Drier and Cooler Weather After Flooding in England and Wales
Drier and cooler weather after flooding in England and Wales has brought a sigh of relief to many, but it’s not all sunshine and rainbows. While the respite from heavy rain offers a chance to assess damage and begin recovery efforts, the shift in weather conditions also presents unique challenges.
From potential public health risks to the impact on infrastructure and the environment, the aftermath of flooding is a complex landscape that requires careful consideration.
The recent flooding, fueled by persistent rainfall and saturated ground, has left a trail of devastation across England and Wales. Homes, businesses, and infrastructure have been damaged, and communities are grappling with the disruption and hardship. The transition to drier and cooler weather offers a window of opportunity to start the long road to recovery, but it’s important to understand the potential impacts of this change.
Weather Patterns and Flooding: Drier And Cooler Weather After Flooding In England And Wales
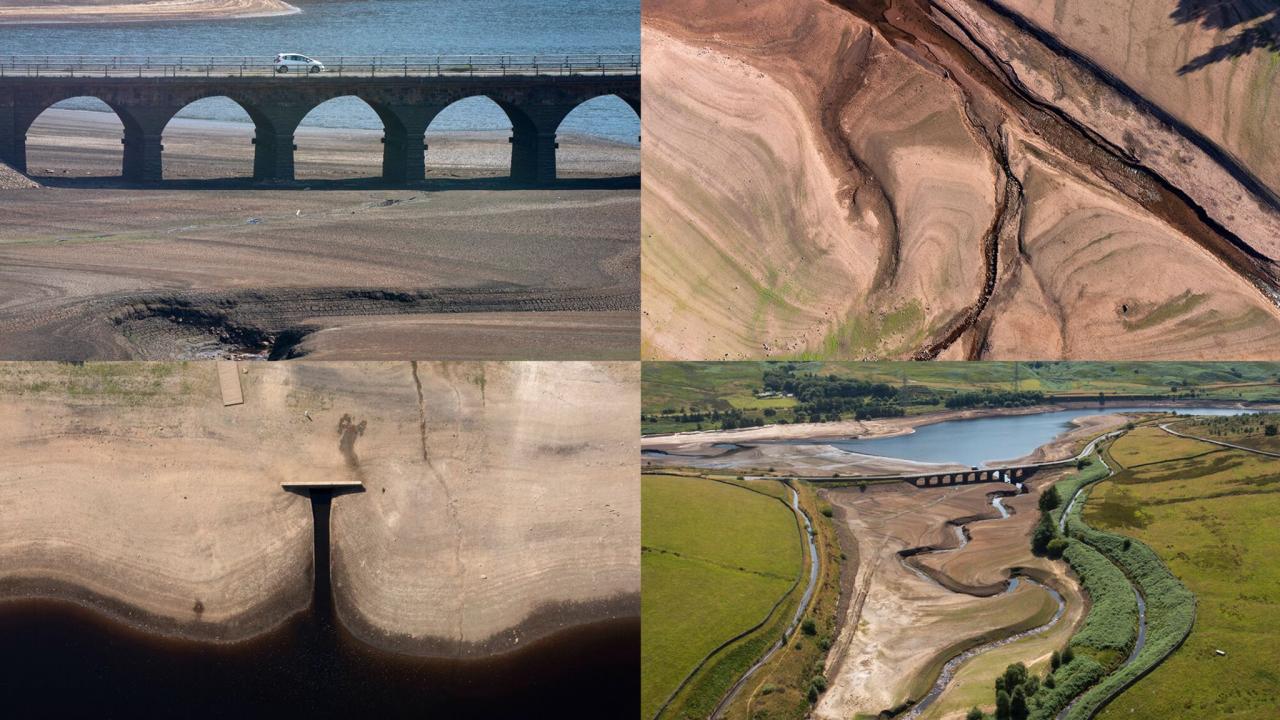

England and Wales are known for their unpredictable weather, which can often lead to severe flooding. The combination of geographical features and atmospheric conditions creates a unique environment where heavy rainfall and storm surges can cause widespread damage.
