
What is PBIS: An Overview for Teachers and Schools
What is pbis an overview for teachers and schools – What is PBIS: An Overview for Teachers and Schools? PBIS, or Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a framework designed to create a positive and productive learning environment for all students. It’s a proactive approach that focuses on teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors, rather than simply reacting to misbehavior.
Think of it as a roadmap for creating a school culture where everyone feels safe, respected, and supported.
PBIS isn’t about punishment, it’s about building a foundation of positive behaviors. This framework is based on the idea that every student can learn and succeed when they feel safe, respected, and connected to their school community. It’s about creating a shared understanding of expected behaviors and providing students with the tools and support they need to thrive.
What is PBIS?: What Is Pbis An Overview For Teachers And Schools
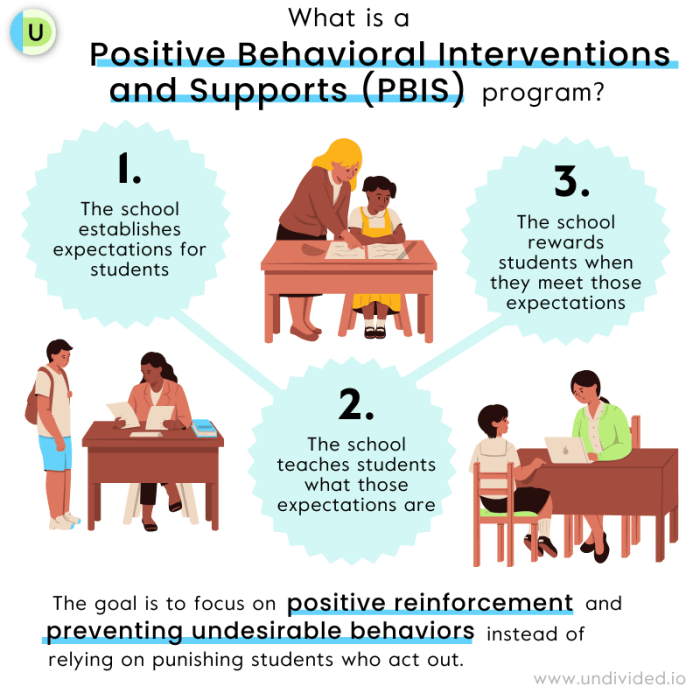
PBIS stands for Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports. It is a framework that schools use to promote positive behavior and create a safe and supportive learning environment for all students. The goal of PBIS is to reduce problem behaviors and increase positive behaviors by teaching students expected behaviors and providing support to those who struggle.
Core Principles of PBIS
PBIS is based on a set of core principles that guide its implementation. These principles ensure that PBIS is effective and sustainable.
PBIS, or Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a framework that schools use to create a positive and supportive learning environment. It focuses on teaching and reinforcing expected behaviors, promoting a sense of community, and addressing challenging behaviors proactively. While I was researching PBIS, I stumbled upon a story about a NYC mom who’s challenging a ban on mothers participating in top beauty pageants – she argues that being a parent isn’t a crime.
It’s interesting to see how different systems, like PBIS and beauty pageants, can create rules that impact individuals. Back to PBIS, it’s a valuable tool for teachers and schools to create a positive and productive learning environment for all students.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: PBIS emphasizes the importance of collecting and analyzing data to identify problem behaviors, track progress, and make informed decisions about interventions. This data-driven approach allows schools to tailor their interventions to the specific needs of their students and ensure that they are effective.
- Tiered System of Supports: PBIS utilizes a tiered system of supports to address the needs of all students. The system consists of three tiers:
- Tier 1:This tier provides universal supports for all students. It includes teaching expected behaviors, creating a positive school climate, and providing consistent consequences for inappropriate behaviors.
- Tier 2:This tier provides targeted supports for students who are at risk for developing behavior problems. It includes small group interventions, social skills training, and individualized behavior plans.
- Tier 3:This tier provides intensive supports for students who are experiencing significant behavior problems. It includes individual therapy, family counseling, and specialized educational programs.
- Positive Reinforcement: PBIS focuses on using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. This means rewarding students for following the rules and engaging in positive behaviors. Positive reinforcement can take many forms, such as praise, rewards, and privileges.
- Proactive Approach: PBIS takes a proactive approach to preventing behavior problems. This means focusing on teaching students expected behaviors and creating a positive school climate. By addressing potential issues before they become problems, PBIS can help create a more positive and productive learning environment for all students.
