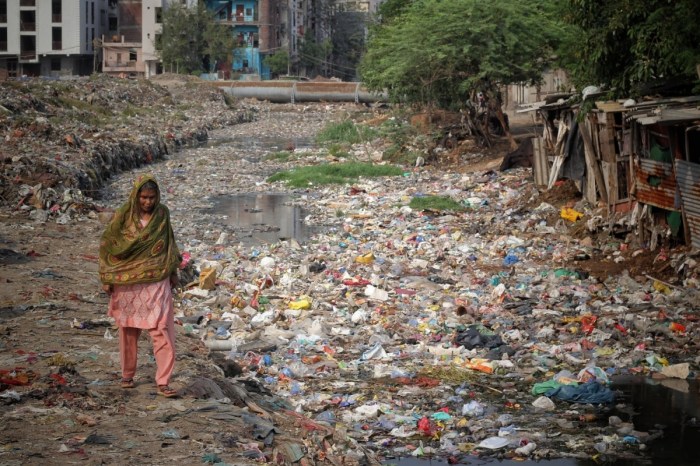
Poverty and the Environment: A Complex Intertwined Story
Poverty and the environment are inextricably linked, forming a complex and often vicious cycle. When poverty forces people to rely on unsustainable practices for survival, the environment suffers. In turn, environmental degradation exacerbates poverty by limiting access to vital resources like clean water, fertile land, and clean energy.
This interconnectedness is a global issue with far-reaching consequences. From deforestation and soil erosion in developing countries to the impact of climate change on vulnerable communities, the effects of this intertwined relationship are felt around the world. Understanding this complex relationship is crucial to finding solutions that address both poverty and environmental challenges.
Poverty and Environmental Degradation
Poverty and environmental degradation are intricately linked, forming a vicious cycle where one exacerbates the other. This complex relationship is characterized by a feedback loop, where poverty often drives unsustainable practices that harm the environment, which in turn further impoverishes communities.
Poverty’s Impact on the Environment
Poverty often compels individuals to prioritize immediate survival needs over long-term environmental sustainability. This can lead to unsustainable practices that degrade the environment, including:
- Deforestation:Poverty can force people to rely on wood for fuel and construction materials, leading to deforestation and habitat loss.
- Overgrazing:Limited access to land and resources can result in overgrazing, which depletes soil fertility and leads to desertification.
- Unsustainable Agriculture:The need to produce food for sustenance can drive unsustainable agricultural practices, such as monoculture, excessive pesticide use, and soil degradation.
- Pollution:Lack of access to sanitation facilities and proper waste management systems can contribute to pollution of water sources and air quality.
Environmental Degradation’s Impact on Poverty
Environmental degradation can significantly worsen poverty by:
- Loss of Livelihoods:Degradation of natural resources, such as forests, fisheries, and fertile land, can lead to the loss of livelihoods for communities that depend on these resources.
- Increased Vulnerability to Disasters:Environmental degradation, such as deforestation and soil erosion, can increase vulnerability to natural disasters, like floods and droughts, further exacerbating poverty.
- Health Impacts:Pollution and lack of access to clean water and sanitation can lead to health problems, which can trap individuals and families in poverty.
Poverty and Access to Resources
Poverty can significantly limit access to essential resources, including:
- Clean Water:Limited access to clean water can lead to waterborne diseases, impacting health and productivity.
- Sanitation:Lack of access to sanitation facilities can spread diseases and create unhygienic living conditions, further perpetuating poverty.
- Energy Resources:Limited access to affordable and reliable energy sources can hinder economic development and limit opportunities for income generation.
