Criticisms of the US: A Deep Dive
Criticisms of the US are often heated, but they are also crucial for understanding the nation’s complexities. From its political system to its social and economic landscape, the US faces a range of challenges that have sparked debate and dissent.
This exploration delves into these criticisms, examining their historical roots, current manifestations, and potential solutions.
This blog post aims to provide a balanced and insightful overview of the various criticisms leveled against the US, covering topics such as political polarization, economic inequality, healthcare access, foreign policy, environmental issues, and social and cultural concerns. By dissecting these criticisms, we can gain a deeper understanding of the US’s strengths and weaknesses, and potentially contribute to constructive dialogue and progress.
Political System and Governance
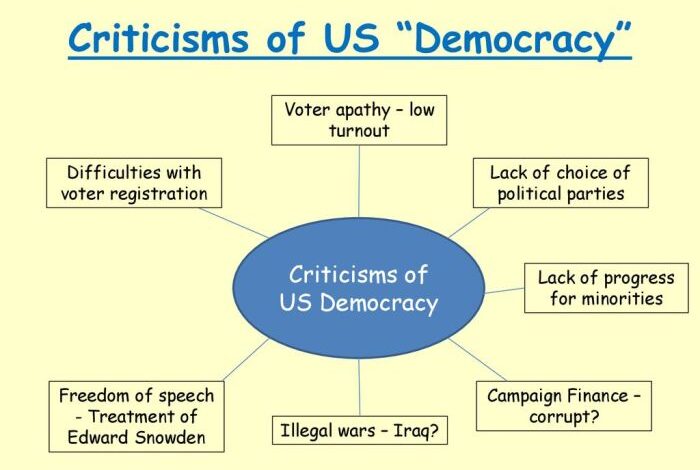
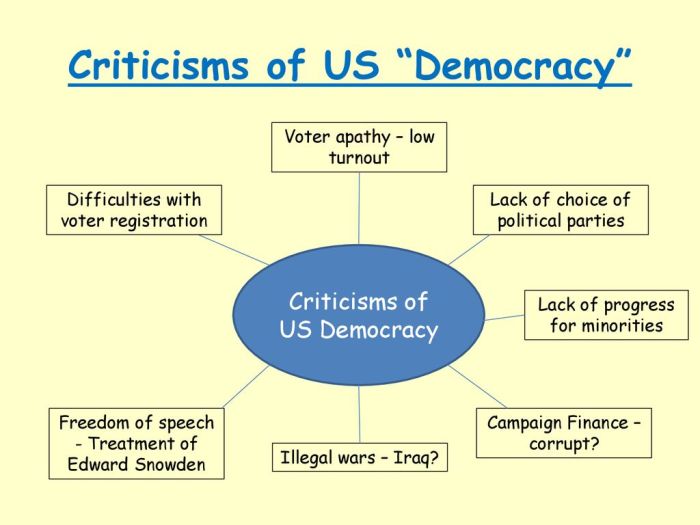
The United States political system, a two-party system with a strong emphasis on individual rights, has been a cornerstone of its identity. However, this system faces criticisms regarding its limitations and potential for dysfunction. This section will explore these criticisms, focusing on the two-party system, the influence of lobbying and campaign finance, the impact of gerrymandering, and a comparison with other democratic systems.
Limitations of the Two-Party System
The two-party system, dominated by the Democratic and Republican parties, has been a defining characteristic of US politics for over a century. While it offers stability and a clear choice for voters, it also faces limitations. One criticism is the lack of diversity in viewpoints and the potential for a “winner-take-all” mentality, where compromise and consensus building are often sidelined.
- The two-party system can limit the range of political ideas and perspectives that are represented in government. Third-party candidates often struggle to gain traction and compete with the established parties, which have access to greater resources and name recognition.
One of the criticisms often levied against the US is its military interventionism, particularly in regions deemed strategically important. This approach, however, is not without its critics who point to the potential for unintended consequences, as seen in the case of North Korea’s nuclear program, which some argue was fueled by a perceived threat from the US.
North Korea and nuclear weapons have become a major international concern, and some argue that the US’s foreign policy has played a role in escalating tensions. Critics argue that the US should focus on diplomacy and engagement rather than military might, which they believe could lead to a more peaceful world.
- The focus on winning elections can lead to a polarized political landscape, where parties prioritize ideological purity over finding common ground. This can make it difficult to address complex issues that require bipartisan support.
