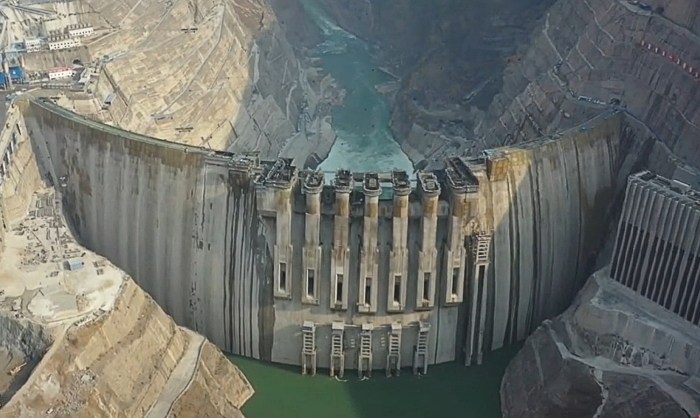
Ethiopias $5 Billion Dam: Why Its Stirring Regional Tensions
Analysis why ethiopias 5 billion dam has riled its neighbors quicktake – Ethiopia’s $5 Billion Dam: Why It’s Stirring Regional Tensions is a story of ambition, conflict, and the ever-present need for water in a thirsty world. The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), a monumental project designed to transform Ethiopia’s energy landscape, has ignited a diplomatic firestorm across the Nile Basin.
While Ethiopia envisions the dam as a key to economic prosperity and a symbol of its rising power, downstream nations like Egypt and Sudan fear its potential to disrupt their water supply, igniting tensions that have simmered for decades.
The GERD, when complete, will be the largest hydroelectric dam in Africa, capable of generating a significant amount of electricity for Ethiopia. This is crucial for a country that currently relies heavily on hydropower, making it vulnerable to droughts. The dam is expected to create thousands of jobs, attract foreign investment, and bolster Ethiopia’s agricultural sector.
However, the GERD’s potential benefits for Ethiopia come at a cost for its neighbors.
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), a massive hydroelectric project under construction on the Blue Nile River, is poised to be a game-changer for Ethiopia’s development trajectory. This ambitious endeavor holds the potential to transform the country’s energy sector, boost its economy, and elevate its standing on the global stage.
Economic Benefits and Social Implications
The GERD is expected to deliver significant economic benefits to Ethiopia. The dam will generate an estimated 6,000 megawatts of electricity, enough to power millions of homes and businesses. This surge in clean energy production will contribute to industrial growth, create new jobs, and improve the quality of life for Ethiopians.
The project is also anticipated to attract foreign investment and stimulate economic diversification. Furthermore, the dam’s construction phase itself has created thousands of employment opportunities for local workers.
Impact on Ethiopia’s Agricultural Sector and Water Security
The GERD is expected to have a profound impact on Ethiopia’s agricultural sector, which is heavily reliant on irrigation. The dam will provide a stable and reliable source of water for irrigation, allowing farmers to grow crops year-round and increase their yields.
This will enhance food security and contribute to rural development. The dam will also improve water security for Ethiopia by providing a buffer against drought and other climate-related challenges.
The GERD and Regional Tensions: Analysis Why Ethiopias 5 Billion Dam Has Riled Its Neighbors Quicktake
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) has become a focal point of tension in the Nile River basin, particularly between Ethiopia, Egypt, and Sudan. The dam, once completed, will be the largest hydroelectric dam in Africa, capable of generating significant power for Ethiopia while also altering the flow of the Nile River, a lifeline for downstream countries.
The Concerns of Egypt and Sudan, Analysis why ethiopias 5 billion dam has riled its neighbors quicktake
Egypt and Sudan have expressed serious concerns about the potential impact of the GERD on their water resources. They argue that the dam could significantly reduce the amount of water flowing downstream, jeopardizing their water security and impacting their agricultural sectors, which heavily rely on the Nile.
