Why Study the Black Lives Matter Movement?
Why is it important to study the blacklivesmatter movement – Why study the Black Lives Matter movement? It’s a question that deserves a deep dive, not just because of the movement’s undeniable impact on contemporary society, but also because it offers a powerful lens through which to understand the ongoing struggle for racial justice.
From its origins in the fight against police brutality and systemic racism to its global reach and influence on policy debates, the Black Lives Matter movement has become a defining force in our time.
The movement’s core principles, centered on the inherent value and dignity of Black lives, are a rallying cry for change. It demands a reckoning with the historical and ongoing injustices faced by Black communities, urging us to confront the systemic inequalities that permeate our institutions and everyday lives.
It’s a movement that calls for action, urging us to move beyond mere awareness and towards meaningful, lasting change.
Historical Context

The Black Lives Matter movement, a contemporary force demanding racial justice and equality, has its roots deeply embedded in the long history of activism against racial oppression in the United States. Understanding its origins helps us grasp the movement’s significance and its enduring fight for a more equitable society.
The Legacy of Earlier Movements, Why is it important to study the blacklivesmatter movement
The Black Lives Matter movement is not a standalone entity but rather a continuation of a long struggle for racial justice that stretches back centuries. The movement draws inspiration from and builds upon the work of earlier generations of activists who fought against slavery, Jim Crow segregation, and systemic racism.
- The Abolitionist Movement:The 19th-century abolitionist movement, led by figures like Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman, played a pivotal role in ending slavery. Their tireless efforts and advocacy for human rights laid the foundation for future movements for racial equality.
- The Civil Rights Movement:The Civil Rights Movement of the mid-20th century, led by Martin Luther King Jr. and others, brought about significant legal and social changes for African Americans. Their nonviolent protests and campaigns against segregation and discrimination inspired generations of activists and paved the way for the Black Lives Matter movement.
The Catalysts for Emergence
The Black Lives Matter movement emerged in the wake of a series of high-profile incidents of police brutality and racial injustice against Black individuals. These incidents, widely documented and shared through social media, sparked outrage and ignited a call for change.
- The Shooting of Trayvon Martin:In 2012, the fatal shooting of Trayvon Martin, an unarmed Black teenager, by George Zimmerman, a neighborhood watch volunteer, sparked national protests and discussions about racial profiling and gun violence. The acquittal of Zimmerman further fueled the movement’s rise.
- The Killing of Michael Brown:The 2014 shooting of Michael Brown, an unarmed Black teenager, by police officer Darren Wilson in Ferguson, Missouri, led to weeks of protests and unrest. The lack of justice for Brown’s death galvanized the Black Lives Matter movement and brought the issue of police brutality to the forefront of national discourse.
Understanding the Black Lives Matter movement isn’t just about history; it’s about recognizing the systemic inequalities that still exist. This isn’t just a matter of social justice, but also a matter of economic justice, as the movement has shed light on the impact of racism on everything from access to healthcare to wealth accumulation.
The concept of “the bad vibes economy” the bad vibes economy , which explores how negativity can affect economic growth, reinforces the importance of addressing these issues. By studying the Black Lives Matter movement, we can gain a deeper understanding of how to create a more equitable and prosperous society for everyone.
- The Death of Eric Garner:The 2014 death of Eric Garner, a Black man who died after being placed in a chokehold by police officer Daniel Pantaleo in New York City, further amplified the movement’s call for accountability and reform within law enforcement.
The Role of Social Media and Technology
Social media platforms and technology have played a crucial role in amplifying the Black Lives Matter movement’s message and mobilizing supporters worldwide.
- Viral Videos and Images:The widespread use of smartphones and social media platforms has enabled the rapid dissemination of videos and images documenting police brutality and racial injustice. These visual accounts have galvanized public opinion and sparked outrage, bringing the movement’s message to a wider audience.
- Social Media Campaigns:The movement has utilized social media to organize protests, raise awareness, and build a global network of supporters. Hashtags like #BlackLivesMatter, #SayHerName, and #JusticeFor [victim’s name] have become powerful tools for collective action and online activism.
- Crowdfunding and Online Donations:Social media platforms have facilitated crowdfunding efforts and online donations, allowing individuals to contribute financially to the movement’s causes and initiatives.
