Anti-Abortion States Face Doctor Shortage
A challenge for antiabortion states doctors reluctant to work there, the increasing restrictions on abortion access are creating a growing doctor shortage in these states. This shortage is a result of various factors, including moral and ethical concerns among medical professionals, legal and professional risks associated with providing abortion care, and the limited availability of training and resources for abortion providers.
The impact of this shortage is particularly felt in rural communities, where access to healthcare is already limited. With fewer doctors willing to work in these areas, women seeking abortion care face even greater challenges. This can lead to increased health risks, delays in care, and even forced pregnancies.
The situation is further complicated by the lack of comprehensive medical education and training regarding abortion care in many medical schools and residency programs.
The Impact of Abortion Restrictions on Healthcare Access
The enactment of restrictive abortion laws across the United States has far-reaching consequences, extending beyond the realm of reproductive rights to impact overall healthcare access and quality in affected states. This impact is multifaceted, potentially leading to a cascade of adverse effects on both individuals and the healthcare system as a whole.
It’s a tough situation for doctors in antiabortion states. Many are reluctant to work there, fearing legal repercussions and ethical dilemmas. It’s a stark contrast to the laid-back atmosphere of Cornwall, where you can find hidden gems like the Idle Rocks, a restaurant known for its delicious seafood and breathtaking views.
While the Idle Rocks offers a peaceful escape, the challenges faced by doctors in antiabortion states remain a pressing concern.
The Potential Consequences of Limited Abortion Access on Overall Healthcare Services, A challenge for antiabortion states doctors reluctant to work there
Restrictions on abortion access can create a ripple effect across the healthcare landscape, potentially affecting the availability and quality of other essential medical services.
- Strained Healthcare Resources:The influx of patients seeking alternative healthcare services, such as family planning, prenatal care, and treatment for complications arising from unsafe abortions, can place a significant burden on healthcare providers and facilities, diverting resources away from other critical services.
- Increased Healthcare Costs:The financial burden of managing complications from unsafe abortions and providing alternative care can lead to increased healthcare costs for both individuals and the healthcare system.
- Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations:Restrictions on abortion access disproportionately impact marginalized communities, including low-income individuals, people of color, and those residing in rural areas, who may lack access to quality healthcare services and resources.
The Impact on Maternal Health Outcomes
Restricting access to safe and legal abortion can have dire consequences for maternal health, potentially leading to increased complications and mortality rates.
- Increased Risk of Maternal Mortality:Denying women access to safe abortion increases the risk of unsafe abortions, which can lead to severe complications, including sepsis, hemorrhage, and death.
- Higher Rates of Maternal Morbidity:Complications from unsafe abortions can result in long-term health problems, such as infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and psychological distress.
- Delayed or Forgone Prenatal Care:Fear of legal repercussions and the logistical challenges of accessing abortion services in restrictive states can deter women from seeking timely and adequate prenatal care, further jeopardizing their health and the well-being of their unborn children.
Challenges Faced by Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers in restrictive environments face numerous challenges in providing comprehensive reproductive healthcare services.
- Legal Uncertainty and Fear of Prosecution:The ambiguous and evolving legal landscape surrounding abortion in many states creates a climate of uncertainty and fear for healthcare providers, making them hesitant to offer abortion services or even provide comprehensive reproductive healthcare counseling.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Moral Conflicts:Healthcare providers may face ethical dilemmas and moral conflicts when their personal beliefs clash with their professional obligations to provide evidence-based medical care, particularly in situations where abortion is medically necessary.
- Limited Resources and Training:Healthcare providers in restrictive states may lack access to adequate training and resources to provide comprehensive reproductive healthcare services, including abortion care.
The Doctor Shortage in Anti-Abortion States
The recent wave of restrictive abortion laws across the United States has sparked a significant concern: a growing doctor shortage in states with these restrictions. This shortage is not just a matter of numbers; it represents a critical threat to the overall health and well-being of individuals and communities in these states.
Reasons for the Doctor Shortage
The reasons behind the doctor shortage in anti-abortion states are multifaceted and complex.
- Limited Access to Training and Education:Many medical schools and residency programs are located in states with more permissive abortion laws. This means that aspiring doctors may not have the opportunity to receive comprehensive training in reproductive healthcare, including abortion care, during their medical education.
