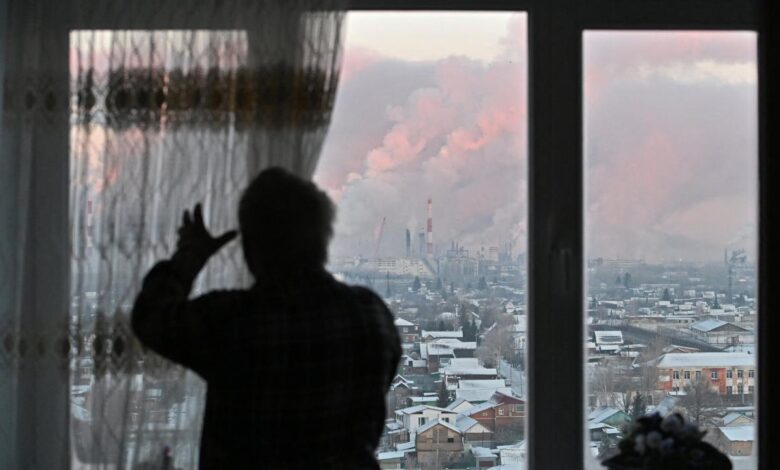
Analysis Capping Russian Oil Prices: Pure Fantasy
Analysis capping Russian oil prices is pure fantasy. It’s a concept that has been floated around in recent months, as the world grapples with the economic and geopolitical fallout of the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. The idea is simple: to limit Russia’s oil revenue by imposing a price ceiling on its exports.
But is this a viable solution, or just wishful thinking? This article delves into the complexities of the global oil market and the potential implications of such a policy.
The global oil market is a complex web of supply and demand, influenced by factors ranging from geopolitical events to technological advancements. Russia, as a major oil producer and exporter, plays a crucial role in this market. The current conflict has disrupted supply chains, leading to volatility in oil prices and raising concerns about energy security.
This has prompted calls for measures to limit Russia’s influence on the market, including the controversial idea of a price cap.
The Global Oil Market Landscape: Analysis Capping Russian Oil Prices Is Pure Fantasy
The global oil market is a complex and dynamic system, influenced by a myriad of factors, including supply and demand, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. Understanding the current dynamics of this market is crucial for comprehending the impact of events like the ongoing conflict in Ukraine on global energy prices.
Global Oil Supply and Demand, Analysis capping russian oil prices is pure fantasy
Global oil supply and demand are constantly fluctuating, influencing prices and market stability. Supply is primarily driven by production levels in major oil-producing countries, while demand is largely determined by global economic activity and energy consumption patterns.
- Production Levels:The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, collectively known as OPEC+, play a significant role in global oil production. OPEC+ has the ability to influence global supply by adjusting production quotas.
- Economic Activity:Global economic growth and industrial activity are major drivers of oil demand. When economies are expanding, demand for oil tends to increase as businesses and consumers require more energy for transportation and manufacturing.
- Energy Consumption Patterns:The shift towards renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures can influence global oil demand. As countries adopt cleaner energy solutions, demand for oil may decrease over time.
Russia’s Role in the Global Oil Market
Russia is a major oil producer and exporter, playing a significant role in the global oil market. Its oil exports are a crucial source of revenue for the country, and its production capacity significantly influences global supply.
- Production Capacity:Russia is among the world’s largest oil producers, with significant reserves and production capacity. It accounts for a substantial portion of global oil exports.
- Export Destinations:Russia exports oil to various countries, including Europe, Asia, and the United States. Its exports are essential for meeting energy needs in several regions.
- Price Impact:Russia’s production and export levels have a significant impact on global oil prices. Changes in its output or export policies can lead to price fluctuations.
Impact of the Conflict on Global Oil Prices
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has significantly impacted the global oil market, leading to price volatility and uncertainty. The conflict has disrupted energy supplies, raised concerns about global energy security, and created geopolitical tensions.
- Supply Disruptions:The conflict has disrupted oil production and exports from Russia and Ukraine, impacting global supply chains and contributing to higher prices.
- Sanctions and Restrictions:Sanctions imposed on Russia by Western countries have further restricted its oil exports, further contributing to price increases.
- Market Volatility:The conflict has created uncertainty and volatility in the oil market, as investors and traders react to evolving geopolitical events and their potential impact on supply and demand.