Core Principles and Demands: Why Is It Important To Study The Blacklivesmatter Movement
The Black Lives Matter movement is founded on a set of core principles that guide its actions and demands for social change. These principles are rooted in the belief that Black lives are inherently valuable and deserve equal protection and respect in society.
Black Lives Matter Movement’s Core Principles
The movement’s core principles emphasize the interconnectedness of various social justice issues and the need for a transformative approach to dismantling systemic racism. These principles serve as a framework for understanding the movement’s goals and demands.
- Black Lives Matter: This core principle emphasizes the inherent value and dignity of Black lives, rejecting the notion that they are disposable or less important than other lives. It underscores the need to acknowledge and address the systemic racism that has historically devalued Black lives.
- Black People Are Human: This principle challenges the dehumanization of Black people, often portrayed as criminals or threats. It asserts that Black people are deserving of the same human rights and dignity as everyone else.
- We Are Interconnected: The movement recognizes that social justice issues are intertwined and that addressing one issue requires acknowledging and tackling others. This principle highlights the interconnectedness of racism, sexism, homophobia, transphobia, and other forms of oppression.
- We Are Resilient: This principle acknowledges the strength and resilience of Black communities in the face of systemic oppression. It celebrates the cultural richness and contributions of Black people throughout history.
- We Are Not Afraid: The movement encourages courage and boldness in the face of injustice. It empowers Black people to speak out against racism and to demand accountability from those in power.
Demands for Systemic Change
The Black Lives Matter movement has articulated a set of demands for systemic change across various sectors of society. These demands aim to address the root causes of racial injustice and create a more equitable society.
Understanding the Black Lives Matter movement is crucial for building a more just and equitable society. It forces us to confront uncomfortable truths about systemic racism and its impact on Black communities. Sometimes, though, these issues can feel overwhelming, and it’s easy to get distracted by personal anxieties, like when a student develops a crush on you, as detailed in this article: help my student has a crush on me and im freaking out.
But ultimately, engaging with the Black Lives Matter movement is essential for creating positive change and fostering a world where everyone feels safe and respected.
- Law Enforcement and Criminal Justice Reform: The movement calls for a complete overhaul of the criminal justice system, including police reform, decarceration, and the abolition of the death penalty. This includes demands for police accountability, transparency, and community oversight.
- Education Equity: The movement advocates for educational equity and access for all Black students, calling for an end to school segregation, the elimination of discriminatory policies, and the implementation of culturally relevant curriculum.
- Healthcare Equity: The movement demands healthcare equity for Black communities, addressing the disparities in access to quality healthcare and calling for policies that ensure health equity for all.
- Economic Justice: The movement seeks economic justice for Black communities, calling for policies that address racial wealth gaps, promote economic opportunity, and combat discriminatory practices in employment and housing.
Intersectionality
Intersectionality is a key concept within the Black Lives Matter movement, recognizing the interconnectedness of various social justice issues. This framework acknowledges that individuals experience oppression based on their multiple identities, such as race, gender, sexual orientation, and socioeconomic status.
- The Interplay of Oppression: Intersectionality highlights how different forms of oppression intersect and reinforce each other. For example, a Black woman may experience racism, sexism, and classism simultaneously, creating a unique set of challenges and barriers.
- Understanding Complexities: This framework emphasizes the need to understand the complex interplay of social identities and the ways in which they shape individuals’ experiences of oppression. It challenges simplistic approaches to social justice that focus on single-issue movements.
- Building Solidarity: Intersectionality encourages solidarity and collaboration among different social justice movements, recognizing that their struggles are interconnected. It emphasizes the need to address all forms of oppression in order to create a truly just society.
