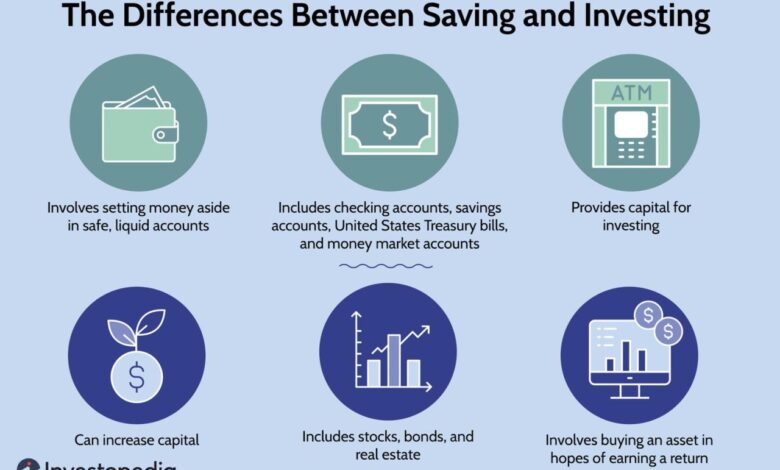
Climate Education: A Must-Have for Businesses
Nice to have or must have a climate education venture puts the case for corporate buy in – Is climate education a nice-to-have or a must-have for businesses? This question takes center stage as we explore the growing need for corporate buy-in on climate education. In a world grappling with the realities of climate change, businesses are no longer immune to its impacts.
From supply chain disruptions to shifting consumer preferences, the effects of climate change are rippling through every industry. This blog post will delve into the compelling reasons why climate education is not just a nice-to-have but a critical investment for businesses looking to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Imagine a world where every employee understands the science behind climate change, its impact on their work, and the role they can play in mitigating its effects. This is the vision of climate education in the corporate world. It’s about empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions, both in their professional and personal lives.
By fostering a culture of climate awareness and action, businesses can reap significant benefits, from enhanced brand reputation and employee engagement to reduced operational costs and a more sustainable future.
The Urgent Need for Climate Education: Nice To Have Or Must Have A Climate Education Venture Puts The Case For Corporate Buy In
The Earth’s climate is changing at an unprecedented rate, driven by human activities that release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This change is already having a significant impact on businesses, disrupting supply chains, increasing operational costs, and posing risks to their long-term viability.
Climate education is crucial for equipping individuals, businesses, and society as a whole with the knowledge and skills needed to understand and address this global challenge.
The Impact of Climate Change on Businesses
Climate change is a multifaceted issue with far-reaching consequences for businesses across all sectors. The following are some of the key ways in which climate change is impacting businesses:
- Increased Costs:Extreme weather events such as floods, droughts, and heat waves can damage infrastructure, disrupt operations, and lead to increased insurance premiums. For example, the 2017 hurricane season in the United States caused billions of dollars in damages to businesses, highlighting the financial risks associated with climate change.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:Climate change can disrupt supply chains by affecting raw material availability, transportation routes, and production processes. For example, droughts in agricultural regions can lead to shortages of key commodities, while extreme weather events can damage infrastructure and disrupt transportation networks.
- Regulatory Changes:Governments around the world are enacting regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the effects of climate change. These regulations can impose costs on businesses, requiring them to adopt new technologies, change their practices, and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Reputational Risks:Consumers are increasingly demanding that businesses take action on climate change. Companies that fail to address climate risks can face reputational damage, loss of customers, and difficulty attracting investors.
The Role of Education in Fostering Climate Awareness and Action
Climate education is essential for raising awareness about climate change, its impacts, and the solutions available. It can empower individuals, businesses, and communities to take action and contribute to a more sustainable future.
When it comes to climate education ventures, the question isn’t just about the impact, but about the long-term sustainability. That’s where the “must-have” argument comes in, and it’s backed by the very mindset traits that drive successful entrepreneurs, like the ability to see opportunity where others see challenges.
Check out this insightful article on 11 mindset traits of successful entrepreneurs for a glimpse into the thinking that can turn a “nice-to-have” into a must-have for corporate buy-in. It’s about understanding the bigger picture, embracing innovation, and building a future that’s not just sustainable, but thriving.
