Fighting Housing & Climate Crises: One Solution
How to fight the affordable housing and climate crises at once sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with personal blog style and brimming with originality from the outset.
The two crises, often seen as separate, are deeply intertwined. Rising temperatures and extreme weather events exacerbate housing insecurity, while inadequate housing contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. This creates a vicious cycle, where both problems worsen each other.
This blog explores innovative solutions that tackle both crises simultaneously. We’ll delve into sustainable housing designs, green urban planning, and policy changes that promote affordability and environmental responsibility. We’ll also discuss community engagement and the crucial role of investment in shaping a more just and sustainable future.
Sustainable Housing Solutions
The climate crisis and the need for affordable housing are intertwined challenges that demand innovative solutions. Sustainable housing design plays a crucial role in addressing both issues by creating homes that are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and accessible to a wider range of people.
Examples of Sustainable and Affordable Housing Designs
Sustainable and affordable housing designs prioritize energy efficiency, resource conservation, and affordability. Here are some examples:
- Passive Houses: These homes are designed to minimize energy consumption through careful orientation, insulation, and airtight construction. They often incorporate features like triple-paned windows, high-performance insulation, and heat recovery ventilation systems, reducing energy bills and carbon footprint.
- Zero-Energy Homes: These homes generate as much energy as they consume, typically through solar panels or other renewable energy sources. They offer a significant reduction in energy bills and reliance on fossil fuels, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run.
- Modular Homes: These homes are built off-site in factories and transported to the building site, reducing construction time and waste. They often feature prefabricated components and standardized designs, which can lead to cost savings and efficient construction.
- Tiny Houses: These small, compact homes prioritize sustainability by minimizing material usage and reducing energy consumption. They can be built with sustainable materials like bamboo and recycled wood, offering a more eco-friendly and affordable housing option.
Reducing Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint
Sustainable housing designs incorporate various strategies to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint:
- Efficient Insulation: Thick insulation layers in walls, ceilings, and floors help to prevent heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems.
- High-Performance Windows: Double or triple-paned windows with low-emissivity coatings minimize heat loss and gain, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Solar Water Heating: Solar panels can be used to heat water, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering energy bills.
- Efficient Appliances: Using Energy Star-rated appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers, can significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Smart Home Technologies: Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and other technologies can automate energy usage, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Benefits of Using Renewable Energy Sources in Housing Projects
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, offer numerous benefits for housing projects:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Renewable energy sources do not emit greenhouse gases, contributing to a cleaner environment and mitigating climate change.
- Lower Energy Costs: Once installed, renewable energy systems can generate electricity at a lower cost than traditional fossil fuel sources, reducing energy bills for homeowners.
- Energy Independence: Renewable energy sources can provide homes with a source of clean energy, reducing dependence on the grid and fossil fuel infrastructure.
- Increased Property Value: Homes with renewable energy systems often have a higher market value, making them a desirable investment for homeowners.
Urban Planning and Development
Urban planning plays a crucial role in addressing the intertwined challenges of affordable housing and climate change. By integrating sustainable development principles into urban design, we can create communities that are both environmentally resilient and socially equitable.
Sustainable Urban Development Strategies
Sustainable urban development strategies aim to create livable, equitable, and environmentally friendly cities. These strategies prioritize affordable housing, green spaces, and efficient transportation systems.
- Mixed-Income Housing Development:Integrating affordable housing units within market-rate developments ensures diverse communities and reduces spatial segregation. By providing a mix of housing options, cities can create a more inclusive and equitable living environment.
- Transit-Oriented Development:This approach promotes the development of high-density, mixed-use communities centered around public transportation hubs. This reduces reliance on private vehicles, minimizes traffic congestion, and encourages walking and cycling, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Adaptive Reuse:Reusing existing buildings for residential purposes can be a cost-effective way to create affordable housing options while preserving historic structures and minimizing the environmental impact of new construction.
- Green Building Standards:Implementing green building standards in new construction ensures energy efficiency, water conservation, and the use of sustainable materials, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint.
The Role of Green Spaces
Green spaces are vital for mitigating climate change and improving urban livability. They act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing greenhouse gases and mitigating the urban heat island effect.
- Urban Forests:Trees planted in urban areas absorb carbon dioxide, reduce air pollution, and provide shade, mitigating the urban heat island effect. They also improve air quality and create a more aesthetically pleasing environment.
