China Holds Rates Steady After Feds Big Cut
China unexpectedly leaves benchmark lending rates unchanged after feds jumbo cut – China unexpectedly leaves benchmark lending rates unchanged after the Federal Reserve’s jumbo interest rate cut, a move that has sent ripples through global markets. This decision, coming on the heels of the Fed’s aggressive action, highlights the divergent paths being taken by the world’s two largest economies in navigating a complex economic landscape.
The Fed’s rate cut was aimed at stimulating the US economy, while China’s decision to hold steady suggests a more cautious approach. This divergence reflects China’s unique economic challenges, including a slowdown in growth, trade tensions with the US, and the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Context and Background
The recent decision by the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) to keep its benchmark lending rates unchanged, despite the Federal Reserve’s significant interest rate cut, has raised eyebrows in the financial world. This move is particularly intriguing given the current global economic climate and the pressures China is facing.To understand this decision, we need to consider the recent Federal Reserve interest rate cut and its potential impact on the global economy, as well as China’s economic situation and its historical approach to benchmark lending rates.
The Federal Reserve’s Interest Rate Cut
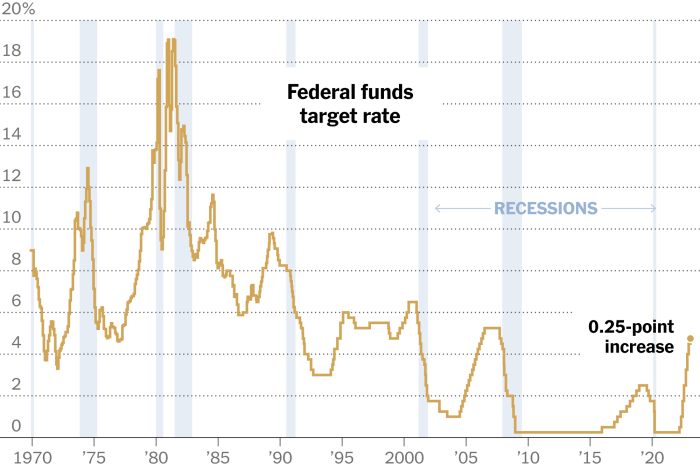
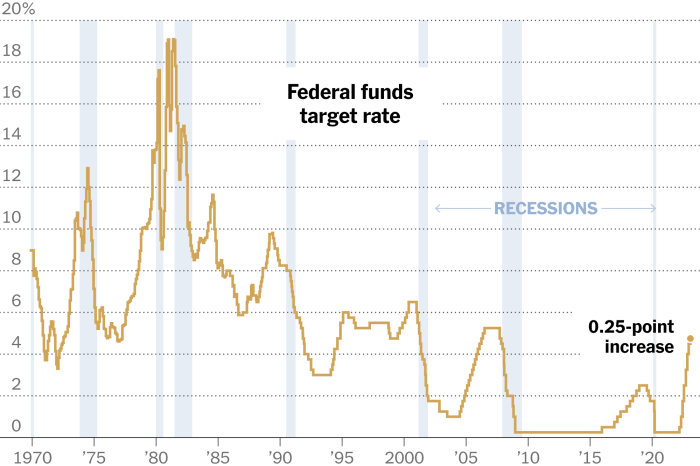
The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, lowered its benchmark interest rate by 0.5 percentage points in March 2023, marking a significant shift in monetary policy. This move was intended to mitigate the potential economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and global uncertainties.
Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth by making it cheaper for businesses and individuals to borrow money, potentially leading to increased investment and spending.
China’s Benchmark Lending Rates
China’s benchmark lending rates, known as the Loan Prime Rate (LPR), are the reference rates for banks to set interest rates on loans. The PBOC sets the LPR based on a combination of factors, including market conditions, inflation, and economic growth targets.
The PBOC typically adjusts the LPR to manage inflation and economic growth, with a focus on maintaining financial stability.
China’s decision to keep its benchmark lending rates unchanged, even after the Federal Reserve’s significant interest rate cut, is a fascinating development. It’s hard to know what’s driving this move, especially considering the global economic landscape. To understand the bigger picture, it’s important to delve into what is going on now in the world.
