Avian Flu Spreads, Egg Prices Soar: Whats Happening?
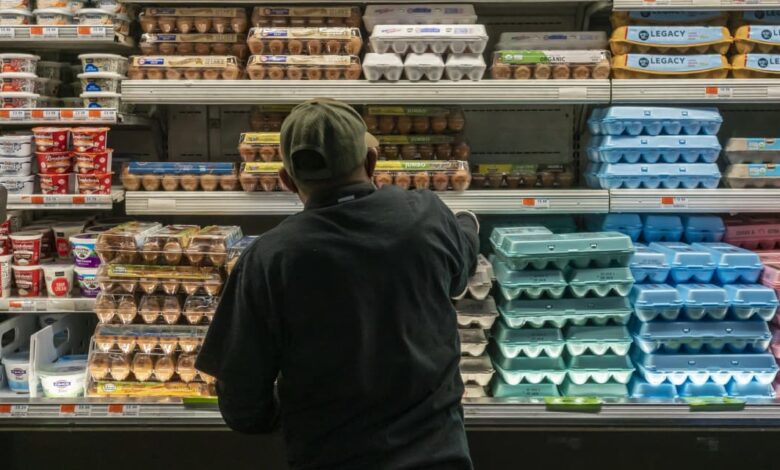
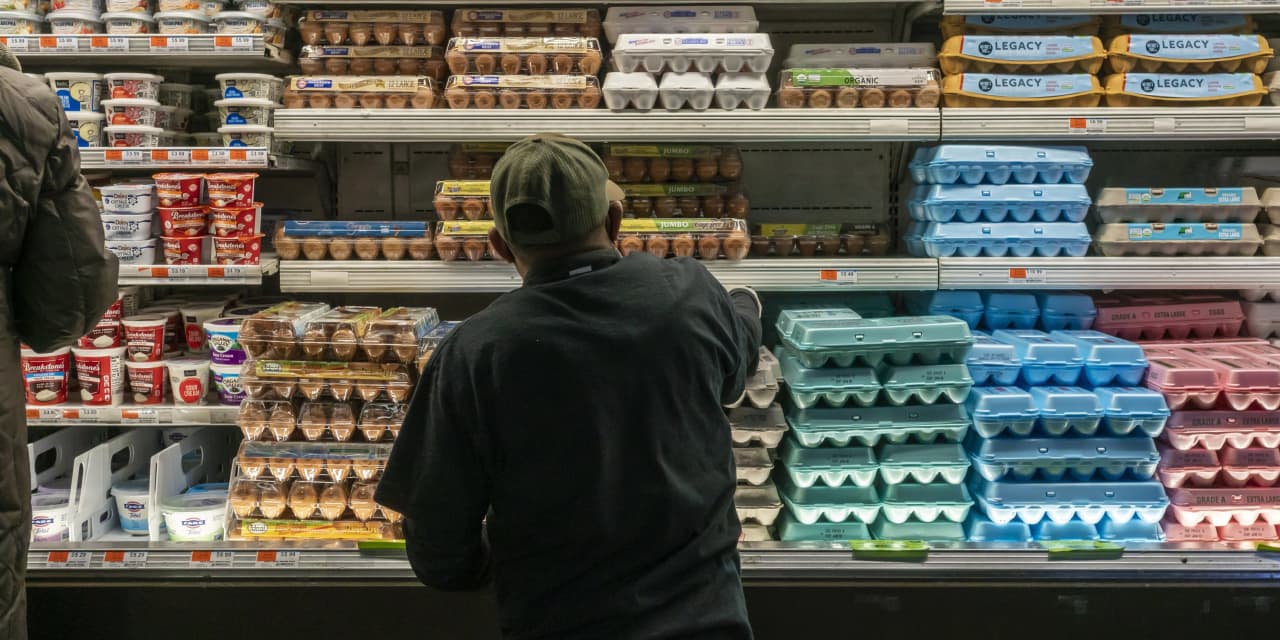
Avian flu has spread to 27 states sharply driving up egg prices, setting the stage for this enthralling narrative. Imagine this: you’re at the grocery store, ready to grab your usual carton of eggs, only to find the price has skyrocketed.
It’s not just a local phenomenon; this avian flu outbreak is affecting the entire country, causing a ripple effect across the poultry industry and leaving consumers scratching their heads.
The avian flu outbreak has led to a significant reduction in egg production, putting pressure on supply and pushing prices higher. This isn’t just a matter of inconvenience; it’s a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. We’ll delve into the details of the outbreak, explore the impact on the poultry industry, and analyze the implications for consumers.
Avian Flu Outbreak

The avian flu outbreak, also known as bird flu, is a significant concern for the poultry industry and public health. It is a highly contagious viral disease that affects birds, primarily poultry like chickens, turkeys, and ducks. The virus can spread rapidly through direct contact between infected birds, contaminated environments, or even through the air.
Impact and Spread of Avian Flu
The avian flu outbreak has been spreading rapidly across the United States, impacting poultry farms and raising concerns about the potential for human transmission. As of [insert current date], the virus has been detected in 27 states, affecting a wide range of poultry, including commercial flocks, backyard chickens, and wild birds.
The avian flu outbreak has been a real pain, spreading to 27 states and sending egg prices skyrocketing. It’s crazy how something like this can impact our daily lives! While we’re all dealing with this, it’s interesting to see how billionaires like Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos are navigating the world.
Elon Musk recently gave some advice to Jeff Bezos , which is pretty intriguing. Anyway, back to the eggs, I’m hoping this flu situation gets under control soon. It’s hard to imagine what our breakfast would be like without them!
The outbreak has resulted in significant losses for the poultry industry, with millions of birds being culled to prevent further spread.
Measures to Control the Spread
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is actively working to control the spread of the avian flu outbreak. The agency has implemented a number of measures, including:
- Surveillance and testing: The USDA is conducting extensive surveillance and testing of poultry flocks to identify and isolate infected birds.
- Quarantine and depopulation: Infected flocks are quarantined, and infected birds are culled to prevent further spread.
- Biosecurity measures: Poultry farmers are encouraged to implement strict biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of the virus onto their farms.
- Public awareness campaigns: The USDA is conducting public awareness campaigns to educate the public about avian flu and how to prevent its spread.
Consumer Impact and Responses
The avian flu outbreak has significantly impacted consumers, particularly those who rely on eggs as a staple in their diet. The sharp rise in egg prices has placed a strain on household budgets, forcing many to adjust their consumption patterns and seek alternatives.
Impact on Consumer Budgets
The rising egg prices have directly affected consumer budgets, especially for families and individuals who regularly consume eggs. The average price of a dozen eggs has increased by over 100% in some regions, making it a significant expense for many households.
For those on fixed incomes or with limited budgets, the price increase has made eggs a less affordable option, forcing them to make difficult choices about their grocery spending.
Consumer Responses to Price Increases
Consumers have responded to the price increases in various ways, seeking alternatives, reducing consumption, and advocating for government intervention.
Seeking Alternatives
Many consumers have sought alternatives to eggs, including:
- Substituting eggs with other protein sources, such as tofu, beans, or plant-based egg substitutes.
- Choosing less expensive egg alternatives, such as powdered eggs or frozen eggs.
- Reducing egg consumption by using fewer eggs in recipes or finding recipes that use fewer eggs.
Reducing Consumption
Some consumers have reduced their overall egg consumption due to the increased cost. This has led to a decline in demand for eggs, potentially impacting egg producers and the overall egg market.
The avian flu outbreak, now spreading across 27 states, has driven up egg prices, leaving many shoppers scrambling for alternatives. While this crisis unfolds, the former GOP lawmaker hearings will paint a picture of Trump as abandoned, isolated, and near solely responsible for the events leading up to January 6th, according to this report.
It’s a stark reminder that while we grapple with immediate challenges like soaring egg prices, the long-term consequences of political decisions can also have a profound impact on our lives.
Government Intervention
Consumers have also called for government intervention to mitigate the impact of rising egg prices. Some potential solutions include:
- Price controls to cap the price of eggs at a reasonable level.
- Financial assistance programs to help low-income households afford eggs.
- Increased funding for research and development of alternative protein sources.
Long-Term Effects on Consumer Behavior
The avian flu outbreak and its impact on egg prices could have long-term effects on consumer behavior. Consumers may develop a preference for alternative protein sources, leading to a shift in demand away from eggs. This shift could have implications for the egg industry and the overall food system.
Poultry Industry Response and Mitigation Strategies
The avian flu outbreak has posed significant challenges to the poultry industry, prompting swift and comprehensive responses to mitigate the spread of the virus and protect both animal health and livelihoods. Poultry producers, along with government agencies and researchers, have collaborated to implement a range of strategies aimed at containing the outbreak, minimizing economic losses, and preparing for future threats.
Biosecurity Measures and Disease Control
Stringent biosecurity protocols are crucial in preventing the spread of avian flu. The poultry industry has implemented measures to limit the introduction and transmission of the virus within flocks and across farms. These measures include:
- Restricting access to poultry farms by unauthorized personnel.
- Implementing strict hygiene practices for workers, including changing clothes and footwear before entering poultry houses.
- Disinfecting vehicles and equipment regularly to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Maintaining a physical barrier between flocks and wild birds, which can act as carriers of the virus.
- Implementing early detection and surveillance systems to identify infected flocks promptly.
These measures are essential for preventing the spread of avian flu and protecting the health of poultry flocks.
It’s crazy how the avian flu has spread to 27 states, causing a major egg shortage and skyrocketing prices. It’s enough to make you wonder if there’s a way to get more stability in your life, even in the face of these unpredictable events.
That’s why I think it’s worth exploring the concept of workplace monogamy, where you commit to a single employer for the long haul. Check out this article, 3 benefits of workplace monogamy and how to find it , to learn more about the potential benefits.
Who knows, maybe a stable career could help cushion the blow of those rising egg prices!
