Consumer Confidence Slumps After Budget Warnings
Consumer confidence slumps following warnings of tough choices in budget ahead are casting a shadow over the economic landscape. As the government grapples with rising inflation and potential economic uncertainty, consumers are feeling the pinch, leading to a decline in spending and a sense of unease about the future.
This shift in consumer sentiment has far-reaching implications, impacting everything from retail sales to business investment.
The recent warnings of tough choices in the upcoming budget have further fueled anxieties among consumers. With the prospect of higher taxes, reduced government spending, or other measures aimed at controlling the deficit, many are bracing for a period of economic hardship.
This uncertainty is leading to a more cautious approach to spending, as consumers prioritize essential needs and delay discretionary purchases.
Economic Context
The recent slump in consumer confidence, following warnings of tough choices in the upcoming budget, reflects a growing sense of economic uncertainty. While the economy has shown signs of resilience in recent months, several factors point to potential headwinds in the near future.
It’s a rough time for everyone right now, with warnings of tough choices in the budget ahead causing consumer confidence to slump. But amidst the economic anxieties, it seems even the internet can’t escape the doom and gloom. Fans of the band Bad Omens are freaking out over a cryptic new post on their social media, bad omens fans freaking out over newest post , leaving many wondering what it all means.
Maybe we should all take a cue from the Bad Omens fans and focus on the things we can control, like finding ways to weather the financial storm ahead.
Inflation and Interest Rates
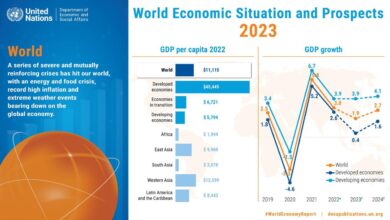
Inflation remains a key concern, with consumer prices continuing to rise at a significant pace. This has eroded purchasing power and forced consumers to cut back on discretionary spending. The central bank has been raising interest rates to combat inflation, which has increased borrowing costs for businesses and individuals, further dampening economic activity.
Unemployment and Job Market
The unemployment rate has remained relatively low, indicating a strong job market. However, recent data suggests that job growth is slowing, and some sectors are experiencing layoffs. This could lead to a decline in consumer confidence as people become more concerned about their job security and future income.
Government Budget and Spending Cuts
The government has warned of tough choices in the upcoming budget, which could include spending cuts and tax increases. These measures are aimed at reducing the budget deficit and controlling government debt. However, they are likely to have a negative impact on consumer spending and economic growth.
Historical Comparisons
The current economic situation bears some resemblance to previous periods of economic uncertainty, such as the global financial crisis of 2008-2009. While the current economic outlook is not as dire, the combination of high inflation, rising interest rates, and potential government spending cuts creates a challenging environment for consumers and businesses alike.
Consumer Confidence
Consumer confidence is a crucial indicator of economic health. It reflects the overall sentiment of consumers regarding the economy and their willingness to spend. A high level of consumer confidence indicates a positive outlook on the economy, leading to increased spending and economic growth.
Conversely, low consumer confidence signals a pessimistic view, resulting in reduced spending and potentially slower economic growth.
Factors Contributing to the Decline in Consumer Confidence
The recent decline in consumer confidence can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Inflation:The persistent rise in inflation has eroded purchasing power and reduced consumer confidence. High inflation erodes the value of savings and makes it more expensive for consumers to buy goods and services, leading to a decline in their spending power.
It’s tough to stay optimistic when the government is warning of tough choices ahead. The news is filled with stories of rising prices and shrinking budgets, and it’s easy to see why consumer confidence is taking a hit. It’s like that old saying, “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it.” But then you read something like this article, guantanamo maybe none of them are terrorists , and you realize that sometimes the things we think are “fixed” might not be so fixed after all.
It’s a sobering reminder that even when times are tough, there are still things worth fighting for, and maybe, just maybe, we can find a way to make things better.
For instance, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in the United States rose by 6.4% in January 2023, highlighting the ongoing inflationary pressures on consumers.
- Rising Interest Rates:The Federal Reserve has been aggressively raising interest rates to combat inflation. This has increased borrowing costs for consumers, making it more expensive to finance purchases such as homes, cars, and other major expenditures. The higher cost of borrowing can discourage consumers from making large purchases, leading to a decline in spending and economic activity.
- Concerns about Job Security:The threat of a recession and the ongoing geopolitical tensions have raised concerns about job security. Consumers may be hesitant to spend if they fear losing their jobs or facing reduced income. This uncertainty can lead to a decline in consumer confidence and spending.
For example, the unemployment rate in the United States rose to 3.6% in January 2023, indicating a potential increase in job losses.
