US Military in Europe: The Pentagons Eastern Obsession
Us military in europe the pentagons eastern obsession – US Military in Europe: The Pentagon’s Eastern Obsession – this phrase encapsulates a complex geopolitical landscape, where the Cold War’s echoes reverberate in the shifting sands of international relations. The US military presence in Europe, once a bulwark against Soviet expansion, has evolved into a multifaceted strategy aimed at deterring Russian influence and bolstering NATO’s eastern flank.
From the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea, the Pentagon’s focus on Eastern Europe has intensified, driven by a perceived threat from Moscow and a desire to solidify US security commitments in the region.
This dynamic relationship has sparked debate, with critics questioning the effectiveness of the US military build-up and its potential to escalate tensions with Russia. Yet, the Pentagon’s Eastern obsession remains a defining feature of contemporary security architecture, shaping the political and economic landscape of Europe and impacting the global balance of power.
Historical Context: Us Military In Europe The Pentagons Eastern Obsession
The presence of the US military in Europe has been a defining feature of the post-World War II era, evolving in response to changing geopolitical realities. From the immediate aftermath of the war to the present day, the US military has played a pivotal role in shaping the security landscape of the continent, with its involvement profoundly influencing both European politics and the broader global order.
The Post-War Era: Establishing a Presence, Us military in europe the pentagons eastern obsession
The end of World War II marked a new chapter in the US-Europe relationship, characterized by the emergence of the Cold War and the need to counter Soviet expansionism. The US military, having played a crucial role in defeating Nazi Germany, remained stationed in Europe, initially as part of the occupation forces.
The Pentagon’s eastern obsession, with its increased military presence in Europe, feels like a symptom of a larger, more complex issue. It’s hard to ignore the unsettling parallels with the Guantanamo Bay detention camp, where the line between “terrorist” and “prisoner of war” often blurs.
As the article guantanamo maybe none of them are terrorists points out, the very definition of “terrorism” is often subjective and politically charged. Perhaps the Pentagon’s focus on the East is less about protecting democracy and more about maintaining a perceived threat, one that justifies its ever-expanding military budget and influence.
However, the growing threat posed by the Soviet Union led to the establishment of a permanent US military presence on the continent.
The Pentagon’s eastern obsession has fueled a massive military buildup in Europe, raising questions about the real motivations behind this surge. Is it truly about containing Russia, or is there a deeper agenda at play? Some experts, like those featured in the article ex feds blast 9 11 panel and bush , believe the focus on a “war on terror” after 9/11 created a convenient justification for expanding military power and influence, and this strategy may be playing out once again in Europe.
Only time will tell what the true consequences of this eastern obsession will be, but the potential for conflict is undeniable.
The Cold War: Containing Soviet Influence
The Cold War era witnessed the US military playing a central role in containing Soviet influence in Europe. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), established in 1949, became the cornerstone of the US-Europe security partnership. NATO’s primary objective was to deter Soviet aggression and provide collective defense for its member states.
The US military, through its forward deployment in Europe, served as a deterrent against Soviet expansionism, while also providing a security umbrella for Western Europe.
The Pentagon’s relentless focus on Eastern Europe, while understandable given recent geopolitical tensions, often overshadows the fundamental issues driving global instability. One such issue, often overlooked, is the deep-rooted connection between poverty and hunger, as outlined in this insightful article causes of hunger are related to poverty.
Addressing this complex issue, which is at the heart of many global conflicts, should be a crucial part of any long-term strategy for stability in Eastern Europe and beyond.
Key Events and Agreements
Several key events and agreements shaped the US-Europe security partnership during the Cold War:
- The Berlin Blockade (1948-1949): This event, which saw the Soviet Union attempt to cut off access to West Berlin, underscored the importance of US military presence in Europe. The US airlift operation to supply West Berlin demonstrated US commitment to the defense of Western Europe.
- The Korean War (1950-1953): The Korean War further solidified the US-Europe security partnership, as it highlighted the threat posed by Soviet-backed communist forces.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): This event, which brought the world to the brink of nuclear war, underlined the importance of nuclear deterrence and the role of the US military in deterring Soviet aggression.
- The Helsinki Accords (1975): These accords, signed by the US, Soviet Union, and 33 other European states, recognized the post-World War II borders in Europe and committed all signatories to respect human rights and fundamental freedoms. The Helsinki Accords contributed to a period of détente between the US and the Soviet Union.
