
Despite Western Sanctions, Russian Ruble and Banks Are Recovering
Despite western sanctions russian ruble and banks are recovering – Despite Western sanctions, Russian ruble and banks are recovering, defying initial predictions and showcasing the resilience of the Russian economy. This unexpected turnaround has surprised many, with the ruble strengthening against the US dollar and Russian banks reporting improved financial health.
This recovery has been attributed to a combination of factors, including the Central Bank of Russia’s decisive actions to stabilize the currency and the burgeoning economic ties Russia is forging with countries outside the West.
The imposition of sanctions by Western countries was a significant blow to the Russian economy, targeting crucial sectors like energy, finance, and technology. The initial impact was felt acutely, with the ruble plummeting and Russian banks facing liquidity challenges. However, the Russian government and its central bank implemented a series of measures to mitigate the impact of these sanctions, including raising interest rates, restricting capital outflows, and diversifying trade partnerships.
These measures, coupled with the increasing demand for Russian energy resources, have contributed to the remarkable recovery of the ruble and the overall resilience of the Russian financial system.
The Impact of Western Sanctions on the Russian Economy: Despite Western Sanctions Russian Ruble And Banks Are Recovering
The imposition of Western sanctions on Russia following the invasion of Ukraine has had a significant impact on the Russian economy. These sanctions, designed to pressure Russia to end its military actions, have targeted various sectors, aiming to cripple the Russian economy and limit its ability to finance the war effort.
Rationale for Western Sanctions
Western sanctions against Russia are intended to deter future aggression and punish the country for its actions. The rationale behind these sanctions rests on the belief that economic pressure can force Russia to change its course and comply with international norms.
The sanctions are a collective response by Western nations to Russia’s violation of international law and its disregard for the principles of sovereignty and territorial integrity.
Targeted Economic Sectors and their Impact
Western sanctions have targeted a wide range of sectors in the Russian economy, aiming to cripple its ability to function effectively.
Financial Sector
- The sanctions have restricted access to the SWIFT international payment system, hindering international transactions and making it difficult for Russian banks to operate globally.
- Restrictions on the Central Bank of Russia have limited its ability to intervene in the foreign exchange market, leading to a depreciation of the ruble.
- Freezing of assets held by Russian individuals and entities has significantly impacted the financial landscape.
Energy Sector
- Sanctions have targeted Russia’s energy exports, including restrictions on oil and gas imports from Russia.
- These measures have aimed to reduce Russia’s energy revenues, a significant source of income for the country.
- The impact on energy exports has been particularly felt in Europe, which has been heavily reliant on Russian energy supplies.
Technology Sector
- Sanctions have targeted Russia’s access to critical technologies, including semiconductors and software.
- These restrictions have hampered Russia’s ability to maintain and upgrade its technological infrastructure.
- The impact on the technology sector has implications for Russia’s long-term economic growth and competitiveness.
Defense Sector
- Sanctions have targeted Russia’s defense industry, limiting its access to advanced weapons and technologies.
- These measures aim to weaken Russia’s military capabilities and its ability to wage war.
- The impact on the defense sector has implications for Russia’s military posture and its ability to project power.
Pre-Sanction and Post-Sanction Economic Performance
The Russian economy has experienced significant changes since the imposition of Western sanctions.
GDP Growth
- Prior to the sanctions, Russia’s GDP growth was modest, averaging around 1.5% per year.
- Following the imposition of sanctions, Russia’s GDP is expected to contract significantly, with estimates ranging from 8% to 15% in 2022.
- The contraction in GDP is primarily driven by the impact of sanctions on key economic sectors, including energy, finance, and technology.
Inflation
- Before the sanctions, Russia’s inflation rate was relatively low, averaging around 4% per year.
- Following the imposition of sanctions, inflation has surged, reaching double-digit levels in 2022.
- The surge in inflation is attributed to the depreciation of the ruble, supply chain disruptions, and increased demand for goods and services.
Unemployment
- Prior to the sanctions, Russia’s unemployment rate was relatively low, hovering around 4%.
- While unemployment has increased slightly since the imposition of sanctions, it remains relatively low compared to other countries.
- The impact of sanctions on unemployment is likely to be more pronounced in the medium to long term as businesses struggle to adapt to the new economic environment.
