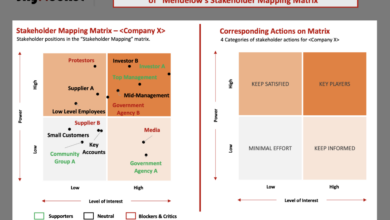
State of the Union, New Commission, and the Green Deal
State of the union the new commission and the green deal – State of the Union, the new commission, and the green deal sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This exploration delves into the ambitious goals of the Green Deal, examining how the President’s vision for a sustainable future is being shaped by the newly established commission.
From clean energy and sustainable transportation to environmental justice, we’ll unpack the key pillars of this transformative agenda, analyzing its potential economic and social impacts.
We’ll also dissect the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, considering the political, technological, and financial hurdles that must be overcome to achieve a greener tomorrow. This journey will highlight the interconnectedness of various factors, exploring the interplay of policy, innovation, and global collaboration in the pursuit of a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Green Deal: State Of The Union The New Commission And The Green Deal
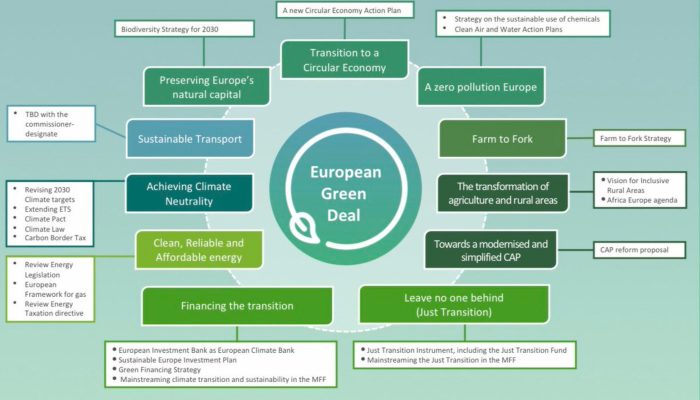
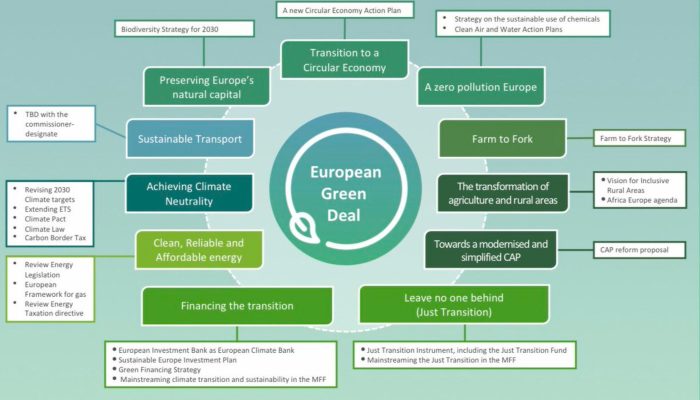
The European Green Deal, a comprehensive plan to achieve climate neutrality by 2050, presents both significant challenges and promising opportunities. It aims to transform the EU’s economy and society by promoting sustainable growth, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and protecting biodiversity.
However, achieving these ambitious goals requires overcoming various hurdles, including political opposition, technological limitations, and financial constraints.
Political Opposition
Political opposition to the Green Deal can arise from various sources, including concerns about economic impacts, national sovereignty, and the pace of transition. Some argue that the Green Deal’s policies could lead to job losses and economic hardship, particularly in industries heavily reliant on fossil fuels.
Others worry about the potential for increased regulation and interference in national decision-making. The Green Deal faces resistance from certain political groups and stakeholders who prioritize short-term economic interests over long-term environmental sustainability. This opposition can manifest in lobbying efforts, legislative delays, and public skepticism.
Technological Limitations
While technological advancements are crucial for achieving the Green Deal’s goals, there are limitations that need to be addressed. For example, renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are often intermittent and require energy storage solutions to ensure reliable supply.
Additionally, the development of carbon capture and storage technologies remains in its early stages, and their widespread deployment poses challenges in terms of cost, safety, and public acceptance.
Financial Constraints, State of the union the new commission and the green deal
The Green Deal’s ambitious objectives require significant financial investments, particularly in infrastructure, research and development, and green technologies. Funding these initiatives presents a challenge, especially in light of competing priorities and potential budget constraints. Securing adequate financial resources will require innovative financing mechanisms, public-private partnerships, and international collaboration.
Opportunities Presented by the Green Deal
Despite the challenges, the Green Deal offers significant opportunities for innovation, technological advancements, and global collaboration.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
The Green Deal’s ambitious goals are driving innovation in various sectors, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, sustainable transportation, and circular economy. The transition to a low-carbon economy is creating new markets and opportunities for businesses to develop and deploy cutting-edge technologies.
For example, the development of electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and smart grids is accelerating due to the Green Deal’s incentives and targets.
Global Collaboration
The Green Deal emphasizes the importance of international cooperation to address climate change and achieve sustainable development. It aims to work with other countries and regions to promote green technologies, share best practices, and build a global green economy. The Green Deal’s global dimension is crucial for addressing the transboundary nature of climate change and for leveraging the collective efforts of nations to achieve a sustainable future.
The State of the Union address highlighted the importance of the new commission tasked with overseeing the Green Deal’s implementation. This ambitious plan, while facing political hurdles, could have a significant impact on our national security, especially in the face of climate change.
The FBI, as seen in their recent investigations into online extremism, is keenly aware of how these environmental concerns can be exploited by those seeking to sow discord and violence. fbi digs deeper into the web The commission’s work will need to address these security concerns, ensuring that the Green Deal’s implementation is not only environmentally sound but also protects our nation from potential threats.
The State of the Union address focused on the new commission for climate change and the ambitious Green Deal. While the address aimed to inspire hope for a greener future, the news cycle was dominated by a different kind of urgency.
Sir Ben Wallace, the UK’s Defence Secretary, denied lacking curiosity over allegations of British soldiers murdering Afghan civilians , a stark reminder of the complex legacy of our involvement in Afghanistan. Despite the focus on climate change, these events highlight the need for a holistic approach to global challenges, one that addresses both environmental and humanitarian concerns.
The State of the Union address highlighted the new commission’s ambitious goals for implementing the Green Deal, but the scale of these plans raises a crucial question: how will we finance such a monumental undertaking? The looming scale of the debt crisis adds another layer of complexity, forcing us to consider the long-term fiscal implications of this ambitious agenda.
Finding a balance between environmental progress and economic stability will be a key challenge as we navigate the future of the Green Deal.