Russias Economy: Gloomy Outlook as Prices Soar
In russia as prices soar the outlook for its economy grows especially gloomy – In Russia as prices soar, the outlook for its economy grows especially gloomy. The war in Ukraine, coupled with crippling sanctions, has unleashed a perfect storm of economic turmoil. Inflation is surging, the ruble is plummeting, and the specter of recession looms large.
This economic crisis is not just a numbers game; it’s a stark reality impacting everyday Russians, forcing them to grapple with rising costs and shrinking purchasing power.
The situation is complex, with a multitude of factors contributing to Russia’s economic woes. Understanding these factors is crucial to grasping the gravity of the situation and its potential implications for the future. From the impact of sanctions on energy exports to the ripple effects on consumer goods and services, the economic landscape in Russia is undergoing a dramatic transformation.
Rising Inflation and its Impact
Russia’s economic outlook is increasingly gloomy, with soaring inflation adding to the challenges posed by the war in Ukraine and international sanctions. Inflation, a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, is a significant concern for the Russian economy.
The economic situation in Russia is dire, with soaring prices and a bleak outlook. It’s a reminder that even in the face of adversity, we must prioritize our own well-being. If you’re feeling overwhelmed by a job share arrangement, remember that you’re not alone.
Ask WeAreTeachers for help , and find a solution that allows you to thrive. Just like Russia’s economy, our personal situations can be unpredictable, but with the right support, we can navigate through the challenges and emerge stronger.
Inflation Rate and Historical Context
Russia’s inflation rate has surged in recent months, reaching a 17-year high in April 2023. The official inflation rate reached 17.8% year-on-year in April 2023, according to the Russian Federal State Statistics Service (Rosstat). This is a stark contrast to the relatively low inflation rates observed in the years preceding the war, with inflation hovering around 4% in 2021.
It’s hard to shake the feeling that the world is getting crazier by the day. In Russia, as prices soar, the outlook for its economy grows especially gloomy, while here in the States, we’re seeing the consequences of spreading dangerous misinformation.
The Alex Jones damages trial, which begins this week, over his false claims about the Sandy Hook shooting being a hoax , is a stark reminder of the devastating impact that lies can have. The world seems to be spiraling, and it’s hard to see a way out of the economic and social turmoil we’re facing.
The sharp increase in inflation can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the war in Ukraine, sanctions imposed by Western countries, and disruptions to global supply chains.
Drivers of Inflation
The war in Ukraine has had a significant impact on the Russian economy, disrupting supply chains, increasing energy prices, and causing uncertainty. Western sanctions imposed on Russia have further exacerbated the situation, limiting access to international markets and financial resources.
- Sanctions and Import Restrictions:Western sanctions have restricted Russia’s access to key imports, including technology, industrial equipment, and consumer goods. This has led to shortages and price increases for essential items.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The war has disrupted global supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs for imported goods. This has also impacted domestic production, as businesses struggle to obtain necessary raw materials and components.
- Energy Price Volatility:Russia is a major energy exporter, and the war has led to significant volatility in global energy prices. This has resulted in higher energy costs for businesses and consumers in Russia.
- Ruble Depreciation:The ruble has depreciated significantly against major currencies since the start of the war, making imports more expensive and contributing to inflation.
Impact on Different Sectors
Inflation has had a significant impact on different sectors of the Russian economy:
- Consumer Goods:Inflation has led to price increases for a wide range of consumer goods, including food, clothing, and electronics. This has eroded consumer purchasing power and reduced demand for non-essential items.
- Energy:Energy prices have soared in Russia, driven by global market volatility and sanctions. This has increased costs for businesses and consumers, particularly those reliant on energy-intensive industries.
- Services:Inflation has also impacted the service sector, leading to price increases for transportation, healthcare, and education. This has put pressure on household budgets and reduced access to essential services.
Purchasing Power of the Ruble
The depreciation of the ruble has significantly impacted the purchasing power of Russian consumers. The ruble has lost about 40% of its value against the US dollar since the start of the war. This means that Russians need to spend more rubles to purchase the same amount of goods and services as before.
