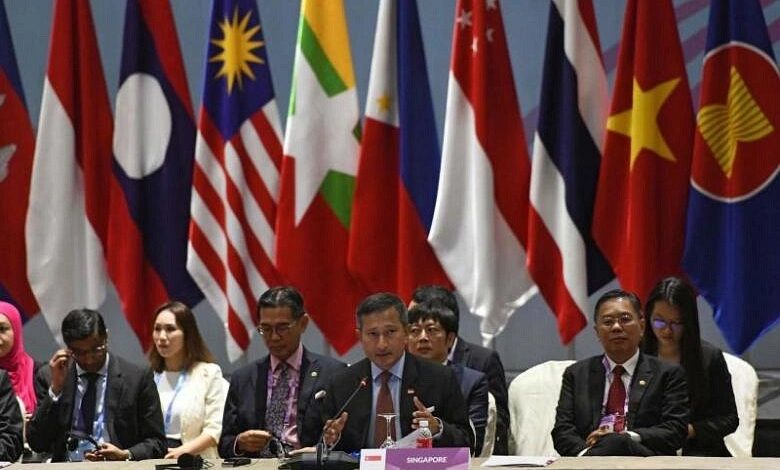
India Rejects Trade Deal, Accuses China of Opaque Practices
India rules out joining worlds largest trade deal accuses china of very opaque trade practices – India has made a bold move, rejecting the world’s largest trade deal and accusing China of employing “very opaque” trade practices. This decision sends shockwaves through the global trade landscape, raising questions about the future of international cooperation and the potential for economic friction between these two Asian giants.
India’s concerns center around the lack of transparency in China’s trade practices, which they believe unfairly disadvantage Indian businesses. The rejection of the trade deal highlights the complex dynamics at play, as India seeks to protect its economic interests while navigating the challenges of a rapidly evolving global trade environment.
Future of India-China Trade Relations

India’s accusations of opaque trade practices against China have significantly strained bilateral relations. These accusations, coupled with India’s decision to not join the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), raise serious questions about the future of trade relations between the two Asian giants.
The implications of this diplomatic rift are far-reaching, impacting not only economic growth but also geopolitical stability in the region.
Potential Implications of India’s Accusations
India’s accusations have cast a shadow over the future of trade relations between India and China. These accusations, if not addressed, could lead to a further deterioration of trust and cooperation, potentially hindering economic growth and collaboration.
Possible Strategies for India
India can adopt a multifaceted approach to address its concerns regarding China’s trade practices. This strategy could include:
- Strengthening Trade Monitoring and Enforcement:India needs to enhance its capacity to monitor and enforce trade regulations, including anti-dumping and anti-subsidy measures. This would help to deter unfair trade practices and protect domestic industries.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability:India should advocate for greater transparency and accountability in China’s trade practices. This could involve demanding access to relevant data, promoting dialogue on trade issues, and working with international organizations to establish clear norms and standards.
- Diversifying Trade Partners:India can mitigate its reliance on China by diversifying its trade partners. This can be achieved by forging stronger economic ties with other countries, such as Japan, South Korea, and the United States.
- Enhancing Domestic Manufacturing:India needs to focus on strengthening its domestic manufacturing base to reduce its reliance on imports from China. This requires investment in infrastructure, technology, and skill development.
Consequences of Strained Trade Relations
Strained trade relations between India and China could have significant consequences for both countries.
- Economic Slowdown:Reduced trade flows could hinder economic growth in both countries, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and services. This could lead to job losses and reduced investment.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Strained trade relations could exacerbate geopolitical tensions in the region. This could lead to increased military spending, border disputes, and regional instability.
- Missed Opportunities for Cooperation:Strained relations could hinder cooperation on issues of common concern, such as climate change, global health, and sustainable development. This would be a missed opportunity for both countries to address global challenges.
Trade Agreements and Economic Diplomacy: India Rules Out Joining Worlds Largest Trade Deal Accuses China Of Very Opaque Trade Practices

Trade agreements are the bedrock of global economic relations, facilitating trade, investment, and economic cooperation between countries. They serve as a framework for setting rules and regulations governing international trade, shaping the flow of goods, services, and capital across borders.
These agreements play a crucial role in fostering economic growth, reducing poverty, and promoting stability in the global economy.
Significance of Trade Agreements
Trade agreements play a vital role in shaping global economic relations by promoting free trade and reducing trade barriers. They establish clear rules for trade, investment, and intellectual property protection, creating a predictable and transparent environment for businesses to operate across borders.
- Reduced Trade Barriers:Trade agreements eliminate or reduce tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers, making it easier and cheaper for businesses to export and import goods and services.
- Increased Market Access:Trade agreements open up new markets for businesses, providing access to a wider range of consumers and suppliers.
- Investment Promotion:Trade agreements often include provisions that promote foreign direct investment, encouraging businesses to invest in new markets and create jobs.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms:Trade agreements typically include dispute resolution mechanisms, providing a framework for resolving trade disputes between countries.
- Economic Integration:Trade agreements can facilitate regional economic integration, leading to the creation of free trade areas, customs unions, and common markets.
Approaches to Trade Negotiations, India rules out joining worlds largest trade deal accuses china of very opaque trade practices
Trade negotiations involve complex discussions and compromises between countries with different economic interests. Different approaches to trade negotiations have emerged, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Bilateral Agreements:These agreements are negotiated between two countries and focus on specific areas of trade, such as agriculture, manufacturing, or services. They offer flexibility and allow for tailored solutions to address specific trade concerns.
- Regional Trade Agreements:These agreements are negotiated between a group of countries in a specific region and aim to promote free trade within the region. Examples include the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the European Union (EU).
- Multilateral Agreements:These agreements are negotiated between multiple countries and aim to establish global trade rules. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is a prime example, with its agreements covering trade in goods, services, and intellectual property.
Trade Agreement Negotiation Process
The negotiation process for trade agreements is a complex and multi-stage process involving various stakeholders. The following flowchart illustrates the key stages involved:
India’s decision to not join the world’s largest trade deal, citing China’s “very opaque trade practices,” raises concerns about transparency and fair competition. This comes at a time when questions are being raised about the extent of government surveillance, particularly with the recent news about the Pentagon possibly spying on Americans.
While the focus might be on trade deals and government surveillance, the bigger picture is about ensuring trust and accountability in a globalized world. Ultimately, India’s decision reflects a broader push for greater transparency and fairness in international trade, a sentiment that resonates with the concerns about potential government overreach.
India’s decision to stay out of the world’s largest trade deal, citing China’s “very opaque trade practices,” feels like a reflection of a larger global trend. It’s almost like a “this war is a fraud” this war is a fraud moment, where trust and transparency are being questioned.
This move by India raises concerns about the future of global trade, especially with China’s growing influence.
India’s decision to stay out of the world’s largest trade deal, citing China’s opaque trade practices, highlights the growing global tensions. This move, coupled with the ongoing war on journalism , paints a picture of a world where transparency and accountability are under constant pressure.
The lack of transparency in China’s trade practices, combined with the suppression of independent media, creates an environment where trust and collaboration are increasingly difficult to achieve.