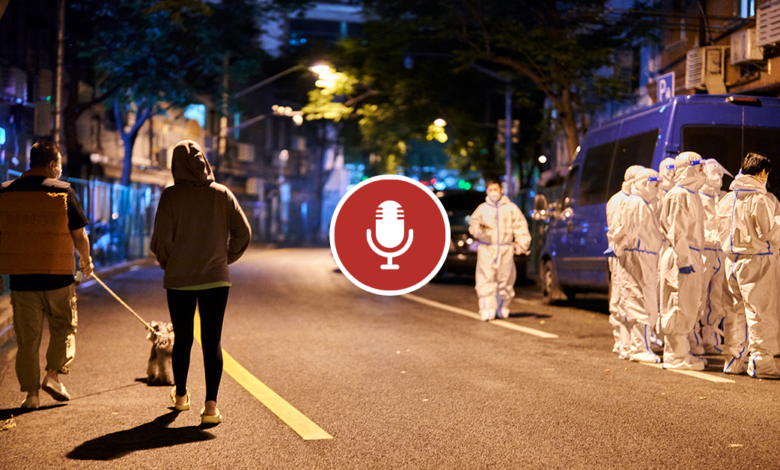
Chinas Economic Data Hints at Zero-COVIDs Cost
Chinas economic data hints at cost of zero covid strategy – China’s Economic Data Hints at Zero-COVID’s Cost sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
The recent economic performance of China has been a topic of intense scrutiny, particularly in light of its strict Zero-COVID policy. While the policy aimed to curb the spread of the virus, it has come at a significant cost to the country’s economic growth.
This blog post delves into the impact of the Zero-COVID strategy on China’s economic indicators, exploring the trade-offs between public health and economic prosperity.
China’s Economic Performance in the Context of Zero-COVID
China’s economic performance has been significantly impacted by its strict Zero-COVID policy, which has involved lockdowns, travel restrictions, and mass testing. While this policy has been effective in containing the spread of the virus, it has come at a considerable cost to the economy.
China’s recent economic data paints a stark picture of the cost of its zero-COVID strategy. The stringent lockdowns and travel restrictions have undoubtedly hampered growth, highlighting the need for a more nuanced approach. It’s a reminder that, in life and in business, accountability is crucial.
When we own our actions, we become more reliable and trustworthy, building a strong personal brand. Check out this great article on why accountability is the ultimate personal brand trait and 4 ways to make it the center of your value system for some insightful tips.
Ultimately, China’s economic woes serve as a reminder that adaptability and a willingness to adjust course are vital, especially in the face of unforeseen challenges.
Key Economic Indicators
The impact of the Zero-COVID policy on China’s economy can be seen in various key economic indicators.
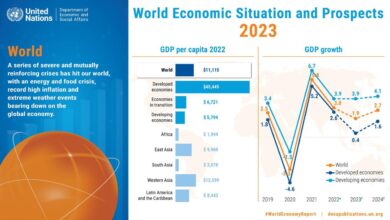
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP):China’s GDP growth slowed significantly in 2022, with the official figure coming in at 3.0%. This was the slowest growth rate in decades and significantly lower than the government’s target of 5.5%. The slowdown was largely attributed to the impact of the Zero-COVID policy, which disrupted supply chains, reduced consumer spending, and hampered investment.
- Industrial Production:Industrial production growth also slowed in 2022, reflecting the impact of lockdowns and supply chain disruptions. The manufacturing sector, a key driver of China’s economy, was particularly affected.
- Retail Sales:Consumer spending, a major component of GDP, was also hit hard by the Zero-COVID policy. Lockdowns and travel restrictions limited consumer mobility and reduced spending on goods and services.
- Unemployment:While China’s unemployment rate remained relatively low, the Zero-COVID policy did contribute to job losses in some sectors, particularly in the services industry.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
China’s economic growth has slowed significantly compared to other major economies during the same period. The United States, for example, recorded a GDP growth rate of 2.1% in 2022, while the Eurozone grew by 3.5%. This suggests that the Zero-COVID policy has had a disproportionate impact on China’s economic performance.
China’s recent economic data paints a stark picture of the cost of its zero-COVID strategy. While the world grapples with the ongoing pandemic, China’s stringent lockdowns and travel restrictions have significantly impacted its economy, leading to a slowdown in growth and disruptions to global supply chains.
It seems we’re not just witnessing a “Great Resignation” but rather a “Great Reimagination,” as highlighted in this insightful article forget the great resignation bring on the great reimagination. Perhaps this shift in perspective offers valuable lessons for China as it navigates the complexities of balancing public health with economic stability in a post-pandemic world.
