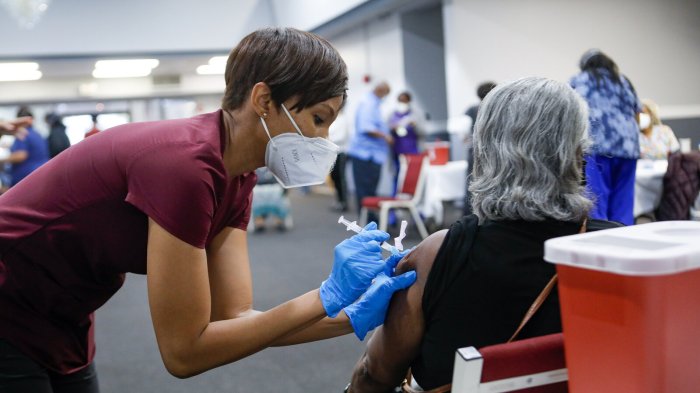
What You Should Know About Rebound COVID
What You Should Know About Rebound COVID: It’s a term that’s been making headlines, and for good reason. Rebound COVID refers to the return of COVID-19 symptoms after you’ve seemingly recovered from an initial infection. This can be a confusing and frustrating experience, leaving you wondering if you’re truly on the mend or if the virus is coming back for round two.
But don’t worry, understanding the phenomenon of Rebound COVID is the first step in navigating this new aspect of the pandemic.
Rebound COVID is not a new variant, but rather a re-emergence of symptoms after treatment. It’s important to note that Rebound COVID is not necessarily a sign of a more severe infection, but rather a reminder that the virus can be unpredictable.
While the exact causes are still being investigated, potential factors include viral variants, immune system responses, and even medication interactions. The symptoms of Rebound COVID can vary, but often include familiar signs like fever, cough, and fatigue. This means that if you’re experiencing these symptoms after previously recovering from COVID-19, it’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosing Rebound COVID involves a careful assessment of symptoms and a consideration of the patient’s recent medical history. The key to differentiating Rebound COVID from other conditions lies in understanding the timing and nature of symptoms.
Differentiating Rebound COVID from Other Conditions
Rebound COVID typically occurs within 2-8 days after completing a course of antiviral treatment, such as Paxlovid. Symptoms are often similar to the initial infection, but they can be milder and less severe. The key differentiator is the timing of the symptoms and the recent history of COVID-19 treatment.
- Timing:Rebound COVID symptoms appear shortly after completing antiviral treatment, usually within a week.
- Symptoms:Rebound COVID symptoms are typically milder than the initial infection and may include fever, cough, sore throat, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
- Recent History:Patients with Rebound COVID will have a recent history of COVID-19 treatment, particularly with antiviral medications like Paxlovid.
To confirm a diagnosis, a healthcare professional may order a PCR test or rapid antigen test. However, these tests may not always be necessary if the symptoms are mild and the timing is consistent with Rebound COVID.
Treatment Options for Rebound COVID
Currently, there is no specific treatment for Rebound COVID. However, the focus is on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
- Supportive Care:This includes resting, staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms such as fever, cough, and sore throat.
- Symptom Management:Treating individual symptoms like fever, cough, and muscle aches with over-the-counter medications can provide relief.
- Antiviral Medications:In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend a second course of antiviral medication, such as Paxlovid, if the symptoms are severe. However, this is not always necessary and should be discussed with a medical professional.
Managing Rebound COVID Symptoms
If you experience symptoms consistent with Rebound COVID, it is important to:
- Stay Home:To prevent spreading the virus, it is essential to stay home and avoid contact with others until symptoms have resolved.
- Monitor Symptoms:Keep track of your symptoms and contact your healthcare provider if they worsen or if you have concerns.
- Rest:Give your body time to recover by getting plenty of rest.
- Stay Hydrated:Drink plenty of fluids to help prevent dehydration.
- Over-the-Counter Medications:Consider using over-the-counter medications to manage fever, cough, and other symptoms.
Seeking Appropriate Medical Attention, What you should know about rebound covid
While Rebound COVID is usually mild, it is essential to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Difficulty Breathing:If you have trouble breathing or experience shortness of breath, seek immediate medical attention.
- Chest Pain:Chest pain can be a sign of serious complications and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
- Confusion or Disorientation:These symptoms may indicate a more severe illness and require prompt medical care.
