Analysis: Europe Must Declare a War Economy
Analysis europe must declare a war economy – Analysis: Europe Must Declare a War Economy – The current war in Ukraine has unleashed a cascade of economic challenges upon Europe, from an energy crisis to rising inflation and supply chain disruptions. These challenges are forcing a fundamental question: should Europe adopt a “war economy” to weather the storm?
This concept, historically associated with wartime mobilization, involves drastic measures like government-controlled resource allocation, price controls, and nationalization of key industries. While such measures might seem extreme in peacetime, they could be necessary to ensure Europe’s economic survival and maintain its strategic advantage in the face of an unpredictable global landscape.
The Urgent Need for a War Economy
Europe is facing a profound economic crisis, exacerbated by the ongoing war in Ukraine. The war has disrupted global supply chains, fueled inflation, and triggered an energy crisis, threatening the stability of European economies. This unprecedented situation calls for decisive action, and a war economy might be the only way to navigate these turbulent times.
The Energy Crisis and its Implications
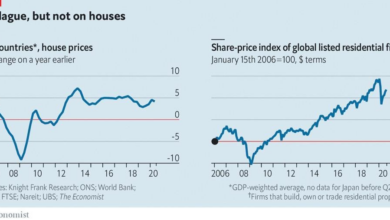
The energy crisis is a major consequence of the war in Ukraine. Russia, a major energy supplier to Europe, has significantly reduced gas exports to the continent, causing prices to skyrocket. This has put immense pressure on European households and businesses, leading to increased energy bills and potentially forcing companies to cut production.
The energy crisis has several implications for European economies:
- Inflation:The surge in energy prices is a key driver of inflation, pushing up the cost of goods and services across the board. This erodes purchasing power, reduces consumer spending, and slows economic growth.
- Recession:The energy crisis is increasing the risk of a recession in Europe. Businesses are struggling to absorb the higher energy costs, and many are forced to cut jobs or even close down. This could lead to a significant decline in economic activity.
- Competitiveness:The high energy prices in Europe make its industries less competitive compared to those in other regions with lower energy costs. This could lead to job losses and a decline in manufacturing activity.
- Social Unrest:The energy crisis is causing significant hardship for many European households, especially those with low incomes. This could lead to social unrest and political instability.
Potential Economic Consequences of Prolonged Conflict
A prolonged conflict in Ukraine could have devastating consequences for the European economy. The following are some of the potential outcomes:
- Deepening Recession:A protracted war could lead to a deeper and more prolonged recession in Europe, as businesses struggle to cope with the ongoing economic shocks. This could result in widespread unemployment and social unrest.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The war has already disrupted global supply chains, and a prolonged conflict could further exacerbate these disruptions. This could lead to shortages of essential goods, further fueling inflation and economic instability.
- Financial Instability:The war could also trigger a financial crisis in Europe. Governments are already spending heavily to support their economies and mitigate the impact of the war. A prolonged conflict could lead to unsustainable levels of debt, putting pressure on public finances and potentially leading to a sovereign debt crisis.
“The war in Ukraine is a major economic shock that is putting immense pressure on European economies. A war economy might be the only way to navigate these turbulent times.”
[Name of Economist]
Key Elements of a War Economy

A war economy is a term used to describe the economic mobilization of a nation during a time of war. It involves a significant shift in resources and production towards military needs, often at the expense of civilian consumption.
Throughout history, nations have adopted various strategies to meet the demands of war, and these have resulted in a range of economic policies and measures.
Historical Examples of War Economies
War economies have existed throughout history, with each era presenting its own unique challenges and responses. Here are some prominent examples:
- World War I:The First World War saw the emergence of a “total war” concept, where entire societies were mobilized for the war effort. This included the introduction of conscription, rationing, and the redirection of industries towards military production. The United States, for instance, implemented the War Industries Board to coordinate industrial production and prioritize military needs.
- World War II:World War II witnessed an even greater intensification of war economies. The United States, under President Franklin D. Roosevelt, implemented a “wartime economy” that saw massive government spending on defense, the nationalization of key industries, and the rationing of essential goods.
The Soviet Union, facing the brunt of the Nazi invasion, also adopted a centralized war economy, with its entire industrial base being redirected towards military production.
