WHO Declares Monkeypox a Global Health Emergency
Who declares rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency – WHO Declares Monkeypox a Global Health Emergency sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The World Health Organization (WHO) took the unprecedented step of declaring the rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency in July 2022.
This decision came after a surge in cases across the globe, with the virus spreading beyond its traditional endemic regions in Central and West Africa. The declaration sparked a flurry of activity, as governments and health organizations around the world scrambled to contain the outbreak and protect their populations.
This declaration highlighted the seriousness of the situation and underscored the need for a coordinated global response. The monkeypox outbreak has raised concerns about the potential for widespread transmission, particularly in countries with limited access to healthcare resources. The declaration served as a wake-up call, urging nations to bolster their public health systems, improve surveillance, and expedite the development of effective vaccines and treatments.
The Monkeypox Outbreak
The monkeypox outbreak, which began in early 2022, has rapidly evolved into a global health emergency. While monkeypox has been endemic in parts of Central and West Africa for decades, its recent spread to non-endemic regions has raised significant concerns about its potential impact on public health and healthcare systems worldwide.
Timeline of the Monkeypox Outbreak
The timeline of the monkeypox outbreak highlights key events and milestones that have shaped its trajectory:
- May 2022:The World Health Organization (WHO) reported the first confirmed case of monkeypox outside of Africa, in the United Kingdom. The case was linked to travel from Nigeria.
- June 2022:The number of monkeypox cases continued to rise globally, with several European countries reporting outbreaks. The WHO declared the outbreak a “public health emergency of international concern” on June 23rd.
- July 2022:The US declared monkeypox a public health emergency, as the number of cases in the country surged. The WHO announced that it was working with countries to increase access to vaccines and treatments for monkeypox.
- August 2022:The monkeypox outbreak continued to spread, with cases reported in more than 70 countries. The WHO emphasized the importance of public health measures, such as contact tracing and isolation, to control the outbreak.
- September 2022:The WHO announced that the monkeypox outbreak was declining in some countries, but that it remained a significant public health concern. The organization continued to work with countries to strengthen surveillance and response efforts.
- October 2022:The WHO reported that the number of monkeypox cases had continued to decline globally, with the outbreak appearing to be stabilizing in many countries. The organization continued to monitor the situation closely and provide guidance to countries.
Characteristics of Monkeypox
Monkeypox is a viral disease that can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Backache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Rash
The rash typically begins as flat lesions that progress to raised bumps, blisters, and scabs. These lesions can appear anywhere on the body, including the face, hands, feet, and genitals.Monkeypox is primarily spread through close contact with an infected person or animal.
This can occur through:
- Direct contact with an infected person’s rash, sores, or bodily fluids
- Indirect contact with contaminated materials, such as bedding or clothing
- Respiratory droplets during prolonged face-to-face contact
The incubation period for monkeypox is typically 5 to 21 days. This means that a person can be infected with the virus but not show symptoms for up to three weeks.
Global Spread of Monkeypox
The monkeypox outbreak has spread to several regions around the world, with significant outbreaks occurring in:
- Europe:The outbreak in Europe began in May 2022, with the UK, Spain, Portugal, and Germany reporting the highest number of cases. The outbreak has since spread to other European countries, including France, Italy, and Belgium.
- North America:The US has experienced a significant increase in monkeypox cases since May 2022, with the outbreak primarily concentrated in large urban areas. Canada has also reported a number of cases.
- Africa:While monkeypox is endemic in parts of Central and West Africa, the recent outbreak has spread to new areas, including Nigeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The WHO has expressed concern about the potential for the virus to spread further in Africa.
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency, a decision that underscores the seriousness of the situation. It’s a stark reminder of the importance of accurate information and the dangers of spreading misinformation, as we’ve seen with the tragic case of Alex Jones, whose trial for damages over his false claims about the Sandy Hook shooting is currently underway, as reported on blognewstweets.com.
The WHO’s declaration aims to encourage a coordinated global response to the monkeypox outbreak, much like the urgent need for accountability in the Alex Jones case.
Impact of the Outbreak on Public Health and Healthcare Systems
The monkeypox outbreak has had a significant impact on public health and healthcare systems around the world. The rapid spread of the virus has strained resources, particularly in countries with limited access to vaccines and treatments.