- Egypt:Egypt, a desert nation with a population of over 100 million, heavily depends on the Nile for its water supply, with almost all of its water resources coming from the river. The country fears that the GERD could significantly reduce its water share, potentially leading to water shortages and impacting its agricultural production, which is a crucial sector for the economy and food security.
The analysis of why Ethiopia’s 5 billion dam has riled its neighbors is a complex issue with geopolitical ramifications. It’s fascinating to see how these international disputes play out, much like the local drama unfolding in New York’s congressional primaries.
Keep an eye on the what to watch for in New York’s congressional primaries for insights into how these local races can mirror larger global conflicts, including the impact of the Ethiopian dam project on regional stability.
- Sudan:Sudan also relies heavily on the Nile for its water needs, particularly for irrigation and drinking water. The country fears that the GERD could disrupt the flow of the Nile, impacting its agricultural production and potentially leading to water shortages.
The analysis of why Ethiopia’s 5 billion dam has riled its neighbors is a complex geopolitical issue, and it’s interesting to see how similar tensions can arise in different contexts. For example, the article trump blames harris biden for second assassination attempt their rhetoric is causing me to be shot at highlights the dangerous consequences of inflammatory rhetoric.
Both situations demonstrate how miscommunication and a lack of understanding can escalate into conflict, making it crucial to prioritize diplomacy and dialogue in international relations.
The dam could also exacerbate existing water challenges in Sudan, which already faces droughts and water scarcity in certain regions.
Water Needs and Dependencies of Egypt, Sudan, and Ethiopia
The three countries have contrasting water needs and dependencies, making the GERD a complex issue with no easy solutions.
- Ethiopia:Ethiopia, with a population of over 110 million, has abundant water resources but lacks access to electricity. The GERD is seen as a crucial project for Ethiopia’s development, providing much-needed power for its growing economy and population. The dam is expected to generate a significant amount of electricity, contributing to Ethiopia’s industrialization and economic growth.
- Egypt:Egypt has a limited water supply, with the Nile providing almost all of its water needs. The country has a long history of relying on the Nile, and its water security is highly dependent on the river’s flow. Egypt’s dependence on the Nile makes it particularly sensitive to any changes in the river’s flow, particularly those caused by upstream dams.
- Sudan:Sudan has a more balanced water situation compared to Egypt, with a larger territory and more diverse water resources. However, Sudan still relies heavily on the Nile, particularly for irrigation and drinking water in the northern parts of the country.
The GERD could impact Sudan’s water security, particularly in regions that rely heavily on the Nile for their water needs.
Historical Context and Water Treaties
The current tensions over the GERD have a long history, rooted in colonial-era agreements and existing water treaties.
- 1929 Anglo-Egyptian Treaty:This treaty, signed between Britain and Egypt, granted Egypt the right to veto any upstream development projects on the Nile. This treaty was seen as unfair by other Nile Basin countries, including Ethiopia, which was not consulted during its negotiation.
- 1959 Agreement:This agreement between Egypt and Sudan divided the Nile’s water resources between the two countries, giving Egypt the lion’s share of the water. Ethiopia, despite being the source of the Blue Nile, which accounts for 85% of the Nile’s flow, was not included in this agreement.
- Nile Basin Initiative:This initiative, established in 1999, aimed to promote cooperation and equitable sharing of the Nile’s water resources among the ten Nile Basin countries. However, the initiative has faced challenges, with Egypt and Sudan resisting attempts to revise the existing water treaties.
The analysis of why Ethiopia’s 5 billion dam has riled its neighbors is a complex one, involving geopolitical tensions, water rights, and economic development. It’s a reminder that even as we grapple with international issues, there’s still a need for entertainment and excitement.
For those looking for a dose of both, the boxing match between Dan Azeez and Lewis Edmondson, added to the undercard of the Adam Azim vs. Ohara Davies fight, dan azeez vs lewis edmondson added to adam azim ohara davies undercard , is sure to deliver.
While the Ethiopian dam situation demands serious consideration, a good boxing match can provide a welcome escape from the complexities of international relations.
