Why EU Tariffs Wont Stop Chinese EV Makers European Expansion
Why eu tariffs are unlikely to dent chinese ev makers european expansion – Why EU tariffs are unlikely to dent Chinese EV makers’ European expansion? It’s a question that’s been swirling around the industry, particularly as the EU seeks to protect its own automakers. But the reality is, the Chinese EV market is a juggernaut, fueled by innovation, aggressive pricing, and government support.
These factors, combined with the growing demand for electric vehicles across the globe, suggest that Chinese EV makers are well-positioned to overcome any tariff hurdles and establish a strong foothold in the European market.
The EU has imposed tariffs on Chinese EV imports, aiming to level the playing field for European manufacturers. While these tariffs will undoubtedly impact the cost of Chinese EVs in the EU market, it’s unlikely to significantly deter consumer demand.
The allure of affordable, technologically advanced EVs, coupled with the increasing environmental consciousness of European consumers, is likely to outweigh any price increases.
EU Tariffs and their Impact
The European Union (EU) has imposed tariffs on Chinese electric vehicle (EV) imports, aiming to protect its domestic automotive industry and promote the adoption of EVs made within the EU. These tariffs have a direct impact on the cost of Chinese EVs in the EU market, potentially influencing consumer demand.
Tariffs on Chinese EV Imports
The EU currently imposes a 10% tariff on imported vehicles from China, which includes EVs. This tariff is applied to the value of the vehicle, adding to the overall cost for consumers. For example, a Chinese EV priced at €30,000 in China would incur an additional €3,000 in tariffs upon entering the EU market, making its final price €33,000.
This increase in price could affect consumer choices and influence the market share of Chinese EVs in the EU.
Impact of Tariffs on Chinese EV Costs
The tariffs imposed by the EU directly increase the cost of Chinese EVs in the EU market. This price increase could make Chinese EVs less competitive compared to European-made EVs, which do not face these tariffs. However, the extent to which tariffs affect the price competitiveness of Chinese EVs depends on various factors, including the specific model, the manufacturer’s pricing strategy, and the overall market conditions.
While the EU tariffs might seem like a hurdle, Chinese EV makers are already making inroads in Europe. They’re offering competitive prices and innovative features, making them attractive to consumers. But what’s really going on now is a global shift towards electric vehicles, with Europe being a key market.
What is going on now is a race to secure battery supply chains and manufacturing capacity, and Chinese companies are well-positioned to capitalize on this. So, even with tariffs, it’s unlikely that Chinese EV makers will be deterred from their European expansion plans.
Consumer Demand for Chinese EVs in the EU
The impact of tariffs on consumer demand for Chinese EVs in the EU is a complex issue. While higher prices due to tariffs could discourage some consumers, other factors might still make Chinese EVs attractive. These factors include:
- Lower initial price compared to European EVs even after tariffs.
- Advanced technology and features offered by some Chinese EV manufacturers.
- Strong brand recognition and positive consumer sentiment towards Chinese EV brands.
The overall impact of tariffs on consumer demand will depend on the specific model, the pricing strategy of the manufacturer, and the consumer’s perception of value.