- Cold War:The Cold War, though not a conventional war, still saw significant economic mobilization. The United States and the Soviet Union engaged in a massive arms race, leading to a significant expansion of their respective military-industrial complexes. This period saw the development of advanced weapons systems and the deployment of troops around the world, all requiring substantial economic resources.
Key Economic Policies and Measures
War economies typically involve a combination of policies and measures aimed at maximizing resource allocation for military purposes. Here are some key elements:
Increased Government Spending on Defense and Infrastructure
War economies often witness a significant increase in government spending on defense. This includes the procurement of weapons, the expansion of military personnel, and the development of new technologies. Additionally, investment in infrastructure, such as transportation and communication networks, is also crucial for supporting military operations.
The idea of Europe declaring a war economy is certainly a bold one, and it raises all sorts of complex questions. But while we’re debating the future of Europe, it’s interesting to note that even in the realm of paleontology, seemingly settled ideas can be challenged.
Take the recent controversial idea that T. Rex was actually three species , which has reignited debate among experts. It’s a reminder that even with the best evidence, there’s always room for new perspectives. Perhaps the same can be said about Europe’s economic future – we need to be open to new approaches and challenges, just like scientists are in their pursuit of understanding the past.
This increased government spending can lead to a significant expansion of the public sector and a shift in the balance of economic power.
Price Controls and Rationing
To control inflation and ensure the equitable distribution of essential goods, war economies often implement price controls and rationing. Price controls limit the prices of essential goods, such as food, fuel, and clothing, preventing them from skyrocketing due to increased demand.
Rationing programs allocate limited supplies of essential goods to individuals based on their needs, ensuring that everyone has access to the basics. While these measures can help maintain stability, they can also lead to shortages and black markets.
Nationalization of Key Industries
In some cases, war economies involve the nationalization of key industries. This means that the government takes control of industries deemed essential for the war effort, such as steel, oil, and transportation. Nationalization allows the government to direct these industries towards military production and ensure that they meet the demands of the war effort.
However, it can also lead to inefficiencies and stifle innovation if not managed effectively.
The analysis urging Europe to declare a war economy highlights the need for drastic measures to address the current crisis. While this focus is critical, it’s equally important to remember the human cost of such decisions. Supporting family caregivers, who often shoulder the burden of caring for loved ones while managing their own work responsibilities, is crucial.
Check out these 3 strategies for supporting family caregivers at work to ensure their well-being during this challenging time. Ultimately, a successful war economy requires a holistic approach that prioritizes both economic stability and the well-being of its citizens.
Mobilization of Labor and Resources
War economies require a massive mobilization of labor and resources. This often involves conscription, where individuals are required to serve in the military. Additionally, the government may introduce policies to encourage individuals to work in industries vital for the war effort.
This could include incentives, wage controls, and restrictions on labor mobility. Furthermore, resources, such as raw materials, are often redirected towards military production, leading to a decline in civilian goods and services.
Impact on Individual Freedoms and Economic Liberties
The implementation of war economy measures can have a significant impact on individual freedoms and economic liberties. Price controls and rationing can limit consumer choice and restrict access to goods and services. Nationalization can lead to a loss of private property rights and entrepreneurial freedom.
Conscription and labor mobilization can infringe on individual autonomy and freedom of movement. Furthermore, the suppression of dissent and the curtailment of civil liberties are often seen in war economies as governments seek to maintain social cohesion and support for the war effort.
However, it is important to note that the extent of these impacts can vary depending on the specific measures adopted and the duration of the war economy.
Challenges and Considerations
The transition to a war economy, while potentially beneficial in mobilizing resources and production, presents significant challenges and considerations. It is crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the drawbacks, analyze the ethical and moral implications, and assess the political and social consequences.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
The potential benefits of a war economy include:
- Increased Production:War economies often prioritize industrial production, leading to increased output and economic growth. This was evident during World War II, when the United States witnessed a surge in industrial output and employment.
- Technological Advancements:The pressure to develop new weapons and technologies can accelerate innovation and scientific breakthroughs. The Manhattan Project, which developed the atomic bomb, is a prime example of technological advancements driven by wartime needs.