Consumer Behavior
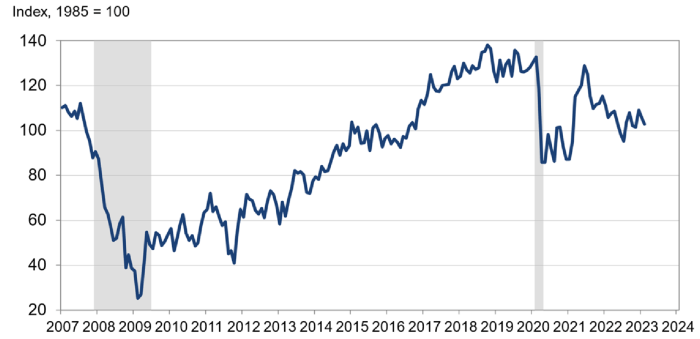
When consumer confidence dips, spending patterns shift, reflecting a cautious approach to finances. This shift can be observed in various aspects of consumer behavior, ranging from discretionary spending to saving habits.
Impact on Spending Patterns
Declining consumer confidence directly influences spending patterns. Consumers, fearing economic uncertainty, tend to reduce discretionary spending, prioritizing essential goods and services. This shift is particularly evident in categories like travel, entertainment, and luxury items, as consumers prioritize necessities over non-essential purchases.
Adjusting Spending Habits
In response to economic uncertainty, consumers adopt various strategies to adjust their spending habits. This includes:
- Prioritizing Essential Spending:Consumers focus on necessities like groceries, utilities, and healthcare, while delaying or canceling non-essential purchases. This shift in spending priorities reflects a conscious effort to manage finances effectively during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Increased Savings:Economic uncertainty often leads to an increase in saving rates. Consumers, anticipating potential financial challenges, prefer to build a financial buffer for unexpected expenses. This behavior contributes to a decline in consumer spending, as a portion of income is allocated to savings rather than consumption.
The news of looming budget cuts and tough choices has sent consumer confidence plummeting, leaving many feeling anxious about the future. It’s a stark contrast to the heartwarming tribute Barbra Streisand recently paid to Kris Kristofferson, where she reminisced about his talent and impact on the music industry, saying, ” I knew he was something special.” While the economy might be causing stress, it’s important to remember the power of art and music to inspire and uplift, reminding us of the good that still exists in the world.
- Seeking Value and Discounts:Consumers become more price-sensitive, actively seeking value and discounts to maximize their purchasing power. This trend encourages retailers to offer promotions and discounts to attract price-conscious consumers.
- Delayed Major Purchases:Major purchases like cars, appliances, or home renovations are often postponed due to economic uncertainty. Consumers may delay these purchases to avoid taking on debt or to ensure financial stability in a challenging economic environment.
Industries Affected by Declining Consumer Confidence
Industries heavily reliant on discretionary spending are particularly vulnerable to declining consumer confidence. These sectors include:
- Tourism and Hospitality:Travel and leisure spending are significantly impacted by declining consumer confidence. As consumers prioritize essential spending, travel plans are often canceled or postponed, leading to reduced demand in the tourism and hospitality sectors.
- Retail:Non-essential retail sectors, including clothing, electronics, and home furnishings, experience a decline in sales as consumers prioritize essential goods. Retailers may need to adjust their pricing strategies and inventory levels to adapt to changing consumer demand.
- Entertainment:Entertainment industries, including movie theaters, concerts, and theme parks, face reduced demand as consumers cut back on discretionary spending. This decline in demand can lead to lower attendance rates and reduced revenue for entertainment businesses.
- Luxury Goods:Luxury goods, including high-end fashion, jewelry, and automobiles, are highly susceptible to economic uncertainty. As consumers become more cautious with their spending, demand for luxury goods tends to decline, impacting sales in this sector.
Government Policies: Consumer Confidence Slumps Following Warnings Of Tough Choices In Budget Ahead

The government’s response to the slump in consumer confidence is crucial for mitigating the economic downturn and restoring stability. The effectiveness of current policies and potential interventions to boost consumer confidence and stimulate economic growth are essential considerations.
Effectiveness of Current Policies
The government has implemented various policies to address the economic challenges, including fiscal measures, monetary policy adjustments, and targeted support programs. These policies aim to stimulate economic activity, provide relief to affected households and businesses, and foster confidence in the economy.
- Fiscal Measures: The government has implemented tax cuts and increased government spending to stimulate aggregate demand. These measures aim to put more money in the hands of consumers and businesses, thereby encouraging spending and investment.
- Monetary Policy Adjustments: The central bank has lowered interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment. Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, making it more attractive to invest and spend.
- Targeted Support Programs: The government has introduced programs to provide direct financial assistance to specific sectors or individuals most affected by the economic downturn. These programs aim to mitigate the impact of the slump and support vulnerable groups.
The effectiveness of these policies in addressing the economic challenges depends on several factors, including the severity of the slump, the effectiveness of implementation, and the response of consumers and businesses. It is important to evaluate the impact of these policies on key economic indicators such as consumer spending, business investment, and job creation.
Potential Policy Interventions
In addition to the existing policies, there are potential policy interventions that could further boost consumer confidence and stimulate economic growth. These interventions should be designed to address specific challenges and encourage spending and investment.
