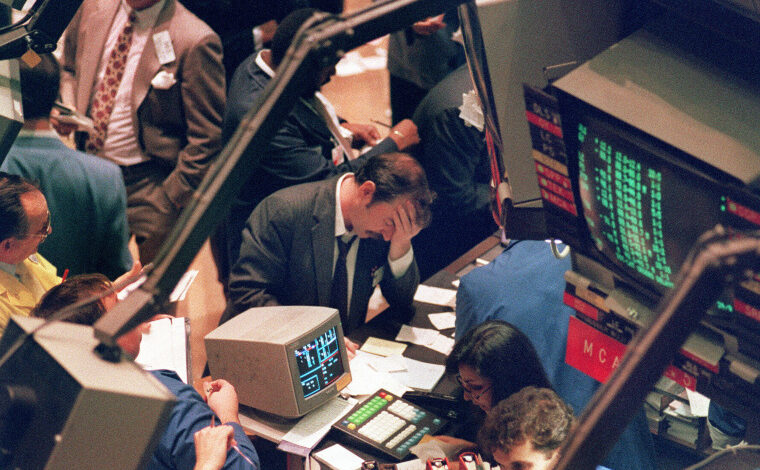
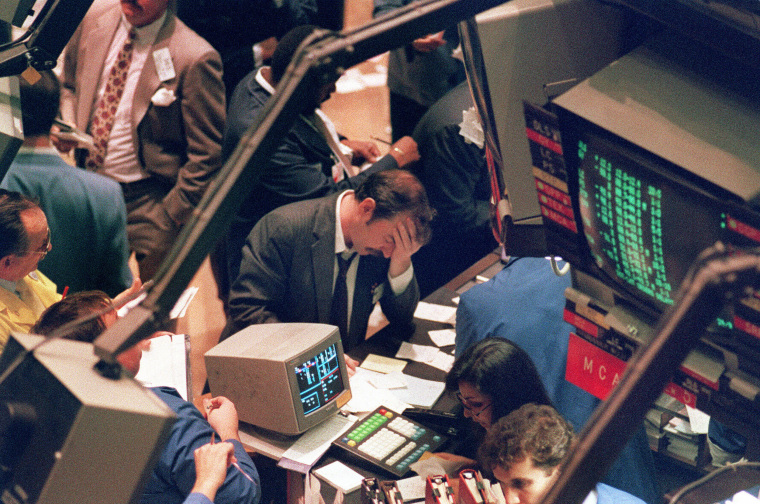
E. Gerald Corrigan, Who Helped Ease 87 Stock Crash, Dies at 80
E gerald corrigan who helped ease 87 stock crash dies at 80 – E. Gerald Corrigan, who helped ease the 1987 stock market crash, dies at 80. Corrigan, a prominent figure in the world of finance, was known for his calm demeanor and strategic thinking during turbulent times. He served as the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York from 1980 to 1993, a period marked by significant economic challenges, including the infamous “Black Monday” crash.
Corrigan’s role in navigating the aftermath of the 1987 crash cemented his legacy as a key player in the financial world. He is credited with calming market fears and preventing a full-blown financial meltdown. His actions and leadership during this crisis set a precedent for future financial regulators in their approach to market volatility.
Gerald Corrigan’s Life and Career
Gerald Corrigan, a prominent figure in the world of finance, was known for his impactful leadership and contributions to the Federal Reserve. His career spanned several decades, marked by a deep understanding of financial markets and a commitment to maintaining economic stability.
Early Life and Education
Gerald Corrigan was born in 1941 and grew up in New York City. He pursued his higher education at Dartmouth College, graduating in 1963 with a degree in economics. Following this, he went on to earn a Master’s degree in economics from the University of Michigan in 1965.
Career Path Leading to the Federal Reserve
Corrigan’s career began at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York in 1965, where he worked as a research economist. His keen analytical skills and understanding of financial markets quickly earned him recognition, leading to his promotion to vice president in 1978.
The passing of E. Gerald Corrigan, the former head of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York who played a key role in calming the markets during the 1987 stock crash, reminds us of the importance of strong leadership in times of crisis.
His legacy, however, is overshadowed by the current political climate, where the January 6th Committee is set to unveil a mountain of new evidence in its first televised hearing, hoping to shock the nation. This hearing is sure to be a defining moment in American history, and it’s a stark contrast to the quiet, yet impactful work of individuals like Corrigan, who worked behind the scenes to maintain stability during a turbulent time.
During his tenure at the New York Fed, he played a pivotal role in developing and implementing monetary policy strategies.
Contributions and Achievements at the Federal Reserve
Corrigan’s rise within the Federal Reserve continued, culminating in his appointment as president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York in 1980. His leadership during this period was marked by several key contributions and achievements.
