Europes Economy: Defying Prophecies, Facing Chinas Trade
Europes economy survived terrible prophecies but must now tackle trade with china eus gentiloni – Europe’s economy survived terrible prophecies but must now tackle trade with China, EU’s Gentiloni. The continent has weathered storms, proving its resilience in the face of dire predictions. From the 2008 financial crisis to the recent pandemic, Europe has shown remarkable adaptability.
However, a new challenge looms on the horizon: navigating the complex landscape of trade with China. This dynamic relationship presents both opportunities and risks for the European economy, and it is a pivotal issue for the EU’s economic future.
The EU and China are intertwined in a vast web of economic connections, with trade flows exceeding €800 billion annually. China is a major market for European goods, while Europe is a significant source of technology and investment for China.
However, this intricate relationship is increasingly complicated by geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and concerns over China’s economic practices.
Europe’s Economic Resilience
Europe’s economy has faced its share of challenges in recent years. From the global financial crisis of 2008 to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the continent has weathered a storm of economic headwinds. Despite these trials, Europe has demonstrated remarkable resilience, defying many of the dire predictions that were made.
This article explores the factors contributing to Europe’s economic resilience and examines how its performance has exceeded expectations.
Europe’s economy has weathered storms, defying dire predictions. Now, the continent faces the challenge of navigating trade relations with China, a task EU Commissioner Gentiloni is tackling head-on. While economic anxieties persist, there’s some good news for consumers: Tesco has announced price drops on popular treats like Quality Street, Cadbury, and Lindt , offering a sweet respite amidst global economic uncertainty.
As Europe navigates these complex challenges, finding balance between economic stability and consumer affordability will be crucial.
Factors Contributing to Europe’s Economic Resilience
The resilience of the European economy can be attributed to a number of key factors.
- Strong Institutions:Europe’s robust institutional framework, including the European Central Bank (ECB) and the European Union (EU), has played a crucial role in stabilizing the economy during turbulent times. The ECB’s monetary policy measures, such as quantitative easing, have helped to stimulate growth and keep inflation under control.
The EU’s fiscal rules and regulations have also contributed to maintaining financial stability.
- Diversified Economy:Europe boasts a diverse economic landscape, with a wide range of industries and sectors. This diversification has helped to cushion the impact of shocks to specific industries. For example, while the automotive sector faced significant challenges during the pandemic, other sectors, such as technology and healthcare, continued to perform well.
- Innovation and Technology:Europe has been a leader in innovation and technology, particularly in areas such as renewable energy, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace. These sectors have fueled economic growth and created new opportunities.
- Strong Social Safety Nets:European countries have extensive social safety nets, including unemployment benefits, healthcare, and education. These programs provide a safety cushion for individuals and families during economic downturns, helping to maintain consumer spending and overall economic stability.
Europe’s Economic Performance
Despite the challenges it has faced, Europe’s economic performance has exceeded expectations in recent years.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery:Europe’s economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic has been faster than many analysts predicted. The continent’s vaccination rollout, coupled with government support measures, helped to revive economic activity.
- Strong Growth Prospects:The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts that the Eurozone economy will grow by 2.7% in 2023, reflecting continued resilience and strong growth prospects.
- Low Unemployment:Unemployment rates in many European countries have fallen to record lows, indicating a healthy labor market and strong economic activity.
Navigating Trade with China: Europes Economy Survived Terrible Prophecies But Must Now Tackle Trade With China Eus Gentiloni
The relationship between the European Union and China is complex and multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of economic, political, and strategic dimensions. Trade is a key pillar of this relationship, with both sides heavily reliant on each other for goods and services.
While the EU is China’s largest trading partner, China is the EU’s second-largest trading partner after the United States. This dynamic relationship presents both opportunities and challenges for both sides.The EU and China have a long history of trade relations, dating back to the early days of the European Economic Community.
In recent years, bilateral trade has grown significantly, driven by China’s rapid economic development and the EU’s increasing demand for Chinese goods. However, this relationship has also been marked by tensions and disagreements, particularly over issues such as market access, intellectual property rights, and fair competition.
Challenges and Opportunities in EU-China Trade, Europes economy survived terrible prophecies but must now tackle trade with china eus gentiloni
Navigating the complex landscape of EU-China trade requires a nuanced understanding of the key challenges and opportunities that exist. These challenges and opportunities are interconnected and influence the overall dynamics of the relationship.
Challenges
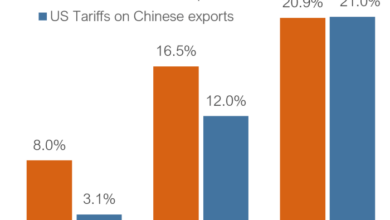
- Market Access:The EU has long complained about restricted market access in China, citing concerns about discriminatory practices and barriers to entry for European companies. This includes sectors like automotive, chemicals, and financial services.
- Intellectual Property Rights:Protection of intellectual property rights is a major concern for the EU, as Chinese companies are often accused of infringing on patents and trademarks. This can discourage European companies from investing in China and hinder innovation.