Typical Weather Patterns Contributing to Flooding
The typical weather patterns in England and Wales that contribute to flooding are influenced by the North Atlantic Current, which brings warm, moist air to the region. This warm air rises and cools, releasing its moisture as rain. The prevailing westerly winds also bring in rain-bearing clouds from the Atlantic Ocean.
Impact of Recent Weather Events on Flooding
Recent weather events have significantly impacted flooding in England and Wales. For instance, the winter storms of 2013-2014 and 2015-2016 caused widespread flooding, leading to extensive damage and disruption. These storms brought heavy rainfall and strong winds, resulting in rivers overflowing their banks and coastal areas being inundated.
Factors Influencing the Severity of Flooding
Several factors influence the severity of flooding in England and Wales, including:
- The amount and intensity of rainfall: Heavy rainfall over a short period can overwhelm drainage systems and cause rivers to rise rapidly.
- The condition of the ground: Saturated ground is less able to absorb rainfall, leading to increased runoff and higher river levels.
- The topography: Areas with low-lying land and steep slopes are more prone to flooding, as water flows rapidly downhill.
- The presence of storm surges: Storm surges can push seawater inland, exacerbating coastal flooding.
- The condition of flood defenses: Poorly maintained or inadequate flood defenses can increase the risk of flooding.
Types of Flooding Experienced in England and Wales
England and Wales experience various types of flooding, including:
- River flooding: Occurs when rivers overflow their banks due to heavy rainfall or snowmelt.
- Surface water flooding: Occurs when rainwater accumulates on the ground surface, often in areas with poor drainage.
- Coastal flooding: Occurs when high tides and storm surges push seawater inland, inundating coastal areas.
- Groundwater flooding: Occurs when groundwater levels rise and saturate the ground surface.
Impact of Drier and Cooler Weather
The shift to drier and cooler weather after the recent flooding in England and Wales brings both potential benefits and challenges to the ongoing recovery efforts. While drier conditions will help to alleviate the immediate threat of flooding, the change in weather patterns could also create new challenges for infrastructure repairs and property restoration.
Impact on Water Levels and River Flows
The drier weather will undoubtedly have a significant impact on water levels and river flows. Reduced rainfall will lead to a decline in river levels, allowing for easier access to flood-affected areas for repair and cleanup operations. This is particularly important for areas where floodwater has receded but left behind debris and damaged infrastructure.
- Reduced flood risk:Lower river levels will decrease the risk of further flooding, allowing communities to focus on recovery and rebuilding.
- Improved access:Drier conditions will allow for easier access to flood-affected areas, facilitating the delivery of essential supplies, equipment, and personnel.
- Faster cleanup:The receding floodwaters will allow for a more efficient cleanup of debris and damaged infrastructure, accelerating the recovery process.
Public Health and Safety Considerations

Flooding poses significant public health risks, and the transition to drier weather after a flood event presents its own set of challenges. It is crucial to prioritize public health and safety during and after a flood, ensuring that communities are equipped to mitigate potential risks and promote a swift and safe recovery.
Water Quality and Sanitation
Monitoring water quality and sanitation is essential during the recovery phase after flooding. Floodwaters can carry contaminants like bacteria, viruses, and chemicals, posing risks to human health.
- Waterborne Diseases:Floodwaters can contaminate drinking water sources, leading to outbreaks of waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid fever, and gastroenteritis.
- Skin Infections:Contact with floodwaters can cause skin infections, particularly if the water is contaminated with sewage or agricultural runoff.
- Respiratory Problems:Mold and mildew growth in flood-damaged buildings can trigger respiratory problems like asthma and allergies.
Public Safety Guidelines
Following guidelines for public safety during and after flooding is crucial for protecting individuals and communities.
