Say Goodbye to the 9 to 5: How to Master the Gig Economy
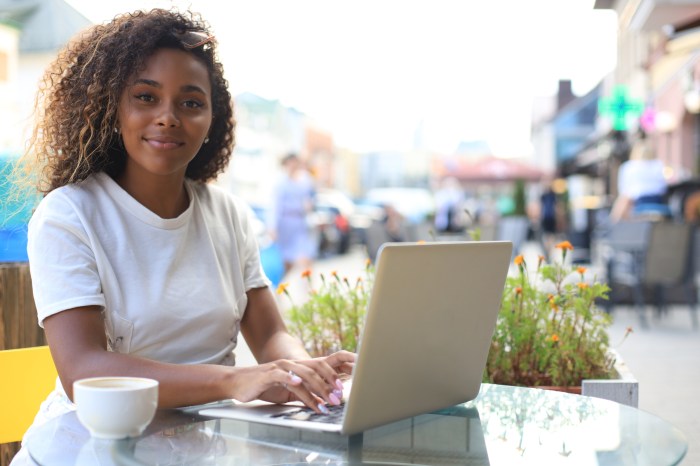
Say goodbye to the 9 to 5 how to master the gig economy – Say goodbye to the 9 to 5: How to master the gig economy. The traditional work model is fading, and the gig economy is booming. More and more people are choosing to be their own boss, ditching the office cubicle for the freedom of freelance work.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional looking for a change or a recent graduate seeking a flexible career path, the gig economy offers a wealth of opportunities.
This guide will delve into the ins and outs of the gig economy, exploring its advantages and challenges, providing practical advice on finding and securing work, and outlining the steps needed to build a successful career in this dynamic landscape.
The Rise of the Gig Economy
The gig economy, a rapidly growing sector of the workforce, is characterized by short-term, flexible work arrangements. It has become increasingly popular in recent years, driven by a confluence of factors, including technological advancements, changing work preferences, and economic shifts.The gig economy offers a wide array of opportunities for individuals seeking alternative employment models, providing flexibility, autonomy, and the potential for higher earnings.
The gig economy offers a unique path to freedom, allowing you to ditch the traditional 9-to-5 and forge your own path. It’s a world where flexibility reigns supreme, and it’s not just for freelancers; it’s for anyone looking to diversify their income.
Just like Kelly Bishop’s iconic role as Emily Gilmore in the beloved show “Gilmore Girls,” which she reflects on in this article , the gig economy allows individuals to embrace diverse roles and experiences, ultimately shaping their own unique narratives.
So, whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, consider exploring the possibilities of the gig economy and see where it takes you.
Factors Driving the Growth of the Gig Economy, Say goodbye to the 9 to 5 how to master the gig economy
The rise of the gig economy is a result of several key factors that have reshaped the traditional employment landscape. These factors include:
- Technological Advancements:The internet and mobile technologies have facilitated the emergence of online platforms that connect workers with employers, enabling efficient task allocation and remote work arrangements. These platforms have lowered barriers to entry for gig workers, allowing individuals to access a diverse range of opportunities.
- Changing Work Preferences:Many individuals seek greater flexibility and autonomy in their work lives. The gig economy caters to this desire, offering opportunities for individuals to set their own hours, work remotely, and choose projects that align with their skills and interests.
- Economic Shifts:The global economic landscape has witnessed a rise in freelance work, particularly in industries like technology, creative services, and consulting. This trend is driven by factors such as the increasing demand for specialized skills and the need for businesses to access talent on a project-based basis.
Types of Gig Work
The gig economy encompasses a diverse range of work arrangements, each with its unique characteristics and requirements. Some of the most common types of gig work include:
- Freelancing:Freelancers provide services on a project basis, often working independently for multiple clients. Common freelance professions include writing, graphic design, web development, and consulting.
- On-demand Work:On-demand platforms connect workers with temporary assignments, often involving tasks such as delivery, transportation, or customer service. Examples include ride-sharing services, food delivery apps, and task-based platforms.
- Platform-based Work:Platforms facilitate the connection between workers and employers, providing opportunities for online tutoring, virtual assistance, and other specialized services.
Examples of Successful Individuals in the Gig Economy
The gig economy has provided a path to success for many individuals who have embraced its flexibility and opportunities. Here are some notable examples:
- Gary Vaynerchuk:A successful entrepreneur and author, Gary Vaynerchuk built his career through online content creation, leveraging platforms like YouTube and social media to build a loyal following and establish himself as an influencer in the digital marketing space. He is a prime example of how individuals can leverage the gig economy to build successful businesses and personal brands.