Environmental Impacts of Poverty
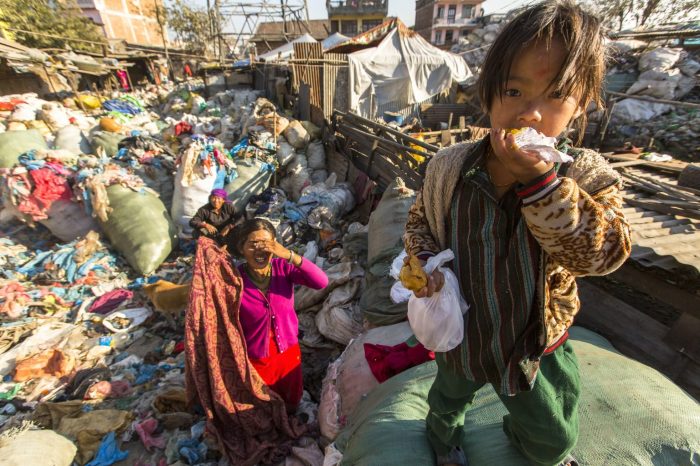

Poverty and environmental degradation are deeply intertwined, forming a vicious cycle that perpetuates hardship for millions around the world. Poverty often compels individuals to exploit natural resources for immediate survival, leading to environmental damage that further hinders their well-being.
Deforestation, Soil Erosion, and Water Pollution
The pressures of poverty often force communities to rely on unsustainable practices that degrade the environment. Deforestation, for instance, is rampant in many impoverished regions as people clear land for agriculture, fuelwood, and construction materials. This not only diminishes biodiversity and disrupts ecosystems but also exacerbates soil erosion, leading to reduced agricultural productivity and further economic hardship.
Similarly, the lack of access to safe sanitation and clean water in poverty-stricken areas contributes to water pollution, contaminating sources and posing health risks to communities.
Health Risks Associated with Environmental Degradation
Environmental degradation in impoverished areas has a direct impact on the health of vulnerable populations. Exposure to polluted air and water can lead to respiratory illnesses, diarrheal diseases, and other health problems. The lack of access to proper sanitation facilities further amplifies these risks, creating a cycle of poverty and ill-health.
For example, the World Health Organization estimates that over 80% of diseases in developing countries are linked to contaminated water and inadequate sanitation.
Climate Change and Environmental Vulnerabilities
Climate change exacerbates the environmental challenges faced by impoverished communities. Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and changes in precipitation patterns threaten livelihoods, displace populations, and undermine efforts to alleviate poverty. For instance, in coastal areas, rising sea levels can lead to salinization of freshwater sources, rendering land unsuitable for agriculture and displacing communities.
In regions prone to drought, climate change can exacerbate water scarcity, leading to food insecurity and conflict over resources.
Poverty and Sustainable Development
Poverty and environmental degradation are inextricably linked. Poverty often forces people to exploit natural resources for survival, leading to deforestation, soil erosion, and pollution. This, in turn, exacerbates poverty by reducing access to clean water, fertile land, and other essential resources.
It’s a harsh reality that poverty often leads to environmental degradation, as people struggle to meet basic needs. But there’s a glimmer of hope in the form of some regional free trade agreements , which can promote sustainable development by fostering economic growth and creating opportunities for environmental protection.
These agreements can help alleviate poverty, allowing communities to invest in cleaner technologies and practices, ultimately leading to a healthier planet for all.
Sustainable development offers a way to break this cycle by promoting economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection simultaneously.
Importance of Sustainable Development in Addressing Poverty and Environmental Issues
Sustainable development is crucial for addressing poverty and environmental issues because it recognizes the interconnectedness of these challenges. By focusing on long-term solutions that meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, sustainable development aims to achieve a balance between economic growth, social progress, and environmental protection.
Integrating Poverty Reduction Strategies with Environmental Conservation Efforts
Poverty reduction strategies and environmental conservation efforts must be integrated to achieve sustainable development. This means incorporating environmental considerations into poverty reduction programs and vice versa. For example, poverty reduction programs should prioritize investments in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green infrastructure.
Similarly, environmental conservation efforts should consider the social and economic impacts on vulnerable communities.
Successful Initiatives that Have Addressed Poverty and Environmental Concerns Simultaneously
Several successful initiatives have demonstrated the effectiveness of integrating poverty reduction and environmental conservation. For example, the “Payment for Ecosystem Services” (PES) program in Costa Rica has been successful in reducing deforestation and improving water quality by providing financial incentives to landowners who conserve their forests.
The link between poverty and environmental degradation is a complex one, often fueled by unsustainable practices driven by economic necessity. Understanding this dynamic requires a deeper look at the dominant economic ideology of our times, a primer on neoliberalism , which prioritizes free markets and deregulation.