- Evacuation Orders:Always heed evacuation orders issued by local authorities. Floodwaters can rise rapidly and become dangerous.
- Stay Away from Floodwaters:Avoid contact with floodwaters as they can be contaminated and pose a risk to health.
- Beware of Electrical Hazards:Floodwaters can energize electrical wires, making them extremely dangerous. Do not touch any downed power lines or electrical equipment that has come into contact with floodwater.
- Use Safe Drinking Water:Do not drink tap water until it has been declared safe by local authorities. Use bottled water or boil water for at least one minute before consumption.
- Food Safety:Discard any food that has come into contact with floodwater. Ensure proper food storage and handling to prevent contamination.
- Home Safety:When returning to a flooded home, take precautions to prevent further injury or illness. Wear protective clothing, including gloves and masks, to prevent contact with contaminated materials.
- Mental Health:Flooding can be a traumatic experience, causing stress, anxiety, and depression. Seek support from mental health professionals if needed.
Public Awareness Campaign
A public awareness campaign can educate residents about flood safety and recovery measures, empowering them to take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities.
- Flood Preparedness:Educate residents about the importance of having a flood preparedness plan, including emergency kits, evacuation routes, and contact information for local authorities.
- Flood Safety Tips:Disseminate information about flood safety measures, such as avoiding contact with floodwaters, recognizing electrical hazards, and practicing safe water consumption.
- Recovery Measures:Provide guidance on safe and effective recovery procedures, including water quality monitoring, sanitation practices, and home safety guidelines.
- Mental Health Support:Highlight the importance of mental health support and provide resources for individuals experiencing stress or trauma related to flooding.
Environmental Impacts of Flooding and Drier Weather
Flooding and drier weather, both extremes of the hydrological cycle, have significant and multifaceted impacts on the environment. These impacts can be short-term, manifesting immediately after the event, or long-term, influencing the ecosystem over an extended period.
Short-Term and Long-Term Impacts of Flooding, Drier and cooler weather after flooding in england and wales
Flooding, while a natural process, can have both positive and negative environmental impacts. Short-term impacts are immediate and often visible, while long-term effects can be more subtle but equally significant.
Short-Term Impacts
- Erosion and Sedimentation:Flooding carries significant amounts of sediment and debris, leading to soil erosion and deposition in new locations. This can alter river channels, create new landforms, and impact downstream ecosystems.
- Nutrient Transport:Floodwaters transport nutrients, both organic and inorganic, from the land to water bodies.
The recent flooding in England and Wales has finally subsided, leaving behind a much drier and cooler weather pattern. While the clean-up efforts continue, it’s important to remember that even in times of crisis, our fundamental rights remain crucial. This includes the right to free speech, which is under attack in some parts of the world, as evidenced by the ongoing discussion about shredding the first amendment.
The freedom to express ourselves is a cornerstone of democracy, and it’s something we should all strive to protect, even as we navigate the challenges of rebuilding after natural disasters.
This can lead to increased nutrient levels in rivers and lakes, potentially causing eutrophication and algal blooms.
- Habitat Disturbance:Floodwaters can disrupt and damage habitats, displacing or killing wildlife. This can impact biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Long-Term Impacts
- Soil Degradation:Repeated flooding can lead to soil compaction, reducing infiltration and increasing runoff. This can affect soil fertility and plant growth.
- Water Quality:Flooding can introduce pollutants, such as sewage, industrial waste, and agricultural chemicals, into water bodies, impacting water quality and harming aquatic life.
The recent flooding in England and Wales has finally subsided, giving way to drier and cooler weather. While the clean-up continues, some are already looking ahead to brighter days. Speaking of brighter days, Unto Others’ Gabriel Franco recently revealed his dream tour pairing , a combination sure to excite fans of heavy music.
Hopefully, the drier weather will hold, allowing for more outdoor activities and perhaps even some live music events as we transition out of the recent flood season.
