
War in Ukraine: Crisis for Millions of Students
War in ukraine creates crisis in education for million students – War in Ukraine: Crisis for Millions of Students – the headline speaks for itself, a stark reality that has cast a long shadow over the lives of millions of Ukrainian students. The conflict has not only uprooted their lives but has also disrupted their education, leaving a trail of uncertainty and hardship.
From the physical destruction of schools and universities to the psychological trauma experienced by students, the war has had a devastating impact on the education system. Access to electricity and internet connectivity has been disrupted, forcing many schools to close their doors, while displaced teachers and students struggle to adapt to new environments.
The situation is further complicated by the refugee crisis, with Ukrainian students seeking refuge in neighboring countries, facing new challenges in accessing education and navigating cultural and linguistic barriers.
The Impact on Education Infrastructure
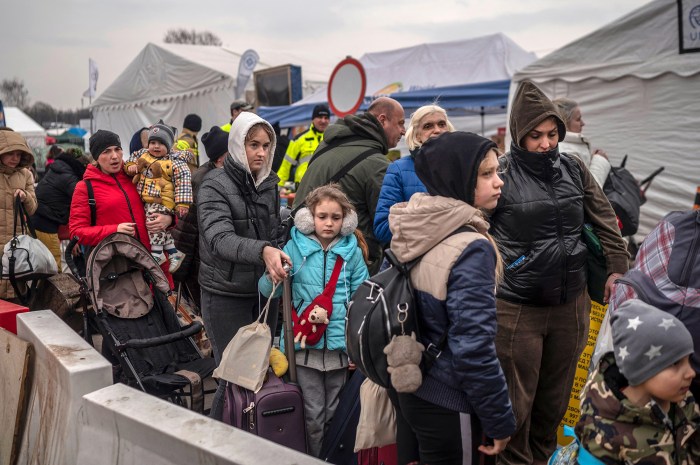

The war in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on the country’s education system, with schools and universities facing significant challenges. The conflict has resulted in physical damage to educational institutions, disruptions to electricity and internet access, and the displacement of both teachers and students.
Physical Damage to Schools and Universities
The conflict has resulted in widespread damage to educational infrastructure in Ukraine. According to UNESCO, as of November 2022, over 2,000 schools and universities have been damaged or destroyed. These attacks have left many students without access to safe and functional learning environments.
- Bombardments and shelling have damaged or destroyed school buildings, libraries, and laboratories, leaving them unusable.
- The conflict has also disrupted access to essential resources, such as textbooks, learning materials, and equipment, further hindering the educational process.
Disruptions to Electricity and Internet Connectivity
The conflict has also significantly disrupted access to electricity and internet connectivity in Ukraine. These disruptions have made it difficult for students to access online learning resources and for teachers to conduct remote classes.
- Frequent power outages have made it challenging for students to complete their schoolwork and for teachers to prepare lessons.
- Limited internet access has hindered online learning opportunities, forcing many students to rely on traditional methods of learning.
Displacement of Teachers and Students, War in ukraine creates crisis in education for million students
The war has forced millions of Ukrainians to flee their homes, including many teachers and students. This displacement has led to disruptions in the educational process and has created challenges for both teachers and students.
- Many teachers have been forced to leave their jobs and relocate to other parts of Ukraine or abroad, leaving a shortage of qualified educators in some areas.
- Students have also been displaced, often facing challenges in accessing education in their new locations. Some students have been unable to continue their education due to the lack of access to schools or the disruption of their studies.
Disruption of Learning Processes: War In Ukraine Creates Crisis In Education For Million Students
The war in Ukraine has had a profound impact on the country’s education system, disrupting the learning process for millions of students. The conflict has forced schools to close, displaced students and teachers, and created significant challenges in maintaining a consistent learning environment.
This section will delve into the challenges of maintaining a consistent learning environment, compare and contrast different remote learning approaches, and detail the difficulties in accessing educational resources and materials.
Challenges in Maintaining a Consistent Learning Environment
The war has created numerous challenges in maintaining a consistent learning environment for Ukrainian students. These challenges can be categorized as follows:
- Physical Safety and Security:The ongoing conflict has created a climate of fear and uncertainty, making it difficult for students to focus on their studies. Many schools have been damaged or destroyed, and students have been forced to flee their homes, disrupting their routines and access to education.
It’s heartbreaking to see the impact of the war in Ukraine on the education of millions of children. The disruption to their schooling is a tragedy, and it’s a reminder of the importance of prioritizing education, even in the face of conflict.
It’s also interesting to see how other parts of the world are tackling labor issues. For example, California could transform how fast food workers are treated with a new law that would give them more rights and protections.
While the situations are different, both issues highlight the need for systemic change to improve the lives of those most vulnerable.
- Mental Health and Well-being:The trauma of war can have a significant impact on students’ mental health and well-being, making it difficult for them to concentrate and learn effectively. The constant threat of violence, displacement, and loss of loved ones can lead to anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Access to Technology and Infrastructure:The war has damaged critical infrastructure, including power grids and internet networks, making it difficult for students to access online learning platforms and resources. Many families have been displaced and lack access to reliable internet connections or suitable devices for remote learning.