- Understanding the Science:Climate education provides individuals with a deeper understanding of the science behind climate change, enabling them to make informed decisions and advocate for effective policies.
- Developing Solutions:Education can foster innovation and entrepreneurship by equipping individuals with the knowledge and skills to develop sustainable solutions to climate change. This includes developing new technologies, implementing energy-efficient practices, and promoting renewable energy sources.
- Promoting Behavioral Change:Climate education can influence individual behaviors, encouraging people to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives, such as reducing energy consumption, conserving water, and choosing eco-friendly products.
- Building Climate Literacy:Climate education is essential for building a climate-literate society, where individuals are equipped to understand and engage with climate change issues. This is crucial for informed decision-making at all levels, from individual households to government policies.
The Business Case for Climate Education
Climate education is no longer a “nice to have” for businesses; it’s a “must have”. The world is facing a climate crisis, and businesses are at the forefront of finding solutions. Investing in climate education is not just about fulfilling a social responsibility, it’s about securing a business’s long-term success and sustainability.
Benefits of Climate Education for Businesses
Climate education equips businesses with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of climate change and its implications. It empowers them to make informed decisions, develop innovative solutions, and build resilience. The benefits of climate education extend beyond environmental sustainability, contributing to a more robust and competitive business environment.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation:Businesses that demonstrate a commitment to climate action through education and initiatives gain a competitive edge. Consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that align with their values, leading to enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty. For example, Patagonia, a company known for its environmental advocacy, has consistently ranked among the most trusted brands in the outdoor apparel market.
It’s easy to see why a climate education venture might seem like a “nice to have” for corporations, but the reality is that it’s a “must have.” The urgency of the climate crisis demands action, and the recent tragedy of a Columbia graduate student brutally beaten in Manhattan, as reported in this article , underscores the need for a safer, more sustainable future.
Investing in climate education empowers employees to make informed choices, fostering a culture of responsibility and contributing to a more resilient society.
- Improved Employee Engagement:Climate education empowers employees to become active participants in sustainability efforts. By understanding the challenges and opportunities of climate change, employees feel more engaged, motivated, and committed to their work. This can lead to increased productivity, innovation, and retention.
- Reduced Operational Costs:Climate education can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By adopting sustainable practices, businesses can reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and optimize resource usage. For example, implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting and smart thermostats, can result in substantial reductions in energy bills.
- Increased Innovation and Competitiveness:Climate education fosters a culture of innovation and creativity within businesses. By embracing sustainability as a core value, companies can develop new products, services, and business models that address the needs of a changing world. For example, companies in the renewable energy sector are constantly innovating to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar and wind power.
- Improved Risk Management:Climate change poses significant risks to businesses, such as supply chain disruptions, extreme weather events, and regulatory changes. Climate education helps businesses identify, assess, and manage these risks, enhancing their resilience and adaptability. For example, companies in the agricultural sector can use climate data to optimize crop yields and adapt to changing weather patterns.
Risks of Ignoring Climate Education
Ignoring climate education can lead to significant risks for businesses, impacting their long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
| Risks of Ignoring Climate Education | Benefits of Investing in Climate Education |
|---|---|
| Increased operational costs due to inefficient resource usage and reliance on fossil fuels. | Reduced operational costs through energy efficiency, waste reduction, and resource optimization. |
| Negative brand reputation and loss of customer loyalty due to lack of environmental responsibility. | Enhanced brand reputation and increased customer loyalty through commitment to climate action. |
| Decreased employee engagement and retention due to lack of purpose and meaning in work. | Improved employee engagement and retention through opportunities for meaningful contributions to sustainability efforts. |
| Increased vulnerability to climate-related risks, such as extreme weather events and regulatory changes. | Enhanced resilience and adaptability to climate-related risks through informed decision-making and innovative solutions. |
| Loss of competitive advantage in a rapidly changing market where sustainability is increasingly valued. | Increased innovation and competitiveness through development of sustainable products, services, and business models. |
Implementing Climate Education in Corporate Settings

Integrating climate education into corporate culture is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for businesses to adapt and thrive in a changing world. It fosters a more informed and engaged workforce, strengthens brand reputation, and aligns with responsible business practices.