Diplomatic Efforts and Negotiations
The GERD dispute has been the subject of intense diplomatic efforts and negotiations, involving a range of actors, including the three riparian countries, regional organizations, and international partners. These efforts have aimed to reach a mutually acceptable agreement on the filling and operation of the dam, addressing the concerns of all parties involved.
Timeline of Negotiations
Negotiations over the GERD began shortly after the dam’s construction commenced in 2011. A series of tripartite talks, facilitated by the African Union (AU), have been held since then.
- 2011-2014:Initial negotiations focused on establishing a framework for cooperation and information sharing regarding the dam’s construction and operation.
- 2015-2017:The focus shifted to developing a framework agreement on the filling and operation of the dam. However, significant disagreements emerged over key issues, including the dam’s filling schedule, the allocation of water resources, and the dispute resolution mechanism.
- 2018-2020:The negotiations intensified, with the involvement of international actors like the United States and the European Union. Several rounds of talks were held, but no consensus was reached.
- 2020-Present:The negotiations have continued, with varying degrees of progress. The AU has played a crucial role in mediating the dispute, and several rounds of talks have been held under its auspices. However, the parties remain divided on several key issues.
Key Issues and Sticking Points
Several key issues have hampered progress in reaching a mutually acceptable agreement on the GERD.
- Filling Schedule:Ethiopia wants to fill the dam’s reservoir as quickly as possible, while Egypt insists on a slower filling schedule to mitigate potential impacts on its water supply.
- Water Allocation:Egypt demands a guaranteed annual water allocation from the Nile, while Ethiopia argues for a more flexible arrangement that takes into account the needs of all riparian countries.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanism:Egypt and Sudan have advocated for a binding dispute resolution mechanism, while Ethiopia has preferred a more flexible approach.
Role of International Actors and Regional Organizations
Several international actors and regional organizations have played a role in mediating the GERD dispute.
- African Union (AU):The AU has been the primary mediator in the dispute, facilitating tripartite talks and issuing statements calling for a negotiated solution.
- United States:The US has been involved in the negotiations, particularly during the Trump administration, when it played a role in facilitating talks between the parties.
- European Union (EU):The EU has also been involved in the negotiations, offering technical assistance and support for dialogue.
- United Nations (UN):The UN has provided technical assistance and support for the negotiations, but it has not played a direct mediating role.
Potential Impacts and Implications
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) has the potential to significantly impact the region, both positively and negatively. While the dam is envisioned to bring numerous benefits to Ethiopia, its construction and operation have sparked concerns among downstream countries, particularly Egypt and Sudan, who rely heavily on the Nile River for water resources.The potential impacts of the GERD can be categorized into economic, social, and environmental aspects.
These impacts are interconnected and can have cascading effects on the entire region.
Potential Impacts of the GERD
The following table Artikels the potential positive and negative impacts of the GERD on the region:| Impact | Positive | Negative ||—|—|—|| Economic|
- Increased electricity generation and export potential for Ethiopia.
- Enhanced agricultural productivity through irrigation in Ethiopia.
- Potential for regional economic integration and cooperation. |
- Potential economic losses for downstream countries due to reduced water availability.
- Increased dependence on Ethiopia for electricity supply.
- Risk of conflict and instability in the region. |
| Social|
- Improved living standards and quality of life in Ethiopia.
- Potential for job creation and economic development.
- Increased access to clean water and sanitation in Ethiopia. |
- Potential for displacement and social disruption in Ethiopia.
- Increased tensions and conflict between Ethiopia and downstream countries.
- Potential for social unrest and instability in the region. |
| Environmental|
- Potential for improved water management and flood control in Ethiopia.
- Increased biodiversity and ecosystem services in Ethiopia.
- Potential for regional environmental cooperation and collaboration. |
- Potential for negative impacts on downstream ecosystems due to reduced water flow.
- Increased risk of water scarcity and drought in downstream countries.