- Increased demand for healthcare services:The outbreak has led to an increase in demand for healthcare services, as individuals seek testing, diagnosis, and treatment for monkeypox. This has put pressure on healthcare systems, particularly in countries with limited resources.
- Disruption of healthcare services:The outbreak has also disrupted healthcare services in some countries, as healthcare workers have been redeployed to respond to the outbreak. This has led to delays in providing other essential healthcare services.
- Social and economic impacts:The monkeypox outbreak has also had social and economic impacts, as people have been forced to isolate or quarantine to prevent the spread of the virus. This has disrupted travel, education, and employment, leading to economic losses and social isolation.
WHO’s Declaration of a Global Health Emergency
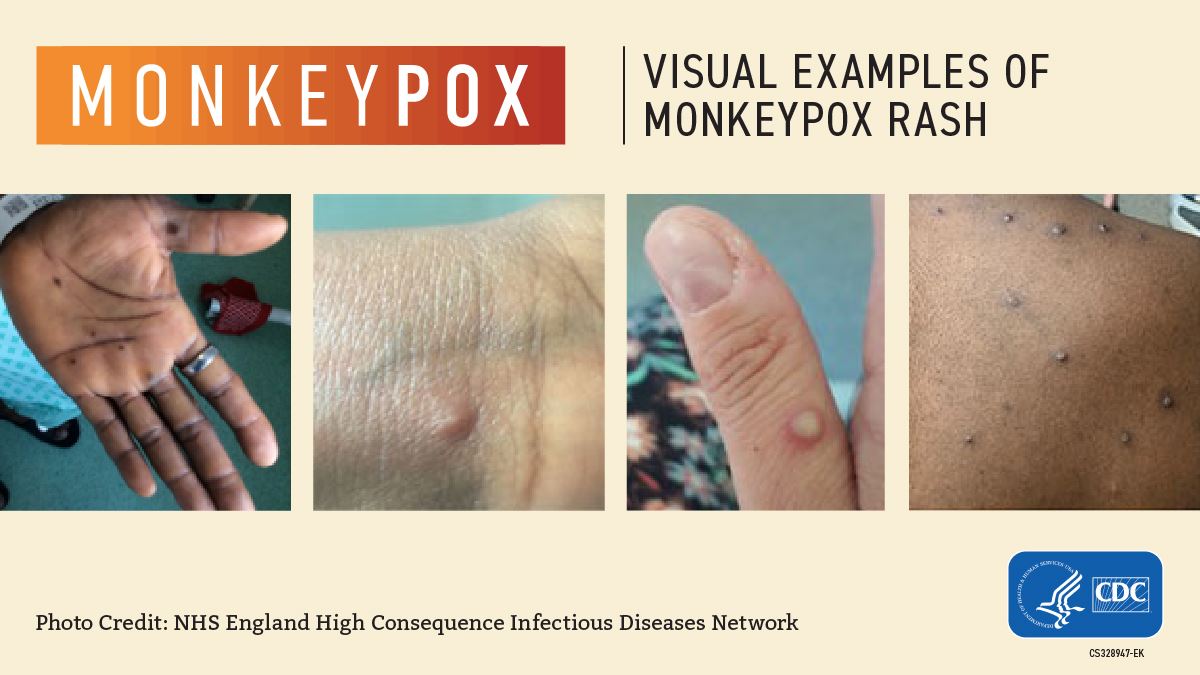
On July 23, 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). This decision was made after a thorough assessment of the situation and its potential impact on global health.
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency, highlighting the need for a coordinated international response. This situation reminds me of the importance of 11 mindset traits of successful entrepreneurs , particularly adaptability and problem-solving.
Entrepreneurs often face unexpected challenges, just like the global health community is doing now with monkeypox, and the ability to think strategically and act decisively is crucial for navigating these complex situations.
Criteria for Declaring a PHEIC, Who declares rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency
The WHO uses a set of specific criteria to determine whether a public health event constitutes a PHEIC. These criteria are designed to ensure that the declaration is made only in cases of serious public health threats that require a coordinated international response.