Tailoring Climate Education Programs to Specific Business Needs and Industry Sectors, Nice to have or must have a climate education venture puts the case for corporate buy in
Tailoring climate education programs to specific business needs and industry sectors ensures that the information is relevant, practical, and impactful.
We can’t afford to treat climate education as a “nice to have” anymore. It’s a must-have for a sustainable future, and that’s why corporate buy-in is crucial. The recent news that the Senate passed a $280 billion industrial policy bill to counter China highlights the need for a robust domestic manufacturing sector, one that prioritizes climate-friendly technologies.
This bill, with its focus on clean energy and advanced manufacturing, is a step in the right direction. But it’s only the first step. We need to ensure that future generations are equipped with the knowledge and skills to build a sustainable future, and that’s where climate education comes in.
- Industry-Specific Climate Impacts:Understanding the unique climate risks and opportunities faced by a specific industry is crucial. For example, a manufacturing company might focus on energy efficiency and supply chain resilience, while a financial institution could prioritize climate risk assessment and sustainable investment strategies.
- Business Operations and Processes:Integrating climate education into existing training programs, such as onboarding for new employees or professional development initiatives, can make it more accessible and impactful. For instance, a retail company could incorporate climate-friendly practices into its customer service training, while a technology firm could highlight the role of its products in climate solutions.
- Leadership and Management:Equipping leaders and managers with the knowledge and skills to champion climate action within their teams is essential. This can involve training on climate change science, policy, and business strategy, as well as practical tools for implementing sustainability initiatives.
Resources and Tools for Effective Climate Education
Numerous resources and tools are available to support effective climate education within corporate settings.
- Online Platforms and Courses:Platforms like Coursera, edX, and FutureLearn offer a wide range of courses on climate change, sustainability, and related topics. These platforms provide flexible learning options and cater to diverse learning styles.
- Expert Guest Speakers:Inviting climate experts, scientists, or sustainability practitioners to deliver presentations or workshops can provide valuable insights and real-world perspectives. This can also foster a sense of engagement and inspire employees to take action.
- Case Studies and Best Practices:Sharing case studies of companies that have successfully implemented climate-friendly practices can inspire and motivate employees. This approach can demonstrate the tangible benefits of climate action and showcase innovative solutions.
- Interactive Simulations and Games:Gamified learning experiences can enhance engagement and make climate education more interactive and enjoyable. These tools can simulate real-world scenarios and help employees understand the complexities of climate change and potential solutions.
Measuring the Impact of Climate Education
Demonstrating the effectiveness of climate education initiatives is crucial to securing ongoing support and maximizing their impact. This involves identifying key metrics, tracking progress, and demonstrating the tangible benefits of climate education on employee behavior, corporate sustainability, and ultimately, business performance.
Identifying Key Metrics for Evaluating Effectiveness
Measuring the impact of climate education requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond simply assessing knowledge gained. A combination of metrics can provide a holistic understanding of the program’s effectiveness.
- Knowledge and Awareness:Pre- and post-program assessments can gauge the increase in employee understanding of climate change, its impacts, and potential solutions. This can be measured through surveys, quizzes, or even knowledge-based games.
- Attitudes and Beliefs:Measuring changes in employee attitudes and beliefs towards climate change and sustainability is critical. This can be done through surveys that assess their level of concern, willingness to act, and perceived responsibility.
- Behavioral Change:The ultimate goal of climate education is to drive positive behavioral change. This can be measured through tracking changes in employee behaviors related to energy consumption, waste reduction, transportation choices, and sustainable purchasing.
- Corporate Sustainability Performance:Tracking improvements in key sustainability metrics such as energy use, greenhouse gas emissions, waste reduction, and water consumption can demonstrate the impact of climate education on corporate sustainability performance.
- Business Performance:Climate education can positively impact business performance through cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved brand reputation. Tracking these factors can showcase the economic benefits of investing in climate education.