The Pentagon’s Eastern Obsession
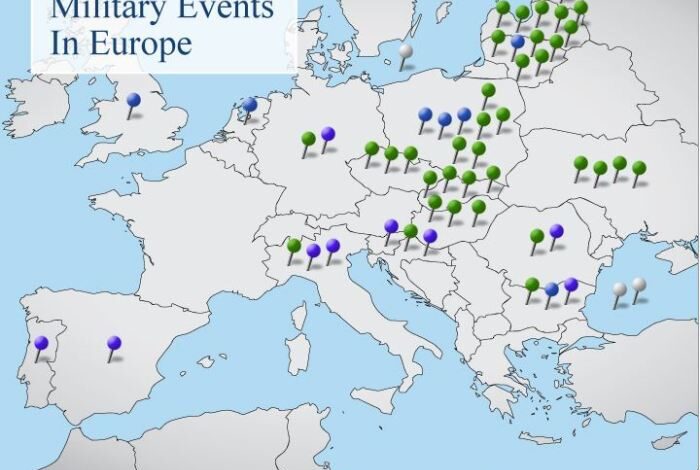
The Pentagon’s growing focus on Eastern Europe is a significant development in the global geopolitical landscape. Driven by a perceived threat from Russia, the United States has significantly increased its military presence and activities in the region, raising concerns about escalating tensions and potential conflict.
The Geopolitical Drivers
The Pentagon’s Eastern obsession is fueled by a complex interplay of geopolitical factors. The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 and its subsequent military intervention in eastern Ukraine were seen as a violation of international law and a direct challenge to the post-Cold War security order in Europe.
The US has interpreted these actions as evidence of Russia’s aggressive intentions and its desire to reassert its influence in the region.
Perceived Threats from Russia
The Pentagon views Russia as a significant threat to its interests in Europe. Russia’s modernization of its military, its development of advanced weapons systems, and its assertive foreign policy have raised concerns about its potential to disrupt the existing security balance.
The US perceives Russia’s actions as a challenge to its leadership role in NATO and its commitment to collective defense.
US Military Deployments and Exercises
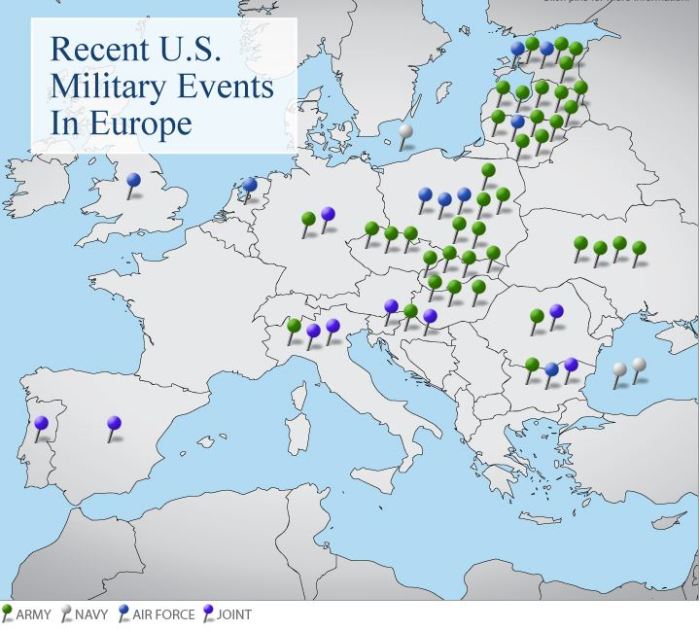
In response to the perceived threat from Russia, the US has significantly increased its military presence and activities in Eastern Europe. This includes:
- The permanent stationing of troops in Poland and the Baltic states.
- The rotation of US troops through Eastern European countries.
- The increased frequency and scale of military exercises in the region.
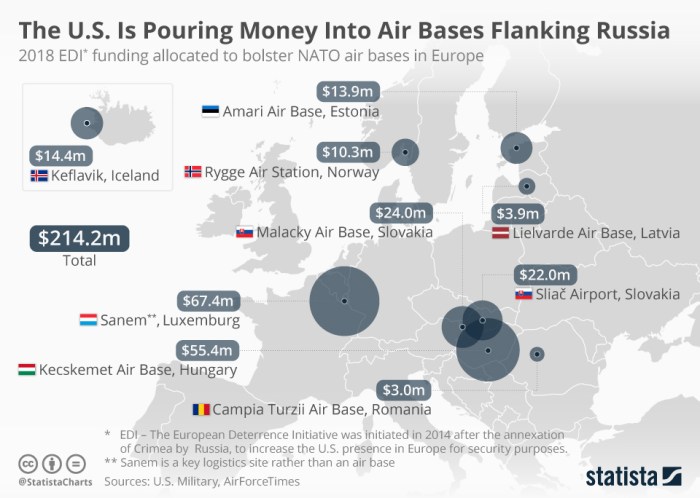
These deployments and exercises are designed to deter Russia and reassure US allies in Eastern Europe of their commitment to their security. However, they have also been criticized for contributing to a climate of fear and suspicion, and for potentially provoking Russia.
