Central Banks in Action: Rate Moves Shake the World
Its a big week for central banks around the world with a slew of rate moves on the table – It’s a big week for central banks around the world with a slew of rate moves on the table. This week, we’re watching closely as major financial institutions grapple with inflation, economic growth, and global uncertainty. The decisions they make will ripple through markets, businesses, and everyday lives, influencing everything from the cost of borrowing to the value of our investments.
The global economic landscape is complex and volatile. Inflation remains a key concern, with prices rising faster than wages in many countries. Meanwhile, the specter of recession looms large, fueled by geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and the ongoing energy crisis.
In this environment, central banks are tasked with navigating a delicate balancing act: taming inflation without stifling economic growth.
Global Economic Context
The global economy is navigating a complex and uncertain landscape. Central banks around the world are facing a delicate balancing act as they try to manage inflation while supporting economic growth.
Current Economic Indicators
The global economy is grappling with a confluence of challenges. Inflation remains stubbornly high in many parts of the world, fueled by supply chain disruptions, energy price volatility, and strong consumer demand. While growth has slowed in recent quarters, it remains positive in most major economies.
However, the outlook is clouded by geopolitical tensions, rising interest rates, and the potential for recession. The unemployment rate in many developed economies is at historically low levels, reflecting a tight labor market. However, wage growth has not kept pace with inflation, leading to a decline in real incomes for many workers.
It’s a big week for central banks around the world with a slew of rate moves on the table, and while the economic landscape is in flux, there’s at least one bit of good news for consumers: Tesco has announced exact dates for when popular brands like Quality Street, Cadbury, and Lindt will be dropping in price – check out this article for the full details.
Hopefully, this sweet news will help ease the pressure on wallets while central bankers grapple with inflation.
Factors Driving Central Bank Decisions
Central banks are closely monitoring these economic indicators and are adjusting monetary policy accordingly. The goal is to bring inflation back down to target levels without triggering a recession. Central bank decisions are influenced by a range of factors, including:* Geopolitical Tensions:The war in Ukraine has disrupted global energy markets and supply chains, contributing to inflation and economic uncertainty.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The pandemic-induced supply chain disruptions continue to impact the global economy, leading to shortages and higher prices.
Energy Prices
It’s a big week for central banks around the world, with a slew of rate moves on the table. I’m trying to stay focused on the economic implications, but it’s hard not to get distracted by the news that Halle Berry has seen the jokes about her characters’ jacked-up wigs, as reported on BlogNewstweets.
Anyway, back to the central banks – it’s going to be a wild ride this week!
The surge in energy prices, driven by the war in Ukraine and other factors, is a significant contributor to inflation.
It’s a big week for central banks around the world with a slew of rate moves on the table, and while those decisions will impact our wallets, it’s nice to have some lighter news to distract us, like Frances Tiafoe and Taylor Fritz advancing to the US Open semifinals and the 49ers getting another star back.
Maybe after the dust settles on the interest rate hikes, we can all get back to enjoying some exciting sports action!
Inflation Expectations
Central banks are also closely watching inflation expectations, as these can become self-fulfilling. If businesses and consumers expect prices to continue rising, they are more likely to demand higher wages and prices, which can further fuel inflation.
Economic Growth
Central banks are also considering the impact of their decisions on economic growth. Raising interest rates too aggressively could stifle investment and consumer spending, leading to a recession.
Central Bank Actions and Objectives: Its A Big Week For Central Banks Around The World With A Slew Of Rate Moves On The Table
This week marks a crucial period for global monetary policy as major central banks prepare to announce their latest decisions on interest rates. These decisions will have significant implications for global economic growth, inflation, and financial markets.
Federal Reserve
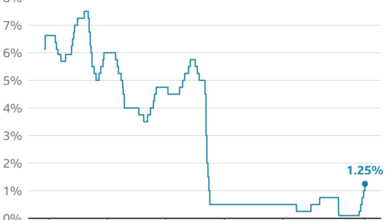
The Federal Reserve is widely expected to raise interest rates by another 25 basis points at its meeting on May 3-4, 2023. This move would bring the federal funds rate to a target range of 5.00% to 5.25%, the highest level in 16 years.