- Teacher Shortages and Training:The conflict has led to a shortage of teachers, as many have been forced to flee the country or have been called up for military service. Those who remain may lack the training and resources needed to effectively teach students in a remote learning environment.
- Disruptions to Curriculum and Assessment:The war has disrupted the traditional school calendar and curriculum, making it difficult for students to keep up with their studies and for teachers to assess their progress. The focus on survival and humanitarian aid has shifted attention away from formal education.
Approaches to Remote Learning
Despite the challenges, Ukraine has made significant efforts to maintain access to education through various remote learning approaches. These approaches can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Online Platforms and Learning Management Systems (LMS):Many schools have adopted online platforms and LMS such as Google Classroom, Moodle, and Edmodo to deliver lessons, assign homework, and provide feedback to students. These platforms offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace and from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Television and Radio Broadcasting:The Ukrainian government has partnered with television and radio broadcasters to provide educational content to students who lack access to the internet. This approach has been particularly effective in reaching students in rural areas and those who have been displaced.
- Printed Materials and Workbooks:Schools have also distributed printed materials and workbooks to students who lack access to digital resources. This approach provides a tangible and offline alternative to online learning, ensuring that students can continue their studies even without internet access.
Difficulties in Accessing Educational Resources and Materials
While Ukraine has implemented various approaches to remote learning, access to educational resources and materials remains a significant challenge. Here are some of the key difficulties:
- Limited Access to Digital Resources:Many students lack access to computers, tablets, or smartphones, making it difficult for them to participate in online learning. Even for those with devices, internet access can be unreliable or expensive, especially in areas affected by the conflict.
- Shortage of Educational Materials:The war has disrupted supply chains, making it difficult to procure textbooks, learning materials, and other educational resources. Many schools have lost their libraries and learning resources due to damage or displacement.
- Language Barriers:Many students have been displaced to countries where they do not speak the local language, making it difficult for them to understand educational materials and participate in learning activities.
- Lack of Teacher Support and Guidance:Students may lack access to adequate teacher support and guidance in remote learning environments. This can lead to difficulties in understanding concepts, completing assignments, and staying motivated.
The Refugee Crisis and Education
The war in Ukraine has triggered a massive refugee crisis, displacing millions of people, including a significant number of children and young adults. This has created unprecedented challenges for education systems in host countries, as they strive to accommodate and integrate Ukrainian refugee students into their existing frameworks.
The war in Ukraine has created a devastating crisis for millions of students, disrupting their education and leaving many with uncertain futures. While the world grapples with this tragedy, it’s important to remember that other crises are unfolding too. In the United States, indiana lawmakers approve abortion ban , a decision that will have a profound impact on women’s lives and access to healthcare.
These events, though seemingly disparate, underscore the importance of advocating for human rights and ensuring access to education and healthcare for all.
Challenges Faced by Ukrainian Refugee Students
The integration of Ukrainian refugee students into education systems in host countries presents numerous challenges. These challenges can be broadly categorized as logistical, cultural, and linguistic.
- Access to Education:One of the primary challenges is ensuring access to education for all refugee students. This includes enrolling them in schools, providing them with necessary learning materials, and ensuring that they have access to qualified teachers who can cater to their specific needs.
In some cases, refugee students may face delays in obtaining necessary documentation, such as visas or residency permits, which can hinder their access to education.
- Language Barriers:A significant challenge is the language barrier. Many Ukrainian refugee students have limited proficiency in the language of instruction in their host countries. This can make it difficult for them to understand their lessons, participate in class discussions, and complete assignments.
Language barriers can also impact their social integration and overall well-being.
- Trauma and Psychological Support:Many refugee students have experienced significant trauma due to the war, displacement, and separation from their families. This can have a profound impact on their mental health and learning abilities. Accessing appropriate psychological support and trauma-informed educational practices is crucial to ensure their well-being and facilitate their learning process.
- Educational Disruptions:Ukrainian refugee students have often faced disruptions in their education due to the war. They may have missed significant portions of their schooling or have had to switch schools multiple times. This can lead to learning gaps and make it difficult for them to catch up with their peers in host countries.
Cultural and Linguistic Barriers
The cultural and linguistic differences between Ukraine and host countries can pose significant challenges for refugee students. These differences can manifest in various ways:
- Cultural Norms and Values:Different cultures have different norms and values regarding education, classroom behavior, and interactions with teachers and peers. Ukrainian refugee students may need time to adjust to these new norms and expectations, which can affect their learning experience and social integration.
The war in Ukraine has created a devastating crisis for millions of students, disrupting their education and leaving them vulnerable to the trauma of conflict. It’s heartbreaking to see the impact on children who are forced to flee their homes and schools, and the uncertainty they face about their future.
Meanwhile, in the US, the Jan. 6th Committee continues its investigation, with Elaine Chao, former Transportation Secretary, joining other cabinet members in meeting with the panel. As the committee investigates the events of that day , the world watches with bated breath, hoping for a peaceful resolution to the crisis in Ukraine and a return to normalcy for the millions of students whose lives have been upended.
