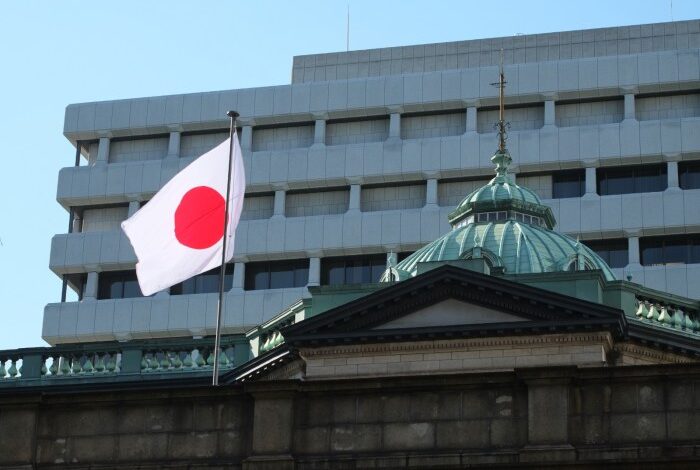
Bank of Japan Holds Steady as It Cautiously Normalizes Policy
The Bank of Japan keeps benchmark interest rate steady as it treads cautiously on normalizing policy, a move that reflects a delicate balancing act between supporting economic growth and managing inflation. While other major economies are aggressively raising rates to combat inflation, Japan remains hesitant, wary of potentially derailing its fragile recovery.
This cautious approach, however, comes with its own set of challenges, leaving the Bank of Japan facing a complex economic landscape.
The decision to hold rates steady was driven by a number of factors, including the current economic conditions in Japan. The country is still recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic, and while inflation has been rising, it remains relatively low compared to other developed economies.
The Bank of Japan is concerned that raising interest rates too quickly could stifle economic growth and hinder the recovery process. Additionally, the bank is facing pressure from the government to maintain low interest rates to support its fiscal policies.
Economic Factors Influencing the Decision: Bank Of Japan Keeps Benchmark Interest Rate Steady As It Treads Cautiously On Normalizing Policy
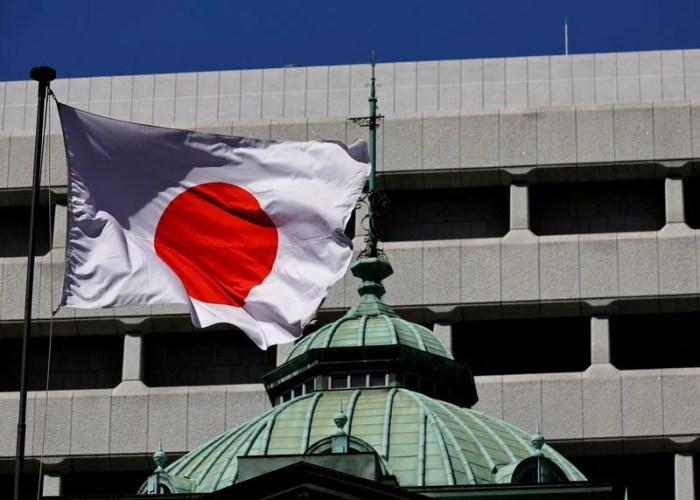

The Bank of Japan’s decision to keep its benchmark interest rate steady reflects its cautious approach to normalizing monetary policy. This decision is driven by a complex interplay of economic factors, with the central bank carefully weighing the potential risks and benefits of any policy adjustments.
Key Economic Indicators
The Bank of Japan considers a range of key economic indicators to assess the health of the Japanese economy and guide its policy decisions. These indicators provide insights into inflation, economic growth, and labor market conditions, which are crucial for understanding the overall economic landscape.
Current State of Key Economic Indicators
| Indicator | Current State | Impact on BOJ Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation | Core inflation (excluding fresh food and energy) remains below the BOJ’s 2% target, indicating that price pressures are still subdued. | The BOJ is likely to maintain its accommodative stance to support inflation towards its target. |
| Economic Growth | Japan’s economy has shown signs of recovery, but growth remains fragile and uneven. | The BOJ is cautious about tightening policy too quickly, as it wants to ensure a sustainable economic recovery. |
| Unemployment | Unemployment rates have remained relatively low, suggesting a healthy labor market. | A strong labor market supports consumer spending and economic growth, but the BOJ is also mindful of potential wage pressures. |
Impact of Economic Indicators on Policy Choices
The Bank of Japan’s policy choices are directly influenced by the performance of these key economic indicators. The central bank aims to maintain a balance between supporting economic growth and achieving its inflation target.
Inflation
The BOJ’s primary objective is to achieve price stability, with a target of 2% inflation. However, inflation has remained stubbornly below this target, indicating that price pressures are weak. This has prompted the BOJ to maintain its accommodative monetary policy, with low interest rates and quantitative easing measures, to stimulate demand and encourage inflation.