- National Unity:Wartime often fosters a sense of national unity and purpose, bringing people together to achieve a common goal. This can lead to increased social cohesion and a shared sense of identity.
However, there are also significant drawbacks to consider:
- Economic Disruptions:The shift to a war economy can disrupt normal economic activity, leading to shortages, inflation, and price controls. This can create hardship for consumers and businesses.
- Civil Liberties Restrictions:Wartime often necessitates restrictions on civil liberties, such as freedom of speech and assembly, to ensure national security. This can erode democratic principles and lead to authoritarian tendencies.
- Human Costs:War inevitably results in human casualties, both on the battlefield and among civilians. The physical and psychological trauma of war can have long-lasting effects on individuals and society.
Ethical and Moral Implications
The ethical and moral implications of a war economy are complex and multifaceted.
“The decision to transition to a war economy is a profound one, with far-reaching ethical and moral consequences.”
- Prioritization of Military Needs:War economies prioritize military needs over civilian ones, leading to resource allocation that can be seen as unfair or unjust. This raises questions about the value of human life and the allocation of scarce resources.
- Exploitation of Labor:Wartime often leads to the exploitation of labor, with workers being forced to work long hours in dangerous conditions for low wages. This raises concerns about worker rights and the ethical treatment of labor.
- Environmental Degradation:The production and use of weapons can have devastating environmental consequences, including pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion. This raises questions about the long-term sustainability of a war economy.
Political and Social Consequences
The implementation of a war economy can have significant political and social consequences.
- Increased Government Power:Wartime often leads to an expansion of government power, as the state takes on a greater role in directing the economy and controlling resources. This can lead to a reduction in individual liberties and an increase in government control.
The analysis that Europe must declare a war economy is a complex one, raising concerns about the potential impact on individual lives. However, it’s important to remember that true happiness doesn’t come from material wealth, but from something much deeper.
Science says the more of this you give the happier you’ll be, hint it’s not money , suggesting that focusing on building meaningful relationships, contributing to society, and pursuing personal growth can bring more lasting joy than material possessions. Perhaps, in the face of a potential war economy, these are the very things that can offer solace and resilience.
- Social Divisions:War economies can exacerbate existing social divisions, as different groups within society may benefit or suffer from the transition. This can lead to social unrest and political instability.
- Long-Term Economic Impacts:The economic disruptions caused by a war economy can have long-term impacts, such as inflation, debt accumulation, and a decline in living standards. This can make it difficult to return to a peacetime economy and rebuild society.
Alternative Strategies
While a war economy might offer a rapid response to immediate threats, it comes with significant drawbacks. Alternative strategies, focusing on long-term resilience and sustainable development, offer a more nuanced approach to tackling Europe’s challenges.
Increased Investment in Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy sources is crucial for Europe’s long-term energy security and independence.
- Reducing dependence on fossil fuels:This strategy reduces Europe’s vulnerability to energy price shocks and supply disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions or climate change.
- Creating new jobs and industries:Investing in renewable energy technologies creates new jobs and industries, boosting economic growth and diversification.
- Combatting climate change:Transitioning to renewable energy sources is essential for mitigating climate change and its devastating consequences.
Examples of successful renewable energy initiatives include the ambitious German Energiewende program, which aims to transition to 100% renewable energy by 2050, and the European Green Deal, which sets ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development.
Diversification of Supply Chains
Diversifying supply chains is crucial for reducing Europe’s reliance on single suppliers and mitigating risks from geopolitical instability or natural disasters.
- Reducing vulnerability to disruptions:Diversification ensures that disruptions in one supply chain do not cripple entire industries or economies.
- Promoting competition and innovation:Diversification fosters competition and innovation, leading to better quality products and services at lower prices.
- Strengthening economic ties:Diversifying supply chains fosters closer economic ties with diverse partners, promoting regional stability and cooperation.
Examples of successful supply chain diversification include the EU’s efforts to reduce reliance on Chinese rare earth minerals and its strategic partnerships with countries in Africa and Latin America for key commodities.
Strengthening of Economic Alliances
Strengthening economic alliances through trade agreements, joint investments, and coordinated policies is essential for promoting economic growth, stability, and resilience.