The Fed’s primary objective is to bring inflation down to its 2% target. While inflation has cooled somewhat in recent months, it remains stubbornly above the Fed’s target. The Fed is also concerned about the potential for further economic disruptions, including the ongoing war in Ukraine and the ongoing global energy crisis.
European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to raise interest rates by 25 basis points at its meeting on June 15, 2023. This would mark the ECB’s eighth consecutive rate hike since July 2022. The ECB’s main objective is to tame inflation, which has risen to record highs in the Eurozone.
However, the ECB faces a more challenging task than the Fed, as the Eurozone economy is more exposed to the global energy crisis and the war in Ukraine. The ECB is also concerned about the potential for a recession in the Eurozone.
Bank of England
The Bank of England (BoE) is expected to raise interest rates by 25 basis points at its meeting on May 11, 2023. This would bring the BoE’s benchmark rate to 4.50%, the highest level since 2008. The BoE’s primary objective is to control inflation, which has been running at a 40-year high in the UK.
The BoE is also concerned about the impact of the war in Ukraine on the UK economy, as well as the ongoing energy crisis.
Potential Impacts of Rate Moves
Central banks around the world are poised to make significant rate moves, and these decisions will have far-reaching implications for various sectors of the economy and financial markets. The potential impacts of these rate moves are multifaceted and will depend on the magnitude and pace of rate changes, as well as the overall economic context.
Impact on Businesses
The anticipated rate increases will have a direct impact on businesses, particularly those with significant debt obligations. Higher borrowing costs will make it more expensive for businesses to invest, expand operations, or finance working capital. This could lead to slower economic growth, reduced investment, and job losses.
- Increased borrowing costs:Businesses will face higher interest rates on loans, credit lines, and other forms of debt financing. This could make it more difficult for businesses to access capital and expand operations.
- Reduced investment:Higher borrowing costs could discourage businesses from investing in new projects, equipment, or technology. This could lead to slower economic growth and job creation.
- Impact on profitability:Increased borrowing costs and potentially slower economic growth could negatively impact business profitability. This could lead to layoffs, reduced investment, and slower growth.
Impact on Consumers
Higher interest rates will also affect consumers, particularly those with variable-rate mortgages, auto loans, and credit card debt.
- Increased borrowing costs:Consumers will face higher interest rates on mortgages, auto loans, and credit cards, leading to higher monthly payments and reduced disposable income.
- Reduced consumer spending:Higher borrowing costs and potentially slower economic growth could lead to reduced consumer spending, which could further slow economic growth.
- Impact on housing market:Higher mortgage rates could slow the housing market, leading to lower home prices and reduced affordability for homebuyers.
Impact on Financial Markets
The anticipated rate increases will have a significant impact on financial markets, particularly asset prices.
- Impact on bond prices:As interest rates rise, bond prices are expected to fall. This is because existing bonds with lower interest rates become less attractive compared to newly issued bonds with higher interest rates.
- Impact on stock prices:Higher interest rates could lead to lower stock prices as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the increased risk of investing in stocks. This could be exacerbated by slower economic growth and reduced corporate earnings.
- Impact on currencies:Higher interest rates can attract foreign capital, leading to an appreciation of the domestic currency. This could make exports more expensive and imports less expensive.
Comparative Analysis of Central Bank Strategies

This week’s flurry of central bank meetings presents a unique opportunity to compare and contrast the approaches different institutions are taking to manage monetary policy. While the ultimate goal of most central banks is to maintain price stability and foster sustainable economic growth, the strategies employed to achieve these objectives can vary significantly, reflecting diverse economic conditions, policy priorities, and risk tolerance.
Central Bank Approaches to Managing Monetary Policy
This section delves into the different approaches adopted by major central banks, examining their similarities and differences.
- The US Federal Reserve (Fed):The Fed’s strategy has been characterized by a gradual and data-dependent approach. The Fed has been raising interest rates in measured increments, closely monitoring economic indicators like inflation and unemployment. The Fed’s approach is based on the belief that gradual rate hikes are less likely to disrupt the economy than aggressive moves.
