Russia Crimps Gas Flows as Europe Prepares for Winter
Russia crimps gas flows just as europe races to stock up for winter – Russia Crimps Gas Flows as Europe Prepares for Winter, a chilling reality that has sent shockwaves through the continent. As the winter months approach, Europe is facing a critical energy crisis, with Russia, its primary gas supplier, drastically reducing gas flows.
This move has left European nations scrambling to fill their storage reserves, with the looming threat of energy shortages casting a shadow over the upcoming winter.
The situation is a complex geopolitical chess game, with Russia citing technical issues and sanctions as reasons for the reduced gas flows. Meanwhile, Europe is desperately trying to diversify its energy sources and find alternative suppliers. The stakes are high, with the potential for economic hardship and social unrest looming large if the energy crisis deepens.
Russia’s Actions
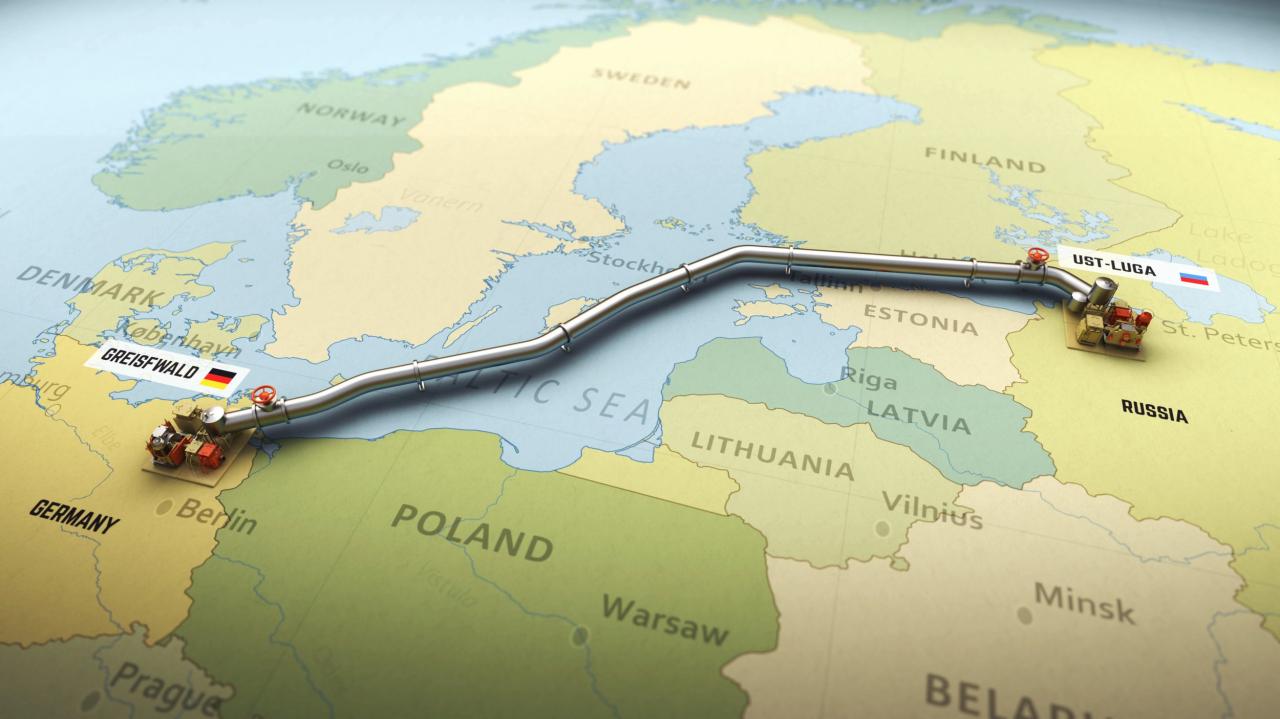

Russia’s actions to reduce gas flows to Europe have been a major source of tension and uncertainty in the region. These actions, often framed as responses to Western sanctions, have raised concerns about Europe’s energy security and its ability to navigate the upcoming winter.
Reasons for Reduced Gas Flows
Russia’s stated reasons for reducing gas flows to Europe include technical issues, maintenance, and the need to comply with sanctions. However, unofficial reasons often point to a deliberate strategy to exert pressure on European countries, particularly in the context of the ongoing conflict in Ukraine.
- Technical Issues:Russia has cited technical issues with the Nord Stream 1 pipeline, which carries natural gas from Russia to Germany, as a reason for reduced flows. However, some analysts believe these issues are exaggerated or politically motivated.
- Maintenance:Russia has also claimed that it needs to conduct maintenance on the Nord Stream 1 pipeline, which requires a temporary reduction in gas flows. However, the timing of these maintenance periods has been questioned, with some suggesting that they coincide with periods of heightened geopolitical tension.
- Sanctions:Russia has also claimed that Western sanctions, imposed in response to its actions in Ukraine, are hindering its ability to supply gas to Europe. However, these sanctions do not specifically target gas exports, and some analysts argue that Russia is using sanctions as a pretext to reduce gas flows.
