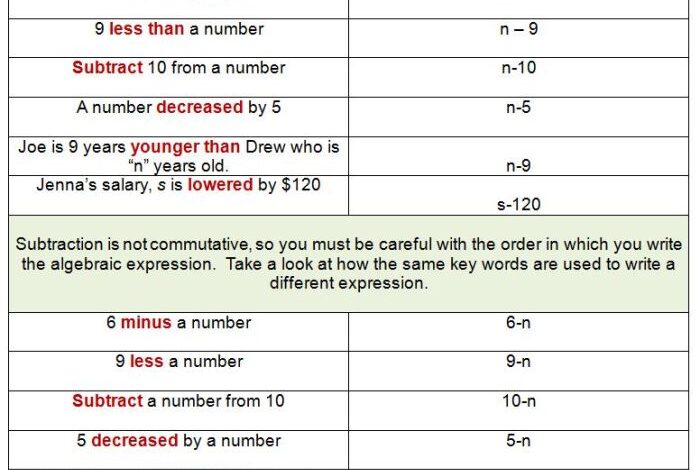
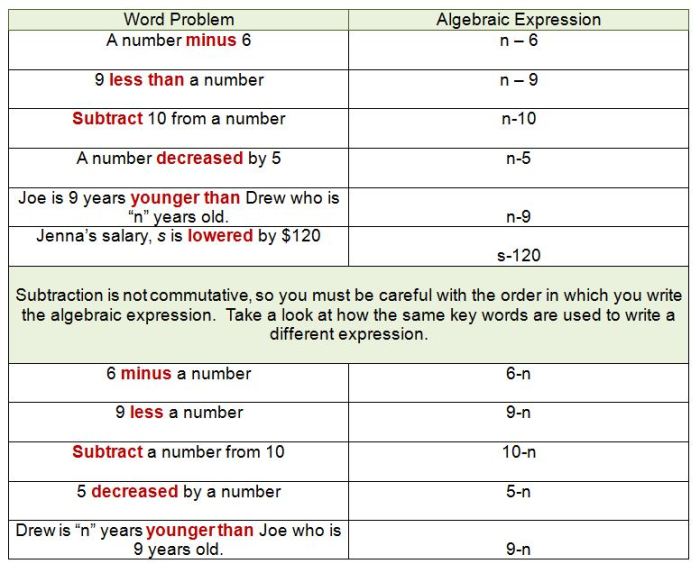
The Algebra of Infinite Justice: A Quest for Unbound Equality
The algebra of infinite justice is a captivating concept that explores the possibility of achieving perfect fairness and equality. It invites us to consider the limitations of traditional justice systems and envision a future where all wrongs are righted and all imbalances are rectified.
This concept transcends the confines of legal frameworks and delves into the realm of philosophical ideals, questioning the very nature of justice and its potential for infinite application.
By drawing upon the principles of algebra, a powerful tool for solving equations and finding solutions, we can gain a new perspective on the pursuit of justice. Just as algebraic equations can be manipulated to reveal hidden truths, so too can the principles of justice be applied to complex social problems, leading to equitable outcomes.
However, the pursuit of infinite justice is not without its challenges. We must confront the limitations of our current systems and grapple with the ethical implications of striving for a seemingly unattainable ideal.
The Role of Individual and Collective Action: The Algebra Of Infinite Justice
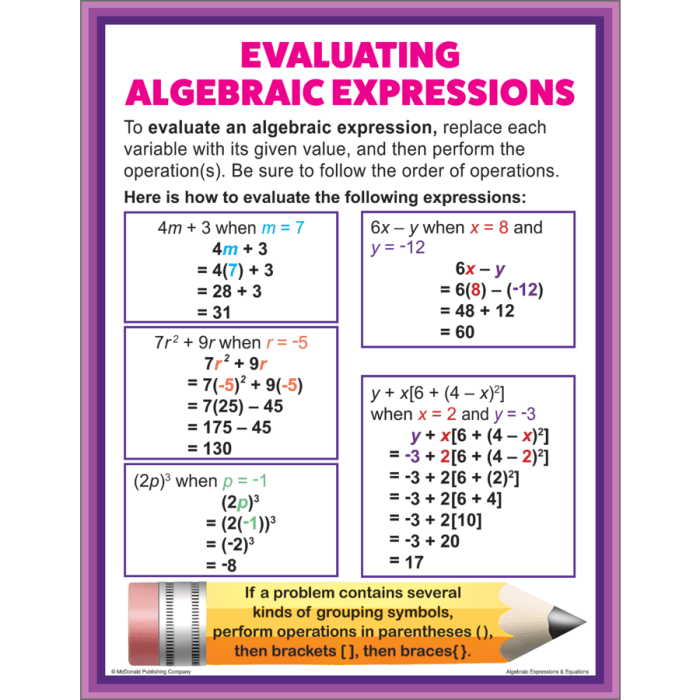
The pursuit of justice, whether on a personal or societal level, is a complex and multifaceted endeavor. It requires a deep understanding of the forces at play, both within individuals and within the broader social context. This understanding is crucial in recognizing the role of individual action and the power of collective mobilization in achieving lasting change.