Tracking and Measuring Impact
Tracking the impact of climate education involves collecting data on the chosen metrics over time. This data can be gathered through various methods:
- Surveys:Regular surveys can be conducted to assess employee knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors before, during, and after the program.
- Focus Groups:Focus groups can provide qualitative insights into employee perceptions, motivations, and challenges related to climate action.
- Data Tracking:Monitoring key sustainability metrics such as energy consumption, waste generation, and water usage can provide quantifiable evidence of the impact of climate education on corporate performance.
- Case Studies:Highlighting specific examples of how climate education has influenced employee behavior and improved business practices can provide compelling evidence of the program’s effectiveness.
Stages of Measuring Impact
Measuring the impact of climate education involves a multi-stage process, starting with initial assessments and culminating in long-term evaluation.
| Stage | Activities | Metrics |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline Assessment | Conduct pre-program surveys and data collection to establish a baseline understanding of employee knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, and corporate sustainability performance. | Knowledge and awareness, attitudes and beliefs, behavioral metrics, key sustainability metrics. |
| Program Implementation | Implement the climate education program and collect data on participation, program delivery, and employee engagement. | Participation rates, program feedback, engagement levels. |
| Mid-Program Evaluation | Conduct mid-program surveys and data analysis to assess the effectiveness of the program and identify areas for improvement. | Changes in knowledge and awareness, attitudes and beliefs, behavioral changes, progress on sustainability goals. |
| Post-Program Evaluation | Conduct post-program surveys and data analysis to evaluate the overall impact of the program on employee knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, corporate sustainability, and business performance. | Knowledge and awareness, attitudes and beliefs, behavioral changes, changes in sustainability performance, cost savings, efficiency improvements, brand reputation. |
| Long-Term Monitoring | Continue tracking key metrics over time to assess the long-term impact of climate education on employee behavior, corporate sustainability, and business performance. | Sustainability performance, cost savings, efficiency improvements, brand reputation, employee engagement. |
The Future of Climate Education in the Corporate World
The future of climate education in the corporate world holds immense potential for positive change. By integrating climate literacy into the core of business operations, companies can not only contribute to a sustainable future but also gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Climate Education
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing climate education initiatives. By leveraging the power of digital platforms, companies can reach a wider audience, personalize learning experiences, and provide access to real-time data and resources.
- Interactive learning platforms:Platforms like Coursera, edX, and FutureLearn offer a wide range of climate-related courses and certifications, providing employees with accessible and flexible learning opportunities. These platforms often utilize gamification techniques to enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR):VR and AR technologies can create immersive and engaging learning experiences that bring climate change concepts to life. For instance, companies can use VR to simulate the impacts of climate change on their operations or create interactive simulations that demonstrate the effectiveness of different sustainability solutions.
- Data analytics and visualization tools:Data analytics and visualization tools can help companies track their environmental impact, identify areas for improvement, and communicate sustainability data effectively. By presenting data in a clear and concise manner, these tools can empower employees to make informed decisions and contribute to their company’s sustainability goals.
Examples of Innovative Climate Education Programs
Forward-thinking companies are already implementing innovative climate education programs that demonstrate the value of integrating climate literacy into the workplace.
- Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan:Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan is a comprehensive program that aims to reduce the company’s environmental footprint and promote sustainable consumption. The plan includes a range of initiatives, including employee training programs on climate change, sustainable sourcing, and responsible consumption.
- Google’s Climate Action Fund:Google’s Climate Action Fund invests in innovative technologies and projects that address climate change. The company also offers a variety of resources and training programs for employees, including workshops on climate change science and policy.
- Apple’s Environmental Responsibility Report:Apple publishes an annual Environmental Responsibility Report that Artikels the company’s progress on its sustainability goals. The report also includes information on Apple’s climate education initiatives, such as employee training programs on energy efficiency and renewable energy.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the case for corporate buy-in on climate education is clear. It’s not just about doing good; it’s about doing well. By investing in climate education, businesses can unlock a range of benefits that enhance their bottom line and contribute to a more sustainable future.
From building a more engaged and resilient workforce to attracting and retaining top talent, the advantages are undeniable. The time to act is now. Let’s empower businesses to become leaders in climate action by embracing the transformative power of climate education.