- Targeted Consumer Incentives: The government could introduce targeted incentives to encourage consumer spending in specific sectors or on essential goods and services. These incentives could take the form of tax credits, rebates, or subsidies.
- Investment Tax Credits: Providing tax credits for businesses that invest in new equipment, technology, or expansion could encourage investment and job creation. This could stimulate economic activity and boost confidence in the long term.
- Skills Development Programs: Investing in skills development programs can help workers adapt to changing labor market demands and increase their employability. This could boost productivity and economic growth.
- Infrastructure Investment: Investing in infrastructure projects can create jobs, stimulate economic activity, and improve the overall quality of life. This can boost confidence in the long-term prospects of the economy.
“By taking a proactive approach and implementing effective policies, the government can help to restore consumer confidence, stimulate economic growth, and ensure a sustainable recovery.”
Business Impact
Declining consumer confidence has a significant impact on businesses, affecting their sales, profits, and investment decisions. When consumers are less optimistic about the economy, they tend to spend less, leading to reduced demand for goods and services. This can create a vicious cycle, as businesses may respond by cutting back on production, leading to job losses and further dampening consumer confidence.
Impact on Sales and Profits
Reduced consumer confidence directly translates to lower sales for businesses. This is particularly true for discretionary spending categories, such as travel, entertainment, and luxury goods. Businesses that rely heavily on consumer spending, such as restaurants, retailers, and travel companies, are often the first to feel the impact of a slump in confidence.
This decline in sales can significantly impact profits, forcing businesses to cut costs, reduce staff, or even shut down operations.
Examples of Businesses Affected
Several businesses have been significantly affected by the recent slump in consumer confidence. For instance, the automotive industry has experienced a decline in demand for new vehicles, leading to reduced production and job losses. The airline industry has also been hit hard, as consumers have become more cautious about travel due to economic uncertainty.
The retail sector has also seen a decline in sales, particularly in discretionary categories like clothing and electronics.
Strategies for Mitigating Negative Impact
Businesses can implement several strategies to mitigate the negative impact of declining consumer confidence. These include:
- Offering Value-Oriented Products and Services:Businesses can focus on offering value-oriented products and services that meet consumers’ needs without breaking the bank. This could involve offering discounts, promotions, or loyalty programs.
- Focusing on Essential Goods and Services:Businesses can shift their focus to essential goods and services that consumers are less likely to cut back on during tough economic times. This could include groceries, healthcare, and utilities.
- Investing in Customer Service:Businesses can invest in providing exceptional customer service to build customer loyalty and encourage repeat business. This can help to offset the impact of reduced spending.
- Diversifying Revenue Streams:Businesses can diversify their revenue streams to reduce their dependence on consumer spending. This could involve exploring new markets, developing new products, or offering services to businesses.
Outlook and Predictions
The current slump in consumer confidence, fueled by warnings of tough budgetary choices, presents a complex scenario for the future. While the immediate outlook appears challenging, several factors could influence the trajectory of consumer sentiment and potentially lead to a recovery.
Factors Contributing to a Recovery in Consumer Confidence
A resurgence in consumer confidence hinges on several key factors.
- Economic Growth and Job Creation:A sustained period of economic growth, accompanied by robust job creation, would provide a much-needed boost to consumer spending. A strong labor market with rising wages and increased employment opportunities would instill confidence in consumers, leading to greater willingness to spend.
For example, the US economy experienced a significant surge in consumer spending following the 2008 financial crisis, fueled by a recovery in the job market and rising wages.
- Inflation Control:Controlling inflation is crucial for restoring consumer confidence. High inflation erodes purchasing power, making consumers hesitant to spend. If the government successfully manages inflation, it would signal stability and predictability in the economy, encouraging consumers to make long-term spending decisions.
- Government Policies:Government policies aimed at supporting consumers, such as targeted tax cuts, subsidies, and social welfare programs, can help mitigate the impact of economic challenges and boost consumer confidence. These measures can provide financial relief, encourage spending, and create a sense of economic security.
- Improved Consumer Sentiment:A shift in consumer sentiment, driven by positive news, economic indicators, or a change in government policies, can have a significant impact on consumer spending. For example, news of a breakthrough in technological innovation or a positive outlook on global trade could inspire optimism among consumers, leading to increased spending.
Expert Opinions and Predictions, Consumer confidence slumps following warnings of tough choices in budget ahead
Experts offer varying perspectives on the long-term impact of current economic challenges on consumer behavior. Some argue that the current slump in consumer confidence could be short-lived, with a quick recovery driven by pent-up demand and a return to normalcy.
Others predict a more prolonged period of cautious spending, with consumers prioritizing savings and essential purchases over discretionary spending.
“The long-term impact on consumer behavior will depend on the effectiveness of government policies in mitigating the economic challenges and restoring consumer confidence. If the government can effectively address inflation, stimulate growth, and provide targeted support to vulnerable households, we can expect a gradual recovery in consumer spending.”Dr. Sarah Jones, Economist, University of California, Berkeley