Implementation of PBIS in Schools
PBIS can be implemented in schools in a variety of ways. Some common examples include:
- School-Wide Expectations: Schools implementing PBIS typically develop a set of clear and concise expectations for student behavior. These expectations are taught to all students and reinforced consistently throughout the school day.
- Positive Behavior Supports: PBIS encourages the use of positive behavior supports, such as praise, rewards, and recognition, to reinforce desired behaviors. These supports can be used by teachers, administrators, and other school staff.
- Behavior Intervention Teams: Many schools implement PBIS by forming behavior intervention teams (BITs). BITs are made up of school staff who work together to identify students who are struggling with behavior problems and develop individualized interventions.
- Data Collection and Analysis: PBIS emphasizes the importance of collecting and analyzing data to track progress and make informed decisions about interventions. This data can be used to identify trends in student behavior, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and make adjustments to the PBIS program as needed.
PBIS, or Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a framework that helps schools create a positive and predictable learning environment. It’s all about teaching students the expected behaviors and providing support when they struggle. Speaking of innovative solutions, did you hear about the NHS’s new trial using drones to transport blood samples around London ?
Just like PBIS aims to streamline behavior, this initiative seeks to streamline healthcare delivery! By focusing on clear expectations and support systems, PBIS can create a more positive and productive learning environment for all.
The Three Tiers of PBIS
PBIS is a framework that uses a tiered system to provide support and interventions for students. The three tiers of PBIS are designed to address the needs of all students, from those who are succeeding to those who need more intensive support.Each tier builds upon the previous tier, creating a comprehensive system that supports positive behavior and reduces problem behavior.
The tiers are not exclusive, and students can receive support from multiple tiers simultaneously.
PBIS, or Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports, is a framework that helps schools create a positive and supportive learning environment. It focuses on teaching students expected behaviors and providing support when they struggle. While this might seem far removed from the excitement of the Champions League, it’s interesting to see how experts are split on who will win this year, with teams like Real Madrid, Barcelona, and Arsenal all in the mix.
Check out this article for a breakdown of the contenders. Just like in the Champions League, PBIS requires teamwork and a commitment to success, making it a valuable tool for educators looking to build a strong school community.
Tier 1: Primary Prevention
Tier 1 interventions are designed to reach all students and promote positive behavior for everyone. They focus on creating a positive school climate and teaching all students the expected behaviors. Examples of Tier 1 interventions include:
- Clear and consistent school-wide rules and expectations
- Positive reinforcement systems, such as praise, rewards, and recognition
- Teaching social-emotional learning skills, such as conflict resolution and empathy
- Creating a positive and supportive school environment
Tier 1 interventions are the foundation of PBIS and are essential for creating a positive school climate. They are designed to prevent problem behavior before it occurs and to support all students in developing positive behaviors.
Tier 2: Secondary Prevention
Tier 2 interventions are designed for students who are at risk for developing behavior problems. These students may be showing early signs of difficulty with behavior or may have a history of behavior problems. Examples of Tier 2 interventions include:
- Small group interventions for students who are struggling with specific behaviors
- Check-in/check-out systems to monitor student behavior and provide support
- Individualized behavior plans to address specific needs
- Parent involvement and communication
Tier 2 interventions are designed to provide targeted support to students who need it. They are a proactive approach to addressing behavior problems before they escalate.
Tier 3: Tertiary Prevention
Tier 3 interventions are designed for students who are experiencing significant behavior problems and require more intensive support. These students may have a history of chronic behavior problems or may be struggling with serious mental health issues. Examples of Tier 3 interventions include:
- Individualized therapy and counseling
- Functional behavioral assessments (FBAs) to identify the causes of behavior problems
- Behavior intervention plans (BIP) to address specific behaviors
- Collaboration with outside agencies, such as mental health professionals
Tier 3 interventions are designed to provide intensive support to students who need it most. They are a last resort for students who have not responded to other interventions.
PBIS in the Classroom
PBIS is not just a school-wide initiative; it’s a framework that can be effectively implemented in individual classrooms to create a positive and productive learning environment. Teachers play a crucial role in bringing PBIS to life within their classrooms, fostering a culture of respect, responsibility, and academic success.
Strategies for Implementing PBIS in the Classroom
To effectively implement PBIS in the classroom, teachers can utilize a variety of strategies that focus on clear expectations, positive reinforcement, and proactive behavior management.
- Establish Clear Expectations: Clearly defined expectations provide students with a roadmap for success. Teachers can work with their students to create a classroom code of conduct that Artikels acceptable behaviors. This code should be concise, positive, and age-appropriate, using language that students can easily understand.
Posting the code prominently in the classroom serves as a constant reminder of the expected behaviors.
