Russias War in Ukraine: The Soviet Unions Final Demise
Analysis russias war in ukraine is how the soviet union finally ends – Russia’s War in Ukraine: The Soviet Union’s Final Demise sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The conflict in Ukraine isn’t just a geopolitical struggle; it’s a reflection of the lingering shadow of the Soviet Union, a ghost that continues to haunt the region.
We’ll delve into the historical context of this conflict, tracing the roots of the current crisis back to the collapse of the USSR and the unresolved tensions that have simmered ever since.
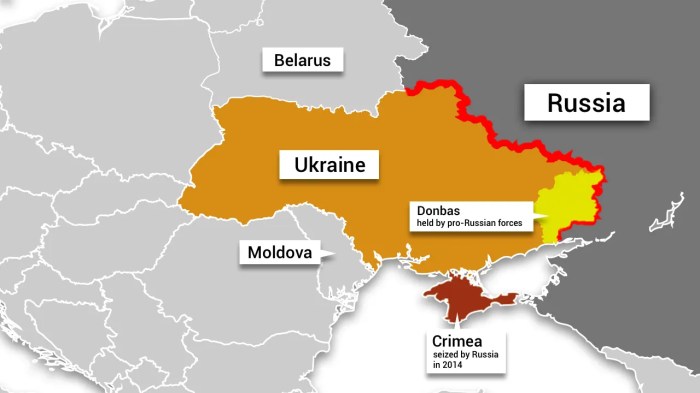
From the annexation of Crimea to the ongoing war in the Donbas, the conflict has brought to light the deep-seated resentments and ambitions that have shaped the relationship between Russia and Ukraine. We’ll explore the geopolitical motivations behind Russia’s actions, analyzing the strategic objectives and perceived threats that have fueled this confrontation.
The conflict has also had a profound impact on both Russia and Ukraine, reshaping their domestic and international landscapes. We’ll examine the consequences of the war, from the economic sanctions imposed on Russia to the human cost of the conflict in Ukraine.
The Legacy of the Soviet Union: Analysis Russias War In Ukraine Is How The Soviet Union Finally Ends
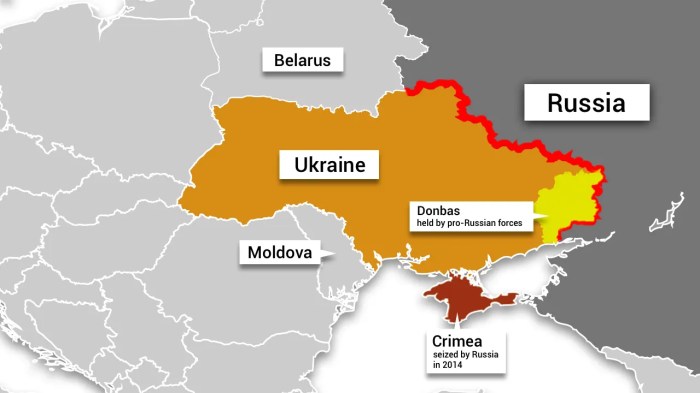
The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a pivotal moment in global history, leaving behind a complex legacy that continues to shape the political landscape of Russia and its former satellite states. Understanding the factors that led to the Soviet Union’s demise is crucial for grasping the current geopolitical situation and its potential future trajectories.
Key Factors Leading to the Soviet Union’s Collapse
The Soviet Union’s collapse was the culmination of a series of intertwined political, economic, and social factors.
- Economic Stagnation:The Soviet Union’s centrally planned economy, while initially successful in achieving rapid industrialization, became increasingly inefficient and unable to keep pace with the technological advancements of the West. The lack of incentives for innovation and the rigid bureaucratic structure stifled economic growth, leading to shortages, low productivity, and widespread dissatisfaction.
- Political Reform and Glasnost:In the mid-1980s, Mikhail Gorbachev implemented reforms aimed at revitalizing the Soviet system, including “perestroika” (restructuring) and “glasnost” (openness). These reforms, while intended to address the Soviet Union’s economic and political shortcomings, inadvertently loosened the grip of the Communist Party and empowered nationalist sentiments.
- Nationalism and Ethnic Tensions:The Soviet Union’s multinational structure, with its diverse ethnic groups and languages, was inherently fragile. The decline of the Soviet system and the loosening of centralized control allowed nationalist movements to flourish, particularly in the Baltic republics and other regions seeking independence.
- The Cold War and Military Spending:The Cold War arms race placed a significant strain on the Soviet economy, diverting resources away from domestic needs and contributing to its economic stagnation. The Soviet Union’s military intervention in Afghanistan, a costly and protracted conflict, further exacerbated the situation.