This lack of training can create a barrier for doctors who are interested in practicing in states with restrictive abortion laws.
- Moral and Ethical Concerns:Many doctors have strong personal and professional convictions about the right to access safe and legal abortion care. They may be unwilling to work in states where these rights are significantly curtailed or even criminalized. The ethical dilemma of being forced to practice in a manner that contradicts their personal beliefs is a significant deterrent for many doctors.
- Legal and Professional Risks:Doctors who provide abortion care in restrictive states face significant legal and professional risks. They may be subject to criminal prosecution, disciplinary action from medical boards, and even civil lawsuits. This creates a chilling effect on doctors, making them hesitant to practice in states with restrictive abortion laws.
- Financial Considerations:Doctors may also be concerned about the financial implications of providing abortion care in restrictive states. They may face higher insurance premiums, increased malpractice liability, and potential loss of income due to reduced patient volume. This can make it financially unfeasible for doctors to practice in these states.
Impact of Moral and Ethical Concerns
The ethical and moral dilemmas faced by doctors are central to the issue of doctor shortages in anti-abortion states. Doctors are bound by the Hippocratic Oath to “do no harm” and to act in the best interests of their patients.
However, in states with restrictive abortion laws, doctors may find themselves in situations where they are unable to provide the full range of medical care that their patients need. This creates a conflict between their ethical obligations and the legal restrictions imposed by the state.
The Impact on Rural Communities
Rural communities in the United States face unique challenges when it comes to accessing abortion care. These challenges are amplified by the increasing restrictions on abortion access in many states, particularly those with large rural populations. This section explores the specific impact of these restrictions on rural communities, highlighting the disparities in healthcare access and outcomes between rural and urban areas.
Limited Provider Access
Rural communities often have a limited number of healthcare providers, including obstetricians and gynecologists (OB-GYNs) who can provide abortion care. This shortage of providers is exacerbated by the increasing reluctance of doctors to practice in rural areas, due to factors such as low reimbursement rates, limited resources, and a lack of specialized training in abortion care.
- A study by the Guttmacher Institute found that only 10% of counties in the United States have an abortion provider, and many of these providers are located in urban areas.
- This limited access to providers means that rural residents often have to travel long distances to reach a clinic that offers abortion services, which can be a significant financial and logistical burden.
Disparities in Healthcare Access and Outcomes
The limited access to abortion care in rural communities can lead to significant disparities in healthcare access and outcomes between rural and urban areas.
- Rural women are more likely to experience unintended pregnancies, have higher rates of maternal mortality, and have less access to prenatal care than their urban counterparts.
- These disparities are further exacerbated by the lack of access to abortion care, which can lead to unsafe abortions and other health complications.
Exacerbating Existing Health Disparities
The impact of abortion restrictions on rural communities is particularly severe for marginalized groups, such as women of color, low-income women, and women living in rural areas.
- These groups already face significant barriers to healthcare access, and abortion restrictions further limit their options.
- For example, a study by the Center for Reproductive Rights found that Black women are three times more likely to die from pregnancy-related causes than white women, and this disparity is even greater in rural areas.
The Role of Medical Education and Training
The current landscape of reproductive healthcare, particularly in states with restrictive abortion laws, underscores the critical importance of comprehensive medical education and training regarding abortion care. This is essential for ensuring that healthcare providers are adequately prepared to address the evolving needs of their patients and navigate the complexities of providing reproductive healthcare in a restricted environment.
Changes in Medical School Curricula and Residency Programs
The changing landscape of reproductive healthcare necessitates a re-evaluation of medical school curricula and residency programs to ensure that future generations of physicians are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide comprehensive reproductive healthcare. This includes addressing the specific challenges faced by healthcare providers in states with restrictive abortion laws.
The ongoing debate surrounding abortion access has created a significant challenge for antiabortion states, as many doctors are reluctant to work in environments where their medical judgment is restricted. It’s a complex issue, and it’s hard to ignore the wider context – like the knee-jerk reactions to Week 2 of the NFL season, with everyone already declaring the Bryce Young era a failure and the Bucs a legitimate contender (check out this great analysis: nfl week 2 knee jerk reactions bryce young era needs to end bucs are for real ).
