More Information on the Middle East: A Deep Dive
More information on the Middle East sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The Middle East, a region steeped in history and culture, has long captivated the world’s attention.
From ancient civilizations to modern conflicts, the Middle East has witnessed a tumultuous journey, shaping the course of human history. This exploration delves into the intricate tapestry of this region, uncovering its geographic wonders, diverse cultures, political landscapes, and economic realities.
We’ll examine the challenges and opportunities that define the Middle East today, exploring its complex social issues, ongoing conflicts, and potential for a brighter future. Join us as we embark on a journey of discovery, unraveling the mysteries and complexities of this fascinating region.
Geography and Demographics: More Information On The Middle East
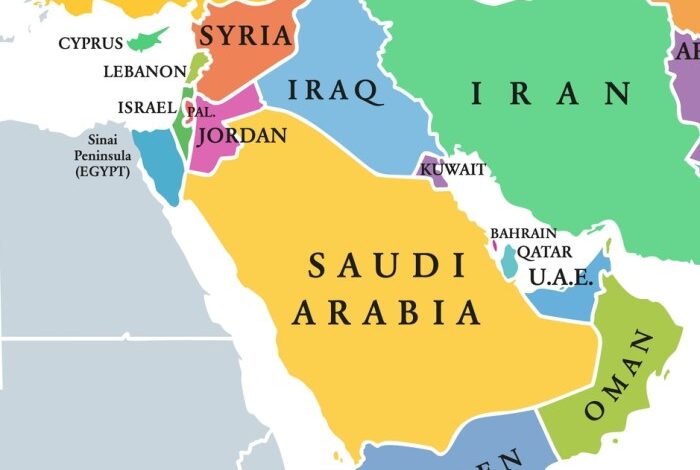
The Middle East is a region of immense cultural, historical, and geopolitical significance. Its diverse geography, ranging from arid deserts to fertile valleys, has shaped the region’s history, culture, and economy. Understanding the Middle East’s geographical features and demographics is crucial to comprehending its complexities and navigating its challenges.
Geographical Features
The Middle East encompasses a vast and diverse landscape, stretching from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east. The region is characterized by several distinct geographical features, including:
- Deserts:The Middle East is home to some of the world’s largest deserts, including the Sahara, Arabian, and Syrian deserts. These deserts cover vast areas, characterized by extreme temperatures, limited rainfall, and sparse vegetation.
- Mountains:The region is also marked by several mountain ranges, such as the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, the Zagros Mountains in Iran, and the Atlas Mountains in North Africa. These mountains provide a natural barrier between different regions and have played a significant role in shaping the region’s history and culture.
- Rivers and Water Bodies:The Middle East has several important rivers, including the Nile, Tigris, Euphrates, and Jordan rivers. These rivers have been crucial for agriculture, trade, and settlement throughout history. The region also includes several important water bodies, such as the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, and the Persian Gulf.
- Climate Zones:The Middle East experiences a wide range of climates, from arid and desert in the interior to Mediterranean in the coastal regions. The region is generally hot and dry, with limited rainfall in most areas.
- Natural Resources:The Middle East is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, and phosphates. The region holds significant reserves of these resources, which have played a major role in shaping its economy and geopolitics.
Population Distribution and Growth
The Middle East has a population of over 400 million people, with a high population density in some areas, particularly in urban centers. The region’s population is growing rapidly, driven by factors such as high birth rates and declining mortality rates.
- Major Cities:The Middle East is home to several major cities, including Cairo, Istanbul, Tehran, Riyadh, and Dubai. These cities are major centers of commerce, culture, and education, attracting people from across the region and beyond.
- Ethnic Groups:The Middle East is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, including Arabs, Persians, Turks, Kurds, and Berbers. These groups have their own distinct languages, cultures, and traditions, contributing to the region’s rich cultural tapestry.
- Population Growth Trends:The Middle East’s population is projected to continue growing in the coming decades, driven by factors such as high birth rates and improvements in healthcare. This growth presents both opportunities and challenges for the region, including the need for increased infrastructure development, job creation, and resource management.
Impact of Geography on History, Culture, and Economy
The Middle East’s geography has played a significant role in shaping its history, culture, and economy.
- Trade Routes:The region’s strategic location at the crossroads of continents has made it a vital hub for trade routes for centuries. The Silk Road, for instance, connected the East and West, passing through the Middle East, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
- Agriculture:The availability of water resources, particularly from rivers like the Nile and Euphrates, has enabled the development of agriculture in the Middle East. This has been crucial for the region’s food security and economic development.