Influence of Lobbying and Campaign Finance
Lobbying and campaign finance play a significant role in US politics, raising concerns about the influence of special interests and wealthy donors.
- Lobbyists, representing corporations, industries, and interest groups, engage in extensive efforts to influence legislation and policy decisions. This can create an uneven playing field, where certain interests have greater access to and influence over policymakers.
- The high cost of running for office in the US creates a dependence on campaign contributions from wealthy individuals, corporations, and political action committees (PACs). This can lead to a system where elected officials are beholden to their donors, potentially prioritizing their interests over those of the general public.
Impact of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating electoral districts to favor a particular political party, has a significant impact on democratic representation.
- By drawing district lines to concentrate voters of a specific party in certain areas, gerrymandering can create safe seats for incumbents and make it difficult for challengers to gain a foothold. This can lead to a lack of competitive elections and reduce voter choice.
- Gerrymandering can also distort the representation of different communities, particularly minority groups. By diluting their voting power, it can undermine the principle of “one person, one vote” and limit their political influence.
Comparison with Other Democratic Systems
The US electoral system, based on a winner-take-all, first-past-the-post system, differs from other democratic systems.
- In many European countries, proportional representation systems are used, where the number of seats a party receives in parliament is proportional to the percentage of votes it receives. This system encourages the formation of coalition governments and promotes broader representation of diverse viewpoints.
One of the most common criticisms leveled at the US is its seemingly endless capacity to squander resources. While the nation boasts immense wealth, it often struggles to effectively utilize its capital, labor, and resources. This inefficiency is a recurring theme in discussions about the US’s economic and social problems, as explored in this insightful article on wasted wealth capital labor and resources.
Critics argue that the US could achieve much more if it addressed these issues, ultimately leading to a more equitable and sustainable society.
- Other systems, such as the mixed-member proportional (MMP) system used in New Zealand and Germany, combine elements of both first-past-the-post and proportional representation, aiming to balance the advantages of both systems.
Hypothetical Alternative Political System
A hypothetical alternative political system for the US could incorporate elements of proportional representation, campaign finance reform, and independent redistricting commissions.
- A proportional representation system could encourage the formation of more diverse political parties and provide greater representation for minority viewpoints. This could lead to more nuanced policy discussions and a more inclusive political landscape.
- Campaign finance reform, such as public financing of elections and limits on campaign contributions, could reduce the influence of special interests and wealthy donors. This could empower ordinary citizens and create a more level playing field for candidates.
- Independent redistricting commissions, composed of non-partisan experts, could draw electoral districts based on fair and impartial criteria, reducing the influence of political parties and promoting competitive elections.
Foreign Policy and Military Intervention
The United States has long been a major player in global affairs, wielding significant economic, military, and political power. Its foreign policy decisions and military interventions have had a profound impact on the world, shaping the geopolitical landscape and influencing the lives of millions.
Examining the historical and contemporary role of the US in global affairs, particularly its military interventions, is crucial to understanding the complexities of international relations and the potential consequences of US actions.
Historical and Contemporary Role of the US in Global Affairs
The US has evolved from a nation focused on isolationism to a global superpower with a wide range of interests and responsibilities. After World War II, the US emerged as the dominant force in the international system, leading the fight against communism and promoting its own vision of a liberal world order.
The US has faced criticism for its foreign policy, often perceived as overly interventionist. Some argue that the US should be held accountable for its actions on the international stage, and the international criminal court introduction provides a framework for addressing such concerns.
However, the US remains hesitant to join the court, citing concerns about its potential for political bias and undermining national sovereignty. This highlights the ongoing debate about the role of international institutions in shaping global justice.
The Cold War saw the US engage in a global competition with the Soviet Union, resulting in military interventions in Korea, Vietnam, and other regions. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 left the US as the sole superpower, but it also faced new challenges, including the rise of terrorism, the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction, and the growing economic power of other countries.
Impact of US Military Interventions on Different Regions of the World
US military interventions have had a mixed impact on different regions of the world. While some interventions have been successful in achieving their stated objectives, others have been controversial and have had unintended consequences. For instance, the US-led invasion of Iraq in 2003, which aimed to remove Saddam Hussein from power and prevent him from developing weapons of mass destruction, resulted in a protracted conflict that destabilized the region and led to the rise of extremist groups like ISIS.
In Afghanistan, the US-led invasion in 2001, which followed the 9/11 attacks, initially drove out the Taliban regime but also led to a prolonged war and the emergence of a new generation of insurgents.