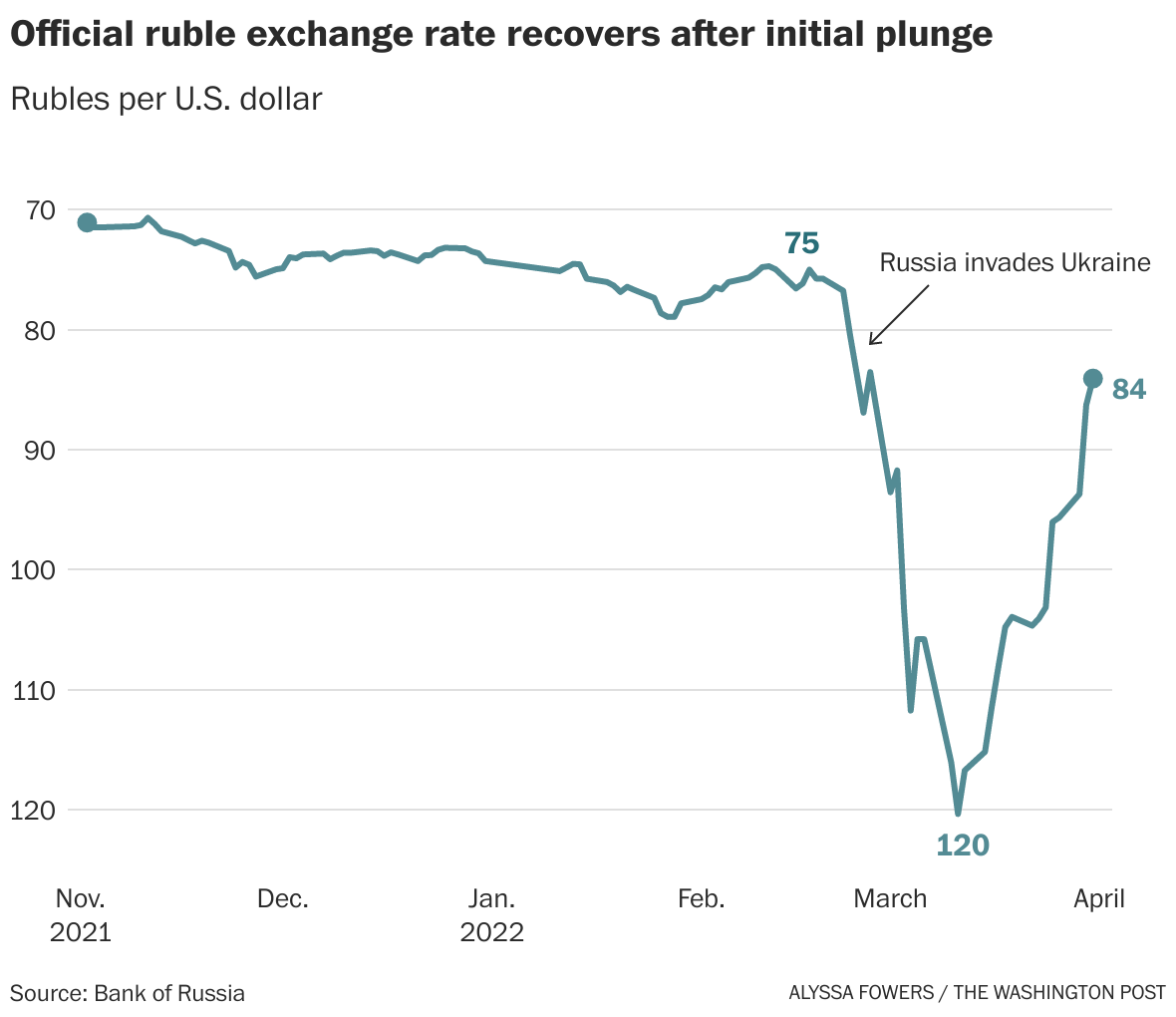
The Resilience of the Russian Ruble
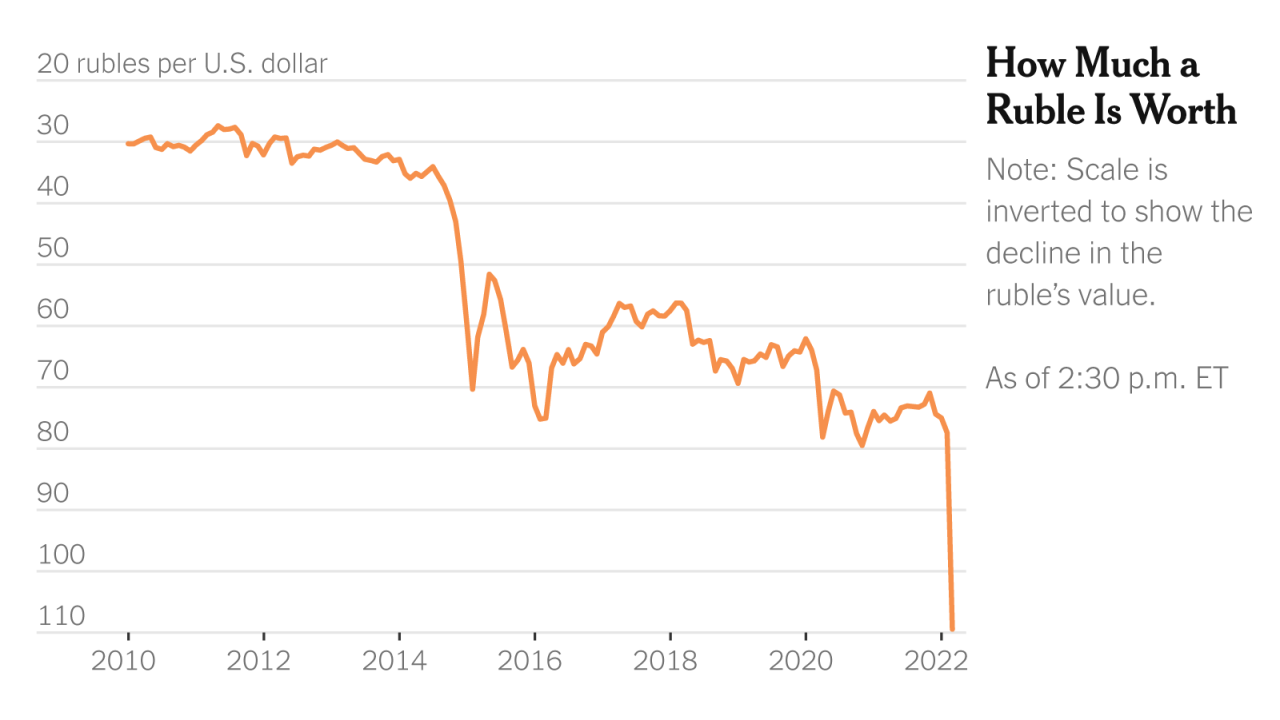
The initial impact of Western sanctions on Russia was severe, causing the ruble to plummet to record lows. However, the Russian ruble has staged a remarkable recovery, defying expectations and demonstrating a surprising resilience. This unexpected rebound can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the Central Bank of Russia’s decisive intervention and the changing dynamics of global energy markets.
The Initial Impact of Sanctions, Despite western sanctions russian ruble and banks are recovering
The imposition of sanctions triggered a wave of panic in the Russian financial markets. Investors, fearing the consequences of the sanctions, rushed to sell their ruble holdings, leading to a sharp depreciation of the currency. The ruble’s value plummeted to record lows, losing more than 50% of its value against the US dollar in the first few weeks after the sanctions were announced.
This sharp depreciation was fueled by several factors, including:
- Capital Flight:Foreign investors pulled their money out of Russia, fearing the economic and political consequences of the sanctions. This massive capital outflow put immense pressure on the ruble, further exacerbating its depreciation.
- Reduced Foreign Currency Reserves:Sanctions targeted the Central Bank of Russia’s foreign currency reserves, limiting its ability to intervene in the currency market and support the ruble. This significantly weakened the ruble’s position, making it more susceptible to further depreciation.
- Disruption of Trade:Sanctions imposed restrictions on trade with Russia, impacting its ability to import essential goods and services. This disruption in trade flows further contributed to the ruble’s decline, as businesses struggled to access necessary supplies and finance their operations.