The decline in the ruble’s purchasing power has reduced consumer spending and dampened economic growth.
Economic Outlook and Projections
The current economic situation in Russia is dire, with inflation soaring and the outlook for the economy becoming increasingly gloomy. The ongoing war in Ukraine, coupled with international sanctions, has created a perfect storm for the Russian economy. While the short-term outlook is bleak, the long-term implications are still unfolding and will depend heavily on the trajectory of the conflict and the effectiveness of sanctions.
Short-Term and Long-Term Economic Projections
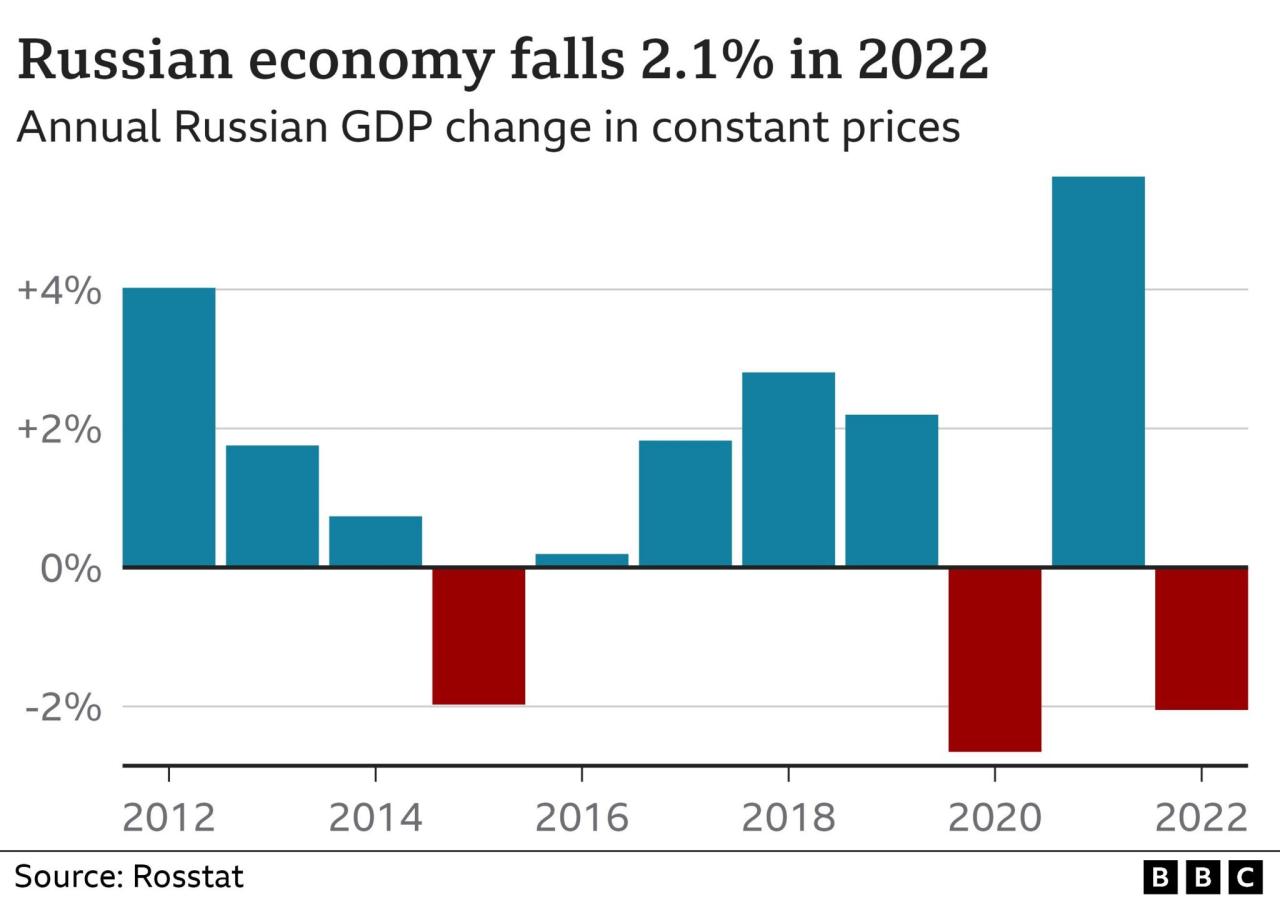
The short-term economic outlook for Russia is bleak, with most projections pointing towards a significant contraction in GDP. The World Bank estimates that the Russian economy will shrink by 11.2% in 2022, while the IMF forecasts a contraction of 8.5%.