- Expanding market access:Trade agreements open up new markets for European businesses, boosting exports and creating jobs.
- Promoting economic cooperation:Joint investments and coordinated policies allow European countries to pool resources and expertise, tackling common challenges more effectively.
- Enhancing competitiveness:Stronger economic alliances allow European countries to compete more effectively in the global economy.
Examples of successful economic alliances include the European Union, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).
The Future of the European Economy

The war in Ukraine has thrown Europe into a period of unprecedented economic uncertainty. The immediate impact has been severe, with soaring energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and a surge in inflation. While the short-term outlook remains bleak, the long-term implications for the European economy are complex and multifaceted.
This section will explore the potential for recovery, the role of international cooperation, and the consequences of implementing a war economy.
The Long-Term Economic Implications
The war’s long-term impact on the European economy will depend on its duration, the severity of its consequences, and the effectiveness of policy responses. Some key challenges include:
- Energy Security:The war has exposed Europe’s dependence on Russian energy, forcing it to seek alternative sources. This transition will require significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure and could lead to higher energy prices in the long term.
- Inflation:The war has exacerbated inflationary pressures, fueled by supply chain disruptions and rising energy prices. Controlling inflation will be crucial to prevent a wage-price spiral and maintain economic stability.
- Economic Growth:The war is likely to dampen economic growth in Europe, as businesses face higher costs and uncertainty. The extent of the slowdown will depend on the duration of the conflict and the effectiveness of government support measures.
- Debt Sustainability:European governments have undertaken significant spending to mitigate the war’s impact, leading to higher public debt levels. Maintaining debt sustainability will be critical to avoid future fiscal crises.
Despite these challenges, there are reasons for optimism. Europe has a strong economic foundation, a skilled workforce, and a commitment to innovation. The war has also highlighted the need for greater economic resilience and self-sufficiency.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation will be crucial in addressing the economic challenges facing Europe. Key actors include:
- The European Union:The EU has a vital role in coordinating policy responses, providing financial support to member states, and strengthening economic ties.
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF):The IMF can provide financial assistance and technical expertise to help countries navigate the economic fallout from the war.
- The World Bank:The World Bank can provide loans and grants to support reconstruction efforts and promote long-term economic development in Ukraine and neighboring countries.
- Other International Organizations:Other international organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the United Nations (UN), can play a role in addressing trade disruptions and promoting global economic stability.
Consequences of a War Economy, Analysis europe must declare a war economy
A war economy in Europe would involve a range of measures aimed at maximizing production and mobilizing resources for the war effort. This could include:
- Centralized Planning:The government would play a more active role in directing economic activity, setting production targets, and allocating resources.
- Price Controls:The government could impose price controls on essential goods and services to prevent inflation and ensure affordability.
- Rationing:The government could ration essential goods and services to ensure equitable distribution.
- Increased Taxation:The government could raise taxes to finance the war effort.
- Labor Mobilization:The government could encourage or mandate labor mobilization to meet the demands of war production.
The potential consequences of implementing a war economy in Europe are significant:
Economic Growth
- Short-Term Boost:A war economy could lead to a short-term boost in economic activity, as resources are directed towards war production.
- Long-Term Stagnation:However, the long-term impact could be negative, as investment in non-military sectors is suppressed and innovation is stifled.
Social Impact
- Increased Inequality:A war economy could exacerbate existing inequalities, as the burden of war falls disproportionately on certain groups.
- Civil Liberties Restrictions:The government could impose restrictions on civil liberties in the name of national security.
International Relations
- Strained Relations:A war economy could strain relations with other countries, as trade and investment are disrupted.
- Increased Military Spending:A war economy would likely lead to increased military spending, potentially diverting resources from other sectors.
End of Discussion: Analysis Europe Must Declare A War Economy
The decision to declare a war economy is a complex one, fraught with ethical and political considerations. While it might offer a path to short-term economic stability, it also carries the risk of long-term social and economic repercussions. The future of Europe’s economy hinges on a delicate balancing act between immediate needs and long-term goals, requiring a nuanced approach that prioritizes both economic resilience and societal well-being.