- Green Roofs:Green roofs are vegetated surfaces on rooftops that help reduce stormwater runoff, improve insulation, and provide habitat for wildlife. They contribute to reducing the urban heat island effect and improving air quality.
- Parks and Open Spaces:Parks and open spaces offer recreational opportunities, enhance biodiversity, and provide a sense of community. They also contribute to climate change mitigation by absorbing carbon dioxide and reducing the urban heat island effect.
Public Transportation and Climate Change
Public transportation plays a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable urban development.
- Efficient and Accessible Systems:Investing in high-quality, reliable, and accessible public transportation systems encourages people to choose public transportation over private vehicles, reducing traffic congestion and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Electric Buses and Trains:Transitioning to electric buses and trains powered by renewable energy sources can significantly reduce transportation-related emissions and improve air quality.
- Bike-Friendly Infrastructure:Creating safe and dedicated bike lanes encourages cycling, reducing traffic congestion and promoting physical activity.
Creating Resilient Communities
Urban planning can create resilient communities that are less vulnerable to climate impacts.
- Flood Mitigation Measures:Incorporating flood mitigation measures such as green infrastructure, raised walkways, and stormwater retention ponds can protect communities from the impacts of increased rainfall and rising sea levels.
- Heat Island Mitigation:Implementing strategies to reduce the urban heat island effect, such as increasing tree canopy cover, using reflective surfaces, and promoting green roofs, can protect communities from extreme heat events.
- Disaster Preparedness and Response:Planning for disaster preparedness and response ensures communities are equipped to cope with extreme weather events and other climate-related hazards.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
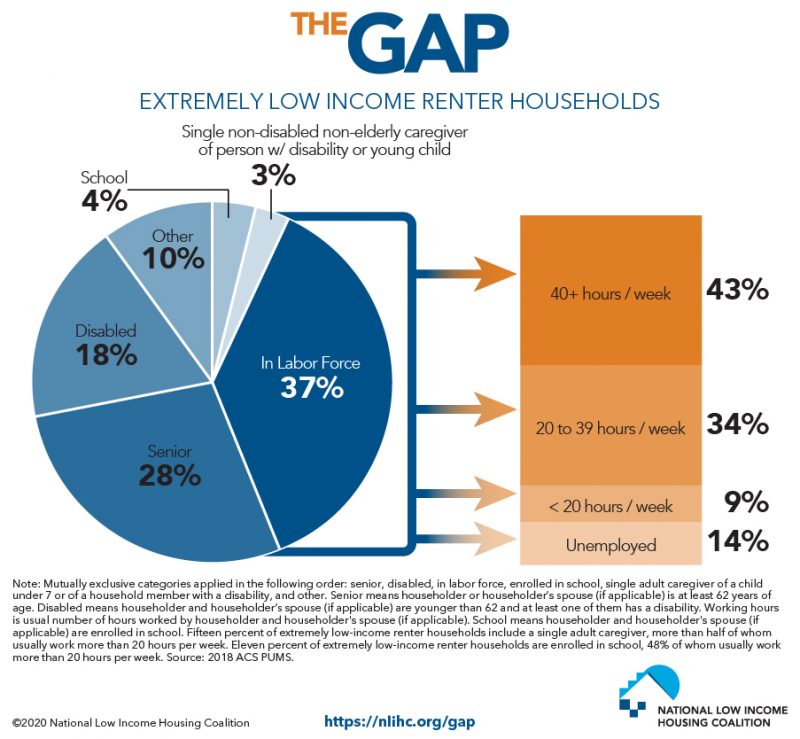
Effective policies and regulatory frameworks are crucial for promoting sustainable and affordable housing while mitigating the climate crisis. They can incentivize green building practices, encourage energy efficiency, and facilitate the development of resilient communities.
Incentives for Green Building and Energy Efficiency
Policies can play a significant role in promoting green building practices and energy efficiency. For instance, tax credits or rebates can be offered to developers and homeowners who incorporate sustainable features into their projects, such as solar panels, energy-efficient appliances, and water-saving fixtures.