These projections are based on the assumption that the war in Ukraine will continue and that sanctions will remain in place. The impact of the war and sanctions is already being felt in Russia, with businesses struggling to operate, supply chains disrupted, and consumer confidence plummeting.
The long-term economic outlook for Russia is highly uncertain. While the sanctions are likely to have a significant impact on the economy, the long-term effects will depend on several factors, including the duration of the war, the effectiveness of sanctions, and the government’s response.
If the war continues for an extended period, the Russian economy is likely to face significant challenges, including a decline in investment, a brain drain, and a weakening of the ruble. However, if the conflict ends quickly and sanctions are lifted, the Russian economy could rebound more quickly.
Impact of Sanctions on the Russian Economy
Sanctions have had a significant impact on the Russian economy, particularly in the energy sector. Russia is a major exporter of oil and gas, and sanctions have made it difficult for Russia to sell its energy products to Western countries.
This has led to a decline in energy revenues, which has had a negative impact on the Russian economy. The sanctions have also had a significant impact on foreign investment in Russia, as many investors have pulled out of the country due to the uncertainty surrounding the future of the Russian economy.
Comparison with Previous Periods of Economic Hardship, In russia as prices soar the outlook for its economy grows especially gloomy
The current economic crisis in Russia is one of the most severe in recent history. While Russia has faced economic challenges in the past, including the 1998 financial crisis and the global financial crisis of 2008, the current situation is unique due to the combination of the war in Ukraine and the international sanctions.
The current crisis is likely to have a more profound and lasting impact on the Russian economy than previous crises.
Impact of the War in Ukraine on the Russian Economy
The war in Ukraine has had a devastating impact on the Russian economy. The conflict has disrupted trade, leading to a decline in exports and imports. It has also led to a decline in industrial production, as many businesses have been forced to shut down or relocate due to the war.
The war has also led to a rise in inflation, as the cost of imported goods has increased. The war in Ukraine has also had a significant impact on the Russian financial system, with many banks facing difficulties due to the sanctions.
Government Responses and Policies

The Russian government has implemented a range of economic policies to combat inflation and address the economic challenges stemming from the war and sanctions. These measures aim to stabilize the ruble, support businesses, and mitigate the impact on ordinary citizens.
Policies Implemented
The Russian government has taken several steps to address the economic crisis. These include:
- Currency Control:The Central Bank of Russia has implemented strict currency controls, limiting the amount of foreign currency that individuals and businesses can buy and sell. This has helped to stabilize the ruble, which had depreciated sharply in the wake of the war and sanctions.
- Interest Rate Hikes:The Central Bank has raised interest rates significantly to curb inflation and attract foreign investment. This has slowed economic growth but has helped to stabilize the financial system.
- Fiscal Stimulus:The government has implemented a series of fiscal stimulus measures, including tax breaks for businesses and direct payments to individuals, to support economic activity and cushion the impact of the crisis on households.
- Import Substitution:The government is promoting import substitution policies to reduce reliance on foreign goods and services. This involves supporting domestic production and encouraging the development of new industries.
- Sanctions Relief:The government is seeking to ease the impact of sanctions by negotiating with international partners and exploring alternative trade routes. This includes seeking exemptions from sanctions for certain sectors and developing new economic partnerships.