- Culture and Identity:The Middle East’s diverse geography has contributed to the development of distinct cultures and identities. The region’s desert landscapes, for instance, have influenced nomadic cultures and traditions, while its coastal regions have fostered maritime cultures.
- Conflicts and Geopolitics:The region’s geography has also played a role in shaping its conflicts and geopolitics. The scarcity of water resources, for instance, has led to tensions between countries, while the presence of oil reserves has made the region a major focus of international attention.
History and Culture
The Middle East, a region spanning from North Africa to Central Asia, boasts a rich and complex history, shaped by ancient civilizations, powerful empires, and modern conflicts. Its cultural tapestry is equally diverse, reflecting a blend of religious beliefs, artistic expressions, and culinary traditions.
The Middle East is a region rich in history and culture, but it also faces many challenges. From political instability to economic disparities, there’s a lot to unpack when it comes to understanding the region’s complexities. To learn more about the work being done to address these challenges, it’s worth exploring the efforts of non governmental organizations on development issues who are working to improve lives in the Middle East.
Their initiatives are vital in fostering positive change and providing essential support to communities in need.
Ancient Civilizations and Empires
The Middle East has been home to some of the world’s oldest civilizations, including Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Persia. These civilizations left behind lasting legacies in art, architecture, literature, and law.
- Mesopotamia:The cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia, located in present-day Iraq, witnessed the rise of the Sumerian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires. These empires developed sophisticated systems of writing, mathematics, and astronomy, and their architectural marvels, such as the Ziggurats of Ur, still stand as testaments to their ingenuity.
The Middle East is a region rich in history and culture, but it’s also been the site of many conflicts and upheavals. One of the most recent and impactful examples is the aftermath of the war in Iraq, which has left a lasting mark on the country.
If you’re interested in learning more about the challenges of rebuilding Iraq and the ongoing efforts to create a more stable and prosperous future, I highly recommend checking out this article: aftermath and rebuilding iraq. Understanding these issues is crucial to gaining a deeper understanding of the complexities of the Middle East and the challenges it faces today.
- Ancient Egypt:Along the Nile River, the ancient Egyptians established a powerful and enduring civilization, known for its magnificent pyramids, intricate hieroglyphic writing, and advancements in medicine and engineering. The pharaohs, considered divine rulers, left behind a legacy of religious beliefs and rituals that continue to fascinate scholars and tourists alike.
- Persian Empire:Spanning a vast territory from modern-day Turkey to India, the Persian Empire, under rulers like Cyrus the Great and Darius I, was known for its administrative efficiency, tolerance of different cultures, and construction of impressive infrastructure, including the Royal Road, a network of roads connecting the empire’s far-flung regions.
Colonial Period and Modern Conflicts
The Middle East’s history has been deeply impacted by colonial powers, primarily the British and French, who sought to control its strategic resources and trade routes. The legacy of colonialism continues to influence the region’s political and economic landscapes.
- British Influence:The British Empire, through its control of Egypt, the Suez Canal, and other territories, exerted significant influence on the Middle East. This influence contributed to the rise of nationalism and calls for independence in the region.
- French Influence:France, with its control of Syria and Lebanon, also played a crucial role in shaping the Middle East. The French Mandate system, established after World War I, aimed to guide these territories towards independence, but its implementation was often fraught with challenges.
I’m always fascinated by the history and culture of the Middle East, and I’m constantly seeking out new information to broaden my understanding. Recently, I stumbled upon a fascinating debate about the best Star Wars movie, specifically whether Star Wars: Phantom Menace or New Hope reigns supreme.
While it’s a fun discussion, I’m more focused on exploring the intricate tapestry of the Middle East’s past and present. There’s so much to learn about this region, from its ancient civilizations to its contemporary challenges.
- Modern Conflicts:The 20th and 21st centuries have witnessed a series of modern conflicts in the Middle East, including the Arab-Israeli conflict, the Iran-Iraq War, and the wars in Iraq and Syria. These conflicts have had devastating consequences for the region, resulting in loss of life, displacement, and political instability.
Cultural Diversity
The Middle East is a melting pot of cultures, with diverse languages, religions, art forms, and culinary traditions. This diversity is a reflection of the region’s long history of interactions and exchanges.