- Jessica Hische:A renowned graphic designer and illustrator, Jessica Hische has built a successful career as a freelancer, working with a wide range of clients on projects ranging from book covers to branding campaigns. She is a testament to the creative potential of the gig economy, demonstrating how individuals can thrive in freelance roles by showcasing their skills and building a strong portfolio.
The gig economy is booming, offering a chance to say goodbye to the 9 to 5 and be your own boss. But even as opportunities grow, it’s important to consider the broader economic landscape. Recent reports, like this one on the worsening impact of the Brexit deal , highlight the challenges facing businesses and individuals alike.
Navigating these uncertainties requires adaptability and a willingness to embrace new skills, making the gig economy an increasingly attractive option for those seeking financial stability and control over their work lives.
Advantages of the Gig Economy
The gig economy, with its flexible work arrangements and diverse opportunities, offers numerous advantages for both workers and businesses. This new model of work has reshaped the traditional employment landscape, providing individuals with greater control over their careers and allowing companies to tap into a global pool of talent.
Flexible Work Schedule
The most significant advantage of the gig economy is the flexibility it offers. Workers can choose their own hours, set their own schedules, and work from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly attractive to individuals with family commitments, students, or those seeking a better work-life balance.
For example, a freelance writer can work from home during the day and take care of their children in the evenings. Similarly, a graphic designer can take on projects as they become available, allowing them to manage their time effectively.
Potential for Higher Earning Potential
The gig economy often presents the potential for higher earnings compared to traditional employment. Gig workers can set their own rates and negotiate directly with clients, allowing them to command competitive compensation. This is especially true for highly skilled professionals who can leverage their expertise to secure high-paying gigs.
For instance, a software developer with specialized skills can charge premium rates for their services, potentially earning more than they would in a traditional job.
Opportunity for Career Advancement and Skill Development
The gig economy provides a platform for individuals to advance their careers and develop new skills. By taking on diverse projects and working with different clients, gig workers can gain valuable experience and build their portfolios. This exposure to various industries and work environments can enhance their skillsets and make them more competitive in the job market.
For instance, a freelance writer can diversify their writing experience by working on projects in different niches, such as technology, healthcare, or finance. This can lead to greater specialization and expertise, increasing their earning potential.
Challenges of the Gig Economy: Say Goodbye To The 9 To 5 How To Master The Gig Economy
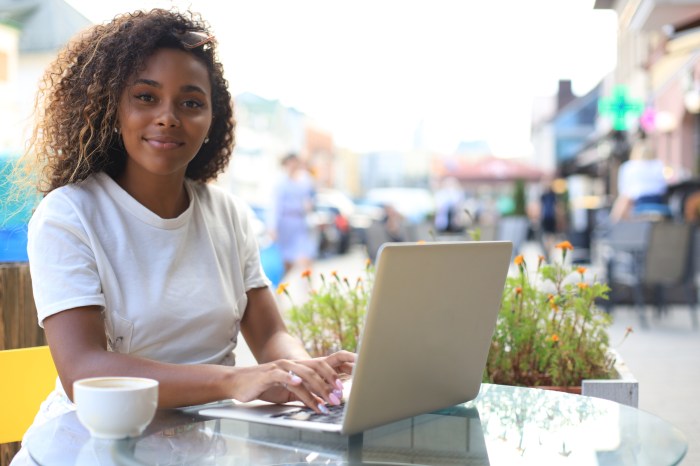

While the gig economy offers flexibility and independence, it also presents several challenges that potential gig workers should be aware of. These challenges can significantly impact financial stability, work-life balance, and overall well-being.
Job Security and Benefits
Gig work often lacks the traditional job security and benefits associated with traditional employment. This can be a significant concern for gig workers, as they may face periods of unemployment or income instability.
- Lack of Employee Status:Gig workers are typically classified as independent contractors, meaning they are not considered employees of the platform or company they work for. This means they are not eligible for traditional employee benefits such as health insurance, paid time off, or retirement plans.
- Unpredictable Income:The income of gig workers can fluctuate significantly depending on the availability of work, demand for their services, and their ability to secure clients. This can make it challenging to budget and plan for the future.
- Risk of Job Displacement:The gig economy is constantly evolving, and new technologies and platforms can quickly displace existing gig workers. This can create a sense of insecurity and make it difficult to build a long-term career.
Managing Finances and Taxes
Gig workers are responsible for managing their own finances and taxes, which can be a complex and time-consuming process. They must track their income and expenses, file quarterly tax returns, and pay self-employment taxes.
