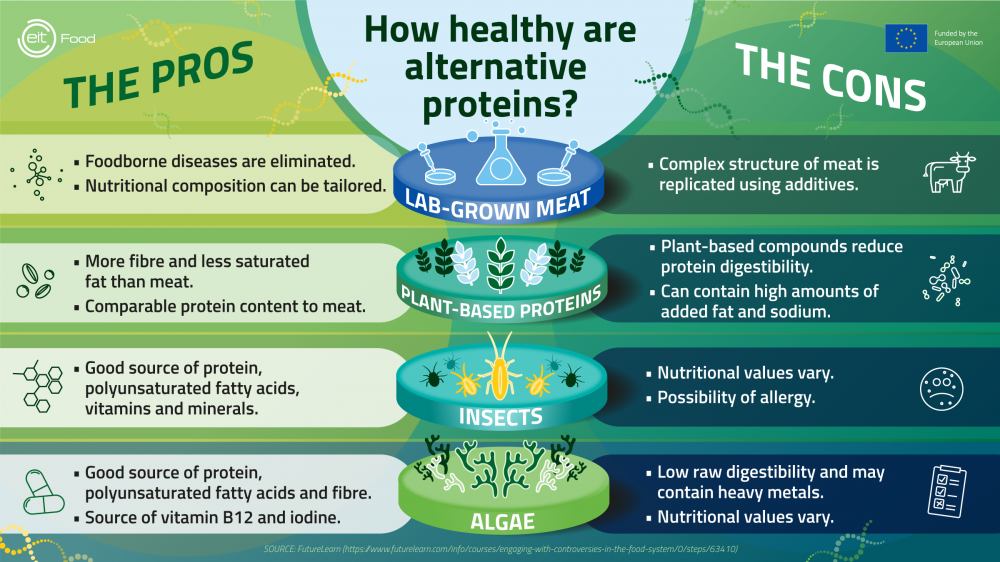
The environmental impact of alt protein production is a complex and multifaceted issue. While alt proteins are often touted as a more sustainable alternative to traditional animal agriculture, their production processes also carry their own environmental burdens. It’s crucial to understand the environmental footprint of different alt protein types to assess their potential benefits and drawbacks.
Land Use
Land use is a critical factor in the environmental impact of food production. Traditional animal agriculture requires vast amounts of land for grazing and feed production, leading to deforestation and habitat loss. Alt protein production, on the other hand, can potentially reduce land use depending on the specific type.
- Plant-based proteins: These typically require less land than animal agriculture for the same amount of protein production. For example, producing a kilogram of plant-based protein from soy requires significantly less land than producing a kilogram of protein from beef.
- Cultivated meat: This emerging technology involves growing meat cells in a lab setting, eliminating the need for land for grazing or feed production. It has the potential to significantly reduce land use compared to traditional animal agriculture.
- Insect-based protein: Insects are highly efficient converters of feed into protein, requiring less land for their production compared to livestock. However, the land use for growing feed for insects still needs to be considered.
Challenges in Scaling Up Alt Protein Production
While alt protein production offers potential solutions to address the environmental and ethical concerns associated with traditional meat production, scaling up its production to meet global demand presents significant challenges. These challenges relate to both the cost-effectiveness of alt protein production and the technical hurdles involved in scaling up production processes.
While alt protein might seem like a silver bullet for environmental sustainability, it’s important to remember that the solution to climate change is multifaceted. We need to address issues like the toxic legacy of burn pits, which have exposed countless veterans to harmful chemicals.
It’s heartening to see bipartisan legislation senators announce bipartisan legislation to help veterans exposed to burn pits , but ultimately, tackling climate change requires a comprehensive approach that includes addressing systemic issues like industrial agriculture and the widespread use of fossil fuels.
Cost-Effectiveness of Alt Protein Production
The cost-effectiveness of alt protein production compared to traditional meat production is a major hurdle in scaling up its production.