- Landslide Risk:Flooding can saturate slopes, increasing the risk of landslides, which can damage infrastructure and threaten human life.
Impact of Drier Weather on Soil Moisture, Vegetation, and Wildlife
Drier weather, characterized by reduced rainfall and increased evaporation, has a profound impact on soil moisture, vegetation, and wildlife.
Soil Moisture
Prolonged dry periods can lead to decreased soil moisture, impacting plant growth and affecting the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Reduced Infiltration:Dry soils are less able to absorb rainfall, leading to increased runoff and erosion.
- Increased Evaporation:Higher temperatures and dry conditions increase evaporation rates, further depleting soil moisture.
- Salinization:In arid and semi-arid regions, drier weather can exacerbate salinization, making the soil unsuitable for plant growth.
Vegetation
Dry weather can negatively impact vegetation by reducing plant growth and increasing the risk of wildfires.
- Drought Stress:Plants experience drought stress when water availability is limited, leading to wilting, leaf drop, and reduced growth.
- Increased Fire Risk:Dry vegetation is highly flammable, increasing the risk of wildfires, which can devastate ecosystems and release harmful pollutants.
- Changes in Species Composition:Drier conditions can favor drought-tolerant species, leading to changes in plant communities.
Wildlife
Drier weather can affect wildlife by impacting food availability, water sources, and habitat conditions.
The rain has finally stopped and the skies are clearing, bringing drier and cooler weather to England and Wales after the recent flooding. It’s a welcome change for those affected by the storms, but the news isn’t all sunshine and rainbows.
It seems the troubles for sub postmasters with the Horizon system are far from over, with most sub postmasters still reporting issues with Horizon as more than half have unexplained discrepancies. Hopefully, this drier weather will give everyone a chance to recover and rebuild, while the post office situation gets resolved.
- Food Scarcity:Drier weather can reduce the availability of food sources for animals, particularly herbivores that rely on vegetation.
- Water Stress:Animals may experience water stress during prolonged dry periods, leading to dehydration and potential mortality.
- Habitat Loss:Drier weather can lead to habitat loss, particularly for species that rely on specific moisture regimes.
Ecological Disruptions Caused by Changing Weather Conditions
The shift in weather patterns from flooding to drier conditions can lead to significant ecological disruptions.
- Changes in Species Distribution:Drier conditions can favor drought-tolerant species, while flooding can benefit species adapted to wet environments. These changes can lead to shifts in species distribution and potentially disrupt ecological interactions.
- Alterations in Food Webs:Changes in vegetation and wildlife populations due to flooding or drier weather can alter food webs, impacting the entire ecosystem.
- Increased Invasive Species:Extreme weather events can create opportunities for invasive species to establish themselves, disrupting native ecosystems.
Environmental Impacts of Flooding and Drier Weather
| Impact | Flooding | Drier Weather |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture | Increased soil moisture, potential for saturation | Decreased soil moisture, increased risk of drought |
| Vegetation | Potential for damage and displacement | Reduced growth, increased fire risk |
| Wildlife | Habitat disturbance, potential displacement or mortality | Food scarcity, water stress, habitat loss |
| Water Quality | Potential for pollution from runoff | Increased salinity, potential for water scarcity |
| Erosion and Sedimentation | Increased erosion and deposition | Increased erosion due to reduced vegetation cover |
Infrastructure and Economic Impacts
The recent flooding in England and Wales has had a significant impact on infrastructure and the economy, disrupting essential services and causing substantial financial losses. The damage to infrastructure, coupled with the economic consequences for businesses and communities, underscores the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of such events.
Damage to Infrastructure
Flooding can cause extensive damage to various infrastructure components, including roads, bridges, railways, power lines, and water treatment facilities. The impact on transportation networks can be particularly severe, leading to road closures, disruptions to public transport, and delays in the delivery of goods and services.