This approach can exacerbate inequalities, leading to resource depletion and pollution in communities struggling to survive, further perpetuating the cycle of poverty and environmental damage.
Similarly, the “Green Belt Movement” in Kenya has empowered women to plant trees, combat desertification, and improve their livelihoods.
Best Practices for Promoting Sustainable Livelihoods in Impoverished Communities
Promoting sustainable livelihoods in impoverished communities requires a multifaceted approach. Some best practices include:
- Investing in education and skills development:Equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to pursue sustainable livelihoods.
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices:Encouraging the adoption of techniques that improve soil fertility, conserve water, and reduce reliance on chemical inputs.
- Developing renewable energy sources:Expanding access to clean and affordable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Promoting ecotourism:Supporting tourism initiatives that benefit local communities while conserving natural resources.
- Empowering women and marginalized groups:Providing women and marginalized groups with equal access to resources, education, and opportunities.
Policy and Governance
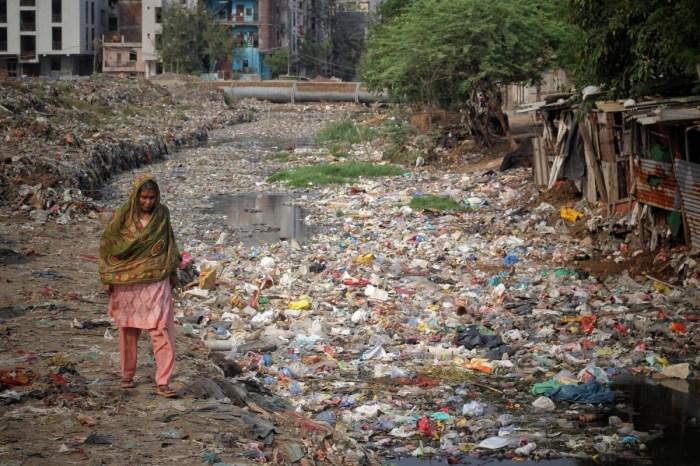

Addressing the intertwined challenges of poverty and environmental degradation requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses effective policy interventions and robust governance structures. This section delves into the crucial role of policy and governance in fostering sustainable development, examining key policy interventions, analyzing the effectiveness of existing policies, and exploring the responsibilities of governments and international organizations in this endeavor.
Key Policy Interventions
Effective policy interventions are essential for addressing poverty and environmental issues. These interventions should aim to promote sustainable development by integrating economic growth, social equity, and environmental protection.
- Investing in Renewable Energy:Shifting towards renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and create new economic opportunities. For instance, India’s ambitious solar energy program has significantly increased renewable energy capacity and created employment opportunities in the sector.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture:Sustainable agricultural practices, such as agroforestry, organic farming, and water conservation techniques, can enhance food security, protect biodiversity, and reduce environmental degradation. The Brazilian government’s “Soy Moratorium” policy, which prohibits soy production in deforested areas of the Amazon rainforest, has been effective in reducing deforestation rates.
- Strengthening Environmental Regulations:Enacting and enforcing robust environmental regulations, including air and water quality standards, waste management policies, and biodiversity conservation measures, is crucial for protecting natural resources and human health. China’s stringent air pollution control measures have significantly reduced air pollution levels in major cities, demonstrating the effectiveness of strong regulations.
- Investing in Education and Skills Development:Equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to participate in sustainable development is essential. Programs that promote environmental awareness, sustainable livelihoods, and green technologies can empower communities to make informed choices and contribute to environmental protection. The Costa Rican government’s investment in education and training programs has led to a highly skilled workforce in the renewable energy sector, contributing to the country’s environmental sustainability.
- Promoting Sustainable Consumption and Production Patterns:Encouraging sustainable consumption and production patterns, such as reducing waste, recycling, and promoting eco-friendly products, can minimize environmental impacts and foster a more sustainable economy. The European Union’s “Circular Economy Package” aims to reduce waste, promote resource efficiency, and stimulate innovation in the circular economy.
Role of Governments and International Organizations
Governments and international organizations play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable development. They can facilitate the implementation of policies, provide financial assistance, and coordinate international efforts.