- Religion:The Middle East is the birthplace of major world religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. These religions have profoundly shaped the region’s history, culture, and politics, influencing its social norms, laws, and art.
- Languages:Arabic is the dominant language of the Middle East, but the region is also home to a wide array of other languages, including Persian, Turkish, Kurdish, and Hebrew. This linguistic diversity reflects the complex ethnic and cultural makeup of the region.
- Art and Music:The Middle East has a rich artistic heritage, with traditions ranging from ancient pottery and calligraphy to contemporary painting and film. Music, an integral part of Middle Eastern culture, encompasses a variety of styles, from traditional folk music to modern pop and electronic genres.
- Cuisine:Middle Eastern cuisine is renowned for its vibrant flavors and diverse ingredients. From the rich and aromatic dishes of Lebanon to the savory stews of Morocco, the region’s culinary traditions are a testament to its cultural richness.
Role of Religion
Religion plays a central role in the Middle East, shaping its history, culture, and politics. It is a source of identity, inspiration, and conflict, influencing social norms, laws, and political systems.
- Religious Identity:Religion is a fundamental aspect of identity for many people in the Middle East. Religious beliefs and practices are often intertwined with cultural traditions, shaping daily life and social interactions.
- Political Influence:Religion has played a significant role in shaping political systems and ideologies in the Middle East. Some countries have established religious laws and institutions, while others have witnessed the rise of religious movements and parties.
- Interfaith Relations:The Middle East is home to diverse religious communities, including Muslims, Christians, Jews, and others. While interfaith relations have historically been complex, efforts are underway to promote dialogue and understanding among different religious groups.
Political Systems and Governance
The Middle East is a region with a diverse range of political systems, reflecting its complex history and cultural landscape. From ancient monarchies to modern republics and theocracies, the region presents a fascinating tapestry of governance models. This section explores the various political systems in the Middle East, analyzes the challenges faced in democratic transitions, and examines the role of international actors in shaping the region’s political landscape.
Types of Political Systems
The Middle East encompasses a spectrum of political systems, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Here are some prominent examples:
- Monarchies:Several countries in the Middle East, such as Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and the United Arab Emirates, are ruled by monarchs. These systems often trace their lineage back to ancient traditions and are characterized by hereditary succession. Monarchies in the region vary in their level of political participation and democratic reforms.
For example, Saudi Arabia operates as an absolute monarchy, while Jordan has a constitutional monarchy with a parliament.
- Republics:Republics, where the head of state is elected, are also prevalent in the Middle East. Examples include Turkey, Egypt, and Lebanon. These republics range from parliamentary systems with multi-party elections to presidential systems with a strong executive branch.
- Theocracies:Theocracies, where religious leaders hold significant political power, are found in countries like Iran. In Iran, the Supreme Leader, a religious figure, wields ultimate authority, and Islamic law forms the basis of the legal system.
Challenges to Democratic Transitions
The Middle East has witnessed numerous attempts at democratic transitions, but these efforts have often been fraught with challenges. Some of the key obstacles include:
- Political Instability:Many countries in the region have experienced periods of political turmoil, including revolutions, civil wars, and regional conflicts. This instability can undermine democratic institutions and make it difficult to establish a stable and functioning government.
- Corruption:Corruption is a widespread problem in many Middle Eastern countries, hindering good governance and eroding public trust in political institutions.
- Sectarianism:Deep-rooted sectarian divisions, often along religious or ethnic lines, can lead to political polarization and instability. These divisions can be exploited by political actors to gain power, further exacerbating tensions and undermining democratic processes.
Role of International Organizations and Foreign Powers
International organizations and foreign powers play a significant role in shaping the political landscape of the Middle East.
- International Organizations:Organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the European Union (EU) have played a role in promoting peace, democracy, and human rights in the region. They provide support for democratic transitions, conflict resolution, and humanitarian aid.
- Foreign Powers:Regional and global powers, including the United States, Russia, and China, have significant influence in the Middle East. Their involvement in regional conflicts, economic relations, and military interventions can have a profound impact on the political dynamics of the region.
Economy and Development
The Middle East is a region of vast economic potential, but it also faces significant challenges. Many countries in the region rely heavily on oil and gas production, making them vulnerable to global price fluctuations. A lack of economic diversification and high unemployment rates are other key challenges that the region’s economies must address.