Effectiveness of Policies
The effectiveness of these policies is mixed. While the currency controls and interest rate hikes have helped to stabilize the ruble and contain inflation, they have also slowed economic growth. The fiscal stimulus measures have provided some support to households and businesses, but their long-term impact is uncertain.
The import substitution policies are still in their early stages and may take time to yield significant results.
Challenges Facing the Government
The Russian government faces several challenges in managing the economy amidst the war and sanctions. These include:
- Long-Term Impact of Sanctions:The sanctions are likely to have a long-term impact on the Russian economy, limiting access to foreign capital and technology. This could hinder economic growth and development.
- Dependence on Energy Exports:Russia’s economy is heavily reliant on energy exports, which are subject to price fluctuations and sanctions. This makes the economy vulnerable to external shocks.
- Capital Flight:The war and sanctions have led to a significant outflow of capital from Russia, as investors seek safer havens. This reduces investment and slows economic growth.
- Inflationary Pressures:The war and sanctions have contributed to rising inflation, eroding purchasing power and increasing the cost of living for ordinary citizens.
- Limited Policy Options:The government’s policy options are limited by the war and sanctions. The need to maintain military spending and the limited access to foreign capital restrict the government’s ability to implement more aggressive economic policies.
Potential Alternative Policies
The Russian government could consider several alternative policies to address the economic crisis. These include:
- Further Fiscal Stimulus:The government could consider increasing fiscal stimulus measures to support economic activity and cushion the impact of the crisis on households and businesses. This could involve additional tax breaks, direct payments, and investment in infrastructure.
- Structural Reforms:The government could implement structural reforms to improve the business environment, reduce corruption, and promote innovation. This could help to attract foreign investment and boost economic growth in the long term.
- Diversification of the Economy:The government could focus on diversifying the economy to reduce dependence on energy exports. This could involve promoting new industries, such as technology and manufacturing, and developing new markets for Russian goods and services.
- Increased Cooperation with International Partners:The government could seek to improve relations with international partners and negotiate a lifting of sanctions. This would provide access to foreign capital and technology, boosting economic growth and development.
Social and Political Implications
The soaring prices and economic hardship in Russia are having a profound impact on the lives of ordinary citizens, leading to a decline in living standards and a widening gap in social inequality. This economic crisis has the potential to trigger significant political repercussions, including a shift in public sentiment and a potential for social unrest.
Impact on the Russian Population
The economic crisis has resulted in a significant decline in living standards for many Russians. The rising cost of essential goods, such as food and energy, has eroded purchasing power, forcing many households to make difficult choices about their spending.
The World Bank estimates that Russia’s poverty rate increased to 12.3% in 2022, up from 11.6% in 2021.
- Reduced purchasing power:The sharp increase in prices has significantly reduced the purchasing power of the Russian ruble, forcing many households to cut back on essential expenses. This has led to a decline in the quality of life for many Russians.
- Increased poverty and inequality:The economic crisis has disproportionately impacted low-income households, leading to a rise in poverty and widening the gap in social inequality.
- Limited access to healthcare and education:The decline in government revenue due to the economic crisis has led to budget cuts in essential services like healthcare and education, making them less accessible to the general population.
Potential Political Implications
The economic crisis has the potential to significantly impact Russian politics. The declining living standards and growing economic hardship could lead to a decline in public support for the government.
- Erosion of public support:The economic hardship and decline in living standards could lead to a decline in public support for the government, particularly among those who are most affected by the crisis.
- Increased political instability:The growing economic hardship could fuel political instability, potentially leading to increased protests and calls for political change.
- Potential for social unrest:The economic crisis could trigger social unrest and protests, as people become increasingly frustrated with the government’s handling of the situation.
Role of Media and Social Networks
The media and social networks play a crucial role in shaping public opinion about the economy. While state-controlled media often present a positive narrative, independent media and social networks provide alternative perspectives and information about the economic challenges faced by ordinary Russians.