Building codes can also be updated to mandate minimum energy performance standards for new construction and renovations. These measures can encourage widespread adoption of green building technologies, leading to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Government Investment in Affordable Housing and Renewable Energy
Government investment is essential for creating a more equitable and sustainable housing landscape. Funding for affordable housing projects can ensure that low- and moderate-income households have access to safe, healthy, and energy-efficient homes. Additionally, investing in renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar and wind farms, can lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
By prioritizing these investments, governments can create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Examples of Policies Promoting Sustainable and Affordable Housing
- Density Bonuses:These policies allow developers to build more units on a site if they incorporate certain sustainability features or set aside a percentage of units for affordable housing. This incentivizes developers to build denser, more sustainable communities.
- Property Tax Exemptions:Offering property tax exemptions or reductions to homeowners who make energy efficiency upgrades can encourage investment in sustainable improvements.
- Green Building Standards:Establishing and enforcing green building standards, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), can ensure that new construction meets minimum environmental performance requirements.
Community Engagement and Participation: How To Fight The Affordable Housing And Climate Crises At Once
Community engagement is crucial in tackling the intertwined challenges of affordable housing and climate change. When residents are involved in shaping solutions, they are more likely to support and implement them, leading to more effective and sustainable outcomes.
The Role of Community Organizations in Advocating for Affordable Housing and Climate Action
Community organizations play a vital role in advocating for affordable housing and climate action. They act as intermediaries between residents and policymakers, amplifying community voices and ensuring that their needs are considered in decision-making processes.
Solving the intertwined crises of affordable housing and climate change requires bold, innovative solutions. We need to look beyond traditional approaches and consider how to build resilient communities that prioritize sustainability and accessibility. It’s a complex challenge, but one that we can’t afford to ignore.
The recent hearings with former GOP lawmakers, as reported in this article , highlight the need for a unified front in addressing these issues, rather than clinging to divisive ideologies. Ultimately, finding common ground is essential if we want to create a future where everyone has a safe, affordable, and sustainable place to call home.
- Building Community Coalitions:Community organizations often form coalitions with other groups, including environmental organizations, housing advocates, and faith-based groups, to amplify their collective voice and increase their influence on policy decisions.
- Raising Awareness and Education:They educate communities about the interconnectedness of affordable housing and climate change, mobilizing residents to advocate for policies that address both issues.
- Organizing and Mobilizing Residents:Community organizations empower residents to engage in advocacy efforts, such as organizing rallies, petition drives, and meetings with elected officials.
- Providing Technical Assistance:They offer technical assistance to residents and developers, helping them navigate complex regulations and access funding opportunities for sustainable housing projects.
A Case Study: The East Harlem Neighborhood Action Plan
The East Harlem Neighborhood Action Plan in New York City exemplifies the power of community-driven initiatives in addressing affordable housing and climate change.
“The East Harlem Neighborhood Action Plan is a comprehensive community-based plan that aims to improve the quality of life for residents by addressing issues related to affordable housing, environmental sustainability, and economic development.”
Tackling the affordable housing and climate crises requires a multifaceted approach, and it’s important to remember that sometimes the things we focus on are just fleeting trends. Take, for instance, the recent news cycle surrounding the volatile cryptocurrency market, where headlines like “buy the rumour sell the news dogecoin erases recent gains” buy the rumour sell the news dogecoin erases recent gains capture our attention.
While these developments are intriguing, we need to remain grounded and focused on the long-term solutions that will truly address the pressing issues of affordable housing and climate change.
NYC Department of City Planning
- Community Engagement:The plan was developed through a collaborative process that involved extensive community engagement, including public meetings, workshops, and surveys. Residents were actively involved in identifying priorities, developing strategies, and evaluating progress.
- Sustainable Housing Solutions:The plan prioritized the creation of affordable housing that incorporates green building features, such as energy-efficient appliances, solar panels, and green roofs. This approach reduces energy consumption, lowers utility bills for residents, and contributes to a more sustainable built environment.
Finding solutions that address both the affordable housing and climate crises is a complex challenge, requiring innovative thinking and collaboration. The recent primary election in Idaho, where Governor Brad Little defeated his own Lieutenant Governor in a contentious race, as reported here , highlights the political divisions that can hinder progress on these critical issues.
It’s clear that we need leaders who are willing to work across party lines to find solutions that benefit all Idahoans, especially those struggling with housing affordability and the impacts of climate change.
- Climate Action:The plan included strategies to address climate change, such as promoting public transportation, improving energy efficiency in existing buildings, and creating green spaces. This comprehensive approach aims to mitigate the impacts of climate change and improve the overall health and well-being of the community.