Impact and Influence
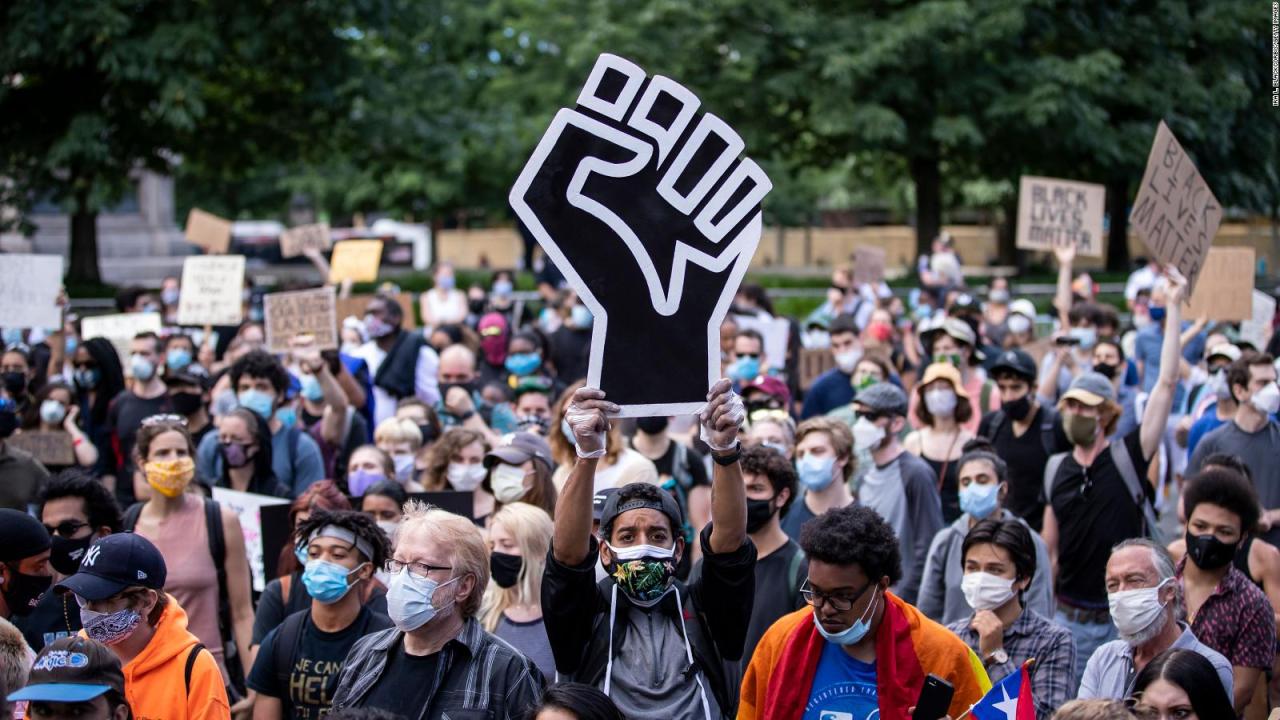

The Black Lives Matter movement has had a profound impact on society, influencing public discourse, policy debates, and global activism. Its influence can be seen in various aspects of life, from legislative changes to cultural shifts.
Impact on Public Discourse and Policy Debates
The Black Lives Matter movement has significantly reshaped the public conversation surrounding race and police brutality. It has brought these issues to the forefront of national and international discussions, prompting widespread dialogue and debate. The movement’s influence can be seen in the increased awareness of systemic racism and its impact on Black communities.
This awareness has led to increased scrutiny of law enforcement practices, prompting calls for police reform and accountability.
Understanding the Black Lives Matter movement is crucial for building a more equitable society, and that includes navigating the digital landscape. Learning how to do digital marketing in the age of privacy, as outlined in this excellent article how to do digital marketing in the age of privacy , is essential for reaching diverse audiences and fostering genuine connections.
By mastering these strategies, we can ensure that our messaging about racial justice is heard and understood by all.
Influence on Global Activism and Solidarity Efforts
The Black Lives Matter movement has inspired global activism and solidarity efforts. The movement’s message of racial justice has resonated with people worldwide, leading to protests and demonstrations in support of Black lives. The movement’s influence can be seen in the rise of anti-racism movements in other countries, as well as in the increased awareness of racial disparities and injustices across the globe.
Legislative Changes and Reforms
The Black Lives Matter movement has played a significant role in driving legislative changes and reforms. The movement’s advocacy has led to the passage of laws and policies aimed at addressing police brutality and racial disparities. Some notable examples include:
- The George Floyd Justice in Policing Act, a comprehensive police reform bill that aimed to address police misconduct and racial bias in policing.