Addressing the 1987 Stock Market Crash
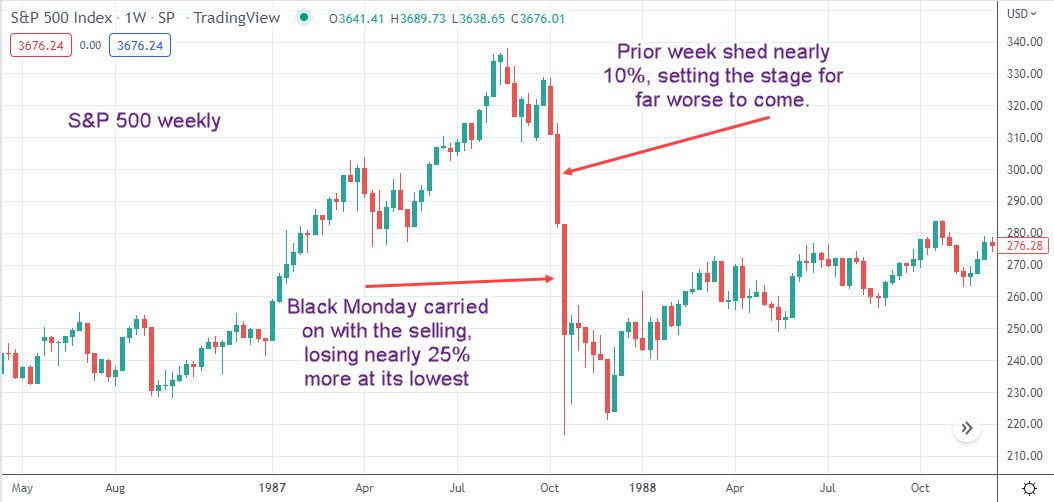
Corrigan’s ability to navigate financial crises was evident during the 1987 stock market crash, known as “Black Monday.” This event witnessed a sharp and sudden decline in stock prices, causing widespread panic and uncertainty in the financial markets. Corrigan’s swift and decisive actions, including injecting liquidity into the market and coordinating with other central banks, helped to stabilize the situation and prevent a larger economic downturn.
Leadership Style and Impact
Corrigan’s leadership style was characterized by his analytical approach, his deep understanding of financial markets, and his commitment to transparency and communication. He believed in building consensus among policymakers and engaging with the public to explain the Federal Reserve’s actions and policies.
Impact on the Federal Reserve’s Operations and Policies
Corrigan’s leadership had a significant impact on the Federal Reserve’s operations and policies. He advocated for a more proactive approach to monetary policy, emphasizing the importance of pre-emptive measures to address potential economic risks. He also played a key role in the development of new financial instruments and regulations to enhance the stability of the financial system.
The 1987 Stock Market Crash and Corrigan’s Response: E Gerald Corrigan Who Helped Ease 87 Stock Crash Dies At 80

The 1987 stock market crash, also known as Black Monday, was a significant event in global financial history. It marked the largest single-day decline in the history of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, plummeting over 22% in a single trading session.
The crash had a profound impact on the global financial system, causing widespread panic and uncertainty among investors.
Events Leading Up to the Crash
Several factors contributed to the 1987 stock market crash, including:
- Rising Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve, under the leadership of Alan Greenspan, had been raising interest rates throughout 1986 and 1987 to combat inflation. Higher interest rates made it more expensive for companies to borrow money, leading to slower economic growth and a decline in corporate profits.
- Excessive Speculation:The stock market was experiencing a period of high speculation, with many investors buying stocks on margin, meaning they were borrowing money to purchase shares. This created a bubble, where stock prices were inflated beyond their true value.
- Program Trading:Program trading, which involves the use of computer algorithms to buy and sell large blocks of stocks, contributed to the rapid decline in prices on Black Monday. These programs were designed to take advantage of market volatility, but they ended up amplifying the crash.
Corrigan’s Response to the Crash
Gerald Corrigan, as the President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, played a crucial role in stabilizing the financial markets during the 1987 crash. His actions and strategies included:
- Communication with Market Participants:Corrigan communicated with major financial institutions, assuring them that the Federal Reserve was prepared to provide liquidity to the markets if necessary. This helped to calm fears and prevent a liquidity crisis.
- Open Market Operations:The Federal Reserve engaged in open market operations, buying U.S. Treasury securities to inject liquidity into the financial system. This helped to lower interest rates and ease the pressure on financial institutions.
- Coordination with Other Central Banks:Corrigan worked closely with central banks around the world to coordinate their responses to the crash. This helped to prevent a global financial meltdown.
Effectiveness of Corrigan’s Response
Corrigan’s actions were widely praised for their effectiveness in preventing a major financial crisis. His communication with market participants helped to restore confidence, while his open market operations provided the necessary liquidity to stabilize the markets. The coordination with other central banks ensured that the crash did not trigger a global financial meltdown.