- Government Responsibilities:Governments are responsible for setting national policies, implementing regulations, and allocating resources to address poverty and environmental issues. They should promote sustainable development through fiscal policies, investments in infrastructure, and social programs. For example, the government of Bhutan has prioritized environmental protection and sustainable development, incorporating Gross National Happiness as a measure of national progress.
- International Organizations’ Role:International organizations, such as the United Nations, World Bank, and International Monetary Fund, can provide technical assistance, financial support, and capacity building to developing countries. They can also facilitate international cooperation and promote the sharing of best practices. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for achieving sustainable development by 2030, emphasizing the interconnectedness of poverty reduction and environmental protection.
Poverty often forces people to make choices that harm the environment, like using unsustainable resources for survival. This is especially true in regions struggling with health crises, like the HIV/AIDS pandemic. The cost of life-saving medications, often controlled by large pharmaceutical corporations, pharmaceutical corporations and aids , can be prohibitive for many, leading to further economic hardship and environmental degradation.
Ultimately, addressing poverty and environmental issues requires a multi-pronged approach that includes affordable access to healthcare and sustainable development.
Effectiveness of Existing Policies and Programs
The effectiveness of existing policies and programs in addressing poverty and environmental degradation varies widely. Some policies have been successful in achieving specific goals, while others have faced challenges in implementation or have had unintended consequences.
- Success Stories:The “Conditional Cash Transfer” (CCT) programs in Latin America, such as Bolsa Familia in Brazil, have been effective in reducing poverty and improving child health and education. These programs provide cash transfers to low-income families conditional on meeting certain requirements, such as school attendance and health checkups.
The CCT programs have also contributed to environmental sustainability by promoting access to healthcare and education, which are essential for long-term environmental protection.
- Challenges and Limitations:Some policies have faced challenges in implementation or have had unintended consequences. For example, policies aimed at promoting economic growth have sometimes led to environmental degradation, particularly in developing countries where environmental regulations are weak. Additionally, policies that rely on market-based mechanisms, such as carbon pricing, can disproportionately impact low-income households.
Policy Recommendations
| Policy Area | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Poverty Reduction |
|
| Environmental Protection |
|
| Governance and Institutional Capacity |
|
Community-Based Solutions: Poverty And The Environment
Empowering communities to take ownership of their development is crucial for addressing poverty and environmental degradation. This approach recognizes the intimate connection between local knowledge, resources, and sustainable solutions. By involving communities in decision-making processes, we can ensure that solutions are tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Community Participation in Environmental Management
Community participation is not merely about involving people in projects; it’s about creating a shared vision for sustainable development. This involves actively engaging communities in planning, implementing, and monitoring environmental initiatives. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, ensuring that solutions are relevant, effective, and sustainable.
“Community participation is not just about involving people, it’s about empowering them to be active agents of change.”
Examples of community-led initiatives highlight the power of this approach. In the Philippines, the “Bantay Dagat” (Sea Watch) program empowers coastal communities to protect their marine resources through community-based monitoring and enforcement. This program has led to significant reductions in illegal fishing and improved marine biodiversity.
Strategies for Empowering Communities
Empowering communities to manage their natural resources sustainably requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes:
- Capacity Building:Providing communities with the skills, knowledge, and resources to manage their resources effectively. This can include training on sustainable agriculture practices, resource management techniques, and conflict resolution.
- Access to Information:Ensuring communities have access to relevant information about environmental issues, best practices, and available resources. This can be achieved through workshops, community forums, and the dissemination of educational materials.
- Financial Inclusion:Supporting community-based organizations with access to funding for sustainable projects. This can involve microfinance initiatives, grants, and partnerships with non-governmental organizations.
- Policy Advocacy:Advocating for policies that support community-based resource management and empower local decision-making. This includes working with governments and other stakeholders to ensure that policies reflect the needs and priorities of communities.
Community-Based Program Design
A successful community-based program addressing both poverty and environmental concerns requires a holistic approach. Here’s a potential program design:
- Needs Assessment:Begin by conducting a thorough needs assessment to identify the specific challenges faced by the community, including poverty, environmental degradation, and resource scarcity. This will inform the program’s objectives and activities.