- The Breonna Taylor Act, a bill that aimed to ban no-knock warrants and increase police accountability.
- The Eric Garner Anti-Chokehold Act, a bill that aimed to restrict the use of chokeholds by law enforcement.
Challenges and Controversies
The Black Lives Matter movement, despite its powerful message of racial justice, has faced numerous challenges and controversies. These issues often stem from differing viewpoints on the movement’s tactics, its relationship with law enforcement, and the media’s portrayal of its activities.
Diverse Perspectives on Tactics
The Black Lives Matter movement encompasses a wide range of individuals and organizations, leading to diverse perspectives on its methods and tactics. Some argue that peaceful protests and civil disobedience are the most effective means of achieving change, while others advocate for more confrontational approaches.
- Peaceful Protests:Many proponents of peaceful protests believe that nonviolent demonstrations are the most effective way to raise awareness and pressure authorities for change. They argue that such tactics maintain a moral high ground and garner public support.
- Confrontational Tactics:Others believe that more confrontational tactics, such as property damage or disruptions, are necessary to force systemic change. They argue that peaceful protests have historically been ineffective in addressing deep-rooted issues of racial injustice.
Relationship with Law Enforcement
The Black Lives Matter movement has frequently clashed with law enforcement, particularly in response to incidents of police brutality against Black individuals. These tensions have resulted in accusations of police overreach and excessive force, while some law enforcement agencies have criticized the movement for its tactics and rhetoric.
- Police Brutality and Accountability:The movement’s focus on police brutality has led to calls for greater police accountability and reform. This includes demands for increased transparency, stricter use-of-force policies, and independent investigations of police misconduct.
- Law Enforcement Responses:Some law enforcement agencies have responded to the movement with skepticism and resistance, arguing that it fuels anti-police sentiment and hinders their ability to effectively enforce the law. They often point to instances of violence or property damage during protests as justification for their response.
Media Portrayal and Public Perception
The media’s portrayal of the Black Lives Matter movement has been a source of controversy, with accusations of bias and misrepresentation. This has influenced public perception of the movement and its goals, leading to differing views on its legitimacy and effectiveness.
- Media Bias and Misrepresentation:Critics argue that the media often focuses on the most sensational aspects of protests, emphasizing violence or property damage while downplaying the movement’s broader message of racial justice. This can lead to a distorted public perception of the movement’s goals and motivations.
- Public Perception and Support:The media’s portrayal of the movement has a significant impact on public opinion. While some individuals are supportive of the movement’s goals, others may be skeptical or even hostile due to negative media coverage.
Future Directions
The Black Lives Matter movement, having ignited a global conversation on racial injustice, continues to evolve and adapt, shaping a future where equality and justice are the norm. While acknowledging the significant strides made, the movement recognizes that the fight for racial equity is an ongoing journey, demanding sustained efforts and strategic approaches.
Policy Advocacy
The movement’s future trajectory involves amplifying its policy advocacy efforts, pushing for systemic changes that dismantle racial disparities and promote equality. This involves advocating for:
- Police Reform:The movement seeks to reform policing practices by advocating for stricter accountability measures, demilitarization of police forces, and increased investment in community-based alternatives to policing. Examples include calls for the defunding of police departments and redirecting funds towards social services and community programs that address the root causes of crime.
- Criminal Justice Reform:The movement advocates for the elimination of mass incarceration and the dismantling of systems that disproportionately impact Black communities. This includes advocating for policies that reduce sentencing disparities, promote restorative justice, and provide opportunities for rehabilitation and reintegration.
- Economic Justice:Addressing economic disparities is a key focus, with the movement advocating for policies that promote equitable access to quality education, healthcare, housing, and employment opportunities. This includes supporting initiatives that promote affordable housing, expand access to quality healthcare, and address wealth disparities.
Conclusion

Studying the Black Lives Matter movement isn’t just about understanding the past; it’s about shaping the future. By engaging with the movement’s history, principles, and impact, we gain a deeper understanding of the challenges we face and the possibilities for creating a more just and equitable society.
It’s a journey of learning, reflection, and action, one that compels us to become active participants in the fight for racial justice.