- The European Central Bank (ECB):The ECB has taken a more cautious approach, raising interest rates at a slower pace than the Fed. This reflects concerns about the eurozone’s economic vulnerability, particularly the impact of the war in Ukraine and energy price increases. The ECB’s strategy prioritizes maintaining financial stability and supporting economic growth.
- The Bank of England (BoE):The BoE has adopted a more aggressive stance, raising interest rates more rapidly than the Fed or the ECB. This reflects the UK’s higher inflation rate and concerns about the potential for a wage-price spiral. The BoE’s strategy aims to control inflation quickly, even at the risk of slowing economic growth.
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ):The BoJ has maintained an ultra-loose monetary policy, keeping interest rates near zero and continuing its massive asset purchase program. This reflects Japan’s unique economic challenges, including deflationary pressures and a rapidly aging population. The BoJ’s strategy aims to stimulate economic growth and maintain price stability.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Each central bank’s approach carries its own set of risks and challenges.
- The Fed’s gradual approachcould be seen as too slow if inflation proves to be more persistent than expected. This could lead to a loss of credibility and a potential for a more aggressive tightening later, which could disrupt financial markets.
- The ECB’s cautious approachcould be criticized as being too slow to address inflation. This could lead to a weakening of the euro and a loss of confidence in the ECB’s ability to control inflation.
- The BoE’s aggressive approachcould lead to a sharper slowdown in economic growth than anticipated. This could increase unemployment and lead to a recession.
- The BoJ’s ultra-loose policycould lead to asset bubbles and financial instability. This could also limit the BoJ’s ability to respond effectively to future economic shocks.
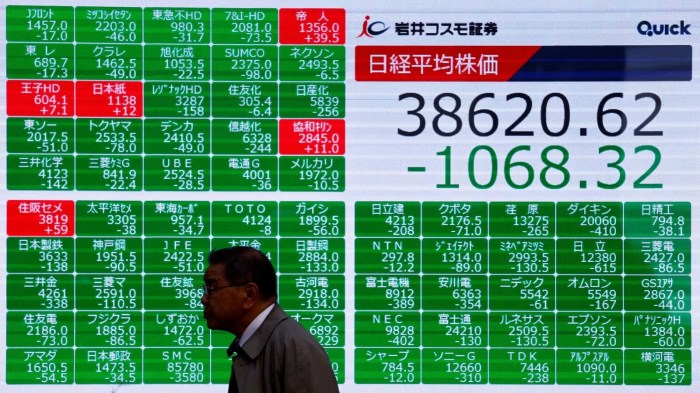
Market Reactions and Outlook
The upcoming central bank decisions will undoubtedly send ripples through global financial markets. Understanding the potential reactions is crucial for investors and market participants alike.
Short-Term Market Volatility, Its a big week for central banks around the world with a slew of rate moves on the table
The immediate aftermath of the rate announcements will likely be marked by heightened volatility. Investors will react to the decisions, and their responses will depend on the magnitude and direction of the rate changes, as well as the accompanying statements from central banks.
The degree of surprise or confirmation of market expectations will significantly influence the initial market response. For instance, if a central bank delivers a larger-than-expected rate hike, it could lead to a sell-off in equities, a strengthening of the currency, and a rise in bond yields.
Conversely, a more dovish stance than anticipated might trigger a rally in stocks and a weakening of the currency.
Investor Sentiment and Risk Appetite
Central bank decisions have a profound impact on investor sentiment and risk appetite. A series of aggressive rate hikes might signal a growing concern about inflation and economic growth, leading to a risk-off environment. Investors may pull back from riskier assets like stocks and move towards safe-haven assets like bonds and gold.
Conversely, a more accommodative stance could boost investor confidence and encourage risk-taking behavior. The perceived risk of recession or a prolonged period of high inflation will also play a significant role in shaping investor sentiment.
Long-Term Market Outlook
The long-term impact of the central bank actions will depend on the broader economic context and the effectiveness of their policies. If central banks successfully tame inflation without triggering a recession, we could see a gradual return to stability in financial markets.
However, if inflation proves more persistent than expected, or if the rate hikes lead to an economic slowdown, markets may experience prolonged volatility and uncertainty. The ability of central banks to navigate the delicate balance between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth will be a crucial factor in determining the long-term outlook for global financial markets.