- Potential for environmental degradation and pollution. |
Consequences of a Failure to Reach an Agreement
A failure to reach a mutually acceptable agreement on the GERD’s operation could have severe consequences for the region.
“A failure to reach an agreement could lead to increased tensions, mistrust, and even conflict between Ethiopia, Egypt, and Sudan. It could also undermine regional stability and cooperation, hindering economic development and social progress in the Nile Basin.”
Water Flow Dynamics and the GERD
The GERD’s construction has significantly altered the water flow dynamics of the Nile River. [ Graphic representing the Nile River water flow dynamics and the impact of the GERD.]The graphic should illustrate the following:
- The Nile River’s flow from its source in the Ethiopian highlands to its delta in Egypt.
- The location of the GERD on the Blue Nile, a major tributary of the Nile.
- The impact of the GERD on the water flow downstream, showing the potential reduction in water availability for Egypt and Sudan.
The graphic should also highlight the importance of the Nile River as a source of water for millions of people in the region.
Future Perspectives and Solutions
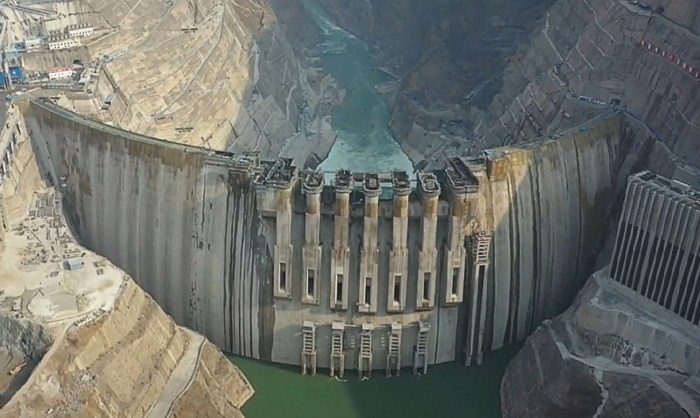

The GERD dispute underscores the urgency of finding a sustainable and equitable solution for the Nile Basin. A collaborative approach is crucial to ensure the shared resource benefits all riparian states while fostering regional stability.
Frameworks for Cooperation and Shared Water Management
Developing a comprehensive framework for cooperation and shared water management in the Nile Basin is vital. Such a framework would require a shift from a zero-sum mentality to a win-win approach, where all stakeholders recognize the interdependence of their water resources.
- Equitable Water Sharing Agreements:Establishing agreements that fairly distribute water resources based on factors like population, water needs, and ecological considerations. Examples include the Nile Basin Initiative (NBI), which aims to promote cooperation and sustainable water management.
- Joint Water Resource Management:Implementing joint projects for water infrastructure development, flood control, and drought mitigation, such as the proposed joint irrigation schemes and hydropower projects. This can foster collaboration and shared ownership of water resources.
- Data Sharing and Transparency:Establishing mechanisms for transparent data sharing on water levels, flows, and usage. This promotes trust and enables informed decision-making regarding water allocation and management.
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms:Developing robust and impartial mechanisms for resolving disputes over water resources, ensuring peaceful and amicable solutions. This could involve international arbitration or mediation, as seen in the UN Convention on the Law of the Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses.
Role of Diplomacy, Technology, and Regional Integration
Diplomacy, technology, and regional integration play crucial roles in fostering cooperation and resolving the GERD dispute.
- Diplomacy and Dialogue:Continued dialogue and negotiations are essential for building trust and understanding between riparian states. This includes involving regional and international actors, such as the African Union and the UN, to facilitate communication and mediate disputes.
- Technology and Innovation:Utilizing advanced technologies like remote sensing, satellite imagery, and water modeling to monitor water resources, predict water availability, and inform decision-making. This promotes transparency and efficient water management.
- Regional Integration:Strengthening regional cooperation through institutions like the NBI, the Nile Council of Ministers, and other platforms. This fosters shared understanding, collaboration, and collective action on water resource management.