Chinese EV Makers’ European Expansion Strategies: Why Eu Tariffs Are Unlikely To Dent Chinese Ev Makers European Expansion

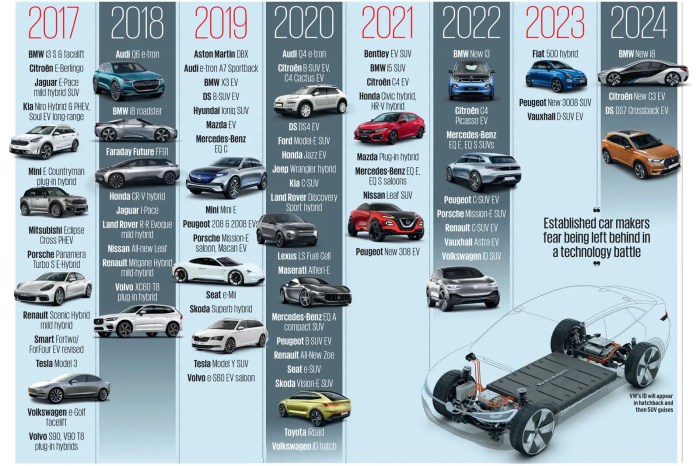
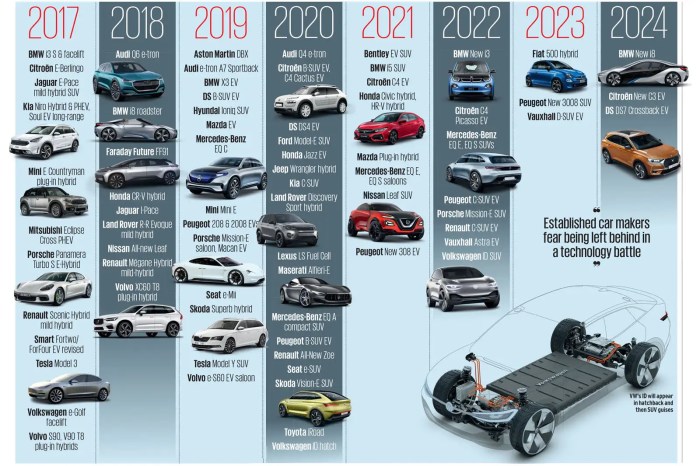
Chinese EV makers are increasingly looking to the European market as a key growth area. This is due to the region’s strong demand for electric vehicles, ambitious climate targets, and supportive government policies. However, the EU’s recent imposition of tariffs on Chinese EV imports has added a new layer of complexity to these expansion strategies.To navigate the European market, Chinese EV makers have adopted various strategies.
These include building local manufacturing facilities, forming partnerships with European companies, and offering competitive pricing.
Building Local Manufacturing Facilities
Establishing local production facilities allows Chinese EV makers to avoid tariffs, reduce transportation costs, and gain access to local supply chains. For instance, BYD, one of the leading Chinese EV manufacturers, has announced plans to build a factory in Hungary, which will serve as a production hub for the European market.
This strategy allows BYD to circumvent the EU tariffs and position itself for long-term growth in the region.
Forming Partnerships with European Companies
Chinese EV makers are actively seeking collaborations with European companies to leverage their expertise, technology, and distribution networks. This strategy allows them to access the European market more efficiently and build brand recognition. For example, NIO, another major Chinese EV player, has partnered with the German automotive supplier Bosch to develop autonomous driving technologies for its European models.
Offering Competitive Pricing
Chinese EV makers are often able to offer more competitive pricing compared to their European counterparts. This is partly due to lower manufacturing costs and government subsidies in China. For instance, the MG ZS EV, a popular Chinese EV model marketed by SAIC Motor, is priced significantly lower than comparable European models.
Adjusting Strategies in Response to Tariffs
The EU tariffs have prompted Chinese EV makers to reconsider their expansion strategies. Some are exploring alternative markets with more favorable trade policies, while others are seeking to mitigate the impact of tariffs by increasing local production or negotiating trade agreements with the EU.
“Chinese EV makers are facing a difficult decision. They can either absorb the tariffs and maintain their competitive pricing, which could impact profitability, or they can raise prices and risk losing market share.”
Chinese EV makers are also actively lobbying the EU to reduce or eliminate the tariffs. They argue that these tariffs hinder fair competition and ultimately harm consumers.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Strategies
Strengths
- Building local manufacturing facilities: This strategy helps to circumvent tariffs, reduce transportation costs, and gain access to local supply chains. It also demonstrates a commitment to the European market and can enhance brand perception.
- Forming partnerships with European companies: This strategy allows Chinese EV makers to leverage the expertise and resources of established European companies, accelerating their entry into the market and building brand credibility.
- Offering competitive pricing: This strategy can attract price-sensitive consumers and increase market share, especially in the early stages of market penetration.