The Mechanics of Price Caps
A price cap is a government-imposed limit on the price of a good or service. In the context of oil, a price cap would set a maximum price that buyers can pay for Russian oil. The goal is to reduce Russia’s oil revenue while still allowing oil to flow to the global market.The mechanism for implementing a price cap would involve a combination of measures:
Setting the Price Cap
The price cap would be set at a level that is deemed acceptable by the participating countries, taking into account the current market price of oil, the cost of production, and the potential impact on supply. The goal is to strike a balance between limiting Russia’s revenue and ensuring that enough oil continues to flow to the market.
Enforcement
The price cap would be enforced through a combination of measures, including:
- Restrictions on insurance:Participating countries could refuse to provide insurance for oil shipments that exceed the price cap. This would make it difficult for buyers to transport Russian oil.
- Financial sanctions:Participating countries could impose financial sanctions on buyers or sellers who violate the price cap.
- Market monitoring:Participating countries could work together to monitor the market and ensure that the price cap is being adhered to.
Potential Benefits
The potential benefits of a price cap include:
- Reduced revenue for Russia:A price cap would reduce the revenue that Russia earns from its oil exports. This would limit Russia’s ability to finance its war in Ukraine.
- Stabilization of the global oil market:A price cap could help to stabilize the global oil market by ensuring that a steady supply of oil continues to flow. This would help to prevent oil prices from spiking.
- Reduced inflation:A price cap could help to reduce inflation by keeping oil prices in check. This would benefit consumers and businesses.
Potential Drawbacks
The potential drawbacks of a price cap include:
- Disruptions to supply chains:A price cap could disrupt supply chains by making it more difficult for buyers to obtain Russian oil. This could lead to shortages and higher prices.
- Increased costs for buyers:A price cap could increase costs for buyers, as they may have to pay more for alternative sources of oil.
- Black market activity:A price cap could lead to increased black market activity, as buyers and sellers try to circumvent the restrictions.
Russia’s Response and Countermeasures
The effectiveness of a price cap on Russian oil hinges on Russia’s response. Moscow has a range of options at its disposal, each with its own implications for the global energy market.
Potential Reactions to a Price Cap
Russia’s response to a price cap is likely to be multifaceted and driven by a desire to minimize the economic impact while asserting its geopolitical influence.
- Production Cuts:Russia could reduce its oil production, aiming to tighten supply and push prices higher, thereby negating the impact of the cap. This strategy, however, carries risks. Reduced production could lead to a loss of market share and revenue, potentially harming Russia’s long-term economic prospects.
- Diverting Exports:Russia could redirect its oil exports to alternative markets, seeking buyers willing to pay higher prices. This could involve strengthening ties with existing partners like China and India or exploring new markets in Latin America or Africa. However, these alternative markets may not be able to absorb the full volume of Russian oil, and transporting oil to these regions can be costly.
- Refusal to Sell to Price-Capped Buyers:Russia could simply refuse to sell oil to countries adhering to the price cap. This would likely lead to a shortage of oil in those countries, potentially pushing prices up and undermining the effectiveness of the cap. However, this strategy could also backfire, as it would limit Russia’s access to key markets.
The idea that capping Russian oil prices will significantly impact their economy is, frankly, a bit of a fantasy. While the idea of curtailing their revenue is tempting, the reality is that Russia will likely find ways to adapt and continue selling their oil, albeit at a slightly lower price.
This brings up the question: is free speech essential for democracy, or could it be the very thing that brings about its downfall? This debate is a fascinating one, and ultimately, it’s the ability to have this discussion freely that truly defines a democracy.
Ultimately, the impact of price caps on Russian oil will likely be minimal, and the real question is whether we can maintain a democratic society in the face of increasingly polarized and volatile discourse.
- Disrupting Oil Production:Russia could disrupt its own oil production, potentially by targeting key infrastructure or disrupting operations. This would be a drastic measure with significant economic and geopolitical consequences. It could also be difficult to implement effectively, as it would likely require a coordinated effort across various sectors.
