Markets Lookahead: Manufacturing PMIs, SNB & RBA Rate Decisions
Markets lookahead manufacturing pmis snb and rba rate decision – Markets Lookahead: Manufacturing PMIs, SNB & RBA Rate Decisions sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This week, the global economic landscape is set to be shaped by a confluence of crucial events, including the release of key manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Indices (PMIs) and highly anticipated rate decisions from the Swiss National Bank (SNB) and the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA).
These events will have far-reaching implications for financial markets, influencing everything from equity prices to currency exchange rates.
The manufacturing PMIs provide valuable insights into the health of the global economy, offering a real-time snapshot of manufacturing activity across major economies. These indicators are closely watched by investors and policymakers alike, as they offer clues about the direction of economic growth and inflation.
Meanwhile, the SNB and RBA rate decisions will shed light on the central banks’ perspectives on inflation, economic growth, and currency valuations. These decisions will have a significant impact on global financial markets, potentially triggering volatility in currencies, bonds, and equities.
Global Manufacturing Outlook: Markets Lookahead Manufacturing Pmis Snb And Rba Rate Decision
The global manufacturing sector continues to navigate a complex landscape, grappling with persistent supply chain disruptions, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical uncertainties. Key indicators, such as the Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI), provide valuable insights into the health and trajectory of manufacturing activity across various economies.
Manufacturing Performance Across Major Economies
The PMI data reveals a mixed picture across major economies. In the United States, the manufacturing sector has shown resilience, with the PMI remaining above the 50-point threshold that separates expansion from contraction. However, the pace of growth has slowed, reflecting concerns about rising interest rates and weakening consumer demand.
In Europe, the manufacturing sector is facing significant headwinds from the ongoing energy crisis and the war in Ukraine. The PMI has fallen below the 50-point mark, indicating contraction in activity. In Asia, China’s manufacturing sector has shown signs of recovery, with the PMI rising in recent months.
However, the recovery remains fragile, as the country continues to grapple with the impact of COVID-19 lockdowns and weak global demand.
Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions, Inflation, and Geopolitical Tensions
Supply chain disruptions continue to pose a major challenge for global manufacturing. The ongoing war in Ukraine has exacerbated existing bottlenecks, particularly in the supply of raw materials, such as energy and metals. Inflationary pressures have also intensified, driven by rising energy prices and supply chain disruptions.
This week’s economic calendar is packed, with key data releases like the manufacturing PMIs and rate decisions from the SNB and RBA. Meanwhile, news from the political sphere is also grabbing attention, with former federal officials criticizing the 9/11 commission report and the Bush administration in a recent article ex feds blast 9 11 panel and bush.
It’s going to be a busy week for market watchers, trying to navigate both economic and political developments.
This has led to increased input costs for manufacturers, putting pressure on profit margins. Geopolitical tensions, such as the trade war between the United States and China, have also created uncertainty and volatility in global manufacturing.
The global manufacturing sector faces a challenging outlook, with a confluence of factors weighing on activity. While some economies, such as the United States, have shown resilience, others, like Europe, are facing significant headwinds. Supply chain disruptions, inflation, and geopolitical tensions continue to pose significant challenges.
Central Bank Actions and Market Expectations
The upcoming rate decisions by the Swiss National Bank (SNB) and the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) are key events for global financial markets. These decisions will provide insights into the central banks’ views on inflation, economic growth, and currency valuations.
SNB Rate Decision
The SNB is expected to maintain its current policy stance, keeping interest rates unchanged at0.75%. The Swiss economy has shown resilience in recent months, with strong exports and a stable labor market. However, inflation remains subdued, and the SNB is likely to remain cautious about raising rates.
RBA Rate Decision
The RBA is expected to keep interest rates on hold at 4.10%. While inflation has eased somewhat, it remains above the RBA’s target range of 2-3%. The RBA is also concerned about the potential for further economic slowdown, as rising interest rates weigh on consumer spending and investment.
Market Expectations
The market expects the SNB to maintain its dovish stance, with no immediate rate hikes anticipated. This is primarily due to the low inflation environment in Switzerland and the SNB’s commitment to maintaining a stable currency.
