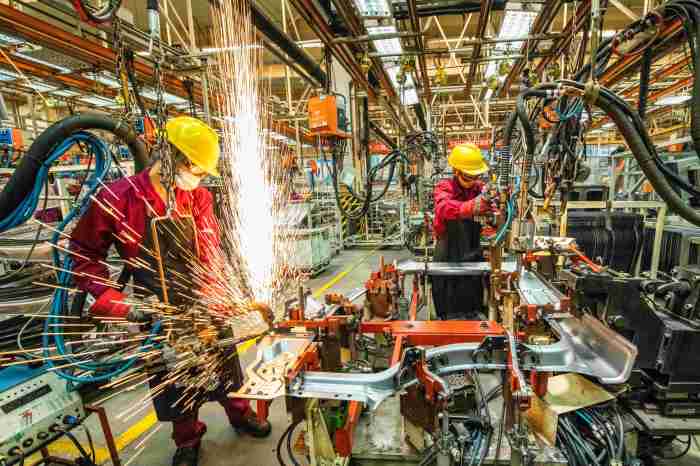

China Stimulus Calls Grow Louder Inside and Outside
China stimulus calls are growing louder inside and outside the country – China Stimulus Calls Grow Louder Inside and Outside the country, and the world is watching closely. The Chinese economy, once a powerhouse of global growth, is facing a complex web of challenges. A combination of factors, including the lingering effects of COVID-19, global trade tensions, and domestic policy choices, have led to a slowdown in growth, raising concerns about the future of the world’s second-largest economy.
The debate over stimulus measures is intensifying, with voices both within and outside China urging the government to intervene and inject more support into the economy. Proponents argue that a stimulus package could help to jumpstart growth, create jobs, and boost consumer confidence.
However, critics warn of the potential downsides, including increased government debt, inflationary pressures, and distortions in market signals.
The Economic Context
China’s economy is navigating a complex and challenging landscape, facing a confluence of factors that are slowing growth and raising concerns about the country’s future trajectory.
Current State of the Chinese Economy
China’s economy is facing a period of slowdown, with growth rates significantly lower than those seen in the past decade. The World Bank forecasts GDP growth of 4.3% in 2023, down from 2.7% in 2022. While this is still a respectable rate of growth for a large economy, it represents a significant deceleration from the double-digit growth rates China experienced in the early 2000s.
Factors Contributing to the Slowdown
- COVID-19 Pandemic:The pandemic had a significant impact on the Chinese economy, leading to lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and a decline in consumer spending. The zero-COVID policy, while initially successful in containing the virus, ultimately proved unsustainable and imposed significant economic costs.
The calls for a China stimulus package are getting louder, both within the country and from international observers. It’s a complex issue, though, with potential benefits and risks. It’s almost like a game of strategy, much like the fascinating analysis presented in the article 911 and the sport of god , which explores the intricate geopolitical forces at play in the aftermath of major events.
Ultimately, China’s decision on stimulus will have far-reaching implications for the global economy, so it’s a move that demands careful consideration.
- Global Trade Tensions:The ongoing trade war between the United States and China has created uncertainty and instability in the global economy. This has negatively impacted Chinese exports and investment, particularly in the manufacturing sector.
- Domestic Policy Choices:China’s government has implemented a number of policies in recent years aimed at reducing debt, controlling asset bubbles, and promoting sustainable growth. These policies, while well-intentioned, have had the unintended consequence of slowing economic activity in some sectors.
Challenges Faced by Various Sectors
Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing sector, a key driver of economic growth, is facing a number of challenges, including rising labor costs, competition from other developing countries, and slowing global demand. The trade war with the United States has also hurt the sector, as Chinese exports have faced higher tariffs.
Real Estate
China’s real estate sector, a major contributor to economic growth in the past, is facing a period of adjustment. The government’s efforts to curb speculation and reduce leverage have led to a decline in property prices and sales. This has had a ripple effect on the economy, as it has slowed construction activity and reduced investment.
Consumer Spending
Consumer spending is a critical component of economic growth, and it has been weak in China in recent years. This is due to a number of factors, including rising unemployment, wage stagnation, and uncertainty about the future. The pandemic has also contributed to a decline in consumer confidence.
Arguments for Stimulus

The calls for a stimulus package in China are growing louder, both within the country and internationally. Proponents argue that such measures are crucial to bolster economic growth, stimulate job creation, and restore consumer confidence in the face of a challenging economic landscape.