The Impact on Western Economies
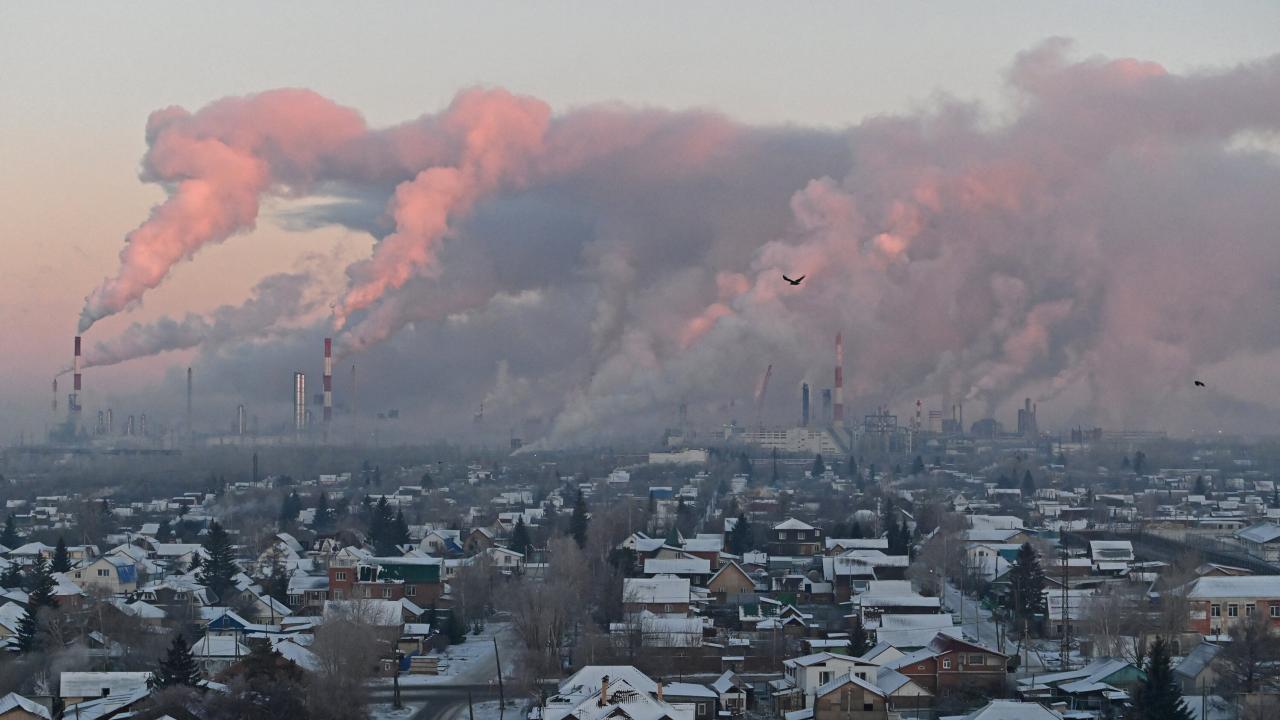

The potential economic impact of a price cap on Russian oil on Western economies is a complex issue with both positive and negative implications. While the price cap aims to limit Russia’s revenue from oil exports, it could also lead to unintended consequences for Western energy security and inflation.
The idea that we can simply cap Russian oil prices is pure fantasy. It’s like thinking we can control the weather or stop the sun from rising. The global energy market is far too complex, and the potential consequences of such a move are simply too great.
Meanwhile, the Pentagon is planning for a possible Pelosi trip to Taiwan , which is a much more immediate and tangible threat. Trying to control the price of oil is a futile effort, especially when there are much more pressing geopolitical issues at hand.
Energy Security
A price cap could potentially disrupt global oil markets, leading to supply shortages and higher energy prices in Western economies. If Russia retaliates by reducing oil exports, Western countries may face difficulties in securing alternative sources of supply, particularly in the short term.
The potential for supply disruptions could exacerbate existing energy security concerns and force Western countries to rely more heavily on domestic production or alternative energy sources, such as renewables.