Economic Structures and Challenges
The Middle East’s economic landscape is heavily influenced by the presence of vast oil and gas reserves. While this has brought significant wealth to some countries, it has also led to a dependence on these resources, making their economies vulnerable to price shocks and fluctuations in global demand.
- Dependence on Oil and Gas:The Middle East is home to the world’s largest oil reserves, with Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, and Kuwait being major producers. This dependence on oil and gas exports has created a significant revenue stream for these countries, but it has also made them susceptible to global price fluctuations.
When oil prices decline, as they have in recent years, the economies of these countries are severely impacted.
- Lack of Diversification:Many Middle Eastern economies have not diversified beyond oil and gas production. This lack of diversification makes them vulnerable to external shocks and hinders long-term economic growth. Countries need to invest in other sectors, such as manufacturing, tourism, and technology, to create a more sustainable and resilient economy.
- High Unemployment:Unemployment is a major problem in many Middle Eastern countries, particularly among young people. The lack of job opportunities, especially in sectors outside of oil and gas, contributes to social unrest and instability.
Role of Foreign Investment and Trade
Foreign investment and trade play a crucial role in the economic development of the Middle East. These factors can help to diversify economies, create jobs, and stimulate growth.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):The Middle East has attracted significant FDI in recent years, particularly in sectors such as infrastructure, tourism, and energy. This investment can help to create new jobs, stimulate economic activity, and introduce new technologies. However, attracting FDI requires a stable political environment, transparent regulations, and a skilled workforce.
- Trade:The Middle East is a major trading hub, with countries in the region exporting oil, gas, and other commodities to global markets. Trade also plays a role in importing goods and services that are not produced locally. Promoting free trade and reducing barriers to trade can help to stimulate economic growth and create new opportunities for businesses in the region.
Impact of Social and Political Factors
Social and political factors can have a significant impact on economic growth and development in the Middle East.
- Political Instability:Political instability and conflict can disrupt economic activity, deter foreign investment, and hinder development efforts. Countries need to address political tensions and create a stable environment to attract investment and promote growth.
- Social Inequality:High levels of social inequality can lead to social unrest and hinder economic development. Addressing inequality by promoting social mobility, access to education, and healthcare can create a more equitable society and foster economic growth.
- Education and Skills:A skilled workforce is essential for economic development. Investing in education and training programs can help to create a workforce that is equipped to compete in the global economy.
Social Issues and Challenges
The Middle East faces numerous social challenges, ranging from gender inequality and human rights violations to the impact of conflict and economic disparities. These issues are deeply intertwined with the region’s history, culture, and political landscape.
Challenges Facing Women in the Middle East
Women in the Middle East face significant challenges in accessing education, employment, and political participation. These challenges vary across countries and are often rooted in deeply ingrained social and cultural norms.
- Education:Despite progress in recent decades, girls in many Middle Eastern countries still face barriers to education. These include cultural expectations, limited access to schools, and a lack of female teachers. This disparity in educational opportunities can have a significant impact on women’s future prospects.
- Employment:Women in the Middle East are often underrepresented in the workforce, facing discrimination in hiring, promotion, and access to leadership positions. This is partly due to cultural norms that limit women’s roles in the public sphere and a lack of policies promoting gender equality in the workplace.
- Political Participation:Women’s political participation in the Middle East remains limited. Although some countries have witnessed an increase in women’s representation in government, they are often underrepresented in decision-making positions. Cultural barriers, political systems, and societal attitudes continue to hinder women’s full participation in the political process.
Impact of Social and Cultural Norms on Human Rights and Freedoms, More information on the middle east
Social and cultural norms play a significant role in shaping human rights and freedoms in the Middle East. These norms can restrict individual liberties, particularly for women and minorities.
- Freedom of Expression:In some countries, freedom of expression is limited, with restrictions on media, speech, and assembly. These restrictions are often justified on the grounds of preserving national security or protecting religious values.
- Freedom of Religion:Religious freedom can be limited in some Middle Eastern countries, particularly for minority groups. Discrimination and persecution based on religious beliefs can occur, leading to social exclusion and marginalization.
- Women’s Rights:Cultural norms can restrict women’s rights in areas such as inheritance, divorce, and child custody. These norms can perpetuate gender inequality and limit women’s autonomy and decision-making power.