The criteria include:
- The severity of the public health event
- The potential for international spread
- The potential for interference with international traffic
- The need for a coordinated international response
Factors Leading to the Monkeypox Declaration
The WHO’s decision to declare the monkeypox outbreak a PHEIC was based on several factors, including:
- The rapid spread of the virus to over 70 countries, many of which had not previously reported monkeypox cases.
- The increasing number of cases, particularly in countries where monkeypox is not endemic.
- The potential for the virus to spread further and more rapidly, especially in countries with weak health systems.
- The lack of a readily available vaccine or treatment for monkeypox.
Implications of the Declaration
The declaration of a PHEIC has several important implications for global health response and collaboration:
- It triggers a coordinated international response, with WHO playing a leading role in coordinating efforts between countries.
- It increases global awareness of the threat posed by monkeypox and encourages countries to take action to prevent further spread.
- It provides a platform for countries to share information and resources, including vaccines, treatments, and expertise.
- It encourages research and development efforts to develop more effective vaccines and treatments for monkeypox.
WHO Recommendations
In response to the PHEIC declaration, WHO issued several recommendations to countries, including:
- Strengthening surveillance and reporting of monkeypox cases.
- Providing accurate and timely information to the public about monkeypox and how to protect themselves.
- Implementing measures to prevent further spread of the virus, such as contact tracing and isolation of infected individuals.
- Ensuring equitable access to vaccines and treatments for monkeypox.
- Supporting research and development efforts to develop more effective vaccines and treatments.
The Impact of the Outbreak

The monkeypox outbreak has had a significant impact on individuals, communities, and healthcare systems worldwide. Beyond the immediate health concerns, the outbreak has also raised concerns about its potential economic and social consequences, as well as its long-term implications for global health security.
Impact on Individuals
The impact of the monkeypox outbreak on individuals has been multifaceted. Individuals infected with monkeypox may experience a range of symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle aches, and a characteristic rash. In some cases, the infection can lead to complications, such as pneumonia or encephalitis.
The stigma associated with the disease can also have a significant impact on individuals’ mental health and well-being. For example, individuals may experience discrimination or social isolation due to the fear and misinformation surrounding the outbreak.
Impact on Communities
The monkeypox outbreak has also had a significant impact on communities. Outbreaks have been reported in various countries, leading to disruptions in daily life, including school closures, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures. These disruptions can have a significant economic impact on communities, particularly in areas heavily reliant on tourism or trade.
Impact on Healthcare Systems
The monkeypox outbreak has placed a strain on healthcare systems around the world. Healthcare providers have been tasked with managing the increasing number of cases, while also ensuring that essential services are available to other patients. The outbreak has also highlighted the need for improved surveillance and response systems, as well as the development of effective vaccines and treatments.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recently declared the rapidly spreading monkeypox outbreak a global health emergency, highlighting the urgency of coordinated international efforts to contain the virus. It’s a stark reminder that while we grapple with global health crises, we also face individual tragedies like the brutal beating of a Columbia graduate student in Manhattan, as detailed in this heartbreaking article columbia graduate student brutally beaten in manhattan mother struggles for answers.
These events underscore the importance of addressing both global and individual health concerns, as they are inextricably linked.
Economic and Social Consequences
The monkeypox outbreak has the potential to have significant economic and social consequences. The outbreak has already led to disruptions in trade and tourism, as well as increased costs for healthcare and public health measures. The stigma associated with the disease can also lead to social isolation and discrimination, which can have a negative impact on individuals’ mental health and well-being.
Long-Term Implications
The monkeypox outbreak has raised concerns about the long-term implications for public health and global health security. The outbreak has highlighted the importance of early detection and response, as well as the need for robust surveillance systems to monitor emerging infectious diseases.
The outbreak has also highlighted the need for increased investment in research and development of new vaccines and treatments.