The Role of the Central Bank of Russia
In response to the crisis, the Central Bank of Russia took swift and decisive action to stabilize the ruble and mitigate the impact of the sanctions. Key measures implemented included:
- Raising Interest Rates:The Central Bank significantly increased interest rates, making it more attractive for investors to hold rubles, thus increasing demand for the currency. This move helped to curb capital flight and stabilize the ruble’s value.
- Restricting Capital Outflows:The Central Bank imposed restrictions on capital outflows, limiting the amount of money that could be transferred out of Russia. This measure aimed to prevent further depreciation of the ruble by reducing the pressure on the currency from capital flight.
- Intervention in the Currency Market:The Central Bank intervened in the currency market, buying rubles and selling foreign currencies to increase demand for the ruble and stabilize its value. This intervention helped to control the ruble’s depreciation and prevent it from falling further.
The Ruble’s Recovery
Despite the initial shock of the sanctions, the ruble has staged a remarkable recovery, rebounding to pre-sanction levels. This recovery can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Increased Demand for Russian Energy:The war in Ukraine has led to a surge in global energy prices, particularly for oil and gas. As a major energy exporter, Russia has benefited from this price increase, boosting its export earnings and strengthening the ruble.
- Government Measures:The Russian government has implemented measures to support the ruble, such as requiring exporters to convert a significant portion of their foreign currency earnings into rubles. This policy has increased demand for the ruble and helped to stabilize its value.
- Reduced Capital Outflows:The initial wave of capital flight has subsided, as investors have become more accustomed to the sanctions and the ruble’s resilience. This reduced outflow of capital has eased pressure on the currency and contributed to its recovery.
The Impact of the Ruble’s Recovery
The ruble’s recovery has had a mixed impact on the Russian economy. While it has helped to reduce inflation and make imports cheaper, it has also made Russian exports less competitive.
- Inflation:The ruble’s recovery has helped to curb inflation, as imported goods have become cheaper. This has eased the pressure on consumers and businesses, who were struggling with rising prices due to the sanctions.
- Imports:The ruble’s appreciation has made imports cheaper, giving Russian consumers access to a wider range of goods and services. This has boosted consumer spending and economic activity.
- Exports:However, the ruble’s recovery has made Russian exports less competitive in global markets. This could negatively impact Russian businesses that rely on exports for their revenue, potentially leading to job losses and reduced economic activity.
The Performance of Russian Banks
The imposition of Western sanctions on Russia in response to the invasion of Ukraine has had a significant impact on the country’s financial sector, particularly its banks. While the Russian ruble has shown remarkable resilience, the immediate aftermath of the sanctions saw Russian banks facing numerous challenges, including limited access to international financial markets and potential liquidity issues.
It’s fascinating to see how the Russian ruble and banking system are bouncing back despite Western sanctions. It’s a reminder that even in the face of global pressure, resilience can emerge. Meanwhile, in a completely different sphere, in a post-Roe world, Illinois vows to be the Midwest’s abortion safe haven , offering a stark contrast to the increasingly restrictive landscape in other parts of the country.
This kind of proactive stance, just like Russia’s economic recovery, demonstrates the power of strong leadership and a commitment to core values, even in the face of adversity.
However, Russian banks have taken proactive measures to mitigate the impact of these sanctions, demonstrating their ability to adapt and maintain financial stability.
It’s fascinating to see how the Russian ruble and banks are bouncing back despite Western sanctions, a testament to their resilience and the strength of their economy. This contrasts sharply with the situation in the US, where the recent school shooting in Texas has sparked a debate about gun control, with top Texas Republicans calling for more guns, fortified schools, and armed teachers.
While the Russian economy seems to be weathering the storm, the US is grappling with its own internal challenges, highlighting the complexities of the global political landscape.
The Initial Impact of Sanctions, Despite western sanctions russian ruble and banks are recovering
The initial wave of sanctions imposed on Russia significantly restricted its access to international financial markets. This meant that Russian banks could no longer easily borrow money from foreign lenders, limiting their ability to secure funding for essential operations. Furthermore, the exclusion of certain Russian banks from the SWIFT messaging system, which facilitates international payments, hampered their ability to conduct cross-border transactions.