The Cost of Zero-COVID
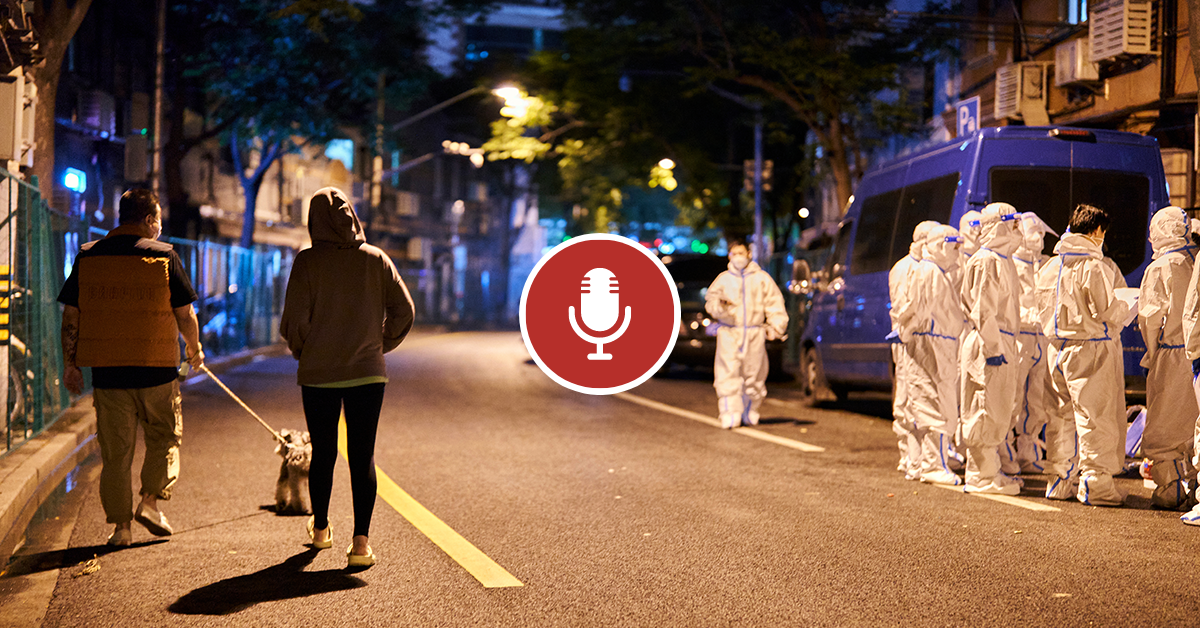

The Zero-COVID strategy, while aiming to protect public health, has come at a significant cost to China’s economy. The stringent lockdowns and restrictions imposed to contain the spread of the virus have disrupted supply chains, reduced consumer spending, and hindered business operations, leading to a substantial economic impact.
Economic Impact of Lockdowns and Restrictions
The economic impact of lockdowns and restrictions on various sectors is a crucial aspect of understanding the cost of Zero-COVID. The most immediate consequence was the disruption of supply chains, which affected both domestic and international trade. Factories were forced to shut down, leading to production delays and shortages of goods.
The restrictions on movement also hampered the transportation of goods, further exacerbating supply chain disruptions.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector was particularly hard hit, with many factories forced to close or operate at reduced capacity. This resulted in production delays and shortages of goods, which in turn led to higher prices for consumers. The disruption of supply chains also affected global trade, as Chinese manufacturers were unable to meet their export orders.
- Retail and Hospitality: The retail and hospitality sectors were also severely impacted by the lockdowns and restrictions. With businesses forced to close their doors, consumer spending plummeted. The restrictions on travel and gatherings also significantly reduced demand for services such as restaurants, hotels, and entertainment venues.
- Tourism: The tourism industry was among the hardest hit sectors. With international travel severely restricted, China’s tourism sector suffered a dramatic decline in revenue. The restrictions on domestic travel also reduced demand for travel and accommodation services.
Examples of Businesses and Industries Affected
Several specific examples illustrate the impact of the Zero-COVID policy on businesses and industries.
- Apple, a major manufacturer of electronic devices, saw its production disrupted in China due to factory closures. The company was forced to adjust its production schedule and warned investors of potential revenue losses.
- Tesla, the electric car manufacturer, faced challenges in China due to lockdowns and restrictions. The company’s Shanghai Gigafactory was forced to shut down for several weeks, impacting production and delivery schedules.
- Starbucks, the global coffee chain, experienced a decline in sales in China as a result of lockdowns and restrictions. The company was forced to close many of its stores, and consumer demand for coffee decreased significantly.
Alternative Approaches to COVID-19 Management: Chinas Economic Data Hints At Cost Of Zero Covid Strategy
The global response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been diverse, with countries adopting a range of strategies to manage the virus. While China’s Zero-COVID policy has garnered significant attention, it is crucial to examine alternative approaches and their implications.