China’s decision may reflect a unique set of economic priorities, perhaps focused on internal stability and long-term growth. Only time will tell what this move signifies for the global financial system.
China’s Economic Situation
China’s economy has faced a number of challenges in recent years, including the COVID-19 pandemic, the trade war with the United States, and a slowdown in global demand. While the Chinese economy has shown signs of recovery, there are still concerns about the sustainability of this growth.
China’s Recent Economic Performance
China’s economy grew by 3% in 2022, a significant slowdown from the previous year’s growth rate of 8.1%. This slowdown was attributed to a number of factors, including the COVID-19 pandemic, lockdowns, and a decline in global demand. Despite these challenges, China’s economy remains the second-largest in the world and is expected to continue to grow in the coming years.
China’s Decision and Potential Implications
China’s decision to keep benchmark lending rates unchanged while the Federal Reserve dramatically cut rates is a significant development with potential implications for both the Chinese and global economies. This unexpected move signals a divergence in monetary policy approaches between the two economic giants.
Reasons for China’s Decision
China’s decision to hold rates steady reflects a complex interplay of factors. The central bank, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC), likely prioritizes stability and control over inflation, even as economic growth slows. The PBOC’s decision may be driven by several factors:
- Inflation Concerns:China’s consumer price index (CPI) has been rising, indicating inflationary pressures. The PBOC might be hesitant to lower rates, fearing it could further fuel inflation.
- Debt Management:China’s corporate and household debt levels are already high. Lowering interest rates could exacerbate this issue by encouraging further borrowing.
- Structural Reforms:The PBOC might be focused on structural reforms to stimulate growth, rather than relying solely on monetary policy tools. These reforms aim to address issues like overcapacity and improve the efficiency of resource allocation.
Potential Impact on China’s Economy, China unexpectedly leaves benchmark lending rates unchanged after feds jumbo cut
The impact of China’s decision on its economy is likely to be multifaceted:
- Slower Growth:Holding rates steady could slow economic growth, as businesses may find it more expensive to borrow and invest. This could further dampen consumer spending and investment.
- Currency Appreciation:The decision to hold rates steady could strengthen the yuan against the US dollar, making Chinese exports less competitive in global markets.
- Increased Risk Appetite:Investors might be drawn to higher-yielding assets outside China, leading to capital outflows. This could put downward pressure on the yuan and potentially destabilize financial markets.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
China’s decision contrasts sharply with the aggressive rate cuts undertaken by the US Federal Reserve and other major central banks. The US Fed has lowered rates twice in 2019, aiming to stimulate economic growth and offset the impact of trade tensions.
China’s decision to keep its benchmark lending rates unchanged after the Fed’s aggressive rate cut is a fascinating development. It shows a willingness to stand apart from global trends, perhaps focusing on internal economic stability. Meanwhile, across the globe, Argentina’s rugby team is gearing up for a tough battle against the world champions, South Africa.
How can they pull off a win? Find out in this insightful article on how Argentina can win the tournament against world champions South Africa: rugby championship how argentina can win the tournament against world champions south africa.
Back to China, it’ll be interesting to see how this independent approach plays out in the global economic landscape.
The European Central Bank (ECB) has also signaled its willingness to ease monetary policy further.
“The Fed’s rate cuts are intended to provide a cushion against the economic headwinds created by the trade war and global slowdown. China’s decision to hold rates steady suggests a different approach, one that prioritizes financial stability and structural reforms.”
Economist, International Monetary Fund
China’s approach to monetary policy reflects its unique economic context, including its commitment to maintaining financial stability and its focus on structural reforms. This divergence from other major economies highlights the complexity of global economic coordination and the challenges of managing interconnected economies in a rapidly changing world.
China’s decision to keep benchmark lending rates unchanged after the Fed’s massive interest rate cut is a significant move, suggesting a different approach to managing their economy. It’s a stark contrast to the recent news about Doug Emhoff, who has been praised by Jen Psaki for reshaping the perception of masculinity.