- State-Led Economy:China’s state-led economic model, with its emphasis on government intervention and subsidies, raises concerns about fair competition. European businesses argue that this creates an uneven playing field, making it difficult to compete with Chinese companies.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Growing geopolitical tensions between the EU and China, particularly over issues like human rights, Taiwan, and the South China Sea, have cast a shadow over trade relations. These tensions can lead to political pressure on businesses and affect investment decisions.
Europe’s economy has defied dire predictions and emerged stronger than expected, but the looming challenge of navigating trade relations with China remains a major concern. The EU’s economic future hinges on finding a delicate balance in this relationship, and Paolo Gentiloni’s role as EU Economic Commissioner will be crucial in this regard.
While Europe grapples with these economic complexities, it’s a good reminder that sometimes, the best way to handle difficult situations is to take a break and focus on something else, like the thrilling victories of Frances Tiafoe and Taylor Fritz at the US Open, or the return of a star player to the San Francisco 49ers, as reported in this article.
Ultimately, Europe’s economic resilience and the excitement of sporting events highlight the diverse facets of our world and the need for a balanced perspective.
Opportunities
- Market Size:China’s vast domestic market offers significant opportunities for European businesses, particularly in sectors like consumer goods, infrastructure, and technology. The growing middle class in China is a key driver of demand for European products.
- Investment Potential:China’s continued economic growth presents attractive investment opportunities for European companies. This includes investing in manufacturing facilities, research and development, and infrastructure projects.
- Technological Collaboration:The EU and China have complementary strengths in technology, offering potential for collaboration in areas like renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology. This collaboration can drive innovation and economic growth for both sides.
- Sustainable Development:The EU and China share a common interest in promoting sustainable development. This includes tackling climate change, promoting green technologies, and fostering responsible business practices. Trade can play a role in advancing these shared goals.
Impact of China’s Economic Growth on the European Economy
China’s economic growth has had a significant impact on the European economy, both positive and negative. This impact is multifaceted and can be analyzed from various perspectives.
Positive Impact
- Increased Trade:China’s economic growth has led to a surge in trade between the EU and China, benefiting European exporters. This has helped to create jobs and boost economic activity in sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and services.
- Investment Opportunities:China’s rapid development has attracted significant European investment, creating opportunities for businesses to expand their operations and tap into the growing Chinese market.
- Technological Advancements:China’s advancements in technology, particularly in areas like renewable energy and artificial intelligence, have created opportunities for collaboration and knowledge sharing with the EU.
Negative Impact
- Competition:China’s emergence as a global economic powerhouse has led to increased competition for European businesses, particularly in manufacturing and export markets. This can put pressure on prices and profits.
- Job Losses:Some European businesses have faced job losses as they relocate production to China to take advantage of lower labor costs and government incentives. This has raised concerns about deindustrialization in Europe.
- Trade Deficits:The EU has a significant trade deficit with China, meaning that it imports more goods from China than it exports. This can put pressure on the balance of payments and affect economic growth.
Gentiloni’s Role in EU-China Relations
Paolo Gentiloni, the EU Commissioner for the Economy, plays a crucial role in shaping the EU’s approach to trade with China. His insights and strategies are essential for navigating the complex economic landscape of the 21st century, where China’s growing influence presents both challenges and opportunities for the European Union.
Gentiloni’s Perspectives on China’s Economic Influence
Gentiloni acknowledges the significant economic influence China has gained globally. He recognizes that China’s economic growth has led to increased trade and investment opportunities for European businesses, but also highlights the need to address potential risks and imbalances. Gentiloni emphasizes the importance of ensuring fair competition and a level playing field for European companies operating in the Chinese market.
Europe’s economy has weathered storms, defying dire predictions. Now, the focus shifts to navigating the complex landscape of trade with China, as EU Commissioner Gentiloni emphasizes. This calls for strategic partnerships, like the one highlighted by Amazon’s 8 billion pound investment in UK cloud and AI infrastructure , which could bolster Europe’s digital competitiveness and contribute to a more robust economic future.
Ultimately, navigating these global challenges requires a blend of resilience and forward-thinking, ensuring Europe remains a key player in the evolving world economy.
Strategies for Managing EU-China Trade Relations
Gentiloni advocates for a multifaceted approach to managing EU-China trade relations, encompassing both cooperation and competition. He emphasizes the need for a balanced strategy that promotes collaboration on areas of shared interest, such as climate change and sustainable development, while simultaneously addressing concerns regarding unfair trade practices and market access.
Gentiloni has proposed several strategies for navigating this complex relationship:
- Strengthening the EU’s internal market:Gentiloni believes that a strong and unified European market is crucial for ensuring the competitiveness of European businesses in the face of China’s economic rise. This involves promoting innovation, fostering a favorable business environment, and enhancing the EU’s ability to attract foreign investment.
- Promoting fair trade practices:Gentiloni stresses the importance of addressing unfair trade practices, such as forced technology transfer and intellectual property theft. He supports efforts to ensure that European businesses have access to the Chinese market on equal terms and that Chinese companies comply with international trade rules.