Potential Impacts of the Outbreak
| Sector | Potential Impacts |
|---|---|
| Health | Increased incidence of monkeypox infections, strain on healthcare systems, potential development of new treatments and vaccines |
| Economy | Disruptions to trade and tourism, increased healthcare costs, potential economic downturn |
| Social | Social isolation and discrimination, increased fear and anxiety, disruptions to daily life |
| Psychological | Increased stress and anxiety, mental health issues, stigma and discrimination |
Lessons Learned and Future Directions: Who Declares Rapidly Spreading Monkeypox Outbreak A Global Health Emergency
The monkeypox outbreak has provided valuable lessons about global health preparedness, response, and communication. While the outbreak was ultimately contained, it highlighted significant weaknesses in our systems and underscored the need for urgent improvements. This section delves into the key takeaways from the outbreak, emphasizing the need for a more robust and responsive global health infrastructure.
Strengthening Global Health Surveillance
The monkeypox outbreak revealed gaps in global health surveillance systems. Early detection and rapid response are crucial for preventing outbreaks from escalating. The following points are essential for enhancing global health surveillance:
- Improved Data Collection and Sharing: Real-time data collection and sharing between countries are vital for tracking outbreaks and identifying emerging threats. Establishing standardized reporting systems and facilitating seamless data exchange are critical for effective surveillance.
- Enhanced Laboratory Capacity: Investing in laboratory infrastructure and training is essential for accurate and timely diagnosis. Increased capacity for molecular testing and genomic sequencing will help to track the spread of the virus and identify potential mutations.
- Strengthening Public Health Laboratories: Public health laboratories play a crucial role in disease surveillance. Adequate funding, advanced equipment, and skilled personnel are essential for their effective operation.
- Active Surveillance and Early Detection: Implementing active surveillance programs, particularly in high-risk areas, is crucial for identifying cases early and preventing widespread transmission. This involves proactive screening, testing, and contact tracing.
Improving Outbreak Response
The monkeypox outbreak exposed shortcomings in global outbreak response. Effective response requires coordinated action, clear communication, and access to resources.
- Rapid and Coordinated Response: The global health community needs to respond quickly and effectively to emerging outbreaks. This involves mobilizing resources, deploying experts, and coordinating actions between countries.
- Effective Communication and Public Engagement: Clear and consistent communication is essential for building public trust and encouraging cooperation. Public health authorities must provide accurate information and address concerns effectively.
- Equitable Access to Vaccines and Treatments: Ensuring equitable access to vaccines, treatments, and other essential resources is crucial for containing outbreaks. This requires addressing disparities in access and ensuring that vulnerable populations are prioritized.
- Strengthening Pandemic Preparedness: The monkeypox outbreak underscores the need for robust pandemic preparedness plans. Countries must invest in developing and maintaining emergency response systems, stockpiling essential supplies, and training healthcare workers.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure and Research
The monkeypox outbreak highlighted the need for significant investments in public health infrastructure and research.
- Strengthening Public Health Infrastructure: Robust public health systems are essential for preventing and responding to outbreaks. This includes investing in surveillance, laboratory capacity, workforce development, and emergency preparedness.
- Investing in Research and Development: Continued research is crucial for developing effective vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools. This includes studying the virus’s evolution, transmission dynamics, and potential long-term health consequences.
- Promoting Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Collaboration between researchers, public health agencies, and other stakeholders is essential for advancing knowledge and sharing best practices. International partnerships and data sharing initiatives are crucial for effective global health responses.
Ongoing Monitoring and Research
Continued monitoring and research are essential for understanding monkeypox and developing effective interventions.
- Monitoring the Spread and Evolution of the Virus: Continued surveillance is essential for tracking the spread of the virus and identifying any potential changes in its characteristics, such as increased transmissibility or severity.
- Developing and Evaluating Vaccines and Treatments: Research and development efforts must continue to focus on developing effective vaccines, antiviral therapies, and other interventions to prevent and treat monkeypox infection.
- Understanding Long-Term Health Consequences: Research is needed to understand the potential long-term health consequences of monkeypox infection, including any possible neurological, cardiovascular, or dermatological complications.
Closing Summary
The monkeypox outbreak has presented the world with a formidable challenge, demanding a collective effort to mitigate its impact. The WHO’s declaration of a global health emergency serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of global health and the need for proactive measures to prevent future outbreaks.
As we navigate this evolving situation, it’s crucial to remain vigilant, informed, and prepared to face any potential challenges that may arise. The lessons learned from this outbreak will undoubtedly shape future responses to emerging infectious diseases, ensuring a more resilient and proactive approach to global health security.