Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found in Cumbria Released into Wild
Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found in Cumbria Released into Wild: A loggerhead turtle, a creature typically found in warmer waters, was discovered injured in the chilly waters of Cumbria, England. This unusual occurrence has sparked both concern and hope for the conservation of this threatened species.
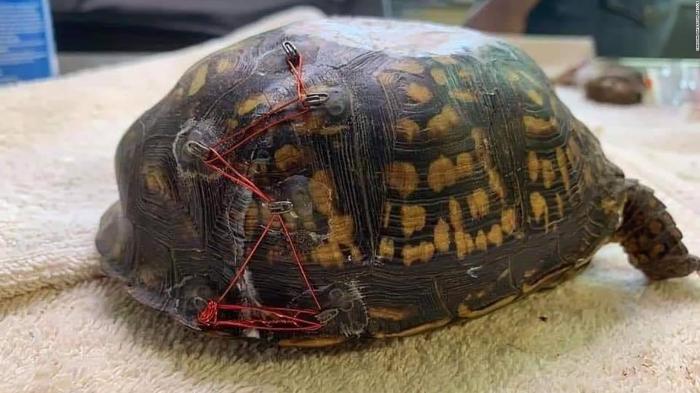
The turtle, a magnificent creature with a shell measuring over three feet in diameter, was found stranded on a beach, weakened and injured. The cause of its injuries remains a mystery, but experts suspect it may have been caught in fishing gear or struck by a vessel during its long journey from its usual habitat in the Mediterranean Sea.
Loggerhead Turtle Biology
Loggerhead turtles, scientifically known asCaretta caretta*, are captivating marine reptiles that play a crucial role in the ocean’s ecosystem. Their unique adaptations and life cycle make them fascinating subjects of study and conservation efforts.
Physical Characteristics
Loggerhead turtles are easily recognizable by their large, robust bodies and distinctive heart-shaped shells. Their shell, also known as a carapace, can range in color from reddish-brown to olive-green, often with a mottled appearance. The shell is covered in bony plates called scutes, which provide protection and support.
Adult loggerheads can reach impressive sizes, with females typically growing larger than males. On average, they measure around 3 feet in length and weigh up to 400 pounds.
Habitat and Geographic Range
Loggerhead turtles are found in warm and temperate waters throughout the world. They prefer coastal areas, particularly those with sandy beaches suitable for nesting. Their geographic range extends from the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans to the Mediterranean Sea. Loggerheads are highly migratory, often traveling long distances between their feeding grounds and breeding sites.
It’s heartwarming to see the injured loggerhead turtle, found in Cumbria, finally released back into the wild. It’s a reminder that even the smallest creatures deserve our care and attention. Speaking of incredible comebacks, the Atlanta Falcons pulled off a dramatic victory against the Philadelphia Eagles, with Kirk Cousins leading a late-game drive to secure a 22-21 win, Falcons Edge Eagles 22-21 Cousins Late Drive Wins It.
Just like the turtle, the Falcons persevered and found their way back to success. The release of the turtle is a symbol of hope and resilience, a reminder that even after challenges, life can find a way to thrive.
Diet and Feeding Habits
Loggerhead turtles are carnivores with a diverse diet. Their primary food sources include a variety of marine invertebrates, such as crabs, jellyfish, sea urchins, and shrimp. They also consume fish, squid, and occasionally sea turtles. Loggerheads use their powerful jaws and sharp beaks to crush and tear their prey.
Reproductive Cycle
Loggerhead turtles are sexually mature around 17-20 years of age. During the breeding season, females migrate to specific nesting beaches, often returning to the same site where they were hatched. They dig nests in the sand and lay clutches of 100-120 eggs.
The eggs are incubated for about 60 days, and hatchlings emerge from the nest and make their way to the ocean. The hatchlings navigate using the moon and stars, swimming towards the open sea.
Loggerhead Turtle Conservation Status: Injured Loggerhead Turtle Found In Cumbria Released Into Wild
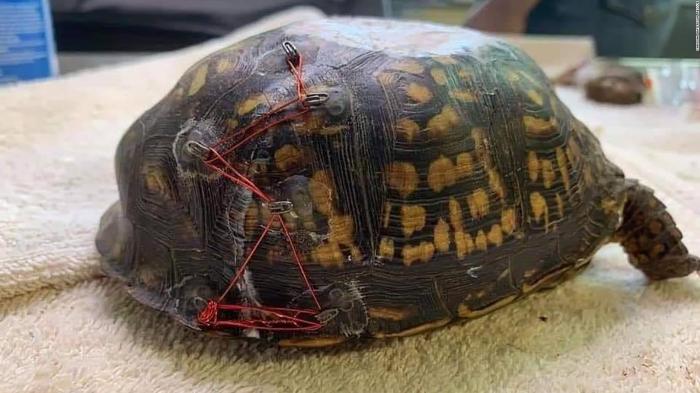
Loggerhead turtles, like the one recently released in Cumbria, face significant challenges in the wild. Their populations are under pressure from a variety of threats, and their conservation status reflects this. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies loggerhead turtles as “Threatened,” highlighting the need for urgent action to protect them.