Effectiveness of US Foreign Policy in Promoting Democracy and Human Rights
The US has often justified its military interventions and foreign policy actions as efforts to promote democracy and human rights. However, the effectiveness of these efforts has been subject to debate. While the US has supported democratic transitions in some countries, it has also been accused of supporting authoritarian regimes when it served its strategic interests.
For example, the US supported the Shah of Iran in the 1970s despite his authoritarian rule, and it has been criticized for its close ties to Saudi Arabia, a country with a poor human rights record.
Comparison of US Foreign Policy with Other Major Powers
The US approach to foreign policy has been compared and contrasted with other major powers, such as China and Russia. While the US emphasizes a liberal world order based on rules and institutions, China and Russia have pursued more assertive foreign policies that challenge the existing order.
China’s growing economic and military power has led to its increasing influence in the Asia-Pacific region, while Russia’s intervention in Ukraine and its assertive stance on international issues have strained relations with the West.
Potential Alternative Approaches to US Foreign Policy
There are several potential alternative approaches to US foreign policy that have been proposed. Some argue for a more restrained approach, emphasizing diplomacy and multilateralism over military intervention. Others advocate for a more active engagement with the world, but with a focus on building partnerships and promoting cooperation rather than unilateral action.
The debate over the future direction of US foreign policy is likely to continue, as the US grapples with the changing global landscape and the challenges of maintaining its leadership role.
Environmental Issues and Climate Change: Criticisms Of The Us
The United States, as a global superpower, has a significant impact on the environment and plays a crucial role in international efforts to address climate change. This section examines the US’s environmental record, its role in international climate agreements, and the potential consequences of climate change.
The Impact of US Policies on Environmental Protection and Sustainability
The US has a long history of environmental policies, with both successes and failures. Notable achievements include the Clean Air Act, which significantly reduced air pollution, and the Clean Water Act, which improved water quality. However, the US has also faced criticism for its reliance on fossil fuels, its lax environmental regulations, and its withdrawal from international climate agreements.
Examples of US Environmental Policies
- Clean Air Act (1970):This landmark legislation set standards for air quality and regulated emissions from industries and vehicles. It has significantly reduced air pollution levels, leading to improved public health and environmental quality.
- Clean Water Act (1972):This law established water quality standards and regulated the discharge of pollutants into waterways. It has helped to improve water quality and protect aquatic ecosystems.
- Endangered Species Act (1973):This law protects endangered and threatened species and their habitats. It has been successful in preventing the extinction of numerous species, but its implementation has been controversial, with some arguing that it hinders economic development.
Criticisms of US Environmental Policies
- Fossil Fuel Dependence:The US remains heavily reliant on fossil fuels, particularly coal, for energy production. This contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
- Lax Environmental Regulations:Some critics argue that the US has weakened environmental regulations under recent administrations, making it easier for industries to pollute and contributing to environmental degradation.
- Withdrawal from International Agreements:The US withdrew from the Paris Agreement on climate change in 2017, raising concerns about its commitment to international efforts to address climate change.
The Role of the US in International Efforts to Address Climate Change
The US has played a mixed role in international climate change negotiations. While it was instrumental in the creation of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), it has also been criticized for its lack of ambition and its withdrawal from key agreements.
US Participation in International Climate Agreements
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC):The US was a key player in the creation of the UNFCCC in 1992, which aims to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system.
- Kyoto Protocol (1997):The US signed the Kyoto Protocol, but did not ratify it, citing concerns about the impact on its economy and the absence of binding commitments for developing countries.
- Paris Agreement (2015):The US joined the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels. However, the US withdrew from the agreement in 2017, citing unfair burdens on its economy and the need for greater flexibility.
Criticisms of US Climate Change Policies
- Lack of Ambition:Some critics argue that the US has not taken sufficient action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and has not been ambitious enough in its climate change policies.
- Withdrawal from the Paris Agreement:The US withdrawal from the Paris Agreement was widely condemned by the international community, which viewed it as a setback for global efforts to address climate change.
The Potential Consequences of Climate Change for the US and the World
Climate change poses significant risks to the US and the world, including more extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and changes in agricultural productivity.
Impacts of Climate Change on the US
- More Extreme Weather Events:The US is already experiencing more frequent and intense heat waves, droughts, wildfires, and hurricanes, which are expected to become more severe in the future.