While alternative proteins might offer a sustainable alternative to traditional meat production, they won’t single-handedly save the planet. We need to address the root causes of climate change, and that includes tackling the political battles surrounding education. It’s heartening to see that California’s education system will be spared divisive statewide election battles this year, according to this recent commentary , as it allows us to focus on more pressing issues like environmental sustainability.
Ultimately, a multifaceted approach is needed to combat climate change, including promoting sustainable agriculture and investing in renewable energy sources.
- Current alt protein production methods are generally more expensive than traditional meat production. This is due to the complex and often energy-intensive processes involved in producing alt protein products.
- The high costs associated with alt protein production are driven by factors such as the need for specialized equipment, skilled labor, and the use of high-quality ingredients. For example, cell-based meat production requires expensive bioreactors and specialized media for cell growth, while plant-based meat alternatives often rely on expensive ingredients like soy protein isolate.
- The high costs associated with alt protein production limit its accessibility to consumers, especially in developing countries. This is a significant challenge in scaling up alt protein production to meet global demand.
Technical Challenges in Scaling Up Alt Protein Production
Scaling up alt protein production to meet global demand requires overcoming significant technical challenges.
While alt protein might sound like a silver bullet for our environmental woes, the reality is far more nuanced. The production of these alternatives often requires significant resources, and their widespread adoption could lead to unintended consequences. Take the recent political drama in Idaho, for example, where Governor Brad Little defeated his own Lieutenant Governor in a contentious primary ( idaho gov brad little defeats his own lieutenant gov in contentious primary ).
This kind of political turmoil highlights the complexities of implementing large-scale solutions, and reminds us that tackling climate change requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond just switching to new food sources.
- Cell-based meat production requires the development of efficient and scalable cell culture processes. This involves optimizing cell growth, nutrient delivery, and waste removal, while ensuring consistent product quality.
- Plant-based meat alternatives often rely on complex formulations and processing techniques to mimic the texture, taste, and nutritional profile of traditional meat. Scaling up production requires ensuring consistent product quality and taste across different production batches.
- The need for specialized equipment and infrastructure is a significant challenge in scaling up alt protein production. This includes developing efficient and scalable bioreactors for cell-based meat production and expanding processing facilities for plant-based meat alternatives.
Potential Solutions for Overcoming the Challenges
To overcome the challenges in scaling up alt protein production, researchers and industry leaders are exploring various solutions.
- Cost reduction: This can be achieved through advancements in technology, process optimization, and economies of scale. For example, the development of more efficient bioreactors and the use of alternative, less expensive ingredients can significantly reduce production costs.
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development are crucial to improve the efficiency and scalability of alt protein production processes. This includes developing new cell lines, optimizing fermentation processes, and exploring innovative food processing techniques.
- Government support and investment: Governments can play a significant role in promoting the development and adoption of alt protein production through policies, incentives, and investments in research and infrastructure.
- Consumer education and awareness: Raising consumer awareness about the environmental, ethical, and health benefits of alt protein can drive demand and support the growth of the industry.
Consumer Acceptance and Demand for Alt Protein

While alt protein holds promise for reducing environmental impact, its widespread adoption hinges on consumer acceptance and demand. Factors such as taste, texture, price, and ethical concerns play a significant role in shaping consumer perceptions and purchasing decisions.
Factors Influencing Consumer Acceptance
Consumer acceptance of alt protein products is influenced by various factors, including:
- Taste and Texture:Consumers are accustomed to the familiar taste and texture of traditional meat products. Alt protein products need to replicate these qualities closely to gain widespread acceptance.
- Price:Currently, alt protein products are often more expensive than conventional meat alternatives. Affordability is a major barrier for many consumers, especially those with limited budgets.
- Ethical Concerns:Consumers are increasingly concerned about animal welfare and environmental sustainability. Alt protein products offer a more ethical and sustainable alternative to traditional meat, appealing to consumers with these values.
- Health Concerns:Some consumers are concerned about the health implications of traditional meat consumption, such as high saturated fat and cholesterol content. Alt protein products often offer a healthier alternative, with lower fat and cholesterol content.