- Deepening economic cooperation:While addressing trade concerns, Gentiloni also advocates for expanding areas of economic cooperation with China. This includes working together on global challenges like climate change, promoting sustainable development, and fostering innovation in areas like renewable energy and digital technologies.
- Strengthening multilateral institutions:Gentiloni believes that strengthening multilateral institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO) is crucial for managing trade relations with China. He advocates for reforming the WTO to address current challenges and ensure a fair and rules-based global trading system.
Future of EU-China Trade

The relationship between the EU and China is one of the most important economic partnerships in the world. Despite the current geopolitical tensions, there is still significant potential for growth in EU-China trade. This is driven by the increasing demand for goods and services from both sides, and the ongoing efforts to strengthen economic cooperation.
Potential for Growth in EU-China Trade
The EU is China’s largest trading partner, and China is the EU’s second-largest trading partner. The volume of trade between the two has been steadily increasing in recent years. In 2021, the total value of bilateral trade reached €756 billion, representing a significant increase from €405 billion in
This growth is expected to continue in the future, driven by several factors, including:
- Increasing demand for goods and services: China’s growing middle class is driving demand for consumer goods, while the EU’s need for manufacturing components and raw materials is fueling demand for Chinese exports.
- Stronger economic ties: The EU and China are increasingly cooperating on economic issues, including through the EU-China Comprehensive Agreement on Investment (CAI), which aims to create a more level playing field for businesses from both sides.
- Technological advancements: The increasing adoption of digital technologies is creating new opportunities for trade in areas such as e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and green technologies.
Areas of Potential Cooperation and Collaboration
The EU and China have a wide range of areas where they can cooperate and collaborate to benefit both economies. Some key areas include:
- Green technologies: Both the EU and China are committed to tackling climate change, and there is significant potential for cooperation in areas such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable transportation.
- Digital technologies: The EU and China can work together to develop common standards for digital technologies, promote cybersecurity, and foster innovation in areas such as artificial intelligence and blockchain.
- Infrastructure development: China’s Belt and Road Initiative and the EU’s Global Gateway initiative offer opportunities for collaboration on infrastructure projects, particularly in developing countries.
- Research and development: The EU and China can share knowledge and expertise in areas such as scientific research, technological innovation, and education.
Implications of Geopolitical Tensions for EU-China Trade Relations
The ongoing geopolitical tensions between the EU and China, particularly in areas such as human rights, security, and technology, are creating challenges for trade relations. These tensions have led to:
- Increased scrutiny of Chinese investments in the EU: The EU has become more cautious about Chinese investments, particularly in strategic sectors such as technology and infrastructure.
- Trade disputes: The EU and China have been involved in several trade disputes, including over market access, intellectual property rights, and subsidies.
- Concerns about unfair trade practices: The EU has expressed concerns about China’s use of unfair trade practices, such as forced technology transfer and state subsidies.
“The EU and China have a complex and multifaceted relationship. It is important to recognize that both sides have common interests in areas such as trade, climate change, and global security. However, there are also significant differences in values and approaches, which can create tensions. It is crucial for both sides to manage these differences constructively and to work towards a mutually beneficial relationship.”
European Commission
Europe’s Economic Outlook
Europe’s economic outlook remains uncertain, with a mix of positive and negative factors influencing its trajectory. While the region has demonstrated resilience in the face of recent challenges, several key issues continue to shape its economic performance.
Current Economic Performance
The European economy has shown signs of recovery in recent quarters, supported by robust consumer spending and a rebound in industrial activity. The Eurozone’s GDP grew by 0.3% in the second quarter of 2023, demonstrating resilience despite the ongoing geopolitical tensions and inflationary pressures.
However, the growth remains fragile and subject to significant downside risks.
Key Factors Influencing Europe’s Economic Performance
- Inflation:Persistent inflation remains a major concern for European economies. While inflation rates have eased somewhat from their peak, they remain elevated, eroding consumer purchasing power and impacting business profitability. The European Central Bank (ECB) has implemented a series of interest rate hikes to combat inflation, but the full impact of these measures is yet to be seen.
- Energy Crisis:The ongoing energy crisis, triggered by the war in Ukraine, continues to weigh heavily on European economies. High energy prices have increased business costs and squeezed household budgets. The EU has implemented measures to reduce its reliance on Russian energy, but these efforts are likely to take time to bear fruit.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The war in Ukraine has significantly disrupted global supply chains and contributed to heightened economic uncertainty. The conflict has also led to increased defense spending, diverting resources away from other economic priorities.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine have exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, leading to shortages and price increases. These disruptions continue to impact European businesses and consumers, contributing to inflation and hindering economic growth.
Impact of Global Economic Trends
Global economic trends, such as the slowdown in China’s economy and the ongoing monetary tightening by major central banks, are likely to have a significant impact on Europe’s economic performance. A slowdown in global demand could reduce exports from European countries, impacting their economic growth.
Additionally, rising interest rates in major economies could make it more expensive for European businesses to borrow money, hindering investment and economic activity.