While the NFL’s drama unfolds, the reality for many doctors in antiabortion states is a difficult one, as they navigate a system that limits their ability to provide comprehensive healthcare.
- Increased Focus on Abortion Care in Medical School Curricula:Medical schools should incorporate more comprehensive and nuanced discussions of abortion care into their curricula. This should include a thorough examination of the medical, legal, and ethical aspects of abortion care, as well as the practical skills required to provide safe and effective abortion services.
- Expanded Training Opportunities in Abortion Care During Residency:Residency programs should offer expanded training opportunities in abortion care, allowing residents to gain hands-on experience and develop the necessary skills to provide this essential service. This could involve partnerships with abortion providers, dedicated training programs, and mentorship opportunities with experienced abortion care providers.
- Addressing the Stigma Surrounding Abortion Care:Medical schools and residency programs should actively address the stigma surrounding abortion care and promote a culture of openness and acceptance among future physicians. This includes fostering an environment where residents feel comfortable discussing and learning about abortion care without fear of judgment or discrimination.
The Economic Impact of Abortion Restrictions
The ramifications of limited abortion access extend beyond individual healthcare choices, significantly impacting the economic well-being of individuals, families, and communities. Restricting abortion access can lead to a ripple effect of financial burdens, decreased workforce participation, and diminished economic productivity.
It’s a tough situation for doctors in antiabortion states, with many reluctant to work there due to the restrictive laws. It’s interesting to contrast this with the news that u s border arrivals drop for second consecutive month but annual tally set to hit 2 million , which highlights a different kind of pressure on healthcare resources.
Ultimately, these challenges underscore the need for comprehensive healthcare solutions that address the needs of all Americans, regardless of their location or beliefs.
The Financial Burden of Seeking Abortion Care
In states with restrictive abortion laws, individuals seeking abortion care often face significant financial obstacles. These obstacles stem from various factors, including:
- Increased Travel Costs:Individuals may have to travel long distances to access abortion services in states with less restrictive laws, incurring substantial travel expenses, including gas, lodging, and time off work.
- Higher Healthcare Costs:Abortion services in states with fewer restrictions may be more expensive due to market forces and the limited availability of providers. Additionally, individuals may need to pay for additional medical services, such as ultrasounds and consultations, required by state regulations.
- Missed Work and Lost Wages:The time and effort required to travel, obtain appointments, and undergo the procedure can lead to missed work and lost wages, further exacerbating the financial burden.
- Financial Aid and Insurance Coverage:Many states with restrictive abortion laws have limited or no financial assistance programs for abortion care, leaving individuals to shoulder the entire cost themselves. Additionally, insurance coverage for abortion is often restricted, forcing individuals to pay out-of-pocket.
These financial burdens can have a significant impact on individuals and families, particularly those with limited financial resources. They may face difficulties meeting basic needs, such as food, housing, and healthcare, further compounding the challenges associated with unintended pregnancies.
The Impact on Workforce Participation and Economic Productivity
The economic impact of limited abortion access extends to the broader workforce and overall economic productivity. Research suggests that:
- Increased Unintended Pregnancies:Restrictions on abortion access can lead to an increase in unintended pregnancies, which can have a significant impact on women’s education, employment, and economic well-being. Unintended pregnancies can disrupt education, force individuals to delay or abandon career aspirations, and limit economic opportunities.
- Reduced Workforce Participation:The economic consequences of unintended pregnancies can lead to reduced workforce participation, as women may face challenges in finding and maintaining employment, particularly in fields requiring flexibility or extensive training. This reduction in workforce participation can have a negative impact on economic growth and overall productivity.
- Increased Financial Strain on Families and Communities:The financial burden associated with raising a child, including healthcare, education, and living expenses, can strain family budgets and lead to increased reliance on public assistance programs. This can put a strain on local and state budgets, impacting public services and economic development.
The economic impact of limited abortion access is not limited to individual women and families. It has broader implications for the workforce, economic productivity, and the overall well-being of communities.
The Role of Public Opinion and Advocacy: A Challenge For Antiabortion States Doctors Reluctant To Work There
The debate over abortion rights in the United States is deeply intertwined with public opinion and advocacy efforts. Public opinion on abortion has evolved significantly over time, and various organizations actively work to influence policy and public discourse on this complex issue.