The calls for a China stimulus package are getting louder, both within the country and from international observers. While the global economic landscape is uncertain, some argue that China’s actions could have a significant impact on the world, especially considering the US’s direct involvement in armed conflicts around the world.
The potential for a global economic downturn is a serious concern, and China’s role in mitigating such a crisis is increasingly being recognized.
Government Officials and Economists Advocate for Stimulus
A range of government officials, economists, and business leaders have voiced their support for a stimulus package. They argue that targeted intervention is necessary to mitigate the impact of economic headwinds and to ensure a sustainable recovery. The rationale behind their calls for stimulus rests on the potential benefits for economic growth, job creation, and consumer confidence.
Potential Benefits of Stimulus
Economic Growth
Proponents of stimulus measures believe that government intervention can provide a much-needed boost to economic activity. By injecting funds into the economy, the government can increase aggregate demand, leading to higher levels of production, investment, and consumption. This, in turn, can drive economic growth and create a more favorable environment for businesses.
The calls for China to implement a stimulus package are growing louder, both within the country and internationally. This echoes a pattern we’ve seen in other nations, where economic hardship often leads to increased government intervention. It’s a delicate balancing act, as we saw with the recent media propaganda and Venezuela , where the narrative around government action can be heavily manipulated.
Ultimately, China’s decision will have far-reaching implications for its own economy and the global landscape.
Job Creation
Stimulus packages can also contribute to job creation. By supporting infrastructure projects, providing tax breaks for businesses, and offering financial assistance to struggling sectors, the government can create new jobs and prevent existing ones from being lost. This is particularly important in a context of rising unemployment and a weakening labor market.
Consumer Confidence
Stimulus measures can also help to restore consumer confidence. By demonstrating a commitment to supporting the economy, the government can signal to consumers that the situation is under control and that there are reasons to be optimistic about the future.
This can encourage consumers to spend more, which can further boost economic activity.
Specific Policy Proposals
Proponents of stimulus measures have proposed a range of policy interventions. These include:
- Infrastructure Projects:Investing in infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and railways, can create jobs, stimulate economic activity, and improve the long-term productivity of the economy.
- Tax Cuts:Reducing taxes for businesses and individuals can increase disposable income and encourage spending and investment.
- Financial Support for Businesses:Providing financial assistance to businesses, such as loans, grants, and subsidies, can help them to stay afloat, avoid layoffs, and continue to operate.
International Perspectives
The global community is closely watching China’s economic trajectory, particularly as calls for stimulus intensify. International institutions, like the IMF and World Bank, have been vocal in their assessments of China’s economic health and the potential implications of stimulus measures.
Impact of Chinese Stimulus on Global Markets, China stimulus calls are growing louder inside and outside the country
The potential impact of Chinese stimulus on global markets is a subject of considerable interest. Increased spending by China could lead to a surge in demand for commodities and manufactured goods, benefiting exporters worldwide. However, the effectiveness of stimulus depends on its implementation and the overall global economic environment.
Implications for Other Countries
The implications of Chinese stimulus for other countries, particularly those with strong economic ties to China, are multifaceted.
- For example, countries like Australia and Brazil, which are major exporters of raw materials to China, could experience a boost in demand and economic activity if Chinese stimulus leads to increased industrial production.
- However, countries heavily reliant on Chinese exports may face challenges if stimulus-driven growth in China leads to increased competition in global markets.
Insights from Global Economic Institutions
The IMF and World Bank have offered insights into the Chinese economy and the need for stimulus.
- The IMF has emphasized the importance of structural reforms alongside fiscal stimulus to address China’s long-term economic challenges.
- The World Bank has highlighted the potential for Chinese stimulus to support global growth, particularly in developing countries.
“The Chinese economy is at a crossroads. While there are opportunities for growth, the government needs to implement structural reforms and address long-term challenges,”
IMF Managing Director, Kristalina Georgieva.