While the economic landscape in China remains uncertain, the government’s decision to maintain stability is a signal that they are taking a cautious approach to navigating the global economic storm.
Market Reactions and Analysis: China Unexpectedly Leaves Benchmark Lending Rates Unchanged After Feds Jumbo Cut
The unexpected decision by China to maintain its benchmark lending rates, despite the Federal Reserve’s significant interest rate cut, sent shockwaves through global financial markets. This move sparked immediate reactions and raised questions about the implications for investors and the broader economic landscape.
Immediate Market Reactions
The decision to leave rates unchanged surprised many market participants, who had anticipated a coordinated response to the Fed’s move.
- The Chinese yuan weakened against the US dollar, reflecting concerns about the potential impact on China’s economic growth and the attractiveness of its assets.
- Equity markets in Asia and Europe experienced initial volatility, with some investors expressing concerns about the implications for global trade and economic growth.
- Bond yields in China rose, indicating that investors were demanding higher returns for holding Chinese debt, reflecting concerns about the potential for slower economic growth.
Short-Term and Long-Term Implications for Investors
The decision to maintain rates unchanged presents both opportunities and challenges for investors.
- Short-Term Implications:In the short term, investors may face increased volatility in Chinese markets as they grapple with the implications of the decision. Some investors might adopt a wait-and-see approach, while others might seek opportunities in sectors that are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
- Long-Term Implications:The long-term implications for investors depend on how China’s economic growth unfolds. If the Chinese economy continues to slow, it could weigh on global growth and impact investor returns. However, if China is able to manage its economic challenges effectively, it could provide opportunities for investors seeking exposure to a rapidly growing market.
Potential Impact on Global Markets
China’s decision to maintain rates unchanged has the potential to impact global markets in several ways.
- Currency Markets:The decision could contribute to further volatility in currency markets, as investors adjust their expectations about the relative value of different currencies. The yuan’s weakness could also impact other emerging market currencies.
- Global Trade:The decision could affect global trade flows, as it could impact the competitiveness of Chinese exports and influence the demand for imported goods.
- Economic Growth:The decision’s impact on global economic growth will depend on how it influences Chinese economic activity and the overall global economic outlook.
Future Outlook and Considerations
China’s decision to hold its benchmark lending rates steady despite the Federal Reserve’s jumbo rate cut has sparked a wave of speculation about the future direction of its monetary policy. While the immediate implications are still being analyzed, understanding the potential factors influencing China’s future decisions is crucial for navigating the evolving economic landscape.
Key Factors Influencing Future Monetary Policy Decisions
The following factors will likely play a significant role in shaping China’s monetary policy stance in the coming months:
- Domestic Economic Growth:China’s economic recovery remains fragile, with uncertainties surrounding the strength and sustainability of growth. The government’s focus on achieving stable growth will heavily influence monetary policy decisions. If growth falters, further easing measures may be implemented to stimulate demand and support businesses.
- Inflation:While inflation has been relatively subdued, the potential for rising prices due to supply chain disruptions and global commodity price increases remains a concern. The People’s Bank of China (PBOC) will need to carefully balance growth objectives with inflation control, potentially leading to a more cautious approach to easing.
- Global Economic Conditions:The global economic outlook remains uncertain, with the ongoing war in Ukraine and persistent inflation adding to volatility. China’s monetary policy decisions will likely consider the impact of global economic conditions on its own economy, potentially leading to a more accommodative stance if external pressures intensify.
- Financial Stability:Maintaining financial stability is a key priority for China. The PBOC will need to carefully manage the potential risks associated with excessive easing, such as asset bubbles and increased leverage. This consideration may limit the extent of future rate cuts or other easing measures.
- US Monetary Policy:The Federal Reserve’s aggressive rate hikes are expected to continue, potentially putting pressure on the Chinese yuan and influencing capital flows. The PBOC may need to adjust its monetary policy stance to manage these external pressures and maintain stability in the yuan.
Potential Implications of China’s Decision
The following table summarizes key takeaways and potential implications of China’s decision to hold its benchmark lending rates steady:






