Australia and Human Rights: A Journey of Progress and Challenges
Australia and human rights, a topic that intertwines history, culture, and the ongoing pursuit of justice, paints a complex picture of a nation grappling with its past while striving for a more equitable future. From the impact of colonial policies on Indigenous Australians to the ongoing debates surrounding refugee rights and LGBTQ+ equality, Australia’s human rights landscape is a reflection of its social and political evolution.
This journey, marked by both strides and setbacks, delves into the historical context of human rights legislation, the key issues that continue to demand attention, and the role of government institutions, social factors, and international comparisons in shaping Australia’s human rights narrative.
By examining these aspects, we can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in ensuring a future where human rights are truly respected and upheld for all Australians.
Historical Context of Human Rights in Australia

Australia’s human rights journey is a complex tapestry woven from both domestic and international influences. While the nation has a long history of advocating for equality and justice, the formal recognition and protection of human rights have evolved significantly over time.
Australia boasts a strong commitment to human rights, but like any nation, it faces complex challenges. One such challenge is the ongoing debate surrounding the value placed on different lives, a topic explored in depth in the article different valuations of life.
This debate is particularly relevant to Australia’s ongoing struggle to reconcile its history of colonialism with its commitment to equality and justice for all.
Evolution of Human Rights Legislation in Australia
The evolution of human rights legislation in Australia can be traced back to the early days of British colonization. The Australian Constitution, adopted in 1901, contains some provisions that implicitly protect certain rights, such as freedom of religion and the right to a fair trial.
However, these provisions are limited in scope and do not provide comprehensive protection for human rights.
- Early 20th Century:The early decades of the 20th century saw the enactment of legislation that addressed specific human rights concerns, such as the Commonwealth Franchise Act 1902, which granted women the right to vote in federal elections, and the Immigration Restriction Act 1901, which aimed to restrict immigration from non-European countries.
- Post-World War II:Following World War II, Australia began to engage more actively in the international human rights arena. The nation became a founding member of the United Nations and signed the Universal Declaration of Human Rightsin 1948. This period saw the establishment of several key human rights institutions, including the Human Rights Commissionin 1986.
- Landmark Cases:Landmark cases, such as the Mabo v Queensland (No. 2)case in 1992, which recognized native title rights, and the Wik Peoples v Queenslandcase in 1996, which further clarified the scope of native title, have significantly shaped the understanding and protection of human rights in Australia.
Influence of International Human Rights Instruments
International human rights instruments have played a pivotal role in shaping Australian law and policy. Australia has ratified numerous international human rights treaties, including the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights(ICCPR) and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights(ICESCR).
Australia’s commitment to human rights is often lauded, but recent events raise questions about our stance on international affairs. The scrutiny surrounding the Iraq weapons inspections double standards highlights the need for consistent and ethical action from all nations, including Australia.
Ultimately, our actions must reflect our values and commitment to a world where human rights are upheld for all.
- Incorporation into Domestic Law:While Australia has not incorporated these treaties directly into domestic law, they are considered to be persuasive authorities in judicial decisions and have influenced the development of Australian human rights legislation.
- Influence on Policy:International human rights instruments have also influenced the development of Australian government policies, such as the National Human Rights Framework, which provides a framework for promoting and protecting human rights in Australia.
Human Rights in Australia Before and After the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Australia and human rights
The adoption of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights(UDHR) in 1948 marked a turning point in the global human rights landscape. The UDHR provided a universal framework for the protection of fundamental human rights, influencing the development of human rights law and policy in Australia and other countries.
- Before the UDHR:Before the UDHR, human rights protection in Australia was largely limited to the provisions of the Australian Constitution and specific legislation. While there were some progressive developments, such as the granting of women’s suffrage, discriminatory practices, such as the White Australia Policy, were still prevalent.
- After the UDHR:After the UDHR, Australia began to adopt a more proactive approach to human rights. The nation ratified several international human rights treaties and established human rights institutions. However, challenges remain in ensuring the full implementation of human rights in Australia.
Government Policies and Institutions: Australia And Human Rights

Australia’s commitment to human rights is enshrined in its Constitution, international treaties, and domestic legislation. The government plays a crucial role in promoting and protecting human rights through various policies, institutions, and legal frameworks.
The Australian Human Rights Commission
The Australian Human Rights Commission (AHRC) is an independent statutory body established in
1986. It plays a significant role in promoting and protecting human rights in Australia. The AHRC’s key functions include
- Providing advice and assistance to individuals and organizations on human rights issues.
- Investigating alleged breaches of human rights.
- Promoting public awareness of human rights.
- Making recommendations to the government on human rights matters.
- Monitoring Australia’s compliance with international human rights obligations.
The AHRC has a broad mandate to address a wide range of human rights issues, including discrimination, equality, freedom of speech, and the rights of children and people with disabilities. Its work has contributed significantly to raising awareness of human rights issues and promoting positive change in Australia.
Social and Cultural Factors

Australia’s social and cultural landscape profoundly influences its human rights record. These factors shape attitudes towards human rights, impact the implementation of policies, and influence the lived experiences of individuals and communities.
Australia has a long history of advocating for human rights, both domestically and internationally. While we’ve seen progress in areas like Indigenous rights, the challenges are ongoing. It’s important to learn from other nations’ experiences, such as the aftermath and rebuilding of Iraq , which highlighted the complex interplay between political stability, human rights, and development.
Understanding these challenges helps us refine our own approach to promoting human rights in Australia.
Media, Education, and Public Opinion
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion on human rights issues in Australia. News reports, documentaries, and social media discussions can raise awareness of human rights violations, promote dialogue, and influence policy decisions. Educational institutions also contribute significantly by fostering critical thinking and understanding of human rights principles.
Australia’s education system incorporates human rights education into its curriculum, aiming to develop informed and responsible citizens. Public opinion surveys and polls provide insights into Australians’ attitudes towards human rights, revealing areas of concern and support for specific rights.
Cultural Diversity and Immigration
Australia’s multicultural society presents both opportunities and challenges for human rights. Immigration has enriched the country’s cultural tapestry, but it has also led to concerns about discrimination and social inclusion. The government has implemented policies to address these concerns, such as anti-discrimination laws and programs promoting cultural diversity.
However, challenges remain, particularly in relation to the rights of Indigenous Australians, refugees, and asylum seekers.
International Comparisons
Australia’s human rights record is generally considered strong, reflecting its commitment to democratic values and the rule of law. However, like all nations, Australia faces challenges in upholding human rights standards. Comparing its human rights situation with other developed nations provides valuable insights into areas of strength and areas requiring improvement.
Comparisons with Other Developed Nations
This section examines how Australia’s human rights performance stacks up against other developed nations, identifying areas where it excels and areas where it lags behind.
- Australia ranks highly in global human rights indices, consistently appearing among the top performers. For example, the 2023 World Report by Human Rights Watch ranked Australia highly for its commitment to freedom of expression, freedom of the press, and protection of refugees.
- However, Australia faces criticism for its treatment of Indigenous Australians, particularly in areas such as health, education, and incarceration rates. These disparities highlight the need for greater efforts to address systemic inequalities and promote reconciliation.
- Australia’s refugee policy has also been subject to international scrutiny, with concerns raised about the detention of asylum seekers and the limited access to resettlement opportunities. This contrasts with other developed nations that have more generous refugee policies and prioritize protection for those fleeing persecution.
- In contrast, Australia is considered a leader in promoting gender equality and women’s rights. The country has strong legal frameworks protecting women from discrimination and violence, and it actively participates in international initiatives to advance women’s empowerment.
International Cooperation and Collaboration
International cooperation and collaboration play a crucial role in addressing human rights challenges. Australia’s engagement with international human rights mechanisms, such as the United Nations Human Rights Council and treaty bodies, demonstrates its commitment to upholding human rights standards.
- Australia actively participates in international human rights dialogues and contributes to the development of human rights norms and standards. For instance, it has played a leading role in promoting the rights of persons with disabilities and the rights of children.
- However, Australia has also been criticized for its reluctance to ratify certain international human rights treaties, such as the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR). This reluctance has raised concerns about its commitment to upholding all human rights, not just civil and political rights.
- Australia’s participation in international human rights mechanisms provides opportunities for constructive dialogue and engagement with other countries. This allows for sharing best practices, addressing concerns, and promoting accountability in the implementation of human rights standards.
- International cooperation is essential for tackling transnational human rights challenges, such as climate change, forced labor, and trafficking in persons. Australia’s collaboration with other nations in these areas is crucial for finding effective solutions and ensuring that human rights are protected in a globalized world.
Future Directions
Australia has made significant progress in promoting and protecting human rights, but there is still much work to be done. To ensure a future where human rights are fully realized for all Australians, a roadmap for enhancing human rights protection is essential.
This roadmap should be built upon a foundation of continuous improvement, collaborative action, and a commitment to accountability.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing Key Human Rights Issues
Several policy recommendations can contribute to a more just and equitable society. These recommendations address key human rights issues that require immediate attention and long-term solutions.
- Strengthening Indigenous Rights:Addressing the ongoing legacy of colonization and systemic discrimination against Indigenous Australians is paramount. This requires implementing the recommendations of the Uluru Statement from the Heart, including establishing a Voice to Parliament.
- Addressing Refugee and Asylum Seeker Rights:Australia’s current policies on asylum seekers and refugees have been widely criticized for their harshness and lack of compassion. Policy changes are needed to ensure that all asylum seekers are treated fairly and have access to safe and legal pathways to Australia.
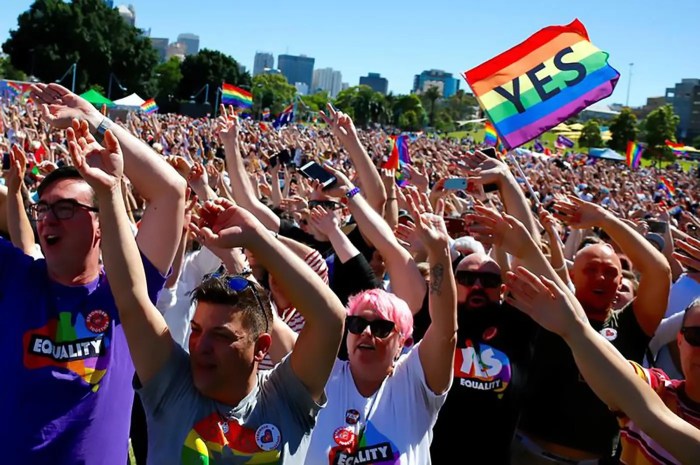
- Protecting the Rights of LGBTQIA+ People:Australia has made significant progress in advancing LGBTQIA+ rights, but more needs to be done. Addressing discrimination in areas such as employment, healthcare, and education is crucial.
- Promoting Gender Equality:Gender inequality persists in Australia, impacting women’s economic participation, safety, and access to healthcare. Policies aimed at closing the gender pay gap, preventing violence against women, and ensuring equal access to education and employment are essential.
The Role of Civil Society Organizations and Individuals in Advocating for Human Rights
Civil society organizations play a vital role in holding governments accountable for their human rights obligations. They act as watchdogs, monitoring government policies and practices, and raising awareness about human rights issues. Individuals can also play a crucial role in advocating for human rights.
They can support civil society organizations, participate in campaigns, and engage in public discourse on human rights issues.