Damaged power lines can result in power outages, affecting homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
Economic Impact of Flooding
Flooding has a profound economic impact on businesses and communities. Businesses may experience significant losses due to damage to property, equipment, and inventory. Disruptions to supply chains and operations can lead to production delays, lost revenue, and job losses. Communities may face increased costs for repairs, clean-up, and recovery efforts, putting a strain on local budgets.
Impact of Drier Weather on Agriculture and Water Resources
While drier weather may provide some respite from flooding, it can also pose challenges for agriculture and water resources. Reduced rainfall can lead to drought conditions, impacting crop yields and livestock production. Drier weather can also exacerbate water scarcity, particularly in areas already facing water stress.
Economic Costs Associated with Flood Recovery and Drier Weather Conditions
| Category | Cost | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Flood Damage Repair | £billions | Repairing damaged homes, businesses, and infrastructure |
| Business Interruption | £millions | Lost revenue, production delays, and job losses |
| Agricultural Losses | £millions | Reduced crop yields, livestock losses, and increased irrigation costs |
| Water Management Costs | £millions | Investments in drought-resistant crops, water conservation measures, and desalination plants |
Government and Community Response
In the wake of the devastating floods that ravaged England and Wales, the government and local communities have come together to address the immediate and long-term challenges posed by the disaster. The government’s response has been multifaceted, encompassing emergency relief, infrastructure repair, and long-term flood mitigation strategies.
Meanwhile, local communities have played a crucial role in supporting affected residents, aiding in recovery efforts, and fostering resilience in the face of future flooding events.
Government Response to Flooding and Drier Weather
The government’s response to the floods has been characterized by swift action and significant financial commitment. The Environment Agency, the government’s primary agency responsible for flood management, deployed resources to affected areas, including flood defenses, pumps, and sandbags. The government also activated emergency response teams, providing support to residents and businesses impacted by the floods.
In the aftermath of the floods, the government announced a comprehensive package of financial aid, including grants and loans to help residents and businesses rebuild their lives and livelihoods. The government has also committed to investing in flood mitigation infrastructure, such as building new flood defenses and improving existing ones.The government’s response to the subsequent drier weather has been focused on managing water resources and mitigating the potential impacts of drought.
The Environment Agency has implemented water conservation measures, including restrictions on water usage for non-essential purposes. The government has also allocated funds for drought mitigation projects, such as improving water storage and distribution infrastructure.
Community Role in Flood Recovery and Mitigation
Local communities have been instrumental in flood recovery and mitigation efforts. Volunteers from across the country have stepped forward to assist with cleanup operations, provide support to affected residents, and organize community initiatives to aid in recovery. Community organizations have played a crucial role in providing food, shelter, and other essential resources to those displaced by the floods.
Importance of Community Collaboration and Support
Community collaboration and support are vital during times of crisis, such as flooding. The shared experiences of hardship and resilience can foster a sense of unity and purpose. Community initiatives, such as neighborhood cleanups and fundraising events, can help to rebuild communities and restore a sense of normalcy.
Community support networks can also provide emotional and practical assistance to those affected by flooding, helping them to cope with the trauma and navigate the recovery process.
Community Outreach Program
A comprehensive community outreach program is essential to address the needs of residents affected by flooding and drier weather. The program should include the following elements:
- Information and Resource Dissemination:Providing residents with accurate and timely information about flood risks, safety precautions, and available resources, including financial assistance, housing support, and mental health services.
- Community Engagement and Participation:Encouraging residents to participate in flood mitigation and recovery efforts, such as volunteering, attending community meetings, and sharing their experiences and ideas.
- Support Networks and Mental Health Services:Establishing support networks and providing access to mental health services for residents who have experienced trauma or distress as a result of flooding.
- Long-Term Recovery Planning:Assisting residents in developing long-term recovery plans, including rebuilding homes, restoring businesses, and adapting to future flood risks.