Weaknesses
- Building local manufacturing facilities: This strategy can be expensive and time-consuming, requiring significant investments and regulatory approvals. It also carries the risk of encountering local market challenges and uncertainties.
- Forming partnerships with European companies: This strategy can be complex and require careful negotiation to ensure alignment of interests and avoid potential conflicts.
- Offering competitive pricing: This strategy can be unsustainable in the long term, especially if tariffs remain in place or if costs increase due to factors such as raw material prices or labor costs.
Factors Contributing to Resilience of Chinese EV Makers

Chinese EV makers are rapidly gaining ground in the global market, posing a significant challenge to established players. Their resilience is fueled by a potent combination of factors, including technological prowess, cost-competitiveness, and strategic government support.
The EU tariffs, while a hurdle, are unlikely to seriously hinder Chinese EV makers’ European expansion. These companies have already proven their ability to adapt and innovate, and the demand for electric vehicles is simply too high to ignore.
It’s a bit like the situation at Guantanamo Bay, guantanamo maybe none of them are terrorists , where despite the controversy, the facility remains operational. Just as the US government continues to operate Guantanamo, Chinese EV makers will find ways to navigate the EU’s trade barriers and continue their push into the European market.
Technological Advantages
Chinese EV makers are known for their innovative approach to electric vehicle technology. They are pushing the boundaries of battery technology, developing advanced electric motors, and integrating cutting-edge features like autonomous driving capabilities. For example, BYD, a leading Chinese EV maker, has developed its own blade battery technology, which offers increased energy density and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Cost Competitiveness
Chinese EV makers benefit from lower production costs compared to their international counterparts. This is due to a combination of factors, including access to cheaper labor, efficient supply chains, and government subsidies. The Chinese government has invested heavily in research and development, creating a robust ecosystem of domestic suppliers and manufacturers.
Government Support
The Chinese government plays a crucial role in supporting the growth of the domestic EV industry. It provides generous subsidies to EV buyers, incentivizes the development of charging infrastructure, and promotes the adoption of electric vehicles through favorable policies. This support has helped to create a favorable environment for Chinese EV makers to flourish.
EU tariffs might slow down Chinese EV makers’ expansion, but it’s unlikely to completely stop them. Just like the ongoing debate around the role of pharmaceutical corporations and medical research in driving innovation, the EV market is evolving rapidly, and these companies are adapting.
Chinese EV makers have already proven their ability to compete on price and technology, and they’re likely to find ways to navigate these new challenges, ultimately contributing to a more diverse and competitive European automotive market.
Comparative Advantages
| Feature | Chinese EV Makers | European EV Makers | Other Global Competitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | Rapidly advancing battery technology, innovative electric motors, integration of autonomous driving features. | Strong focus on luxury and performance EVs, established expertise in traditional automotive manufacturing. | Focus on specific niches, such as electric buses or commercial vehicles. |
| Cost Competitiveness | Lower production costs due to cheaper labor, efficient supply chains, and government subsidies. | Higher production costs due to labor regulations, established manufacturing processes, and environmental regulations. | Varying levels of cost competitiveness depending on location and scale of operations. |
| Government Support | Significant government subsidies for EV buyers, investments in charging infrastructure, and favorable policies promoting EV adoption. | Government support for EV development and infrastructure, but often less extensive than in China. | Government support varies widely, with some countries offering incentives for EV adoption. |
The Broader Context of EU-China Trade Relations
The EU and China are major trading partners, with a complex and evolving relationship. While trade between the two has grown significantly in recent years, it has also been marked by increasing tensions and competition. This is particularly evident in the automotive industry, where the rise of Chinese electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers has raised concerns in Europe.
Key Issues and Points of Friction
The EU-China trade relationship is characterized by several key issues and potential points of friction.
- Trade Imbalance: China consistently enjoys a large trade surplus with the EU, which has led to concerns about unfair trade practices and a lack of reciprocity.
- Market Access: The EU has expressed concerns about market access in China, citing barriers to foreign investment and discriminatory treatment of European businesses.
