Poverty Around the World: A Global Challenge
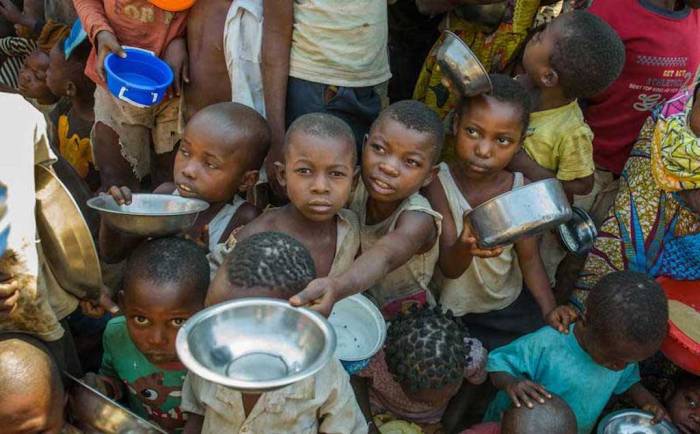
Poverty around the world is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects billions of people. It’s not just about a lack of money; it’s a lack of opportunity, a lack of access to basic necessities, and a lack of hope for a better future.
This pervasive problem manifests in various ways, from hunger and malnutrition to limited access to education and healthcare, ultimately hindering the progress of individuals, communities, and entire nations.
Understanding the root causes of poverty is crucial for finding effective solutions. Factors such as economic inequality, lack of access to education and healthcare, conflict and displacement, climate change, and discrimination all contribute to the perpetuation of poverty. These factors are often interconnected, creating a vicious cycle that can be difficult to break.
Global Poverty Statistics: Poverty Around The World
Poverty is a complex and multifaceted issue that affects millions of people around the world. Understanding the scope and nature of global poverty is crucial for developing effective strategies to alleviate it. This section delves into global poverty statistics, providing insights into the number of people living in poverty, the regions most affected, and the different poverty lines used by international organizations.
Global Poverty Rates
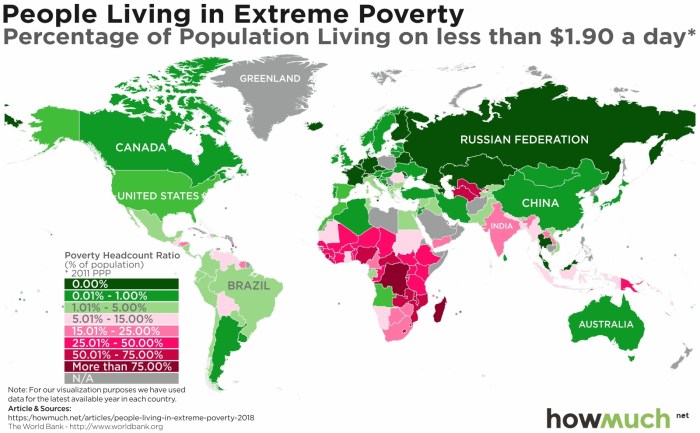
The World Bank defines extreme poverty as living on less than $1.90 per day. According to the World Bank, in 2015, 736 million people lived in extreme poverty, down from 1.9 billion in 1990. This represents a significant reduction in global poverty, but the number of people living in poverty is still unacceptably high.
- Sub-Saharan Africais the region with the highest poverty rate, with 413 million people living in extreme poverty in 2015.
- South Asiais the second most affected region, with 229 million people living in extreme poverty in 2015.
- East Asia and the Pacifichave also seen significant reductions in poverty, with 143 million people living in extreme poverty in 2015.
Poverty Lines, Poverty around the world
The World Bank uses two poverty lines: the international poverty line ($1.90 per day) and the upper-middle-income poverty line ($3.20 per day). These lines are based on the cost of a basic basket of goods and services necessary for survival.
- The international poverty lineis used to measure extreme poverty, while the upper-middle-income poverty lineis used to measure moderate poverty.
- The poverty lines are adjusted for inflation and purchasing power parity (PPP), which takes into account the cost of living in different countries.
Impact of Poverty
Poverty has a devastating impact on various aspects of human life, including:
- Health: Poverty is linked to poor health outcomes, such as malnutrition, infectious diseases, and higher rates of infant and maternal mortality.
- Education: Poverty can limit access to education, leading to lower literacy rates and reduced opportunities for economic advancement.
- Economic Opportunity: Poverty can create a cycle of deprivation, as people living in poverty often lack the resources and opportunities to escape it.
