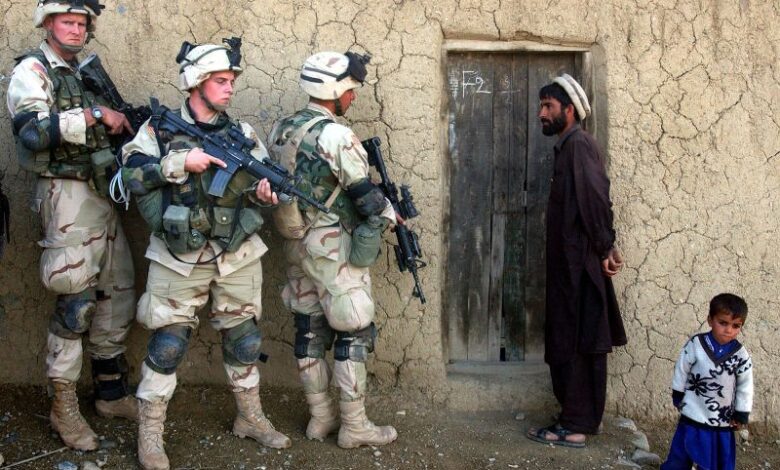
US Says Al-Qaeda Has Not Regrouped in Afghanistan
U s says al qaeda has not regrouped in afghanistan – US Says Al-Qaeda Has Not Regrouped in Afghanistan takes center stage, raising questions about the future of the terrorist organization in the region. Despite the US withdrawal and the Taliban’s return to power, the US government maintains that Al-Qaeda has not been able to rebuild its presence in Afghanistan.
This assessment is based on a combination of intelligence gathering, surveillance, and analysis of Al-Qaeda’s activities. However, the situation remains complex and there are legitimate concerns about the potential for Al-Qaeda’s resurgence.
The US government’s claim that Al-Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan is based on a number of factors. Intelligence agencies have been actively monitoring Al-Qaeda’s activities and have not detected any significant signs of a resurgence. The US also continues to maintain a presence in the region, with drone strikes and other counterterrorism operations aimed at disrupting Al-Qaeda’s operations.
Background of Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan
Al-Qaeda’s history in Afghanistan is deeply intertwined with the country’s turbulent political landscape and the rise of Islamic extremism. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial to comprehending the group’s impact on global security.
Origins and Relationship with the Taliban, U s says al qaeda has not regrouped in afghanistan
Al-Qaeda, meaning “The Base,” was founded by Osama bin Laden in the late 1980s during the Soviet-Afghan War. The group’s origins can be traced back to the mujahideen, Afghan fighters who received support from the United States and other Western countries in their fight against the Soviet Union.
Bin Laden’s network attracted foreign fighters, including many from the Arab world, who saw Afghanistan as a battleground against the Soviet Union and a platform for spreading their ideology. After the Soviet withdrawal in 1989, Afghanistan descended into civil war.
The US says Al Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan, but the news cycle moves fast. If you’re looking for a break from the headlines, check out this island with its own rules, language, and vodka. It’s a world away from the geopolitical complexities of the Middle East, offering a unique cultural experience that’s sure to leave a lasting impression.
But even as we escape into these idyllic landscapes, it’s important to remember the ongoing challenges facing the world. The US assessment on Al Qaeda’s presence in Afghanistan is just one piece of the complex puzzle, and it’s something we should continue to monitor closely.
Al-Qaeda, along with other factions, became involved in the conflict. The Taliban emerged as a dominant force in the mid-1990s, seizing control of most of the country. Al-Qaeda’s relationship with the Taliban was one of mutual benefit.
The Taliban provided Al-Qaeda with safe haven, allowing them to establish training camps and operate freely within Afghanistan. In return, Al-Qaeda supported the Taliban militarily and financially.
The US says Al Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan, but it’s hard to ignore the sense of unease that persists. Meanwhile, back in New York City, the Department of Buildings is investigating a truly bizarre incident – a woman fell through the floor of her Bronx apartment, landing in the cellar below! You can read more about it here.
It’s a reminder that even amidst global anxieties, the unexpected can happen anywhere, anytime.
Al-Qaeda’s Role in the 9/11 Attacks and the US Invasion of Afghanistan
On September 11, 2001, Al-Qaeda launched a series of coordinated terrorist attacks against the United States, targeting the World Trade Center in New York City and the Pentagon in Washington, D.C. The attacks, which killed nearly 3,000 people, were a turning point in the global war on terror.