Financing and Investment Opportunities

Financing sustainable and affordable housing projects is crucial for tackling both the housing affordability and climate crises. It requires a multi-pronged approach, leveraging diverse funding sources and innovative investment models.
Public Funding Sources
Public funding plays a vital role in supporting the development of sustainable and affordable housing. Governments at various levels can allocate funds through a variety of mechanisms.
- Direct Grants and Subsidies:These programs provide financial assistance to developers, non-profits, and individuals to cover construction costs, land acquisition, and other expenses associated with affordable housing projects.
- Tax Credits:Tax credits offer incentives to investors who contribute to affordable housing projects. These credits can reduce the tax liability of investors, making affordable housing investments more attractive.
- Low-Interest Loans:Government agencies often offer low-interest loans to developers and homeowners to make affordable housing more accessible.
- Land Use Regulations:Local governments can use zoning regulations and density bonuses to encourage the development of affordable housing projects in strategic locations.
Green Bonds and Impact Investing
Green bonds and impact investing are emerging financial instruments that can channel capital towards sustainable and affordable housing projects.
Green Bonds
Green bonds are debt securities that are specifically issued to finance projects with environmental benefits. They offer investors the opportunity to contribute to sustainable development while earning a return on their investment.
Green bonds can be used to fund projects that improve energy efficiency, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote sustainable materials in housing construction.
Impact Investing
Impact investing focuses on generating both financial returns and positive social and environmental impact. Investors seek to align their investments with their values, contributing to solutions for social and environmental challenges.
Impact investments in affordable housing can support projects that address housing affordability, energy efficiency, and community development.
Private Sector Partnerships, How to fight the affordable housing and climate crises at once
Private sector partnerships are essential for leveraging the expertise and resources of businesses in developing sustainable and affordable housing.
- Real Estate Developers:Private developers can contribute land, construction expertise, and project management skills to affordable housing projects.
- Financial Institutions:Banks and other financial institutions can provide loans, mortgages, and other financial products to support affordable housing development.
- Corporate Social Responsibility Programs:Many corporations have established corporate social responsibility programs that allocate resources to social causes, including affordable housing.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements play a crucial role in tackling the dual crises of affordable housing and climate change. By embracing innovative solutions, we can create more sustainable and cost-effective housing options, leading to a more equitable and environmentally responsible future.
Smart Homes and Energy-Efficient Appliances
Smart homes and energy-efficient appliances offer significant potential for reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions in residential buildings. These technologies can optimize energy usage based on real-time data and user preferences, leading to substantial cost savings and a reduced environmental footprint.
- Smart thermostatslearn occupant preferences and adjust heating and cooling systems accordingly, minimizing energy waste. For example, Nest Learning Thermostat, a popular smart thermostat, can automatically adjust temperatures based on user behavior and weather conditions, resulting in up to 15% energy savings.
- Energy-efficient appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and dishwashers, use less energy to operate, contributing to lower energy bills and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, Energy Star-rated appliances typically use 10-50% less energy than standard models.
- Smart lighting systemsautomatically adjust lighting levels based on natural light and occupancy, reducing energy consumption and extending the lifespan of bulbs. Philips Hue, a popular smart lighting system, allows users to control lighting remotely and schedule personalized lighting routines, resulting in significant energy savings.
Sustainable Building Materials
The construction industry has a significant impact on the environment, with traditional building materials often contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and resource depletion. Sustainable building materials offer an alternative, promoting environmental responsibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Recycled materials, such as recycled plastic, glass, and wood, offer a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to virgin materials. For example, using recycled concrete aggregates in construction can significantly reduce the embodied carbon footprint of buildings.
- Bio-based materials, derived from renewable sources like plants and agricultural waste, provide a sustainable and often biodegradable alternative to traditional materials. For instance, bamboo, a fast-growing and renewable resource, can be used as a structural material in construction, offering a lightweight and sustainable option.
- Cross-laminated timber (CLT), a wood-based panel material, offers a sustainable and high-performance alternative to concrete and steel. CLT panels are prefabricated off-site, reducing construction time and waste on-site, and contribute to a more efficient and sustainable building process.
Epilogue
By tackling the affordable housing and climate crises together, we can create a world where everyone has access to safe, affordable, and environmentally sustainable homes. It’s a challenging task, but by embracing innovative solutions, fostering collaboration, and prioritizing a just and equitable approach, we can build a better future for all.