- The August Coup Attempt:In 1991, a group of hardliners attempted to seize control of the Soviet government, leading to a brief period of uncertainty and instability. The failure of the coup attempt further weakened the Soviet Union and accelerated its disintegration.
The Lasting Impact of Soviet Ideology and Policies
The Soviet Union’s ideology and policies left a profound and lasting impact on Russia and its neighboring countries, both positive and negative.
- Economic Development and Industrialization:Despite its inefficiencies, the Soviet Union’s centralized economic planning played a significant role in promoting industrialization and raising living standards for many citizens, particularly in the early decades after World War II.
- Social Welfare and Education:The Soviet Union implemented extensive social welfare programs, providing universal healthcare, education, and housing. This led to a significant increase in literacy rates and a reduction in poverty.
- Political Control and Repression:The Soviet Union’s authoritarian political system, based on one-party rule and suppression of dissent, resulted in widespread political repression, including imprisonment, exile, and executions. This legacy continues to cast a long shadow over Russia’s political culture and human rights record.
- National Identity and Historical Narratives:The Soviet Union’s ideology promoted a sense of shared Soviet identity and a specific historical narrative that emphasized the country’s role as a liberator and champion of the working class. This narrative has been challenged and reinterpreted since the Soviet Union’s collapse, leading to ongoing debates about national identity and historical memory.
Comparing and Contrasting the Soviet Union and Contemporary Russia, Analysis russias war in ukraine is how the soviet union finally ends
While the Soviet Union and contemporary Russia share a common history and cultural heritage, their political and economic systems differ significantly.
- Political System:The Soviet Union was a one-party communist state with a centralized command economy. Contemporary Russia is a semi-presidential republic with a multi-party system, although political power remains highly concentrated in the hands of the president.
- Economic System:The Soviet Union’s centrally planned economy was characterized by state ownership of the means of production, price controls, and a lack of competition. Contemporary Russia has transitioned to a market-based economy with private ownership and free enterprise, although the state continues to play a significant role in key sectors.
- Social Welfare:The Soviet Union provided extensive social welfare programs, including universal healthcare and education. Contemporary Russia’s social welfare system has been scaled back since the collapse of the Soviet Union, although it still provides some essential benefits, such as pensions and unemployment insurance.
- Foreign Policy:The Soviet Union pursued a policy of global expansion and confrontation with the West during the Cold War. Contemporary Russia, while maintaining a strong military and pursuing its own national interests, has adopted a more pragmatic and less confrontational foreign policy approach.
Analyzing Russia’s war in Ukraine reveals the final act of the Soviet Union’s demise. The economic sanctions imposed on Russia are a direct consequence of its actions, mirroring the international isolation the Soviet Union faced before its collapse. While the global impact is undeniable, the markets are still responding positively.
The news that Asia Pacific markets opened higher, tracking rises in the Dow and S&P 500 is a testament to the resilience of the global economy, even amidst geopolitical turmoil. This resilience, however, should not be mistaken for indifference to the humanitarian crisis unfolding in Ukraine.
The war serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of peace and the enduring legacy of the Soviet Union’s collapse.
Watching Russia’s war in Ukraine unfold feels like a historical turning point. It’s almost as if the Soviet Union, in all its flawed glory, is finally being laid to rest. But back to the present, I’m also keeping an eye on the Wolverines.
Michigan’s offense is looking to bounce back, and I’m excited to see what Alex Orji can do at quarterback. Here’s a breakdown of why I think he’s the answer. Ultimately, though, I’m still drawn back to the larger picture of the world stage, and the historical echoes of the Cold War that seem to be reverberating through the conflict in Ukraine.
The ongoing analysis of Russia’s war in Ukraine reveals a stark reality: the Soviet Union, in its modern iteration, is finally collapsing. This conflict isn’t just about territorial gains, it’s about the unraveling of a system built on imperial ambitions and flawed ideology.
It’s a reminder that even the most formidable empires can crumble under the weight of their own contradictions. Speaking of contradictions, the recent benching of Bryce Young in favor of Andy Dalton is a curious development, prompting questions about the team’s strategy and the young quarterback’s future.
Why was Bryce Young benched update after Andy Dalton was chosen ? Just as the Soviet Union’s demise highlights the fragility of power structures, the decision to bench Young raises questions about the future of the team and its ability to compete.
The parallels between these seemingly disparate events are striking, offering a glimpse into the complexities of power dynamics and the unpredictable nature of change.