With winter fast approaching, Europe is scrambling to fill its gas reserves, a task made all the more challenging by Russia’s ongoing gas flow restrictions. While the continent grapples with energy security, a different kind of scientific debate is heating up: the controversial idea that T.
Rex was actually three distinct species is facing scrutiny. It seems that even dinosaurs can’t escape the geopolitical tensions that are shaping our world, as Europe’s energy woes and the T. Rex debate both highlight the challenges of navigating uncertainty and change.
- Geopolitical Pressure:Many experts believe that Russia’s actions are intended to exert pressure on European countries, particularly those that have been critical of its actions in Ukraine. By reducing gas flows, Russia aims to create economic hardship and force European countries to reconsider their support for Ukraine.
Comparison with Previous Instances
The current reduction in gas flows is not unprecedented. In 2006 and 2009, Russia reduced gas flows to Ukraine, leading to energy shortages in Europe. These events highlighted the vulnerability of European energy security to Russian actions.
It’s a tough time for Europe, with Russia playing games with gas flows just as they race to fill their reserves for winter. It’s a reminder that energy security is a critical issue, and we should all be thinking about the potential for disruptions.
It’s also a reminder of how quickly things can change, as we’ve seen with the recent Supreme Court ruling on abortion in the US , which has raised concerns about the potential for other rights to be eroded. The situation in Europe underscores the importance of diversifying energy sources and building resilient infrastructure to protect against future shocks.
- 2006 Gas Crisis:In 2006, Russia cut off gas supplies to Ukraine due to a dispute over gas prices. This resulted in a shortage of gas in several European countries, highlighting the region’s dependence on Russian gas.
- 2009 Gas Crisis:In 2009, Russia again cut off gas supplies to Ukraine, this time due to a disagreement over transit fees. This event further emphasized the vulnerability of European energy security to Russian actions.
Impact on European Energy Security
The current reduction in gas flows has raised concerns about European energy security, particularly as the winter approaches. The potential impact on European energy security is significant, with the possibility of energy shortages, higher energy prices, and economic disruption.
Russia’s decision to crimp gas flows to Europe just as the continent races to stock up for winter is a recipe for disaster. The situation is further complicated by the news that the U.S. economy shrank again in the second quarter, reviving recession fears.
This global economic uncertainty only adds to the pressure on Europe to find alternative energy sources, a task that’s becoming increasingly difficult as the winter months approach.
- Energy Shortages:Reduced gas flows could lead to energy shortages, particularly during peak demand periods, such as the winter months. This could force European countries to rely on alternative energy sources, such as coal, which could have negative environmental consequences.
- Higher Energy Prices:Reduced gas flows could lead to higher energy prices, putting a strain on consumers and businesses. This could also lead to inflation and economic instability.
- Economic Disruption:Energy shortages and higher energy prices could have a significant impact on the European economy. Businesses could be forced to reduce production, and consumers could face higher living costs. This could lead to a recession or other economic disruptions.
The Global Energy Landscape

Russia’s actions have sent shockwaves through the global energy market, triggering a complex interplay of supply and demand dynamics. The reduction in Russian gas flows has exposed vulnerabilities in Europe’s energy security and forced a scramble for alternative energy sources.
This situation has broader implications for the global energy landscape, potentially reshaping energy markets, geopolitical alliances, and the trajectory of the energy transition.
Shifting Supply and Demand Dynamics, Russia crimps gas flows just as europe races to stock up for winter
The reduction in Russian gas exports has created a significant supply gap in Europe, forcing countries to explore alternative sources of energy. This has led to increased demand for liquefied natural gas (LNG) from other producers, such as the United States, Qatar, and Australia.
The surge in demand for LNG has driven up prices, creating a challenging environment for energy importers. The situation has also accelerated the shift towards renewable energy sources, as countries seek to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
Alternative Energy Sources
The crisis has highlighted the importance of diversifying energy sources and accelerating the transition to renewable energy. European countries are rapidly expanding their investments in renewable energy technologies, including solar, wind, and geothermal power. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in exploring other alternative energy sources, such as hydrogen and nuclear power.
The potential of these technologies to replace Russian gas remains uncertain, but they offer a pathway towards greater energy independence and sustainability.
Geopolitical Implications
The energy crisis has deepened geopolitical tensions and reshaped alliances. The United States has strengthened its energy partnerships with European countries, supplying additional LNG and working to reduce their dependence on Russian gas. Meanwhile, Russia has sought to strengthen its ties with energy-hungry countries in Asia, particularly China.
The crisis has also accelerated the global shift towards energy security, with countries seeking to secure their energy supplies through diversification and strategic partnerships.
End of Discussion: Russia Crimps Gas Flows Just As Europe Races To Stock Up For Winter
The energy crisis unfolding in Europe is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our world and the vulnerabilities that exist within our global energy systems. The implications of this crisis are far-reaching, impacting not just European economies but also global energy markets and geopolitical relations.
As Europe races to secure its energy future, the world watches with bated breath, hoping for a resolution that avoids the worst-case scenario of widespread energy shortages and economic turmoil.