Threats to Loggerhead Turtles
Threats to loggerhead turtles are diverse and widespread. These threats can be categorized into several key areas:
- Habitat Loss and Degradation:Loggerhead turtles rely on specific habitats for nesting, feeding, and migration. Coastal development, pollution, and climate change are leading to the loss and degradation of these critical habitats.
- Pollution:Marine debris, plastic pollution, and chemical contaminants pose significant risks to loggerhead turtles. Entanglement in plastic debris can cause injury or death, while ingestion of plastic can lead to starvation or internal injuries.
- Entanglement in Fishing Gear:Loggerhead turtles are often caught as bycatch in fishing gear, particularly longlines and trawls. Entanglement can result in drowning, injury, or death.
- Climate Change:Climate change is altering ocean currents and temperatures, which can disrupt loggerhead turtle migration patterns and nesting sites. Rising sea levels also threaten coastal nesting beaches.
International Conservation Efforts
Recognizing the threats facing loggerhead turtles, several international conservation efforts have been implemented. These efforts aim to address the key threats and promote the recovery of loggerhead turtle populations:
- The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna (CITES):CITES regulates the international trade of loggerhead turtles and their products to prevent overexploitation.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN):The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species assesses the conservation status of loggerhead turtles and provides recommendations for their protection.
- The Convention on Migratory Species (CMS):CMS works to protect loggerhead turtles during their migratory journeys, promoting cooperation among countries along their migration routes.
Conservation Programs and Initiatives
Numerous conservation programs and initiatives are focused on loggerhead turtle recovery. These programs address specific threats and work to improve the survival and reproduction of loggerhead turtles:
- Nesting Beach Protection:Conservation organizations and governments work to protect nesting beaches from development and disturbance. This includes measures like beach monitoring, nest relocation, and artificial nesting sites.
- Bycatch Reduction:Efforts are underway to reduce bycatch of loggerhead turtles in fishing gear. This includes using modified fishing gear, setting fishing limits, and implementing turtle excluder devices (TEDs) in trawls.
- Research and Monitoring:Ongoing research and monitoring programs provide valuable data on loggerhead turtle populations, their movements, and the threats they face. This information is essential for guiding conservation efforts.
- Public Education and Awareness:Raising public awareness about the importance of loggerhead turtle conservation and the threats they face is crucial. This includes education programs, outreach campaigns, and promoting responsible tourism practices.
The Cumbria Incident
The discovery of an injured loggerhead turtle in Cumbria, England, in 2023, was an extraordinary event. This species, typically found in warmer waters of the Atlantic Ocean, is rarely seen in the cold, turbulent waters of the North Sea.
It’s heartwarming to hear about the injured loggerhead turtle found in Cumbria being released back into the wild, a testament to the dedication of those who rescued and rehabilitated it. While nature takes its course, the world of finance is also experiencing its own kind of comeback, with big names like David Tepper and Michael Burry quietly increasing their stakes in the Chinese economy, as reported in Big Names Bet on China: Tepper and Burry Up Their Stakes.
It’s fascinating to see how these seemingly disparate worlds, nature and finance, can intertwine, each offering its own unique stories of resilience and opportunity.
This finding raised questions about how the turtle ended up so far from its usual habitat and the potential threats it faced during its journey.
It’s heartwarming to see the rescued loggerhead turtle, found injured in Cumbria, finally released back into the wild. It reminds me of how nature’s resilience mirrors the way we all evolve and adapt, just like Lily Collins who, as reported in Lily Collins Ditches Emily in Paris Style for a New Era , has embraced a new, more mature style.
Watching the turtle swim free after its ordeal is a reminder that even in the face of adversity, there’s always hope for a fresh start, a new chapter, and a brighter future.
The Turtle’s Journey
The presence of a loggerhead turtle in the North Sea is highly unusual. These turtles are primarily found in the warmer waters of the Atlantic Ocean, where they breed and feed. Their migration patterns are well-documented, and they typically follow currents that lead them along the coasts of the United States, Africa, and Europe.