Role of Education, Healthcare, and Infrastructure in Addressing Social Challenges
Education, healthcare, and infrastructure play a crucial role in addressing social challenges in the Middle East. Investing in these areas can empower individuals, promote social mobility, and foster sustainable development.
- Education:Providing quality education for all, regardless of gender, is essential for breaking down social barriers and promoting economic growth. Education empowers individuals to participate in society, challenge traditional norms, and advocate for their rights.
- Healthcare:Access to affordable and quality healthcare is crucial for improving health outcomes and reducing disparities. Investing in healthcare infrastructure, training healthcare professionals, and promoting preventive healthcare practices can contribute to a healthier and more equitable society.
- Infrastructure:Developing modern infrastructure, including transportation, communication, and energy systems, is essential for economic development and social progress. Infrastructure improvements can create jobs, enhance connectivity, and facilitate access to essential services.
Conflict and Security
The Middle East has been a region marked by protracted conflicts and instability for decades. These conflicts, often rooted in historical grievances, territorial disputes, and ideological differences, have had devastating consequences for the region’s people, economies, and political systems. Understanding the causes and consequences of these conflicts is crucial for promoting peace and stability in the Middle East.
The Arab-Israeli Conflict
The Arab-Israeli conflict is one of the most complex and enduring conflicts in the world. It stems from competing claims to the same land, dating back to the early 20th century. The conflict has witnessed multiple wars, including the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the 1967 Six-Day War, and the 1973 Yom Kippur War, resulting in significant loss of life and displacement.
The conflict’s core issues include the status of Jerusalem, the Israeli settlements in the West Bank, and the right of return for Palestinian refugees.
The Syrian Civil War
The Syrian Civil War, which began in 2011, is a multifaceted conflict involving the Syrian government, various rebel groups, foreign powers, and extremist organizations. The conflict’s origins lie in the Syrian government’s repressive policies, the Arab Spring uprisings, and the rise of sectarian tensions.
The war has led to a humanitarian catastrophe, with millions displaced and thousands killed. The war has also created a power vacuum, allowing extremist groups like ISIS to gain a foothold in the country.
The Rise of ISIS
ISIS, also known as ISIL, emerged in the chaos of the Syrian Civil War. The group, which espouses a radical and violent interpretation of Islam, gained control of large swaths of territory in Iraq and Syria. ISIS’s rise was fueled by a combination of factors, including the sectarian violence in Iraq, the instability in Syria, and the group’s effective use of propaganda and social media.
The group’s brutality and its attacks on civilians have sparked international condemnation and military action.
The Role of Regional and International Powers
Regional and international powers have played a significant role in mediating conflicts and promoting peace in the Middle East. The United States, Russia, and the European Union have all been involved in peace negotiations and humanitarian aid efforts. The United Nations has also played a critical role in peacekeeping and humanitarian assistance.
However, the involvement of these powers has often been complex and controversial, with accusations of double standards and interference in internal affairs.
The Impact of Conflict on Human Rights, Displacement, and Humanitarian Crises
Conflicts in the Middle East have had a devastating impact on human rights, displacement, and humanitarian crises. Millions of people have been forced to flee their homes, creating refugee crises in neighboring countries. The conflicts have also led to widespread human rights abuses, including extrajudicial killings, torture, and arbitrary detention.
The ongoing conflicts have also exacerbated existing social and economic problems, leading to widespread poverty and unemployment.
Future Prospects
The Middle East faces a complex tapestry of challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. While the region grapples with legacy issues like political instability, conflict, and economic disparities, it also stands poised for transformation driven by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and a growing need for regional cooperation.
Climate Change and Water Security
Climate change poses a significant threat to the Middle East, a region already characterized by arid and semi-arid climates. Rising temperatures, increased droughts, and unpredictable rainfall patterns are exacerbating water scarcity, impacting agriculture, energy production, and human health. The region’s reliance on fossil fuels further contributes to climate change, creating a vicious cycle.
- Water Scarcity:The Middle East is home to some of the world’s most water-stressed countries, with many relying heavily on groundwater reserves that are being depleted at unsustainable rates. This situation is further compounded by the growing population and urbanization, leading to increased water demand.
- Agricultural Impacts:Drought and water scarcity are severely impacting agriculture, a vital sector in the Middle East. Reduced crop yields, livestock losses, and food insecurity are becoming increasingly prevalent, impacting livelihoods and regional stability.