- Rising Sea Levels:Coastal communities in the US are vulnerable to rising sea levels, which could lead to flooding, erosion, and displacement.
- Changes in Agricultural Productivity:Climate change could disrupt agricultural production in the US, leading to lower yields and increased food prices.
Impacts of Climate Change on the World
- Global Warming:Climate change is causing the Earth’s average temperature to rise, which is leading to a range of negative consequences, including melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather events.
- Ocean Acidification:As the ocean absorbs more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it becomes more acidic, which threatens marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of people who depend on them.
- Biodiversity Loss:Climate change is contributing to biodiversity loss, as species struggle to adapt to changing conditions.
Innovative Solutions and Initiatives Addressing Environmental Challenges
Despite the challenges, there are many innovative solutions and initiatives being developed to address environmental challenges and promote sustainability.
Examples of Innovative Solutions
- Renewable Energy:The US is investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power, which can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency:Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry can reduce energy consumption and emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage:This technology captures carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and other industrial sources and stores it underground.
Examples of Initiatives
- Green New Deal:This proposal aims to address climate change and economic inequality by investing in renewable energy, creating jobs, and improving infrastructure.
- Climate Action Plan:The US government has developed a Climate Action Plan, which Artikels strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
- State and Local Initiatives:Many states and cities in the US have implemented their own climate action plans, which go beyond federal policies.
Hypothetical Plan for the US to Achieve Carbon Neutrality by 2050, Criticisms of the us
Achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 would require a significant transformation of the US economy, with a focus on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture and storage.
Key Components of the Plan
- Transition to 100% Renewable Energy:This would involve a massive investment in solar, wind, geothermal, and other renewable energy sources.
- Improve Energy Efficiency:Implement policies and programs to improve energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industry.
- Invest in Carbon Capture and Storage:Develop and deploy carbon capture and storage technologies to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Promote Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry:Support sustainable agricultural practices and forest management to enhance carbon sequestration.
- Invest in Research and Development:Continue to invest in research and development of clean energy technologies and climate change solutions.
Social and Cultural Issues
The United States, a nation built on ideals of liberty and equality, continues to grapple with complex social and cultural issues that shape its identity and impact its citizens’ lives. From debates over gun control and immigration to the evolving role of technology and the media, these issues are often contentious and deeply intertwined with the nation’s history, values, and political landscape.
The Ongoing Debates on Gun Control, Immigration, and Racial Justice
These issues are deeply divisive, sparking passionate arguments and protests. The debate on gun control revolves around the Second Amendment’s right to bear arms and the need to balance individual freedoms with public safety. The issue of immigration centers on the rights of undocumented immigrants, border security, and the economic and social impacts of migration.
The fight for racial justice focuses on systemic racism, police brutality, and the pursuit of equality for all citizens.
The Impact of Social Media and Technology on American Society and Culture
The rise of social media and technology has significantly impacted American society and culture, transforming how people communicate, consume information, and interact with the world. Social media platforms have become powerful tools for social activism and political mobilization, allowing individuals to organize protests, share information, and amplify their voices.
However, they have also been criticized for promoting echo chambers, spreading misinformation, and contributing to social polarization.
The Role of the Media in Shaping Public Opinion and Political Discourse
The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and political discourse in the US. Traditional media outlets, such as newspapers, television networks, and radio stations, have historically been influential in setting the agenda and framing issues. However, the rise of digital media and social media has created a more fragmented and decentralized media landscape, making it increasingly challenging to discern accurate information and navigate the complex world of news and information.
Emerging Social and Cultural Trends in the US
The US is constantly evolving, with new social and cultural trends emerging and influencing the nation’s landscape. One notable trend is the growing emphasis on diversity and inclusion, reflected in increased representation of marginalized groups in media, politics, and society.
Another trend is the rise of a more environmentally conscious generation, pushing for sustainable practices and addressing climate change. Additionally, the rise of social activism and online movements has empowered individuals to challenge societal norms and advocate for social justice.
Examples of How the US is Responding to Cultural and Social Change
The US is responding to cultural and social change in various ways. Policymakers are enacting new laws and regulations to address issues like gun control, immigration, and climate change. Social movements are mobilizing to raise awareness and demand change on issues such as racial justice and LGBTQ+ rights.
Educational institutions are revising curricula and incorporating diverse perspectives to promote understanding and inclusivity. The media is evolving to adapt to new technologies and platforms, while also facing scrutiny over its role in shaping public opinion and political discourse.