However, the North Sea is significantly colder and less hospitable than their usual habitat. The turtle’s presence in this region suggests a possible deviation from its typical migration route.
Possible Causes of the Turtle’s Injuries
The turtle’s injuries were a cause for concern. While the specific causes of the injuries were not immediately clear, several potential threats could have contributed to its condition.
- Collisions with Boats:Loggerhead turtles are known to surface for air, making them vulnerable to collisions with vessels. The North Sea is a busy shipping lane, increasing the likelihood of such encounters.
- Entanglement in Fishing Gear:Turtles can become entangled in fishing nets and lines, which can lead to injuries, drowning, or starvation. This is a common threat to sea turtles worldwide.
- Ingestion of Marine Debris:Loggerhead turtles are known to mistake plastic debris for food. Ingesting plastic can cause blockages in their digestive system, leading to starvation and death.
- Climate Change:Climate change is altering ocean currents and temperatures, which can impact the migration patterns and distribution of marine species, including sea turtles. This may have contributed to the turtle’s presence in the North Sea.
Rescue and Rehabilitation
The injured loggerhead turtle was discovered by a member of the public on a beach in Cumbria. It was immediately reported to the local wildlife rescue organization, which transported the turtle to a specialized rehabilitation center. The turtle received medical attention for its injuries, and it was carefully monitored during its recovery.
Releasing the Turtle Back into the Wild
The day finally arrived when our loggerhead turtle, after months of dedicated care and rehabilitation, was ready to return to the vast expanse of the Atlantic Ocean. This was a moment of immense joy and satisfaction for everyone involved in her recovery.
It was a testament to the collaborative efforts of dedicated individuals and organizations, who worked tirelessly to ensure her survival.
Preparing the Turtle for Release
Releasing a rehabilitated turtle back into the wild is not simply a matter of opening a tank and letting it go. It involves a meticulous process to ensure the turtle’s health and fitness for survival in its natural environment.
- Physical Assessment:Before release, the turtle underwent a comprehensive physical examination to confirm its recovery. This included checking its weight, body condition, and overall health, ensuring it was strong enough to navigate the challenges of the ocean.
- Behavioral Assessment:The team observed the turtle’s behavior to assess its ability to swim, dive, and forage for food. They ensured it could navigate effectively and avoid predators.
- Pre-Release Conditioning:The turtle was gradually introduced to a larger, more natural environment, simulating the conditions it would encounter in the wild. This helped it acclimate to the temperature changes, currents, and other environmental factors.
Choosing the Release Location
Selecting the right release location is crucial for the turtle’s survival. The team considered several factors:
- Oceanographic Conditions:The chosen site was a location with favorable currents and water temperatures, ensuring the turtle could easily navigate towards warmer waters and potential feeding grounds.
- Distance from Shore:The release location was chosen at a distance from the coast, minimizing the risk of the turtle being re-stranded or encountering human activities.
- Historical Data:The team analyzed historical data on loggerhead turtle movements in the region, identifying areas where the turtle had the highest chance of encountering suitable habitat and prey.
Monitoring and Tracking, Injured loggerhead turtle found in cumbria released into wild
After the release, the team used various methods to monitor the turtle’s progress and gather valuable data:
- Satellite Tagging:A satellite tag was attached to the turtle’s shell, allowing researchers to track its movements in real-time. This provided insights into its migration patterns, feeding habits, and overall survival.
- Passive Acoustic Monitoring:Underwater listening devices were deployed in the release area to detect the turtle’s vocalizations. This technique helped researchers understand its communication patterns and interactions with other turtles.
- Citizen Science:The team encouraged members of the public to report any sightings of the turtle. This provided valuable information about its movements and potential encounters with other marine life.
The Significance of the Event
The discovery and release of a loggerhead turtle in Cumbria, an area far from its usual habitat, is not just a heartwarming story; it’s a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet and the vital importance of marine conservation.
This event serves as a stark reminder of the challenges faced by migratory species and highlights the need for collaborative efforts to protect these magnificent creatures.
The Importance of Loggerhead Turtle Conservation
The loggerhead turtle is classified as “endangered” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This event highlights the critical need for conservation efforts to ensure the survival of this species. Loggerhead turtles play a vital role in maintaining healthy marine ecosystems.
They are apex predators, contributing to the balance of marine food webs by controlling populations of jellyfish and other invertebrates.