Future Directions
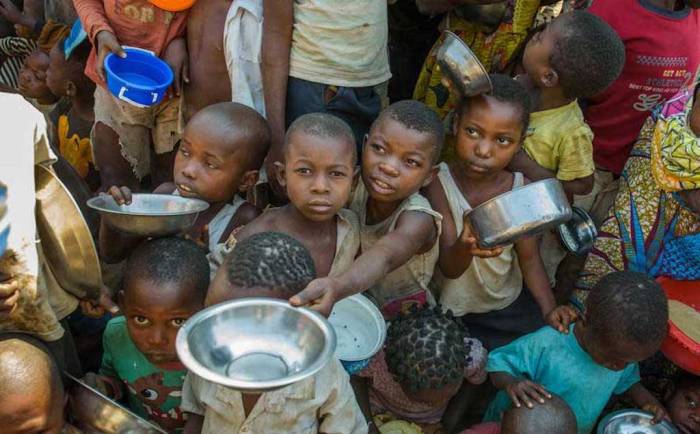

The fight against poverty is a complex and multifaceted challenge, requiring a dynamic approach to address emerging trends and leverage new opportunities. While significant progress has been made in reducing poverty globally, persistent challenges remain, necessitating innovative strategies and collaborative efforts.
Technological Advancements and their Impact on Poverty
Technological advancements have the potential to be a powerful tool in the fight against poverty. The increasing availability and affordability of technology, particularly mobile devices and internet access, can empower individuals and communities.
- Improved Access to Information and Services:Mobile phones and internet access can provide access to essential information, such as market prices, weather forecasts, and healthcare services. This can help farmers improve their yields, individuals make informed decisions about their health, and communities better prepare for natural disasters.
- Financial Inclusion:Mobile banking and digital payment platforms can extend financial services to underserved populations, facilitating savings, micro-loans, and remittances. This can promote economic participation and provide a safety net for vulnerable households.
- Education and Skills Development:Online learning platforms can offer educational opportunities and skills development programs, enabling individuals to acquire new knowledge and improve their employability. This can be particularly impactful in areas with limited access to traditional educational institutions.
However, it is crucial to ensure that technological advancements are accessible and equitable. Digital divides, lack of infrastructure, and digital literacy challenges can hinder the positive impact of technology on poverty reduction. Strategies to bridge these gaps are essential, such as providing affordable internet access, promoting digital literacy programs, and adapting technology to local contexts.
The Role of Climate Change in Exacerbating Poverty
Climate change is a significant threat to poverty reduction efforts, disproportionately impacting vulnerable communities. The effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events, droughts, and sea-level rise, can exacerbate poverty by:
- Disrupting Livelihoods:Climate-related disasters can destroy crops, livestock, and infrastructure, leaving communities without income and resources.
- Increasing Food Insecurity:Changing weather patterns can affect agricultural yields, leading to food shortages and price spikes, particularly in regions heavily reliant on agriculture.
- Displacement and Migration:Rising sea levels and extreme weather events can force people to relocate, disrupting communities and creating challenges for social services and integration.
Addressing climate change is crucial for poverty reduction. This requires a multifaceted approach, including investments in climate-resilient infrastructure, sustainable agriculture practices, and adaptation measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
The Need for Innovative Solutions and Partnerships
Innovative solutions and collaborative partnerships are essential to address the complex challenges of poverty in the 21st century. This requires a shift towards:
- Investing in Human Capital:Investing in education, healthcare, and social protection programs is crucial for empowering individuals and promoting sustainable development. This can include targeted programs for vulnerable groups, such as children, women, and persons with disabilities.
- Promoting Inclusive Economic Growth:Policies and programs that promote inclusive economic growth, such as supporting small and medium enterprises, creating decent work opportunities, and fostering entrepreneurship, can help lift people out of poverty.
- Strengthening Governance and Institutions:Good governance, transparent institutions, and rule of law are essential for effective poverty reduction strategies. This includes ensuring accountability, participation, and equitable access to resources.
- Building Sustainable and Resilient Communities:Investing in sustainable infrastructure, promoting climate-smart agriculture, and strengthening disaster preparedness and response mechanisms can build resilience and reduce vulnerability to shocks and stresses.
“No one is born a criminal. No one is born a terrorist. No one is born a refugee. No one is born poor. We are made that way.”
Malala Yousafzai
Partnerships between governments, civil society organizations, the private sector, and international organizations are essential for mobilizing resources, sharing knowledge, and implementing effective solutions. This requires a collaborative approach that leverages the strengths of each stakeholder and ensures that the voices of the poor are heard and their needs are met.