Economic Growth
Japan’s economy has shown signs of recovery in recent quarters, but growth remains fragile and uneven. The BOJ is cautious about tightening policy too quickly, as it wants to ensure a sustainable economic recovery. The central bank is likely to prioritize maintaining accommodative conditions to support growth and avoid a premature slowdown.
Unemployment
Low unemployment rates in Japan indicate a healthy labor market. This suggests that consumer spending and economic activity are relatively strong. However, the BOJ is also mindful of potential wage pressures that could arise from a tight labor market. The central bank may consider adjusting its policy stance if wage growth starts to accelerate significantly, as this could lead to higher inflation.
Global Context and International Comparisons
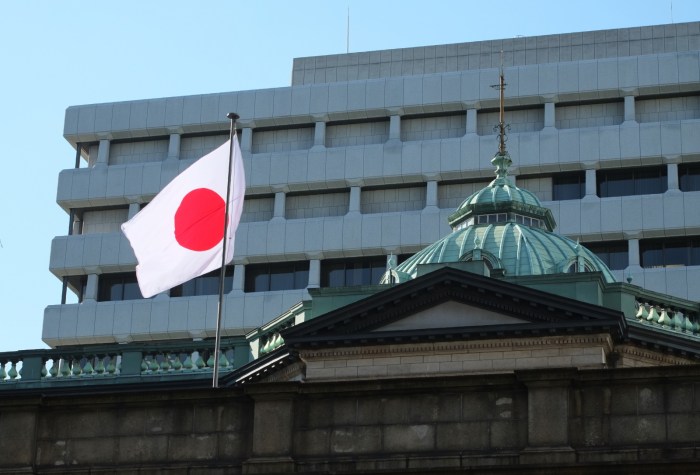

The Bank of Japan’s decision to maintain its ultra-loose monetary policy stands in stark contrast to the tightening measures adopted by other major central banks, such as the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank. This divergence reflects the unique economic challenges facing Japan and the global context in which these decisions are made.
Comparison of Interest Rate Policies, Bank of japan keeps benchmark interest rate steady as it treads cautiously on normalizing policy
The Bank of Japan’s current stance reflects its commitment to stimulating economic growth and overcoming deflationary pressures. In contrast, the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank have been raising interest rates to combat inflation, which has surged to multi-decade highs in many developed economies.
The following table provides a snapshot of interest rate policies among major central banks:
| Central Bank | Benchmark Interest Rate |
|---|---|
| Bank of Japan | -0.1% |
| Federal Reserve | 5.00%
|
| European Central Bank | 3.50% |
Global Economic Conditions and International Monetary Policy Trends
Global economic conditions and international monetary policy trends play a significant role in shaping the Bank of Japan’s decisions. The war in Ukraine, supply chain disruptions, and rising energy prices have contributed to global inflation, prompting many central banks to tighten monetary policy.
However, Japan’s economy faces unique challenges, including a shrinking population, low inflation, and a large public debt. The Bank of Japan’s cautious approach aims to support domestic growth while minimizing the risks of exacerbating deflationary pressures.
Implications of Divergent Monetary Policies
Divergent monetary policies across different economies can lead to various implications, including:* Currency Fluctuations:As interest rates rise in some countries, their currencies tend to appreciate against those of countries with lower rates. This can impact trade flows and competitiveness.
Capital Flows
Divergent monetary policies can attract capital flows to countries with higher interest rates, potentially affecting asset prices and economic stability.
Inflationary Pressures
Divergent monetary policies can contribute to inflation in countries with more accommodative policies, as imported goods become more expensive due to currency depreciation.
“The Bank of Japan’s current policy stance is a delicate balancing act, aimed at supporting domestic growth while minimizing the risks of exacerbating deflationary pressures.”
The Bank of Japan’s decision to keep its benchmark interest rate steady reflects a cautious approach to normalizing policy. This measured response is reminiscent of the need for careful consideration in other areas, such as healthcare, where a recent article highlights the alarming trend of harm at risk of being normalized in maternity care.
Just as the Bank of Japan is navigating a delicate balance between economic growth and inflation, healthcare providers must ensure that patient safety remains paramount, even amidst pressures to streamline processes.
The Bank of Japan’s cautious approach to normalizing interest rates is a bit like the NBA’s top big men – they’re both playing it smart. While the Bank keeps its benchmark rate steady, waiting for the right moment to act, NBA’s top 10 big men like Anthony Davis and Victor Wembanyama are strategically positioning themselves for dominance.
Just as the Bank carefully monitors inflation and economic growth, these players are analyzing their opponents and adjusting their game plans. Both the Bank and the NBA’s top players are demonstrating a calculated approach to success, aiming for sustainable growth and dominance.
The Bank of Japan’s decision to hold steady on interest rates while navigating the tricky path to normalizing policy feels a bit like watching Bob Dylan resurrect “Desolation Row” while clanking a tiny wrench – a touch unexpected, maybe even a bit jarring, but ultimately a fascinating spectacle.
The careful balancing act of maintaining stability while attempting to adjust course is a delicate one, and the world will be watching to see how this unfolds.