This week, investors are keeping a close eye on the manufacturing PMIs, particularly in light of the upcoming rate decisions from the SNB and RBA. These indicators, along with global economic sentiment, will provide insight into the health of the manufacturing sector and the potential impact on monetary policy.
It’s crucial to remember that economic growth hinges on the efficient allocation of resources, and a closer look at how we can avoid wasted wealth, capital, labor, and resources is essential for sustainable economic development. As we analyze the upcoming data releases, it’s important to consider the broader implications for global economic stability and the potential for long-term growth.
The SNB’s focus on currency stability is a key factor in its policy decisions.
This week’s economic calendar is packed with key data releases, including the manufacturing PMIs, which will provide insights into global economic health. The SNB and RBA rate decisions will also be closely watched, with investors seeking clues about future monetary policy.
However, amidst the economic news, a story about a boy not prosecuted over riots due to the wrath of parents highlights the complexities of societal unrest and the impact on families. It’s a reminder that while markets focus on economic indicators, the human cost of these events can be significant.
The RBA is expected to keep rates on hold for the time being, but the market is closely watching for any signs of a potential shift towards a more hawkish stance. The RBA’s decision will depend on the evolving inflation outlook and the impact of rising interest rates on the Australian economy.
Impact on Financial Markets
The manufacturing PMIs and central bank rate decisions can have a significant impact on global financial markets. These economic indicators provide insights into the health of the manufacturing sector and the monetary policy stance of major economies, influencing investor sentiment and asset prices.
Impact on Equity Markets
The manufacturing PMIs are a leading indicator of economic growth. A strong PMI reading suggests robust manufacturing activity, which can boost investor confidence and drive up equity prices. Conversely, a weak PMI reading can signal slowing economic growth, leading to a decline in equity prices.
Central bank rate decisions also play a crucial role in shaping equity market performance. Rate hikes can increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially dampening economic growth and leading to a sell-off in equities. Conversely, rate cuts can stimulate economic activity and support equity markets.
Impact on Currency Exchange Rates
Central bank rate decisions can significantly influence currency exchange rates. For instance, a rate hike by the Swiss National Bank (SNB) would make the Swiss Franc (CHF) more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, leading to appreciation of the CHF against other currencies.
Conversely, a rate cut by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) could weaken the Australian Dollar (AUD) as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
Impact on Bond Yields
Central bank rate decisions have a direct impact on bond yields. Rate hikes typically lead to higher bond yields as investors demand a higher return for holding bonds in a rising interest rate environment. Conversely, rate cuts can lead to lower bond yields as investors are willing to accept lower returns in a low-interest rate environment.
The manufacturing PMIs can also influence bond yields, as a strong PMI reading can indicate higher inflation expectations, potentially leading to higher bond yields.
Key Economic Indicators
The recent manufacturing PMI data and central bank decisions provide valuable insights into the current state of the global economy. To gain a deeper understanding of these developments, it’s essential to consider the key economic indicators that are driving these trends.
These indicators offer a comprehensive view of the health of major economies, including manufacturing activity, inflation, and unemployment rates.