- Availability and Accessibility:Consumers need easy access to alt protein products in their local supermarkets and restaurants. Wider availability and accessibility are crucial for increasing adoption.
Current Consumer Demand and Market Growth
The market for alt protein products is rapidly growing, driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental and ethical concerns related to traditional meat production.
- Growing Demand:According to a 2023 report by the Good Food Institute, global demand for alt protein products is expected to reach $140 billion by 2035.
- Market Growth:The alt protein market is experiencing significant growth, with several major players investing heavily in research and development. For example, Beyond Meat and Impossible Foods have achieved significant market penetration and are expanding their product lines.
- Consumer Preferences:Surveys indicate that a growing number of consumers are open to trying alt protein products, with a significant portion already incorporating them into their diets.
Strategies for Increasing Consumer Adoption
Several strategies can be employed to increase consumer adoption of alt protein products:
- Improving Taste and Texture:Continued research and development are essential to enhance the taste and texture of alt protein products, making them more appealing to consumers.
- Reducing Production Costs:Innovations in production processes and economies of scale can help reduce the cost of alt protein products, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Marketing and Education:Effective marketing campaigns can raise awareness of the benefits of alt protein products and address consumer concerns. Educational initiatives can inform consumers about the environmental and ethical implications of traditional meat production.
- Expanding Distribution Channels:Increasing the availability of alt protein products in supermarkets, restaurants, and other food service outlets can make them more convenient for consumers to purchase.
- Government Policies:Government policies that support the development and adoption of alt protein products, such as subsidies and tax incentives, can accelerate market growth.
Role of Government Policies and Regulations: Why Alt Protein Wont Save The Planet
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of the alt protein industry, influencing its development, adoption, and ultimately, its potential impact on the environment. By creating a supportive regulatory environment, governments can foster innovation, encourage investment, and accelerate the transition towards more sustainable food systems.
Impact of Subsidies and Incentives
Subsidies and incentives can significantly influence the growth of the alt protein industry. Governments can provide financial support to alt protein companies through grants, tax breaks, and research funding, encouraging innovation and driving down production costs. These incentives can be particularly impactful in the early stages of development, when alt protein companies face significant challenges in scaling up production and competing with established animal-based protein industries.
For example, the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) has provided funding for research and development of plant-based proteins, while the European Union has implemented policies promoting sustainable food systems, including the development of alternative proteins.
Policy Barriers to Widespread Adoption, Why alt protein wont save the planet
Despite the potential benefits of alt protein, several policy barriers can hinder its widespread adoption. One key challenge is the lack of clear regulatory frameworks for novel food products, such as cultivated meat. Current regulations may not adequately address the unique characteristics of these products, leading to delays in approval and market entry.
Furthermore, existing regulations on food labeling and marketing can pose challenges for alt protein companies seeking to promote their products as healthier and more sustainable alternatives.
- Regulatory uncertainty:Lack of clear guidelines for the approval and labeling of novel alt protein products can create uncertainty for companies and investors, slowing down innovation and investment.
- Existing regulations:Current regulations on food labeling and marketing may not adequately address the unique characteristics of alt protein products, making it difficult for companies to promote their products as healthier and more sustainable alternatives.
- Consumer perception:Negative public perception towards alt protein, fueled by misinformation and skepticism, can hinder consumer acceptance and adoption.
- Limited infrastructure:The lack of infrastructure for large-scale production and distribution of alt protein products can pose a challenge to scaling up production and reaching a wider market.
Conclusion
While alt protein offers a promising alternative to traditional meat, it’s not a silver bullet for saving the planet. Its environmental impact, economic viability, and consumer acceptance are all factors that need to be carefully considered. Ultimately, a sustainable future requires a multifaceted approach that includes reducing meat consumption, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and investing in innovative solutions like alt protein.
This will require collaboration between governments, businesses, and consumers to create a more sustainable food system for generations to come.