Public Opinion on Abortion Rights
Public opinion on abortion rights has shifted over the decades, with notable trends emerging. While a majority of Americans consistently support access to legal abortion, the level of support varies depending on specific circumstances and restrictions. For example, public opinion on late-term abortions differs significantly from that on early-term abortions.
- A 2022 Gallup poll found that 80% of Americans believe abortion should be legal in at least some circumstances.
- However, the same poll found that 39% of Americans believe abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while 37% believe it should be illegal in all or most cases.
- A 2023 Pew Research Center survey found that 61% of Americans believe abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while 38% believe it should be illegal in all or most cases.
Key Advocacy Groups and Organizations
Numerous advocacy groups and organizations are actively involved in promoting access to abortion care. These groups employ various strategies, including public awareness campaigns, legal advocacy, and lobbying efforts, to advance their goals.
- Planned Parenthood: A leading reproductive healthcare provider and advocate, Planned Parenthood offers a wide range of services, including abortion care, and actively engages in policy advocacy and public education.
- NARAL Pro-Choice America: This organization advocates for reproductive rights and access to abortion care through legislative advocacy, public education, and grassroots organizing.
- The American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU): The ACLU is a prominent civil liberties organization that defends reproductive rights, including access to abortion, through legal challenges and advocacy efforts.
The Impact of Public Awareness Campaigns and Advocacy Efforts
Public awareness campaigns and advocacy efforts play a crucial role in shaping public discourse and influencing policy decisions on abortion. These campaigns aim to educate the public about reproductive rights, challenge misconceptions, and mobilize support for access to abortion care.
- Public Education: Advocacy groups use various media platforms, including social media, websites, and traditional media outlets, to raise awareness about abortion rights and the impact of restrictive laws. These campaigns often highlight personal stories, medical facts, and legal arguments to counter misinformation and promote understanding.
- Legislative Advocacy: Advocacy organizations engage in lobbying efforts to influence legislation related to abortion rights. This involves advocating for the passage of pro-choice laws and opposing restrictive measures.
- Grassroots Organizing: Advocacy groups often organize grassroots campaigns to mobilize public support for their cause. This can involve organizing protests, rallies, and community outreach events to engage with voters and advocate for policy changes.
The Legal Landscape of Abortion Restrictions
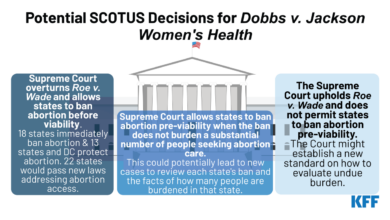
The legal landscape of abortion in the United States has undergone significant changes in recent years, particularly with the overturning of Roe v. Wade in 2022. This decision has left the regulation of abortion largely to individual states, leading to a patchwork of laws across the country.
This section examines the current legal landscape of abortion restrictions, analyzes the potential legal challenges and implications of restrictive abortion laws, and discusses the role of the courts and legal advocacy in shaping abortion rights.
The Current Legal Landscape
Following the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization, states have been enacting a wide range of abortion restrictions, from outright bans to significant limitations on access. These restrictions vary considerably, with some states implementing bans after a certain stage of pregnancy, others requiring parental notification or waiting periods, and still others restricting access to medication abortion.
The current legal landscape is characterized by a significant degree of variation across states, leading to a situation where access to abortion can be highly dependent on one’s location.
Potential Legal Challenges and Implications
The proliferation of restrictive abortion laws has sparked numerous legal challenges. Many legal experts argue that some of these laws violate constitutional rights, such as the right to privacy or the right to equal protection. These challenges are often centered around the argument that state restrictions unduly burden women’s access to abortion, potentially leading to serious health consequences and even death.
Additionally, the legal landscape is further complicated by the potential for federal legislation that could either expand or restrict abortion access nationwide.
The Role of the Courts and Legal Advocacy
The courts and legal advocacy groups play a crucial role in shaping the legal landscape of abortion. Advocacy groups are actively challenging restrictive abortion laws in court, seeking to overturn them on constitutional grounds. Meanwhile, courts are tasked with interpreting and applying the law, often making decisions that have significant implications for abortion access.
This dynamic interplay between the courts and legal advocacy groups is likely to continue, shaping the future of abortion rights in the United States.