- Teach Expected Behaviors: Beyond simply stating expectations, teachers should actively teach and model desired behaviors. This can be done through role-playing, discussions, and real-life examples. For instance, teachers can demonstrate how to resolve conflicts peacefully or how to ask for help respectfully.
- Provide Consistent Feedback: Regular and specific feedback is essential for student growth. Teachers can use praise, positive reinforcement, and encouragement to acknowledge and reinforce desired behaviors. This can be done through verbal praise, written notes, or even small rewards.
- Use Data to Inform Instruction: Tracking student behavior can help teachers identify patterns and trends. This data can be used to inform classroom management strategies and adjust interventions as needed. Teachers can use simple tools like checklists or charts to track student behavior.
Benefits of PBIS for Teachers and Students

Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) offers a framework for creating a positive and supportive school environment that fosters student success. It benefits both teachers and students by promoting a more structured and predictable learning environment, improving student behavior, and enhancing academic performance.
Impact on Classroom Management
PBIS provides teachers with effective strategies for managing student behavior and creating a more positive classroom environment. It emphasizes proactive approaches, such as clear expectations, consistent routines, and positive reinforcement, which can significantly reduce disruptive behavior and improve student engagement.
- Reduced Disruptions:PBIS strategies like clear expectations and consistent consequences help create a predictable environment, minimizing disruptions and allowing teachers to focus on instruction.
- Increased Engagement:By fostering a positive and supportive environment, PBIS encourages students to participate actively in learning activities and develop a sense of belonging.
- Improved Teacher Well-being:By reducing classroom disruptions and promoting a positive environment, PBIS can reduce teacher stress and improve their overall well-being, allowing them to focus on teaching and student support.
Impact on Student Behavior and Academic Performance
PBIS has been shown to improve student behavior and academic performance by creating a structured and supportive learning environment that encourages positive behaviors. It emphasizes positive reinforcement and individualized support, which can help students develop self-regulation skills and achieve their full potential.
- Improved Behavior:Studies have shown that schools implementing PBIS have seen significant reductions in disciplinary referrals, suspensions, and expulsions, indicating a positive impact on student behavior.
- Enhanced Academic Performance:PBIS has been linked to improved academic performance, as students who feel safe and supported in a positive learning environment are more likely to engage in learning and achieve academic success.
- Increased Social-Emotional Learning:PBIS promotes social-emotional learning (SEL) by teaching students valuable life skills such as empathy, communication, and conflict resolution, which can contribute to their overall well-being and success.
Creating a More Positive and Supportive School Environment
PBIS fosters a positive and supportive school environment by promoting a sense of community, belonging, and respect among students, teachers, and staff. It emphasizes collaboration and shared responsibility for creating a safe and nurturing learning environment where everyone feels valued and supported.
- Positive School Climate:PBIS contributes to a positive school climate by promoting respectful interactions, fostering a sense of community, and reducing bullying and other negative behaviors.
- Increased Student Engagement:When students feel supported and valued, they are more likely to be engaged in learning and participate actively in school activities.
- Improved Relationships:PBIS encourages positive relationships between teachers, students, and staff, creating a more collaborative and supportive school environment.
Resources for Teachers and Schools
Implementing PBIS effectively requires access to valuable resources that provide guidance, training, and support. This section explores a range of resources available to teachers and schools interested in adopting PBIS.
PBIS Training Programs and Materials
PBIS training programs and materials provide teachers and school staff with the necessary knowledge and skills to implement PBIS effectively. These resources often include comprehensive curriculum, practical strategies, and examples for different grade levels and settings.
- The Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP): The OSEP website offers a wealth of resources, including training materials, technical assistance, and funding opportunities for PBIS implementation.
- The National Center on PBIS: The National Center on PBIS is a leading resource for PBIS information and support. They offer online training modules, webinars, and a variety of downloadable materials, including implementation guides and fidelity checklists.
- The PBIS World website: PBIS World is a comprehensive resource that provides access to research, best practices, and tools for implementing PBIS.
Finding Support and Guidance for PBIS Implementation, What is pbis an overview for teachers and schools
Implementing PBIS requires ongoing support and guidance. Many resources are available to help schools navigate the process, including:
- State and Local PBIS Networks: Many states and local communities have established PBIS networks that provide support, training, and networking opportunities for schools.
- PBIS Coaches and Consultants: Schools can hire PBIS coaches and consultants to provide on-site support and guidance during the implementation process.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Numerous professional development opportunities are available, including workshops, conferences, and online courses, that focus on PBIS implementation and best practices.