This led to concerns about potential liquidity issues, as banks faced difficulties in accessing foreign currency reserves and fulfilling their obligations to foreign creditors.
Measures Taken by Russian Banks
In response to these challenges, Russian banks have implemented several measures to mitigate the impact of sanctions. A key strategy has been to rely more heavily on domestic funding sources. This includes attracting deposits from individuals and businesses within Russia, as well as tapping into the domestic bond market.
Additionally, banks have been working to strengthen their capital positions by increasing their reserves and reducing their reliance on foreign borrowing. This has helped to bolster their financial resilience and provide them with a more secure foundation.
It’s fascinating to see how the Russian ruble and banks are bouncing back despite the Western sanctions. It reminds me of that townhouse community I found near the beach – it’s close to the beach but still feels very private.
The community has a sense of resilience, just like the Russian economy seems to be demonstrating. It’s a reminder that even in the face of adversity, things can still find a way to thrive.
The Current State of Russian Banks
Despite the initial challenges, Russian banks have shown a remarkable degree of resilience. They have managed to maintain their operations, albeit with some adjustments. While profitability has been affected by the sanctions, banks have been able to adapt by focusing on domestic lending and expanding their presence in key sectors of the Russian economy.
The overall financial health of Russian banks remains relatively stable, with strong capital buffers and a relatively low level of non-performing loans. However, the long-term impact of sanctions on the Russian banking sector remains uncertain. The extent to which banks can continue to rely on domestic funding sources and maintain their operations in a restricted international environment remains to be seen.
The Role of Alternative Economic Partnerships
The resilience of the Russian economy in the face of Western sanctions has been underpinned by its growing economic ties with countries outside the West, particularly in emerging markets. This diversification of economic partnerships has become a crucial strategy for Russia to mitigate the impact of sanctions and secure its economic future.
Economic Ties with China and India
Russia’s economic relationship with China has strengthened significantly in recent years. The two countries have forged strategic partnerships in various sectors, including energy, finance, and technology. China has become Russia’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade exceeding $190 billion in 2022.
The two countries have also collaborated on major infrastructure projects, such as the Power of Siberia gas pipeline. Similarly, Russia’s economic ties with India have also grown considerably. The two countries have strengthened cooperation in areas such as defense, energy, and technology.
India has become a major importer of Russian oil and weapons, and the two countries are exploring opportunities for joint ventures in various sectors.
Impact on the Russian Economy
These alternative economic partnerships have had a significant impact on the Russian economy.
- Increased Trade Flows:The growth in trade with China and India has helped to offset the decline in trade with Western countries. The diversification of trade partners has provided Russia with alternative markets for its exports and sources of imports.
- Investment Opportunities:China and India have become important sources of investment for Russia. Chinese companies have invested heavily in Russian energy projects, while Indian companies have shown interest in sectors such as technology and infrastructure.
- Access to Financial Markets:Russia has been able to access financial markets in China and India, providing it with alternative sources of funding. This has been particularly important given the limitations imposed by Western sanctions.
Benefits and Risks of Alternative Partnerships
While these alternative economic partnerships offer significant benefits for Russia, they also come with certain risks.
- Economic Dependence:Russia’s increasing reliance on China and India could create a new form of economic dependence, potentially making it vulnerable to external pressures or shifts in geopolitical dynamics.
- Technological Limitations:China and India are still developing economies with technological limitations. This could limit Russia’s access to advanced technologies and hinder its economic development.
- Geopolitical Risks:Russia’s growing economic ties with China and India could complicate its relationship with the West and increase geopolitical tensions. This could potentially lead to further sanctions or other economic pressures.
End of Discussion

The recovery of the Russian ruble and banks in the face of Western sanctions is a testament to the country’s economic adaptability and its ability to navigate complex geopolitical challenges. While the long-term implications of these sanctions remain to be seen, the resilience demonstrated by the Russian economy suggests that it is capable of weathering significant economic storms.
The country’s strategic pivot towards alternative economic partnerships, particularly with emerging markets like China and India, further strengthens its economic position and offers a path for continued growth. As the global economic landscape continues to evolve, the Russian economy’s ability to adapt and leverage its strengths will be crucial in determining its future trajectory.