Alternative Approaches
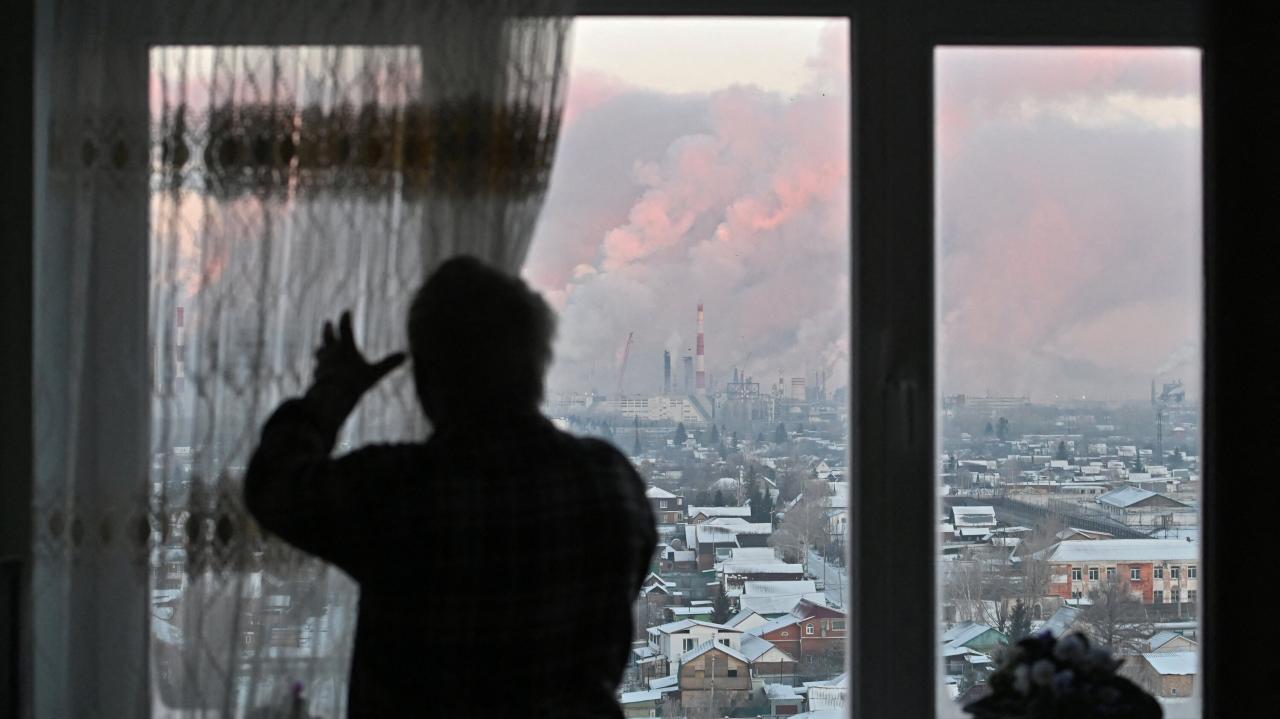

While the price cap on Russian oil is a bold attempt to curb its revenue, its effectiveness remains uncertain. This raises the question of whether other approaches could be more effective in achieving the same goal.This section delves into alternative strategies for limiting Russia’s oil revenue, analyzing their feasibility and potential impact.
Targeted Sanctions
Targeted sanctions, specifically aimed at crippling Russia’s oil industry, could be a more effective alternative to a price cap. This involves targeting specific companies, individuals, or assets involved in the production, transportation, and sale of Russian oil.
- Sanctions on specific oil companies:Imposing strict sanctions on key Russian oil companies, such as Rosneft and Gazprom Neft, could significantly disrupt their operations and limit their ability to produce and export oil. This could involve asset freezes, restrictions on financing, and bans on key equipment and technology imports.
- Sanctions on individuals:Targeting individuals responsible for key decisions within the Russian oil industry, such as executives and government officials, could exert significant pressure on the industry. This could involve travel bans, asset freezes, and restrictions on their financial activities.
- Sanctions on oil infrastructure:Targeting critical oil infrastructure, such as pipelines, refineries, and storage facilities, could disrupt the flow of oil and significantly reduce Russia’s export capacity. This could involve restrictions on the use of certain technologies, bans on the supply of essential components, and targeted attacks on specific infrastructure assets.
Diversifying Energy Sources
The reliance on Russian oil highlights the vulnerability of Western economies to energy dependence. Diversifying energy sources is crucial for reducing this vulnerability and limiting Russia’s leverage.
Capping Russian oil prices is a pipe dream, a fantasy based on wishful thinking. It’s like expecting India’s world-beating growth to automatically translate into a booming job market, a phenomenon explored in detail in this insightful article analysis why indias world beating growth isnt creating jobs.