- Self-Employment Taxes:Gig workers are responsible for paying self-employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare taxes. These taxes are typically higher than the taxes paid by traditional employees, as employers usually contribute a portion of these taxes.
- Tax Deductions and Credits:Gig workers may be eligible for certain tax deductions and credits, such as deductions for business expenses and home office deductions. However, understanding and claiming these deductions can be challenging, and many gig workers may miss out on valuable tax savings.
- Financial Planning:Gig workers need to develop a strong financial plan to manage their income and expenses, save for retirement, and plan for unexpected events. This can be difficult given the unpredictable nature of gig work.
Burnout and Work-Life Balance
The flexibility of gig work can be a double-edged sword. While it allows workers to set their own hours, it can also lead to overwork and difficulty setting boundaries between work and personal life.
- Blurred Work Boundaries:Gig workers often find it difficult to separate work from their personal lives, as they can work from anywhere at any time. This can lead to feelings of burnout and exhaustion.
- Constant Availability:Gig workers are often expected to be available at all times to respond to clients or complete tasks. This can make it difficult to take time off or enjoy leisure activities.
- Lack of Support:Gig workers often work independently, which can lead to feelings of isolation and lack of support. This can be particularly challenging during difficult times or when facing personal or professional challenges.
Mastering the Gig Economy
The gig economy offers flexibility, freedom, and the potential for higher earnings, but navigating this dynamic landscape requires strategic planning and a proactive approach. Mastering the gig economy involves a multi-faceted strategy encompassing effective job searching, establishing a compelling online presence, and optimizing time management.
The gig economy offers flexibility and freedom, but it also comes with its own set of challenges, like navigating fluctuating income and finding reliable work. As we explore this new world of work, it’s interesting to see how policy changes, like the proposal to impose a pay-per-mile scheme on electric cars , might impact those who rely on driving for their income.
Whether you’re a rideshare driver, delivery person, or freelance contractor, understanding these evolving regulations is key to navigating the gig economy successfully.
Finding and Securing Gig Work
Finding and securing gig work effectively requires a comprehensive strategy. This involves leveraging multiple platforms, tailoring your profile, and actively networking.
- Explore Multiple Platforms:The gig economy encompasses various platforms catering to different skills and interests. Popular platforms include Upwork, Fiverr, Guru, and Freelancer for freelance work, while Uber, Lyft, and DoorDash cater to transportation and delivery services. Explore multiple platforms to identify opportunities that align with your expertise and preferences.
- Optimize Your Profile:Your online profile is your digital resume, showcasing your skills and experience. Craft a compelling profile highlighting your key strengths, relevant experience, and past achievements. Use s that potential clients are likely to search for and ensure your profile is visually appealing and easy to navigate.
- Build a Portfolio:A portfolio showcasing your work is essential for attracting clients. Gather samples of your previous projects, testimonials from satisfied clients, and relevant certifications to demonstrate your capabilities and build credibility.
- Network Actively:Networking plays a crucial role in securing gig work. Engage with other gig workers, attend industry events, and participate in online communities to expand your network and access valuable referrals.
Building a Strong Online Presence and Personal Brand
In the gig economy, your online presence is your most valuable asset. Establishing a strong online presence and personal brand is crucial for attracting clients and building a sustainable career.
- Create a Professional Website:A website serves as your online hub, showcasing your skills, experience, and portfolio. Consider using platforms like Wix, Squarespace, or WordPress to create a professional-looking website that reflects your brand identity.
- Engage on Social Media:Social media platforms provide opportunities to connect with potential clients and build your brand. Create engaging content, share your expertise, and interact with your followers. Focus on platforms relevant to your industry and target audience.
- Develop a Consistent Brand Identity:Consistency in your online presence is crucial for building a recognizable brand. Develop a consistent brand identity across all platforms, including your website, social media profiles, and marketing materials. This includes using a consistent logo, color scheme, and messaging.
Managing Time Effectively and Prioritizing Tasks
Effective time management is essential for success in the gig economy. Juggling multiple projects, managing deadlines, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance requires a structured approach.
- Set Clear Goals and Deadlines:Define your goals and set realistic deadlines for each project. Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps to make them less overwhelming.
- Utilize Time Management Tools:Utilize time management tools such as calendars, task managers, and productivity apps to track deadlines, schedule appointments, and prioritize tasks. Popular options include Google Calendar, Asana, and Trello.
- Minimize Distractions:Identify and eliminate distractions that hinder your productivity. This could include turning off notifications, scheduling dedicated work hours, and creating a quiet work environment.