The United States, under President George W. Bush, responded by launching a military campaign against Al-Qaeda and the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. The US invasion, supported by allies, aimed to dismantle Al-Qaeda’s network, overthrow the Taliban, and prevent Afghanistan from being used as a safe haven for terrorist groups.
Impact of the US Military Campaign on Al-Qaeda’s Operations in Afghanistan
The US military campaign in Afghanistan dealt a significant blow to Al-Qaeda. The group’s leadership was scattered, its training camps were destroyed, and its ability to operate freely in Afghanistan was severely curtailed. However, Al-Qaeda was able to adapt and survive, shifting its focus from large-scale attacks to smaller-scale operations and relying on its network of affiliates and sympathizers.
The group’s presence in Afghanistan remained a source of concern, particularly as the US withdrawal in 2021 created opportunities for the group to regroup and potentially re-emerge as a threat.
US Assessment of Al-Qaeda’s Current Status
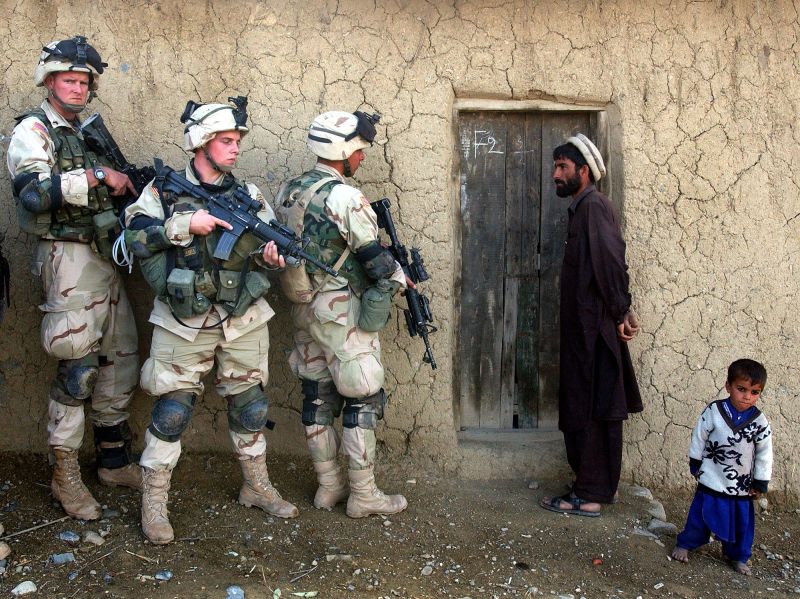

The US government has consistently maintained that Al-Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan to the point where it poses a significant threat to the United States. This assessment is based on a complex analysis of intelligence gathering, surveillance, and the evaluation of Al-Qaeda’s activities in the region.
Factors Influencing the US Assessment
The US government’s assessment is based on a variety of factors, including:
- Intelligence Gathering:The US has access to a wide range of intelligence sources, including human intelligence, signals intelligence, and satellite imagery. This information is used to track Al-Qaeda’s movements, communications, and activities.
- Surveillance:The US conducts extensive surveillance operations in Afghanistan and surrounding regions. This includes aerial surveillance, electronic monitoring, and the deployment of special forces units.
- Analysis of Al-Qaeda’s Activities:The US government carefully analyzes Al-Qaeda’s activities, including its propaganda, recruitment efforts, and operational planning. This analysis helps to determine the group’s capabilities and intentions.
Rationale for the US Assessment
The US government has provided several reasons for its assessment that Al-Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan:
- Reduced Capabilities:The US government believes that Al-Qaeda’s capabilities in Afghanistan have been significantly reduced since the fall of the Taliban regime in 2001. This is due to a combination of factors, including the loss of safe havens, the death or capture of key leaders, and the disruption of its operational networks.
While the U.S. insists that al-Qaeda hasn’t regained its footing in Afghanistan, it seems the world’s attention is fixated on something else entirely: the upcoming spacewalk by the SpaceX Polaris Dawn crew, which is being touted as the riskiest yet.
This mission will push the boundaries of space exploration, leaving us all wondering if the potential for a renewed al-Qaeda threat will be overshadowed by the excitement of the cosmos.