- Community Participation:Establish a community-based committee or council to lead the program. This committee should represent diverse interests within the community and actively engage in decision-making processes.
- Sustainable Livelihoods:Develop and implement projects that promote sustainable livelihoods, such as agroforestry, ecotourism, and sustainable fishing practices. These projects should aim to improve income generation while minimizing environmental impacts.
- Environmental Conservation:Integrate environmental conservation activities into the program, such as reforestation, watershed management, and biodiversity conservation. These activities should be designed to address specific environmental challenges identified in the needs assessment.
- Capacity Building and Training:Provide training and capacity building opportunities for community members in areas related to sustainable livelihoods, environmental management, and community organizing. This will empower communities to manage the program effectively.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:Establish a system for monitoring and evaluating the program’s progress and impact. This will ensure that the program is achieving its objectives and making a positive difference in the lives of community members.
The Role of Technology
The potential of technology to address poverty and environmental challenges is immense. Technological innovations can offer sustainable solutions to poverty and environmental degradation by enabling access to clean energy, improving agricultural practices, and promoting efficient water management. However, ethical considerations are crucial when implementing these technologies to ensure equitable access and minimize unintended consequences.
Renewable Energy Technologies, Poverty and the environment
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power have the potential to provide clean and sustainable energy to impoverished communities.
- Solar Power: Solar panels can generate electricity from sunlight, providing a reliable source of energy for homes, businesses, and communities. Solar home systems are increasingly popular in rural areas where access to the grid is limited.
- Wind Power: Wind turbines can harness the power of wind to generate electricity. Wind power is particularly suitable for areas with consistent wind speeds, such as coastal regions and open plains.
- Hydro Power: Hydroelectric dams can generate electricity from the flow of water. This technology is well-suited for areas with rivers and streams, but it can also have significant environmental impacts, such as altering river ecosystems and displacing communities.
These technologies can contribute to sustainable development by reducing reliance on fossil fuels, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving energy security.
Agricultural Technologies
Agricultural technologies can enhance food security and reduce poverty by increasing crop yields, improving water efficiency, and promoting sustainable farming practices.
- Precision Agriculture: Precision agriculture involves using technology to optimize crop management practices, such as fertilization, irrigation, and pest control. Sensors, drones, and data analytics can help farmers make informed decisions about resource allocation, reducing waste and increasing yields.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Climate-smart agriculture focuses on adapting to climate change and mitigating its impacts. This includes adopting drought-resistant crops, improving soil health, and implementing water-efficient irrigation systems.
- Vertical Farming: Vertical farming involves growing crops in stacked layers, maximizing space and minimizing land use. This technology can be particularly beneficial in urban areas with limited land availability.
By improving agricultural productivity and sustainability, these technologies can contribute to food security and reduce poverty in vulnerable communities.
Water Management Technologies
Access to safe and clean water is essential for human health and well-being. Technological innovations can improve water management by providing efficient irrigation systems, treating wastewater, and ensuring access to clean drinking water.
- Water Harvesting: Water harvesting technologies collect and store rainwater for use in irrigation and other purposes. This can be particularly beneficial in arid and semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a major challenge.
- Wastewater Treatment: Wastewater treatment technologies can purify wastewater for reuse in irrigation or for safe discharge into the environment. This reduces pollution and conserves water resources.
- Water Filtration: Water filtration technologies remove impurities from water, providing safe drinking water to communities without access to clean water sources.
By improving water management practices, these technologies can contribute to sustainable development and reduce poverty by improving health outcomes, increasing agricultural productivity, and promoting economic growth.
Ethical Considerations
The use of technology to address poverty and environmental challenges must be guided by ethical considerations.
- Equity and Access: It is crucial to ensure that technological solutions are accessible to all, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
- Environmental Sustainability: Technological solutions should be environmentally sustainable and minimize negative impacts on ecosystems.
- Community Participation: Communities should be involved in the design and implementation of technological solutions to ensure that they meet their needs and priorities.
Ethical considerations are essential for ensuring that technological interventions benefit all and contribute to a just and sustainable future.