Public Health Implications: Avian Flu Has Spread To 27 States Sharply Driving Up Egg Prices
While the avian flu outbreak primarily affects poultry, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks to human health and the public health measures in place to mitigate those risks.
Avian Flu Transmission to Humans
The avian flu virus can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected birds or their contaminated environments. This typically occurs in individuals who work closely with poultry, such as farmers or poultry workers. Human-to-human transmission is rare and usually requires close contact with an infected individual.
Public Health Measures
Public health authorities worldwide are actively monitoring the situation and implementing measures to prevent human infections. These include:
- Surveillance and testing of poultry and humans to detect and track the virus.
- Strict biosecurity measures on poultry farms to prevent the spread of the virus among birds.
- Public awareness campaigns to educate the public about the risks of avian flu and the importance of hygiene practices.
- Prompt isolation and treatment of individuals who develop symptoms consistent with avian flu.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are essential in preventing the spread of avian flu. The public should be informed about:
- The signs and symptoms of avian flu in humans.
- The importance of avoiding contact with sick or dead birds.
- Proper handwashing and hygiene practices after handling poultry or visiting poultry farms.
- The importance of reporting any suspected cases of avian flu to public health authorities.
Impact on Food Safety and Consumer Confidence
The avian flu outbreak can have a significant impact on food safety and consumer confidence. The outbreak can lead to:
- Increased prices for poultry products due to supply chain disruptions.
- Concerns about the safety of poultry products, even though proper cooking methods effectively kill the virus.
- Reduced consumer demand for poultry products, potentially leading to economic losses for poultry farmers.
Global Perspective
The current avian flu outbreak in the United States is part of a global trend, with similar outbreaks occurring in various countries around the world. Understanding the global context is crucial for comprehending the impact of this outbreak and for developing effective mitigation strategies.
International Comparisons
Avian influenza outbreaks have been reported in numerous countries across the globe, including Asia, Europe, and Africa. While the specific strains and severity of the outbreaks may vary, the underlying challenges and consequences are often similar. For instance, in 2016, a highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N6 outbreak in South Korea led to the culling of millions of poultry, causing significant economic losses.
Similarly, in 2017, a HPAI H5N8 outbreak in Europe resulted in widespread poultry mortality and trade restrictions. Comparing these outbreaks to the current situation in the United States highlights the interconnectedness of the global poultry industry and the potential for rapid spread of avian influenza.
Global Implications
Trade Restrictions
Avian flu outbreaks can trigger trade restrictions, disrupting global poultry markets and affecting food security. For example, during the 2017 HPAI H5N8 outbreak in Europe, several countries imposed import bans on poultry products from affected regions, leading to supply chain disruptions and economic losses for poultry producers.
Similar trade restrictions are likely to be implemented in response to the current outbreak in the United States, impacting both domestic and international markets.
International Collaboration
International collaboration is crucial for effectively managing avian flu outbreaks. The World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) plays a key role in coordinating global surveillance and reporting efforts, providing technical assistance to countries facing outbreaks, and promoting best practices for disease control.
Other international organizations, such as the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), also contribute to global efforts by providing expertise in disease management, food safety, and public health.
Global Food Security, Avian flu has spread to 27 states sharply driving up egg prices
Avian flu outbreaks can pose a significant threat to global food security, particularly in regions heavily reliant on poultry production. The culling of infected poultry stocks can lead to shortages in meat and egg supplies, potentially driving up prices and impacting food affordability, especially for vulnerable populations.
Additionally, disruptions to international trade can further exacerbate these challenges, making it difficult to access essential poultry products from other countries.
Best Practices for Management
Managing avian flu outbreaks on a global scale requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing the following key elements:
- Enhanced Surveillance and Early Detection:Implementing robust surveillance systems to monitor poultry populations for signs of avian influenza is crucial for early detection and rapid response. This includes active surveillance in high-risk areas, as well as passive surveillance through reporting of suspected cases.
- Rapid Response and Control Measures:Once an outbreak is detected, swift and decisive action is needed to contain the spread of the virus. This includes culling infected poultry, implementing strict biosecurity measures, and restricting movement of poultry and poultry products.
- Vaccination Strategies:Vaccination can play a role in reducing the impact of avian flu outbreaks, but its effectiveness depends on the specific strain of the virus and the availability of suitable vaccines. Research and development of new vaccines are ongoing, and international collaboration is crucial for sharing knowledge and expertise.
- International Cooperation and Information Sharing:Open and timely communication between countries is essential for sharing information about outbreaks, coordinating control measures, and facilitating trade. International organizations like the OIE play a vital role in facilitating these communication channels.
Outcome Summary
The avian flu outbreak has highlighted the fragility of our food supply chain and the importance of preparedness. While the situation is challenging, it’s important to remember that we’re not helpless. By understanding the dynamics of this outbreak, we can take steps to mitigate the impact and ensure the long-term health of the poultry industry.
From biosecurity measures to innovative solutions, the future holds promise for a more resilient and sustainable approach to poultry production.