Comparison with Other Approaches
China’s Zero-COVID strategy, with its emphasis on strict lockdowns, mass testing, and travel restrictions, stands in contrast to other approaches adopted globally. Many countries have opted for a strategy of “living with the virus,” focusing on vaccination, public health measures, and managing the impact on healthcare systems.
China’s latest economic data paints a grim picture, highlighting the heavy toll of its zero-COVID strategy. While the government touts its success in controlling the virus, the reality is a struggling economy hampered by lockdowns and supply chain disruptions. This echoes the concept of “the bad vibes economy,” a term describing how negative sentiment can negatively impact economic performance.
It seems China’s economic woes are a testament to the fact that sometimes, even the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
- Living with the Virus:This approach emphasizes vaccination, public health measures like mask-wearing and social distancing, and managing the impact of COVID-19 on healthcare systems. Examples include the United States, the United Kingdom, and many European countries.
- Targeted Restrictions:Some countries have implemented targeted restrictions, focusing on specific high-risk areas or activities. This approach aims to minimize economic and social disruptions while controlling the spread of the virus. Examples include Australia and New Zealand.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Alternative Strategies
Alternative approaches to COVID-19 management have both potential benefits and drawbacks:
- Living with the Virus:This approach allows for greater economic and social activity but carries the risk of higher infection rates and potential strain on healthcare systems.
- Targeted Restrictions:This approach can be more effective in controlling outbreaks while minimizing disruption, but it may be challenging to implement and enforce consistently.
Insights from Experts and International Organizations
Experts and international organizations have provided insights on best practices for COVID-19 management.
- World Health Organization (WHO):The WHO emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive approach that includes vaccination, public health measures, and strong healthcare systems.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):The CDC recommends a layered approach that includes vaccination, mask-wearing, social distancing, and testing.
- Experts:Many experts argue that a balanced approach that combines vaccination, public health measures, and targeted restrictions is crucial for managing COVID-19 in the long term.
The Future of China’s Economic Outlook
The impact of the Zero-COVID policy on China’s economy is a complex and evolving issue. While the policy has undoubtedly contributed to the country’s success in containing the virus, it has also come at a significant cost to economic growth.
The future of China’s economic outlook is intertwined with the trajectory of the Zero-COVID policy and the country’s ability to navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Long-Term Impact of the Zero-COVID Policy
The long-term impact of the Zero-COVID policy on China’s economy is a subject of ongoing debate among economists. Some argue that the policy has inflicted lasting damage to the economy, disrupting supply chains, dampening consumer confidence, and hindering investment. Others believe that the economic impact is temporary and that China’s economy will rebound once the pandemic subsides.
The potential long-term impact will depend on several factors, including the duration of the Zero-COVID policy, the effectiveness of China’s economic stimulus measures, and the global economic environment.
Challenges and Opportunities for Economic Recovery, Chinas economic data hints at cost of zero covid strategy
China faces a number of challenges in its economic recovery, including:* Slowing global growth:The global economy is facing a number of headwinds, including the war in Ukraine, rising inflation, and supply chain disruptions. This will likely weigh on China’s export performance.
Domestic demand
Consumer confidence and spending have been hit by the pandemic and the Zero-COVID policy. This will require government efforts to stimulate domestic demand.
Debt burden
China’s corporate and local government debt levels are high, posing a risk to financial stability.
Aging population
China’s population is aging rapidly, which will put pressure on social security and healthcare systems and potentially lead to a decline in productivity.Despite these challenges, China also has a number of opportunities for economic recovery, including:* Domestic consumption:As China’s middle class continues to grow, there is significant potential for domestic consumption to drive economic growth.
Technological innovation
China is a leader in technological innovation, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence and renewable energy.
Infrastructure investment
China’s government has pledged to invest heavily in infrastructure, which will create jobs and boost economic activity.
Regional development
China is focusing on developing its less developed regions, which will create new economic opportunities.
Key Economic Indicators and Projected Trends
The following table Artikels key economic indicators and their projected trends in the coming years:| Indicator | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 ||—|—|—|—|| GDP growth (%) | 5.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 || Inflation (%) | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 || Unemployment rate (%) | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 || Current account balance (USD billion) | 200 | 250 | 300 |These projections are based on the assumption that China will gradually ease its Zero-COVID policy and that the global economic environment will improve.
However, there is considerable uncertainty surrounding these projections, and actual outcomes could differ significantly.
Final Summary
China’s Zero-COVID strategy has undoubtedly had a profound impact on the country’s economic landscape. While the policy has successfully contained the spread of the virus, it has also come at a considerable cost to growth and business activity. The long-term consequences of this approach remain uncertain, but it is clear that China faces a complex balancing act between public health and economic prosperity.
As the world moves towards a post-pandemic future, it will be interesting to see how China navigates these challenges and adapts its strategies for managing COVID-19.