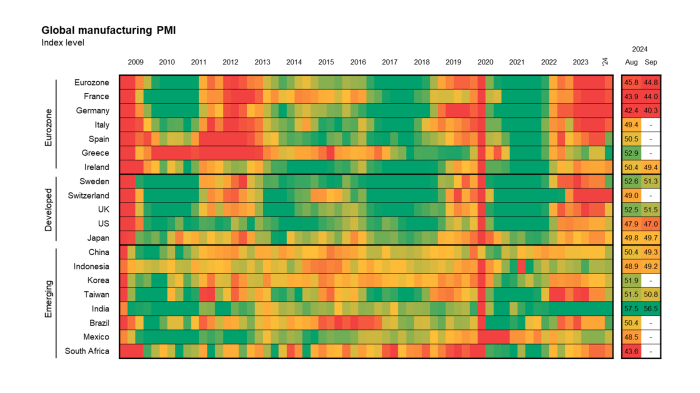
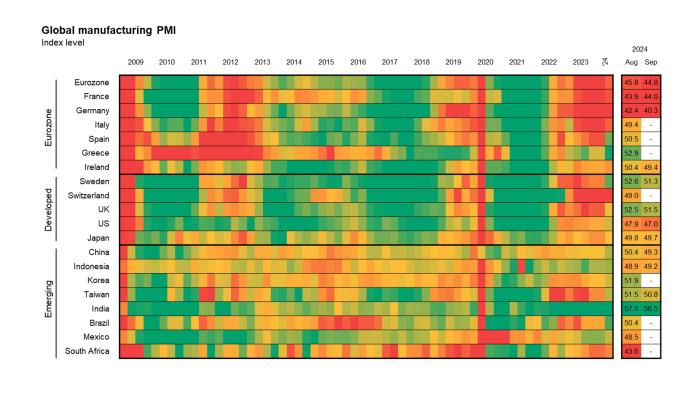
Manufacturing PMI Data, Markets lookahead manufacturing pmis snb and rba rate decision
The Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) is a widely used indicator of manufacturing activity. A PMI reading above 50 indicates expansion, while a reading below 50 suggests contraction. Here’s a table showcasing the latest PMI data for major manufacturing economies:
| Country | Sector | PMI Value |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Manufacturing | 47.0 |
| China | Manufacturing | 49.2 |
| Germany | Manufacturing | 40.1 |
| Japan | Manufacturing | 49.8 |
Economic Indicators for Switzerland and Australia
To understand the context of the SNB and RBA rate decisions, it’s crucial to examine the key economic indicators for Switzerland and Australia. This table provides a snapshot of their respective GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment rates:
| Country | GDP Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switzerland | 0.5 | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| Australia | 2.3 | 6.0 | 3.7 |
Interest Rate Trajectories of the SNB and RBA
Comparing the interest rate trajectories of the SNB and RBA over the past few years provides valuable insights into their monetary policy responses to economic conditions. A visual representation can help illustrate these trends effectively.
[Visual representation of the interest rate trajectories of the SNB and RBA over the past few years. This could be a line graph with time on the x-axis and interest rates on the y-axis. The graph should clearly show the different paths taken by the two central banks in setting interest rates. It’s important to note that the actual visual representation will need to be created separately and inserted here.]
Investment Strategies
The upcoming manufacturing PMIs and central bank rate decisions will likely have a significant impact on global financial markets. Investors should carefully consider the implications of these events for their portfolios and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Equity Strategies
The performance of equities is closely tied to economic growth prospects. If the manufacturing PMIs indicate a slowdown in economic activity, investors may become more cautious and reduce their exposure to equities. Conversely, strong PMIs could boost investor confidence and lead to higher equity valuations.
Central bank decisions also play a crucial role. Rate hikes can negatively impact corporate earnings and stock prices, while rate cuts can stimulate economic growth and support equities.
- Investors with a higher risk appetite may consider investing in sectors that are expected to benefit from economic growth, such as technology, consumer discretionary, and industrials.
- Investors with a lower risk appetite may prefer to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to defensive sectors like healthcare and utilities, which tend to be less sensitive to economic fluctuations.
Bond Strategies
Bond yields are inversely related to interest rates. If central banks raise interest rates, bond yields will rise, leading to a decline in bond prices. Conversely, rate cuts will push bond yields lower, resulting in higher bond prices. The manufacturing PMIs can also influence bond yields.
Weak PMIs could signal a potential recession, prompting investors to seek the safety of bonds, pushing yields down.
- Investors anticipating a rise in interest rates may consider short-term bonds or bonds with higher yields, which offer more potential for capital appreciation.
- Investors expecting lower interest rates may favor longer-term bonds, which are more sensitive to interest rate changes and could provide higher returns in a low-interest-rate environment.
Currency Strategies
Currency movements are influenced by a range of factors, including interest rates, economic growth, and political stability. Central bank decisions can have a significant impact on currency values. If a central bank raises interest rates, its currency is likely to appreciate as investors seek higher returns.
Conversely, rate cuts can weaken a currency. Manufacturing PMIs can also influence currency valuations. Strong PMIs can strengthen a currency, while weak PMIs can weaken it.
- Investors anticipating a rise in interest rates in a particular country may consider buying its currency, expecting it to appreciate.
- Investors expecting a decline in interest rates may consider selling a currency, anticipating its depreciation.