Corrigan’s Legacy and Impact on Financial Markets
Gerald Corrigan’s impact on the financial markets extended far beyond his role in navigating the 1987 stock market crash. His contributions to the Federal Reserve and his insights into financial stability left a lasting mark on how policymakers and market participants understand and manage risk.
Key Lessons from the 1987 Crash
Corrigan’s experience during the 1987 crash provided valuable lessons for managing financial crises. He emphasized the importance of transparency, communication, and decisive action by central banks. His approach, which focused on providing liquidity and reassuring markets, was instrumental in preventing the crash from spiraling into a full-blown financial meltdown.
It’s a strange juxtaposition, isn’t it? The passing of E. Gerald Corrigan, a figure who helped calm the turbulent waters of the 1987 stock market crash, coincides with the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, as exemplified by the recent news that “buy the rumour, sell the news” is playing out with Dogecoin erasing its recent gains ( buy the rumour sell the news dogecoin erases recent gains ).
Corrigan’s legacy of stability and measured action in the face of crisis stands in stark contrast to the wild swings and meme-driven sentiment that characterize the crypto market. It’s a reminder that even as we move forward with new technologies, the fundamentals of risk management and sound financial practices remain timeless.
Corrigan’s actions demonstrated the crucial role of central banks in maintaining financial stability and preventing systemic risks.
“The central bank must be prepared to act decisively and decisively in the face of a crisis, and it must be willing to take the necessary steps to restore confidence in the financial system.”
Gerald Corrigan
Corrigan’s Approach to Crisis Management
Corrigan’s approach to crisis management was characterized by a strong emphasis on transparency, communication, and decisive action. He believed that central banks should be open and honest with the public about the challenges they face, and that they should take swift and decisive action to address those challenges.
This approach was in contrast to some other central bankers who preferred a more hands-off approach to crisis management.
Comparison with Other Central Bankers
Corrigan’s approach to crisis management was often compared to that of other central bankers, such as Alan Greenspan, who was then the chairman of the Federal Reserve. While Greenspan was known for his more cautious and gradualist approach, Corrigan favored a more proactive and interventionist approach.
This difference in style reflected their different views on the role of central banks in managing financial crises.
The passing of E. Gerald Corrigan, the former Federal Reserve Bank of New York president who helped calm the markets during the 1987 stock market crash, reminds us of the importance of steady leadership in times of crisis. It also makes me wonder if legendary investors like Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger saw the same problem that I outlined in my recent analysis, analysis did buffett and munger see byds one problem , regarding BYD’s growth trajectory.
Corrigan’s legacy of stability serves as a valuable lesson for navigating volatile markets, a lesson that applies to both seasoned investors and those just starting out.
Corrigan’s Legacy, E gerald corrigan who helped ease 87 stock crash dies at 80
Corrigan’s legacy is one of a pragmatic and principled leader who understood the importance of financial stability and the role of central banks in maintaining it. His contributions to the Federal Reserve and his insights into financial crises continue to inform policymakers and market participants today.
The Current State of Financial Regulation and Risk Management
The 1987 stock market crash, a stark reminder of the fragility of financial markets, served as a catalyst for significant changes in financial regulation and risk management. While the regulatory landscape has evolved considerably since then, the lessons learned from this event remain highly relevant in navigating the complexities of modern financial systems.
The Effectiveness of Current Regulatory Frameworks
The aftermath of the 1987 crash saw the introduction of numerous regulatory measures aimed at enhancing market stability and mitigating systemic risk. The most notable among these include the establishment of the Basel Accords, which introduced capital adequacy requirements for banks, and the creation of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which oversees the US stock market.
These regulations have played a crucial role in reducing the likelihood of another crash of similar magnitude. However, the effectiveness of these frameworks is not without its limitations. The global financial crisis of 2008 demonstrated that even with stringent regulations in place, complex financial instruments and interconnectedness within the global financial system can lead to unforeseen vulnerabilities.
Challenges and Opportunities for Financial Regulators
Financial regulators in the 21st century face an array of challenges in their efforts to maintain financial stability. The rapid evolution of financial technology, the rise of non-bank financial institutions, and the increasing interconnectedness of global markets have introduced new complexities and potential sources of risk.
Furthermore, the ongoing threat of cyberattacks and the potential for geopolitical events to trigger market disruptions pose significant challenges to effective regulation. Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities for regulators to leverage technological advancements and data analytics to improve their understanding of market dynamics and enhance their ability to identify and manage risks.
The development of sophisticated risk management models, the use of real-time data analysis, and the adoption of innovative regulatory tools can play a crucial role in mitigating future financial crises.
Closing Notes
Corrigan’s passing marks the end of an era in finance. He was a true leader who navigated complex economic situations with a blend of intellect and pragmatism. His contributions to the Federal Reserve and his role in stabilizing the financial markets during the 1987 crash will be remembered for years to come.
His legacy serves as a reminder of the critical role that central banks play in maintaining financial stability, and his approach to crisis management continues to inform the practices of financial regulators today.