Individual Action as a Catalyst for Change
The impact of individual actions on the pursuit of justice cannot be understated. Every act of courage, every instance of speaking truth to power, every effort to amplify marginalized voices, and every demonstration of compassion contributes to a larger movement for change.
These individual actions can be as simple as speaking up against injustice in everyday conversations or as profound as risking personal safety to defend the rights of others.
Collective Action: The Force of Unity
While individual actions are essential, it is through collective action that movements for justice truly gain momentum. The power of collective action lies in its ability to amplify individual voices, mobilize resources, and create a critical mass of support for change.
Collective action can take many forms, including protests, boycotts, strikes, and the formation of advocacy groups.
- The Civil Rights Movement: This movement, led by individuals like Martin Luther King Jr. and Rosa Parks, exemplifies the power of collective action. Through peaceful protests, sit-ins, and boycotts, the movement challenged segregation and discrimination, ultimately leading to landmark legislation like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
- The Women’s Suffrage Movement: This movement, which spanned decades, demonstrates the importance of sustained collective action. Through marches, rallies, and lobbying efforts, women fought for the right to vote, eventually achieving victory with the passage of the 19th Amendment in 1920.
- The Environmental Movement: This movement, driven by concerns about climate change and environmental degradation, highlights the power of collective action to raise awareness and influence policy. Through grassroots organizations, international agreements, and public campaigns, environmental activists have brought about significant changes in the way we think about and address environmental issues.
The Future of Justice
The concept of justice is dynamic, constantly evolving to adapt to societal shifts, technological advancements, and the changing nature of human interaction. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, the pursuit of justice faces unprecedented challenges and opportunities.
The future of justice will be shaped by a confluence of factors, including the rise of artificial intelligence, the increasing interconnectedness of the world, and the growing awareness of social inequalities.
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities, The algebra of infinite justice
The 21st century presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for achieving justice. Technological advancements, particularly in the realm of artificial intelligence, have the potential to revolutionize how we administer justice. AI-powered systems can assist with tasks such as evidence analysis, risk assessment, and even sentencing.
However, these systems also raise concerns about bias, transparency, and the potential for algorithmic discrimination.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting algorithms may perpetuate and even amplify those biases. This can lead to unfair outcomes in areas such as criminal justice, employment, and loan applications.
- Transparency and Accountability: AI algorithms can be complex and opaque, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability and make it challenging to identify and correct biases.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of AI in justice systems raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Sensitive personal information must be protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
Another challenge is the increasing interconnectedness of the world. Globalized trade, migration, and communication have created a complex web of interactions that can make it difficult to hold individuals and institutions accountable for their actions. This is particularly true in cases of transnational crime, human rights violations, and environmental damage.
A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a future where AI plays a central role in administering justice. Imagine a world where advanced AI systems are used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns of injustice, and recommend solutions. These systems are designed to be transparent, unbiased, and accountable.
In this scenario, a global network of interconnected courts uses AI to facilitate cross-border cooperation and ensure that justice is served regardless of geographic boundaries. This network can track the movement of goods and people, identify potential threats, and provide real-time information to law enforcement agencies.
The AI systems can also be used to address systemic inequalities by identifying and mitigating biases in existing laws and policies. By analyzing data on demographics, socioeconomic status, and access to resources, the AI can help policymakers develop more equitable and just policies.
This hypothetical scenario illustrates the potential for infinite justice in the future. It highlights the power of technology to enhance transparency, accountability, and fairness in the administration of justice. However, it also emphasizes the importance of careful consideration of ethical implications and the need to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed in a responsible and equitable manner.
The algebra of infinite justice is a complex equation, with variables constantly shifting and recalibrating. It’s a system where the actions of individuals and corporations, like tax avoidance and havens undermining democracy , ultimately contribute to a larger, overarching balance.
This balance, though unseen, is the ultimate measure of fairness, where every act, no matter how small, eventually finds its place in the grand equation.
The algebra of infinite justice is a fascinating concept, prompting us to consider the long-term consequences of our actions. It forces us to grapple with the interconnectedness of all things, from the smallest particle to the vast expanse of the universe.
This interconnectedness is especially evident when we consider the effects on the environment of our choices. The ripple effects of our actions can be far-reaching, influencing not only future generations but also the delicate balance of ecosystems. In this sense, the algebra of infinite justice reminds us that every action has a consequence, and that our choices today can shape the world of tomorrow.
The algebra of infinite justice, with its intricate equations of karma and retribution, often feels like a cosmic balancing act. To truly understand its workings, we must challenge our traditional narratives. A fresh perspective, like an alternative view of east west history , might reveal hidden connections and shed light on the intricate dance of cause and effect that governs the universe.
Perhaps, then, the algebra of infinite justice will become less of a mystery and more of a guiding principle, shaping our actions and leading us towards a more just and harmonious world.