Impact on US Military Strategy
The Pentagon’s focus on Eastern Europe has had a significant impact on US military strategy. It has led to a shift in resources and attention away from other regions, such as the Middle East. It has also prompted a renewed emphasis on conventional warfare, as opposed to counter-terrorism operations.
The US military is now preparing for a potential conflict with Russia, which could involve a large-scale conventional war in Europe.
NATO Expansion and Russian Response
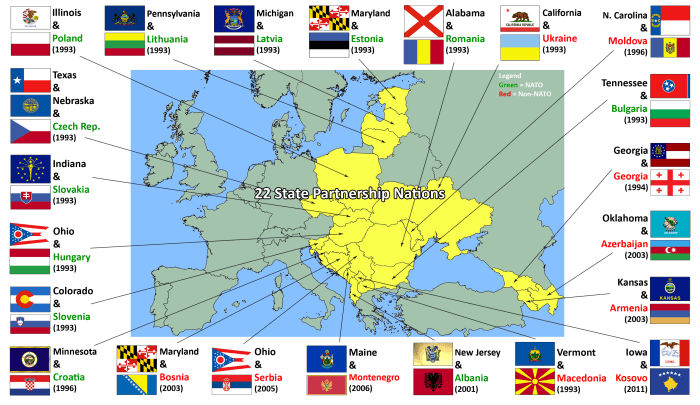
The eastward expansion of NATO, a military alliance formed in 1949, has been a significant factor in shaping the current security landscape in Europe. Since the end of the Cold War, NATO has expanded its membership to include several former Soviet republics, prompting concerns and responses from Russia.
NATO Expansion and the Changing Security Landscape
NATO expansion has been a complex and multifaceted process. After the fall of the Berlin Wall and the dissolution of the Soviet Union, NATO sought to redefine its role and purpose in a new world order. The organization expanded its membership to include countries in Central and Eastern Europe, which had previously been part of the Soviet bloc.
This expansion was driven by a number of factors, including:
- Security concerns: The expansion of NATO was seen by many Western countries as a way to deter Russian aggression and provide security guarantees to newly independent states in Eastern Europe. The expansion was also viewed as a way to consolidate democracy and promote stability in the region.
- Strategic considerations: The expansion of NATO also had strategic implications. By incorporating countries in Eastern Europe, NATO was able to extend its military presence and influence closer to Russia’s borders. This was seen as a way to counterbalance Russia’s military power and prevent it from reasserting its dominance in the region.
- Political and economic factors: The expansion of NATO was also driven by political and economic considerations. Many of the countries that joined NATO were seeking to integrate themselves into the Western political and economic system. NATO membership was seen as a symbol of their commitment to Western values and a way to access Western markets and investment.
The Russian Perspective on NATO Expansion
Russia has consistently viewed NATO expansion as a threat to its national security. From the Russian perspective, NATO expansion represents a hostile encroachment on its sphere of influence. The expansion of NATO to include countries bordering Russia has been seen as a direct challenge to Russia’s security and a threat to its territorial integrity.
“The expansion of NATO is a serious threat to Russia’s security. It is a deliberate attempt to undermine our security and to encircle us with hostile forces. We will not allow this to happen.”
Vladimir Putin, Russian President
Russia has also argued that NATO expansion has undermined the principles of European security and stability. Russia believes that the expansion of NATO has led to a new Cold War and has increased tensions in Europe. Russia has also pointed to the fact that NATO has conducted military exercises near its borders, which it sees as a provocation.
US and Russian Narratives on Security Concerns in Eastern Europe
The US and Russia have very different narratives regarding security concerns in Eastern Europe. The US argues that NATO expansion is a defensive measure and that it is necessary to deter Russian aggression. The US also points to Russia’s annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its support for separatists in eastern Ukraine as evidence of its aggressive intentions.
The US argues that NATO expansion is essential for maintaining peace and stability in Europe.Russia, on the other hand, argues that NATO expansion is a threat to its security and that it is a provocation. Russia also argues that the US is using NATO as a tool to contain Russia and to prevent it from regaining its former status as a superpower.
Russia points to the fact that NATO has conducted military exercises near its borders and that it has deployed troops and weapons systems in Eastern Europe as evidence of its aggressive intentions.