- Independent media:Independent media outlets and social media platforms provide alternative perspectives and information about the economic challenges faced by ordinary Russians. They can play a crucial role in mobilizing public opinion and highlighting the impact of the crisis on people’s lives.
- State-controlled media:State-controlled media outlets often present a more positive narrative about the economy, downplaying the severity of the crisis and highlighting government efforts to address the challenges. This can contribute to a disconnect between public perception and the reality of the economic situation.
- Social media:Social media platforms provide a platform for ordinary Russians to share their experiences and concerns about the economy, creating a space for collective action and mobilization.
Potential for Social Unrest
The economic crisis has the potential to trigger social unrest and protests, particularly if the government fails to address the concerns of the population. The combination of declining living standards, growing inequality, and limited access to essential services could fuel public anger and frustration, leading to widespread protests.
It’s hard to ignore the bleak outlook for the Russian economy as prices skyrocket, but amidst the global uncertainty, it’s refreshing to see a tech giant like Apple apple starts connecting the dots for its next big thing and forging ahead with innovation.
Perhaps, amidst the economic storm clouds, Apple’s bold moves will offer a glimmer of hope for a brighter future, even as Russia faces a challenging path ahead.
- Protests and demonstrations:There have been several protests in Russia in recent years, often fueled by economic grievances. The current economic crisis could lead to an increase in protests and demonstrations as people express their dissatisfaction with the government’s handling of the situation.
- Potential for political instability:The potential for social unrest could lead to political instability, particularly if protests turn violent or if the government responds with excessive force.
International Perspectives
The escalating economic crisis in Russia has drawn significant attention from international organizations and policymakers worldwide. The implications of the crisis extend beyond Russia’s borders, impacting global markets, trade, and geopolitical relations. This section will explore the perspectives of international organizations, the potential impact on the global economy, and the geopolitical implications of the crisis.
International Organizations’ Perspectives
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank have expressed concerns about the Russian economic outlook. The IMF has projected a significant contraction in Russia’s GDP in 2022 and 2023, citing the impact of sanctions and the war in Ukraine.
The World Bank has also predicted a sharp decline in Russia’s economic output, emphasizing the disruption to trade and investment caused by the crisis.
The IMF’s projections indicate a significant contraction in Russia’s GDP in 2022 and 2023, highlighting the severe economic impact of the sanctions and the war in Ukraine.
Impact on Global Markets and Trade
The Russian economic crisis has already had a noticeable impact on global markets. The sanctions imposed on Russia have disrupted supply chains and increased energy prices, leading to higher inflation worldwide. The war in Ukraine has also caused disruptions to global food supplies, as both countries are major exporters of wheat and other agricultural products.
The economic fallout from the crisis has exacerbated existing global economic vulnerabilities, including supply chain disruptions, rising inflation, and increased volatility in financial markets.
Geopolitical Implications
The Russian economic crisis has significant geopolitical implications. The sanctions imposed on Russia have strained relations between Russia and Western countries. The war in Ukraine has also led to a deepening divide between Russia and its former allies in Europe.
The crisis has prompted a reassessment of global security arrangements and has increased tensions between major powers.
Potential Scenarios for the Future
The future of the Russian economy is uncertain and will depend on a number of factors, including the duration of the war in Ukraine, the effectiveness of sanctions, and the response of the Russian government. Some analysts believe that the Russian economy could experience a prolonged period of stagnation or even decline, while others predict a more rapid recovery once the crisis subsides.
The future of the Russian economy is uncertain and will depend on a number of factors, including the duration of the war in Ukraine, the effectiveness of sanctions, and the response of the Russian government.
Ultimate Conclusion: In Russia As Prices Soar The Outlook For Its Economy Grows Especially Gloomy
The future of Russia’s economy remains shrouded in uncertainty. The war in Ukraine continues to cast a long shadow, and the impact of sanctions is far from fully realized. The government’s ability to navigate this economic storm and mitigate its consequences will be a critical test of its resilience.
As the situation evolves, it’s crucial to monitor developments closely and consider the potential implications for both Russia and the global economy.