- Language Differences:The language barrier is a major obstacle to effective communication and learning. Students may struggle to understand instructions, participate in class discussions, and complete assignments. This can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and academic difficulties.
- Curriculum Differences:Educational systems in different countries have different curricula, teaching methods, and assessment practices. Ukrainian refugee students may need to adapt to new learning styles and expectations, which can be challenging.
Educational Policies and Resources
Several countries have implemented policies and resources to support Ukrainian refugee students. Here is a table highlighting some key initiatives:
| Country | Educational Policies and Resources |
|---|---|
| Poland | – Free access to education for Ukrainian refugee students at all levels.
|
| Germany | – Free access to education for Ukrainian refugee students.
|
| Czech Republic | – Free access to education for Ukrainian refugee students.
|
| United Kingdom | – Free access to education for Ukrainian refugee students.
|
International Support and Collaboration

The war in Ukraine has triggered a global response, with international organizations and countries rallying to support the education sector. Numerous initiatives have been launched to address the educational needs of Ukrainian students, teachers, and institutions.
Financial and Logistical Aid
International support for Ukraine’s education system encompasses both financial and logistical aid. Many countries and organizations have pledged significant funds to help rebuild schools and universities damaged by the conflict.
- The European Union has allocated over €1 billion to support Ukraine’s education sector, including funding for teacher training, school infrastructure, and digital learning platforms.
- The World Bank has provided over $1 billion in emergency funding for Ukraine, a significant portion of which is directed towards education recovery efforts.
- The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) has committed over $1 billion to Ukraine, with a focus on supporting education, health, and humanitarian assistance.
Beyond financial aid, several countries and organizations are providing logistical support to Ukrainian schools and universities.
- The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) has delivered essential learning materials, including textbooks, stationery, and educational games, to Ukrainian children.
- The International Organization for Migration (IOM) has provided transportation and temporary accommodation for displaced students and teachers.
- Several countries have opened their schools and universities to Ukrainian refugee students, offering them temporary access to education.
Technology’s Role in Remote Learning
Technology has played a crucial role in facilitating remote learning and providing educational resources for Ukrainian students displaced by the war.
- The Ukrainian Ministry of Education and Science has launched a platform called “Online School” to provide access to online learning materials and resources for students across all grade levels.
- International organizations like UNESCO and the Global Partnership for Education have partnered with technology companies to provide free access to online learning platforms and educational resources for Ukrainian students.
- Several online learning platforms, including Coursera, edX, and FutureLearn, have offered free access to their courses for Ukrainian students.
The Future of Education in Ukraine
The war in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on the country’s education system, leaving millions of students displaced and their futures uncertain. As the conflict continues, it is crucial to consider the long-term implications for education in Ukraine and develop strategies for rebuilding and restoring the system.
This section explores the challenges and opportunities facing Ukrainian education, focusing on the key priorities for recovery and the long-term vision for a resilient and equitable education system.
The Long-Term Implications of the War
The war has had a profound impact on the education system in Ukraine, affecting access to education, the quality of learning, and the mental well-being of students and educators. The destruction of schools and infrastructure, the displacement of families, and the ongoing psychological trauma are significant challenges that require immediate and long-term solutions.
The war has also disrupted learning processes, leading to learning gaps and a decline in educational standards.
Rebuilding and Restoring Education Infrastructure
The reconstruction of education infrastructure in Ukraine will be a complex and multifaceted task, requiring a comprehensive approach that prioritizes safety, accessibility, and quality. The following key priorities should be considered:
- Safety and Security:Ensuring the safety and security of schools and students is paramount. This involves assessing and repairing damaged infrastructure, implementing security measures, and providing psychological support to students and educators who have experienced trauma.
- Accessibility:Rebuilding schools and providing alternative learning spaces are crucial to ensure access to education for all students, regardless of their location or circumstances. This includes providing transportation, adaptive learning materials, and support services for students with disabilities.
- Quality:Rebuilding schools should prioritize quality learning environments that meet the needs of all students. This includes investing in modern equipment, curriculum development, and teacher training programs.
- Sustainability:The reconstruction of education infrastructure should be sustainable and resilient, incorporating energy-efficient technologies, green building practices, and disaster preparedness plans.
Addressing Learning Gaps and Psychological Needs
The war has created significant learning gaps and psychological challenges for Ukrainian students. Addressing these needs will require a multifaceted approach that combines academic support, mental health services, and social-emotional learning programs.
- Academic Support:Developing individualized learning plans, providing remedial instruction, and offering accelerated learning programs can help students catch up on lost learning.
- Mental Health Services:Providing access to mental health professionals, creating safe spaces for students to process their experiences, and offering trauma-informed care are essential for addressing the psychological impact of the war.
- Social-Emotional Learning:Integrating social-emotional learning into the curriculum can help students develop coping mechanisms, build resilience, and foster positive relationships.