Potential Implications of Stimulus: China Stimulus Calls Are Growing Louder Inside And Outside The Country
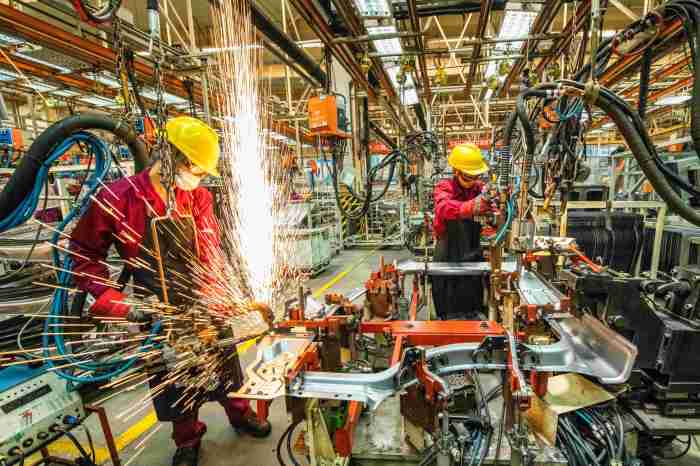

The potential implications of a stimulus package in China are multifaceted, encompassing both short-term and long-term effects on the economy. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the complex landscape of economic policy and assessing the effectiveness of stimulus measures.
Short-Term Effects of Stimulus
The immediate impact of a stimulus package is often focused on boosting economic activity and mitigating the immediate economic downturn. The most common methods include:
- Increased government spending:Direct government spending on infrastructure projects, social welfare programs, or research and development can create jobs, stimulate demand, and boost economic growth. For example, China’s massive infrastructure projects, like the Belt and Road Initiative, have been instrumental in generating employment and stimulating economic activity in the short term.
- Tax cuts and subsidies:Reducing taxes for businesses and individuals can increase disposable income, leading to higher consumer spending and investment. Subsidies can also encourage businesses to invest in new technologies or expand operations. China has a history of implementing tax cuts and subsidies, particularly during economic downturns, to stimulate economic activity.
- Lowering interest rates:Lowering interest rates can make borrowing more affordable for businesses and individuals, leading to increased investment and spending. China’s central bank has often employed this strategy to stimulate economic growth, with a focus on easing credit conditions for businesses and encouraging investment.
Long-Term Effects of Stimulus
While short-term benefits are evident, the long-term effects of stimulus can be more nuanced and depend on the specific measures implemented.
- Debt accumulation:Extensive stimulus measures can lead to a significant increase in government debt. If not managed effectively, this debt burden can constrain future economic growth and fiscal flexibility.
- Inflation:Excessive stimulus, particularly through increased government spending, can lead to inflation if it outpaces the growth in the supply of goods and services. This can erode purchasing power and create economic instability.
- Dependence on stimulus:Continued reliance on stimulus measures can create a dependency syndrome, where the economy becomes accustomed to government intervention and fails to generate sustainable growth on its own. This can lead to a lack of innovation and a stagnant economic environment.
- Misallocation of resources:Stimulus measures, if not carefully targeted, can lead to the misallocation of resources, favoring inefficient projects or industries over more productive ones. This can ultimately hinder long-term economic growth.
Risks and Opportunities of Stimulus Packages
Different stimulus packages come with their own set of risks and opportunities.
- Infrastructure-focused stimulus:This approach can generate immediate jobs and boost economic activity, but it can also lead to overinvestment in infrastructure, creating “ghost cities” or projects with limited economic viability. The potential for wasteful spending and long-term debt accumulation is a significant concern.
- Consumer-focused stimulus:Tax cuts and subsidies aimed at boosting consumer spending can be effective in the short term, but they can also lead to increased consumption of non-essential goods and services, contributing to inflation and unsustainable consumption patterns.
- Innovation-focused stimulus:Investing in research and development, supporting start-ups, and fostering innovation can create long-term economic growth, but it requires a longer-term commitment and can be less effective in addressing immediate economic challenges.
Addressing Structural Challenges
Stimulus measures can be used to address underlying structural challenges in the Chinese economy.
- Rebalancing the economy:Stimulus measures can be directed towards promoting domestic consumption, reducing reliance on exports, and fostering a more balanced economic structure. This can involve investing in sectors like services, education, and healthcare, which are less reliant on exports and have higher potential for job creation.
- Enhancing productivity:Stimulus measures can be used to invest in education, training, and technology to enhance productivity and competitiveness. This can help China transition towards a more innovation-driven economy and reduce reliance on low-cost manufacturing.
- Addressing income inequality:Stimulus measures can be targeted at improving social welfare programs, increasing access to healthcare and education, and creating more equitable income distribution. This can help create a more sustainable and inclusive economic model.