- Limited Presence:The US government estimates that Al-Qaeda has a limited presence in Afghanistan, with a small number of core members operating in remote areas. The group is believed to be struggling to recruit new members and maintain its operational capacity.
- Focus on Other Regions:The US government believes that Al-Qaeda has shifted its focus to other regions, such as the Sahel and Yemen, where it has a stronger presence and is able to operate more effectively.
Potential for Al-Qaeda’s Resurgence: U S Says Al Qaeda Has Not Regrouped In Afghanistan
While the U.S. has declared that Al-Qaeda has not regrouped in Afghanistan, the possibility of a resurgence remains a concern. Several factors could contribute to Al-Qaeda’s reemergence, creating a volatile situation in the region.
Factors Contributing to Al-Qaeda’s Resurgence
The current political instability in Afghanistan, coupled with security vulnerabilities, creates a conducive environment for extremist groups like Al-Qaeda to exploit. The Taliban’s control over the country, while not explicitly supporting Al-Qaeda, could inadvertently facilitate its operations. The presence of other extremist groups, such as ISIS-K, adds to the complexity of the situation, potentially providing Al-Qaeda with opportunities to collaborate or compete for influence.
Comparison with Past Conditions
The current situation in Afghanistan shares similarities with the conditions that allowed Al-Qaeda to thrive in the past. The presence of a weak central government, coupled with widespread insecurity, provided fertile ground for Al-Qaeda to establish a base of operations and recruit members.
Furthermore, the Taliban’s control over large swaths of territory, similar to the past, could again offer Al-Qaeda safe havens and logistical support.
Threats Posed by Al-Qaeda
The resurgence of Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan poses several threats to regional and global security. These threats, their impact, and possible mitigation strategies are Artikeld in the table below.
| Threat | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Increased terrorist attacks in Afghanistan and the region | Destabilization of the region, displacement of civilians, economic disruption | Strengthening Afghan security forces, intelligence sharing with regional partners, countering extremist propaganda |
| Recruitment of new members and expansion of Al-Qaeda’s network | Growth of Al-Qaeda’s influence and capabilities, potential for attacks beyond Afghanistan | Countering extremist ideologies, promoting alternative narratives, disrupting recruitment networks |
| Collaboration with other extremist groups | Increased threat from a united front of extremist organizations, potential for more sophisticated attacks | Monitoring and disrupting collaborations between extremist groups, targeting key leaders and financiers |
US Counterterrorism Efforts in Afghanistan
The US government has been engaged in counterterrorism efforts in Afghanistan since the aftermath of the 9/11 attacks. These efforts have evolved over time, encompassing a range of strategies including military operations, intelligence sharing, and support for Afghan security forces.
While the US has made significant progress in degrading Al-Qaeda’s capabilities, the challenges and limitations of these efforts remain substantial.
US Counterterrorism Operations in Afghanistan
The US military has conducted numerous counterterrorism operations in Afghanistan, targeting Al-Qaeda and other terrorist groups. These operations have involved airstrikes, special forces raids, and training of Afghan security forces. The US military presence in Afghanistan has played a crucial role in disrupting terrorist networks and preventing attacks.
- Airstrikes:The US has carried out numerous airstrikes against Al-Qaeda and other terrorist groups in Afghanistan. These strikes have targeted training camps, safe havens, and leadership figures. While airstrikes can be effective in disrupting terrorist activities, they also raise concerns about civilian casualties and the potential for collateral damage.
- Special Forces Raids:US special forces have conducted numerous raids against Al-Qaeda and other terrorist groups in Afghanistan. These raids have been highly successful in capturing or killing key terrorist leaders. However, they also carry a high risk to US personnel and can be controversial due to the potential for civilian casualties.
- Training Afghan Security Forces:The US has invested heavily in training and equipping Afghan security forces. The goal of these efforts is to build a capable and sustainable Afghan military and police force that can maintain security in the country. While progress has been made in training Afghan security forces, they continue to face challenges in terms of leadership, logistics, and combat effectiveness.
Intelligence Sharing and Counterterrorism Cooperation
The US government has established a robust intelligence-sharing network with Afghan security forces and international partners. This network plays a critical role in identifying and tracking terrorist threats. The US has also provided significant financial and technical support to Afghan intelligence agencies to enhance their capabilities.