Just as India’s growth is a complex puzzle, so too is the global energy landscape, and trying to artificially control prices will only create unintended consequences, potentially even fueling instability and further complicating an already delicate situation.
- Increased investment in renewable energy:This involves a significant shift towards solar, wind, geothermal, and other renewable energy sources. Governments can incentivize this transition through subsidies, tax breaks, and regulatory frameworks that support renewable energy development. This approach requires substantial investment and time, but it offers a long-term solution to energy dependence.
- Expansion of domestic oil and gas production:Countries can explore and exploit their own oil and gas reserves to reduce their reliance on imports. This can be achieved through increased exploration and production activities, incentivizing domestic energy companies, and relaxing regulations on fossil fuel extraction. However, this approach may have environmental implications and can contribute to climate change.
- Strengthening energy partnerships:Building stronger energy partnerships with other countries can provide alternative sources of energy. This can involve establishing long-term contracts, joint ventures, and collaborative infrastructure projects to ensure reliable energy supplies. This approach requires strategic diplomacy and cooperation with other countries.
International Cooperation on Energy Policy
International cooperation is crucial for effectively addressing the challenges posed by Russia’s oil exports. Collaborative efforts can create a more unified front against Russia and promote energy security for all participating countries.
- Joint sanctions and enforcement:Coordinated sanctions imposed by a coalition of countries can be more effective than unilateral actions. This requires close collaboration on enforcement mechanisms and monitoring to prevent sanctions circumvention.
- Shared energy infrastructure:Developing shared energy infrastructure, such as pipelines and transmission networks, can reduce reliance on individual countries and create more diversified energy supplies. This requires international agreements and joint investments.
- Research and development:Collaborative research and development efforts in renewable energy technologies can accelerate the transition to cleaner energy sources and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. This can involve sharing expertise, funding joint projects, and promoting technology transfer.
Long-Term Implications
The price cap on Russian oil, while intended as a short-term measure to curb Moscow’s war chest, carries significant long-term implications for the global oil market, energy transition, and geopolitical landscape.
Impact on the Energy Transition
The price cap could inadvertently slow down the energy transition by making it more difficult for renewable energy sources to compete with cheaper fossil fuels. While the price cap aims to reduce Russian oil revenue, it could also reduce investment in renewable energy, as the price of oil becomes more attractive to producers and consumers.
This could potentially hinder the global effort to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
Geopolitical Shifts
The price cap could further strain relations between Russia and the West, leading to a more fragmented global energy market. This could potentially result in:
- Increased dependence on alternative suppliers:Countries seeking to replace Russian oil may turn to other producers, potentially leading to new geopolitical alliances and dependencies. This could create new challenges for global energy security and stability.
- Formation of new energy blocs:The price cap could encourage the formation of new energy blocs, potentially isolating Russia and creating a more fragmented global energy market. This could lead to increased competition and tension between energy-producing and energy-consuming nations.
- Escalation of geopolitical tensions:The price cap could further escalate tensions between Russia and the West, potentially leading to more aggressive actions from Moscow. This could have significant implications for global security and stability.
Impact on the Global Oil Market
The long-term impact on the global oil market remains uncertain, but several possibilities exist:
- Increased volatility:The price cap could lead to increased volatility in the global oil market, as producers and consumers adjust to the new market conditions. This could make it more difficult for businesses to plan and invest, potentially hindering economic growth.
- Reduced investment in oil production:The price cap could discourage investment in new oil production, as producers become less confident in the long-term profitability of their operations. This could lead to a decline in oil supply and potentially higher oil prices in the future.
- Shift in production patterns:The price cap could encourage producers outside of Russia to increase production, potentially shifting the global oil market away from Russia’s dominance. This could have significant implications for the global energy landscape.
Concluding Remarks
The idea of capping Russian oil prices is a tempting one, but it is ultimately a fantasy. The global oil market is too complex and interconnected for such a policy to be effective. It would likely lead to unintended consequences, including disruptions to supply chains and increased volatility in oil prices.
Furthermore, Russia has shown a willingness to use its energy resources as a weapon, and a price cap could simply encourage them to further restrict exports or seek alternative markets. Instead of pursuing this unrealistic solution, policymakers should focus on diversifying energy sources, promoting renewable energy, and strengthening international cooperation to address the challenges of the global oil market.