- High Fever:A high fever that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter medications may warrant medical attention.
Prevention and Mitigation: What You Should Know About Rebound Covid
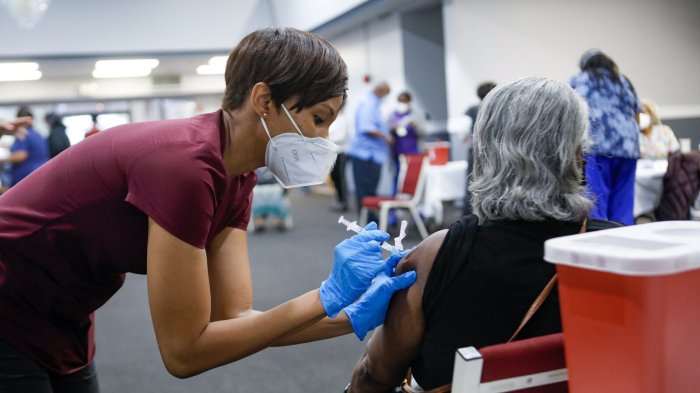
Rebound COVID, while a relatively new phenomenon, is not entirely uncharted territory. The strategies employed to combat the initial COVID-19 infection, particularly in its early stages, remain relevant and effective in mitigating rebound cases. This section explores preventive measures and strategies that can help individuals reduce their risk of experiencing rebound COVID.
Vaccination and Booster Shots
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing severe COVID-19 infections and minimizing the likelihood of rebound cases. The initial vaccination series primes the immune system to recognize and fight off the virus, while booster shots provide an additional layer of protection by enhancing the immune response.
Regular vaccination and booster shots are vital to maintaining a robust immune defense against COVID-19 variants.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene practices is essential in preventing the spread of COVID-19 and reducing the risk of rebound cases. These practices include:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after touching surfaces or interacting with others.
- Using alcohol-based hand sanitizers when soap and water are unavailable.
- Covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or the crook of your elbow.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Regularly cleaning and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces.
Isolation and Contact Tracing
Isolation and contact tracing are crucial in mitigating the spread of rebound COVID.
- Isolation: Individuals who experience rebound COVID should isolate themselves to prevent further transmission. This involves staying home and avoiding contact with others for a specific duration, as advised by healthcare professionals.
- Contact Tracing: Contact tracing involves identifying individuals who may have been in close contact with a person who has rebound COVID. These individuals are then advised to monitor their health and take necessary precautions, such as testing or isolation, to prevent further spread.
Monitoring Symptoms and Seeking Medical Guidance
Early detection and medical intervention are essential in managing rebound COVID. Individuals should be vigilant in monitoring their health for any signs or symptoms that may indicate a rebound infection.
- If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly. They can provide appropriate guidance and medical care, including testing and treatment options, if necessary.
- It’s important to remember that rebound COVID symptoms may differ from the initial infection, so it’s crucial to remain aware of any changes in your health and seek professional advice when in doubt.
Rebound COVID is a phenomenon where symptoms return after initial recovery, and it’s important to be aware of it, especially if you’re experiencing a second wave of illness. It’s a reminder that even after feeling better, the virus can still linger.
Sadly, the tragic news of ballerina Michaela Mabinty Deprince’s mother, Elaine, passing away within 24 hours highlights the unpredictable nature of health issues , even when they seem to be on the mend. Understanding the potential for rebound COVID can help us navigate this ongoing pandemic with more caution and preparedness.
Rebound COVID is a phenomenon where symptoms return after initially improving, and while it’s not fully understood, it seems to be more common with Paxlovid treatment. It’s like the movie “The Menu,” where the trailer suggests a luxurious dining experience turns into a nightmare , except instead of a culinary twist, it’s a viral one.
Rebound COVID is usually milder than the initial infection, but it’s still a good idea to talk to your doctor if you experience it.
Rebound COVID is a phenomenon where symptoms return after a period of improvement. It’s important to understand that it’s not a new variant, but rather a potential consequence of antiviral treatment. While researching this topic, I stumbled upon a fascinating story about John Travolta and Kirstie Alley’s relationship, which you can read about here: john travolta and kirstie alley a love story cnn.
Back to rebound COVID, it’s crucial to remember that even if your symptoms return, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’re reinfected.