- Intellectual Property Rights: The protection of intellectual property rights (IPR) in China remains a significant concern for European businesses, with accusations of forced technology transfer and counterfeiting.
- Subsidies and State Support: The EU has raised concerns about the use of subsidies and state support by Chinese companies, arguing that it distorts competition and creates an unfair advantage.
- Human Rights and Sustainability: Concerns about human rights abuses in China, including the treatment of Uyghur Muslims in Xinjiang, and environmental sustainability practices have also impacted the trade relationship.
Impact of Tariffs on EVs on the Broader Trade Relationship, Why eu tariffs are unlikely to dent chinese ev makers european expansion
The imposition of tariffs on EVs could further exacerbate existing tensions in the EU-China trade relationship.
- Escalation of Trade War: Tariffs on EVs could be seen as a protectionist measure and trigger retaliatory actions from China, potentially escalating into a trade war.
- Damage to Bilateral Relations: Tariffs could damage broader bilateral relations, hindering cooperation on other issues of mutual interest, such as climate change and global security.
- Impact on Consumers: Tariffs could increase the cost of EVs for consumers in both the EU and China, potentially hindering the adoption of electric vehicles and harming efforts to combat climate change.
Timeline of Significant Events in EU-China Trade Relations
The EU-China trade relationship has been marked by several significant events, including:
- 1979: The EU establishes diplomatic relations with China.
- 1985: The EU and China sign a trade agreement, paving the way for increased bilateral trade.
- 2004: The EU and China establish a strategic partnership, aiming to deepen cooperation on a range of issues.
- 2014: The EU and China launch negotiations for a comprehensive investment agreement (CAI).
- 2019: The EU officially classifies China as a “systemic rival,” recognizing its growing economic and geopolitical power.
- 2020: The CAI negotiations are put on hold due to concerns about human rights and forced labor in Xinjiang.
- 2021: The EU imposes sanctions on Chinese officials over human rights abuses in Xinjiang, leading to retaliatory sanctions from China.
Long-Term Implications for the European EV Market
The introduction of Chinese EV makers into the European market, coupled with the imposition of EU tariffs, presents a complex and dynamic scenario with long-term implications for the European EV market. This section will explore the potential impact of these factors on the European EV landscape, considering the evolving dynamics of the market and the competitive strategies of key players.
The Potential for Chinese EV Makers to Become Major Players
The resilience of Chinese EV makers in the face of EU tariffs suggests a strong potential for them to become major players in the European market. Several factors contribute to this potential:
- Cost competitiveness:Chinese EV makers often benefit from lower production costs, access to a robust supply chain, and government support, allowing them to offer competitive pricing in the European market.
- Technological advancements:Chinese EV makers are rapidly advancing in battery technology, autonomous driving, and connected car features, making their offerings increasingly attractive to European consumers.
- Strategic partnerships:Chinese EV makers are forming strategic partnerships with European companies, including car manufacturers, battery suppliers, and technology providers, facilitating their entry and expansion into the European market.
- Brand building and marketing:Chinese EV makers are investing heavily in brand building and marketing campaigns to establish a strong presence in the European market and appeal to local consumers.
A Hypothetical Scenario of the European EV Market in the Next 5-10 Years
Consider a scenario where Chinese EV makers continue to expand their presence in the European market, driven by their competitive advantages and strategic initiatives.
- Increased market share:Chinese EV makers could capture a significant market share in the European EV market, potentially exceeding the market share of some established European brands.
- Price competition:The entry of Chinese EV makers could intensify price competition in the European EV market, putting pressure on European manufacturers to lower their prices or offer more value-added features.
- Technological innovation:Chinese EV makers could drive technological innovation in the European EV market, pushing European manufacturers to accelerate their own R&D efforts to remain competitive.
- Shift in consumer preferences:European consumers could become more receptive to Chinese EV brands, particularly those offering attractive features, competitive pricing, and strong performance.
“The long-term implications of Chinese EV imports and EU tariffs on the European EV market will depend on the complex interplay of factors such as technological advancements, consumer preferences, government policies, and the competitive strategies of key players.”