- Prioritize Tasks:Prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. Focus on high-priority tasks first and delegate or postpone low-priority tasks to ensure you’re working on the most crucial items.
Building a Successful Gig Economy Career
The gig economy offers a wealth of opportunities for individuals seeking flexible work arrangements and the freedom to build their own careers. However, transitioning to a gig economy career requires careful planning, skill development, and strategic networking. This section provides a step-by-step guide to navigate this exciting yet challenging path.
Transitioning to a Gig Economy Career
- Identify your skills and passions:Begin by reflecting on your existing skills, experiences, and areas of interest. What are you good at? What do you enjoy doing? This introspection will help you pinpoint potential gig opportunities that align with your strengths and passions.
- Research and select platforms:Numerous platforms connect gig workers with potential clients. Explore platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, Freelancer, Guru, and others that cater to your skillset and desired work. Each platform has its unique features, pricing structures, and client base, so research and choose the ones that best suit your needs.
- Build a professional online presence:Create a compelling online profile on chosen platforms, highlighting your skills, experience, and relevant projects. A strong online presence is crucial for attracting potential clients and showcasing your expertise.
- Craft a compelling portfolio:Showcase your skills and experience through a portfolio that demonstrates your capabilities. Include examples of your work, testimonials, and relevant certifications to build credibility and attract clients.
- Set competitive rates:Research industry standards and competitor rates to determine competitive pricing for your services. Consider your experience, skill level, and the value you bring to clients when setting your rates.
- Start small and build momentum:Begin with smaller gigs to gain experience and build a positive track record. As you gain experience and positive reviews, you can gradually take on larger and more challenging projects.
Essential Skills and Resources
- Time management:Effective time management is crucial for managing multiple projects, meeting deadlines, and maintaining a consistent workflow.
- Communication skills:Strong communication skills are essential for clear and effective interactions with clients, collaborators, and other stakeholders.
- Marketing and self-promotion:Learn to market your services effectively and promote your skills to attract potential clients. This may involve creating a personal website, utilizing social media, and engaging in networking activities.
- Financial management:Mastering financial management is vital for tracking income, expenses, taxes, and managing your finances effectively.
- Technology skills:Develop proficiency in relevant technology tools and platforms, such as project management software, communication tools, and online payment systems.
- Continuous learning:The gig economy is constantly evolving. Embrace a mindset of continuous learning and stay updated on industry trends, new technologies, and emerging opportunities.
Networking and Building Relationships
- Attend industry events and conferences:Connect with other gig workers, potential clients, and industry experts at relevant events. This is an excellent opportunity to network, learn about new opportunities, and build relationships.
- Join online communities and forums:Engage in online communities and forums related to your industry or niche. Participate in discussions, share your expertise, and connect with other professionals.
- Collaborate with other gig workers:Partner with other gig workers in your field or complementary areas. This can lead to joint projects, referrals, and expanded opportunities.
- Provide exceptional service:Deliver high-quality work and exceed client expectations. This will build a positive reputation and lead to repeat business and referrals.
- Build relationships with clients:Go beyond transactional relationships and build genuine connections with your clients. This can lead to long-term partnerships and valuable referrals.
The Future of the Gig Economy
The gig economy, once a fringe phenomenon, is rapidly becoming a mainstream force in the global workforce. Technological advancements, shifting societal values, and evolving business models are all driving its growth, and the future holds exciting possibilities.
The Impact of Technology
Technology is a key driver of the gig economy’s evolution, enabling new platforms, connecting workers and clients, and automating tasks.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI-powered platforms can automate tasks, optimize matching between workers and clients, and personalize work experiences. This can lead to greater efficiency, improved worker satisfaction, and increased accessibility for diverse talent pools. For example, AI-powered platforms can analyze a worker’s skills and experience to recommend relevant gigs, ensuring a more efficient and personalized experience.
- Blockchain Technology:Blockchain can enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in gig economy transactions. It can facilitate secure payments, streamline contract management, and create a verifiable record of work history, which is valuable for workers building their reputation and credibility. For instance, blockchain can be used to track and verify the completion of tasks, ensuring that workers are paid fairly and on time.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR):VR/AR technologies can create immersive training programs, enable remote collaboration, and enhance the gig economy experience. Workers can receive training in a virtual environment, collaborate on projects with clients in real-time, and experience tasks in a more engaging and realistic way.
For example, VR can be used to simulate complex tasks, allowing workers to practice and refine their skills before working on real-world projects.