- Joint Intelligence Operations:The US and Afghan intelligence agencies have conducted numerous joint operations to gather intelligence on Al-Qaeda and other terrorist groups. This collaboration has been crucial in identifying and disrupting terrorist networks.
- Intelligence Sharing:The US has shared intelligence on Al-Qaeda and other terrorist groups with Afghan security forces and international partners. This intelligence sharing has helped to improve the effectiveness of counterterrorism operations.
- Technical Support:The US has provided significant technical support to Afghan intelligence agencies, including training, equipment, and software. This support has helped to enhance the capabilities of Afghan intelligence agencies in gathering and analyzing intelligence.
Challenges and Limitations of US Counterterrorism Efforts
Despite significant efforts, US counterterrorism efforts in Afghanistan face numerous challenges and limitations. These challenges include the complex political landscape, the presence of other insurgent groups, and the difficulty of eliminating Al-Qaeda’s ideological influence.
- Complex Political Landscape:The political landscape in Afghanistan is complex and often unstable. This instability can make it difficult to maintain security and carry out counterterrorism operations.
- Presence of Other Insurgent Groups:Al-Qaeda is not the only insurgent group operating in Afghanistan. The Taliban and other groups pose significant challenges to security and counterterrorism efforts.
- Difficulty of Eliminating Al-Qaeda’s Ideological Influence:Even if Al-Qaeda’s physical presence in Afghanistan is reduced, its ideological influence may persist. This influence can inspire individuals to carry out attacks in other countries.
Hypothetical Scenario: US Response to Al-Qaeda Resurgence
In the event of a resurgence of Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan, the US government would likely respond with a combination of military, intelligence, and diplomatic measures. These measures would aim to degrade Al-Qaeda’s capabilities, disrupt its operations, and prevent attacks.
- Increased Military Operations:The US would likely increase its military presence in Afghanistan and conduct more counterterrorism operations. These operations would target Al-Qaeda’s leadership, infrastructure, and training camps.
- Enhanced Intelligence Sharing:The US would intensify its intelligence sharing with Afghan security forces and international partners. This intelligence sharing would help to identify and track Al-Qaeda’s activities.
- Diplomatic Efforts:The US would engage in diplomatic efforts to build support from regional and international partners. These efforts would aim to isolate Al-Qaeda, prevent it from receiving support, and promote stability in Afghanistan.
International Cooperation and Counterterrorism
The fight against Al-Qaeda and other terrorist organizations necessitates a global approach. International cooperation is paramount in countering the threat, sharing intelligence, and coordinating efforts to dismantle terrorist networks. This collaborative effort involves intelligence sharing, joint operations, and diplomatic initiatives, ultimately aiming to prevent terrorist attacks and disrupt their activities.
Examples of Successful Collaborations
Successful international collaborations in combating terrorism demonstrate the effectiveness of a unified approach. These collaborations highlight the crucial role of intelligence sharing, joint operations, and diplomatic efforts in disrupting terrorist activities.
- The capture of Osama bin Laden in 2011 was a significant achievement resulting from a joint effort between the United States and Pakistan. Intelligence sharing and coordinated operations played a vital role in locating and neutralizing the Al-Qaeda leader.
- The disruption of numerous terrorist plots in recent years, including the 2006 transatlantic aircraft plot, has been attributed to effective intelligence sharing and collaboration between various countries. These collaborations involve sharing information about suspected terrorists, their activities, and potential targets, enabling authorities to prevent attacks before they occur.
- Joint military operations, such as those conducted in Afghanistan and Iraq, have been crucial in targeting and degrading terrorist organizations. These operations involve sharing resources, expertise, and intelligence to effectively combat terrorism.
Importance of Intelligence Sharing and Coordinated Efforts
Intelligence sharing and coordinated efforts are essential in disrupting Al-Qaeda’s networks.
- Intelligence sharing allows countries to pool their resources and expertise, providing a comprehensive picture of terrorist activities. This shared intelligence enables authorities to identify potential threats, track terrorist movements, and disrupt their operations.
- Coordinated efforts involve joint operations, training, and information exchange. These collaborative efforts allow countries to work together to target terrorist networks, dismantle their infrastructure, and prevent them from carrying out attacks.
- Effective intelligence sharing and coordinated efforts are crucial in countering the evolving nature of terrorism. Terrorist organizations constantly adapt their tactics and strategies, requiring a collaborative response from the international community.