- Energy Production:Water is essential for energy production, particularly in the Middle East, where many countries rely on thermal power plants that require large quantities of water for cooling. As water scarcity intensifies, energy production faces disruptions, impacting economic development and social well-being.
To mitigate these challenges, the Middle East needs to prioritize water conservation, invest in sustainable water management practices, and explore alternative water sources, such as desalination and rainwater harvesting. Additionally, regional cooperation on water resource management is crucial to ensure equitable access and sustainable utilization.
Population Growth and Urbanization
The Middle East’s population is growing rapidly, driven by high birth rates and declining mortality rates. This growth is putting pressure on resources, infrastructure, and social services, particularly in urban areas, where most of the population resides. The region is witnessing a rapid pace of urbanization, with cities becoming centers of economic activity and attracting migrants from rural areas.
- Resource Strain:Population growth exacerbates the strain on water resources, energy supplies, and agricultural land. This puts pressure on governments to provide adequate infrastructure and services, posing challenges to sustainable development.
- Urban Challenges:Rapid urbanization leads to overcrowding, inadequate housing, unemployment, and social unrest. Cities struggle to cope with the influx of people, leading to challenges in providing basic services, transportation, and infrastructure.
- Economic Opportunities:While population growth presents challenges, it also presents opportunities. A young and growing population can contribute to economic growth and development if provided with education, skills training, and employment opportunities.
Addressing the challenges of population growth and urbanization requires effective urban planning, investment in infrastructure and social services, and the creation of job opportunities that can absorb the growing workforce. The region also needs to focus on education and skills development to equip its youth with the necessary skills for a rapidly changing economy.
Economic Diversification and Innovation
The Middle East’s economies are heavily reliant on oil and gas exports, making them vulnerable to fluctuations in global energy prices. Diversifying economies away from oil dependence is crucial for long-term economic sustainability and stability. This requires fostering innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of new industries.
- Knowledge-Based Economy:Investing in education, research, and development is crucial for building a knowledge-based economy. This involves supporting universities, research institutions, and technology parks to promote innovation and create a skilled workforce.
- Entrepreneurship and Small Businesses:Creating a supportive environment for entrepreneurship and small businesses is essential for economic diversification. This includes access to financing, mentorship, and regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation and job creation.
- Tourism and Hospitality:The Middle East has a rich cultural heritage and natural beauty that can be leveraged to develop the tourism and hospitality sector. This can create jobs, generate revenue, and promote cultural exchange.
Economic diversification requires strategic planning, investment in infrastructure, and a commitment to innovation. The region needs to embrace new technologies, attract foreign investment, and foster a culture of entrepreneurship to create a more diversified and sustainable economy.
Regional Cooperation and Integration
Addressing the challenges facing the Middle East requires regional cooperation and integration. This involves working together to address shared concerns such as climate change, water scarcity, economic development, and security.
- Economic Integration:Establishing free trade zones, harmonizing regulations, and promoting cross-border investment can boost regional trade and economic growth. This can create new markets, attract foreign investment, and enhance competitiveness.
- Infrastructure Development:Developing regional infrastructure, such as transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems, can facilitate trade, tourism, and investment, promoting economic integration and development.
- Security Cooperation:Addressing common security threats, such as terrorism, extremism, and cross-border crime, requires regional cooperation and intelligence sharing. This can contribute to stability, peace, and economic development.
Regional cooperation is essential for the Middle East to overcome its challenges and realize its full potential. It requires political will, trust-building measures, and a shared vision for a more prosperous and peaceful future.
Technology, Innovation, and Education
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the Middle East. Advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digital infrastructure have the potential to transform economies, improve social services, and enhance connectivity.
- Digital Economy:The Middle East has the potential to become a leader in the digital economy. Investments in broadband infrastructure, e-commerce, and digital services can create new opportunities for businesses and individuals.
- Renewable Energy:Harnessing renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can reduce dependence on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and create new economic opportunities. The region’s abundant sunshine and wind resources make it well-suited for renewable energy development.
- Education and Skills Development:Investing in education and skills development is crucial for a future driven by technology. This involves promoting STEM education, fostering entrepreneurship, and ensuring that the workforce is equipped with the skills needed for a rapidly changing economy.
Technology, innovation, and education are key drivers of progress in the 21st century. The Middle East needs to embrace these forces to create a more sustainable, inclusive, and prosperous future.






